Order abana 60 pills on line
Humans acquire the bacteria through contact with dust from bird feathers definition of cholesterol in food purchase 60pills abana visa, bird droppings, or from the bite of a bird carrying the bacteria. People who keep birds as pets or who work where birds are kept have the highest risk for this type of pneumonia. This pneumonia, called psittacosis, causes fever, cough, and the production of sputum containing pus. Chlamydia psittaci may linger, and severe cases have a death rate of as high as 30%. Prevention Prevention of Chlamydia trachomatis pneumonia involves recognizing the symptoms of genital infection in the mother and treating her prior to delivery of her baby. Aspiration-When solids or liquids that should be swallowed into the stomach are instead breathed into the respiratory system, or when substances from the outside environment are accidentally breathed into the lungs. Choking is a common cause of accidental death in young children who are apt to put toys or coins in their mouths, then unintentionally inhale them. Strangulation puts external pressure on the trachea causing another form of choking. Smoking, heavy alcohol use, lung diseases such as emphysema, and an inherited tendency toward a narrowed airway and throat all increase the risk of choking during sleep. Because people can contract psittacosis from each other, a person sick with this infection should be kept in isolation, so as not to infect other people. Chlamydia pneumoniae is difficult to prevent because it is spread by respiratory droplets from other sick people. Because people with this type of pneumonia do not always feel very sick, they often continue to attend school, go to work, and go to other public places. They then spread the bacteria in the tiny droplets that are released into the air during coughing. Therefore, this pneumonia is very difficult to prevent and often occurs in outbreaks within communities. In choking due to infection, the person, usually a child, will have a fever and signs of illness before labored breathing begins. Eventually sleep may be interrupted so frequently that daytime drowsiness becomes a problem. A tube extending from below the voice box into the chest where it splits into two branches, the bronchi, that go to each lung. Tracheotomy-The surgical creation of an opening in the trachea that functions as an alternative airway so that the patient may breathe. The risk of obstructive sleep apnea choking can be reduced by avoiding alcohol, tobacco smoking, tranquilizers, and sedatives before bed. If choking is due to allergic reaction or infection, people should summon emergency help or go immediately to an emergency room. If choking is due to obstructed airways, the Heimlich maneuver (an emergency procedure in which a person is grasped from behind in order to forcefully expel the obstruction) should be performed immediately. In severe cases a tracheotomy (an incision into the trachea through the neck below the larynx) must be performed. Patients who suffer airway obstruction during sleep can be treated with a device similar to an oxygen mask that creates positive airway pressure and delivers a mixture of oxygen and air. The term applies to inflammation of any portion of the bile ducts, which carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and intestine. Prognosis Many people are treated successfully for choking with no permanent effects. In cases where the airway is restored after the critical period passes, there may be permanent brain damage. During meals, the gallbladder contracts and the sphincter between the gallbladder and intestine relaxes, permitting bile to flow into the intestine and take part in digestion. This is partly due to its antibacterial properties; these are produced by the immunoglobulins (antibodies) secreted in bile, the bile acids which inhibit bacterial growth themselves, and mucus. A small number of bacteria may be present in the bile ducts and gallbladder, getting there by moving backward from the intestine, which unlike the bile ducts, contains large numbers of bacteria. The normal flow of bile out of the ducts and into the intestine also helps keep too many organisms from multiplying. Bacteria also reach the bile ducts from the lymph tissue or from the blood stream. When the passage of bile out of the ducts is blocked, the few bacteria that are there rapidly reproduce. Tumors, on the other hand, cause a more complete blockage of bile flow, both in and out, so fewer infections occur. The reproducing organisms are often able to enter the bloodstream and infect multiple organs such as the liver and heart valves. Another source of inflammation of the bile ducts occurs in diseases of altered immunity, known as 'autoimmune diseases. The body thinks these cells are foreign and produces antibodies to fight them off, just as it fights against bacteria and viruses. Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a typical example of an autoimmune disease involving the bile ducts. The three symptoms present in about 70% of patients with cholangitis are abdominal pain, fever, and jaundice. Jaundice or yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes occurs in about 80% of patients. The color change is due to bile pigments that accumulate in the blood and eventually in the skin and eyes. Inflammation due to the autoimmune disease primary sclerosing cholangitis leads to multiple areas of narrowing and eventual infection. Tumors can block the bile duct and also cause cholangitis, but as noted, infection is relatively infrequent; in fact cholangitis occurs in only about one in six patients with tumors. Another type of bile duct infection occurs mainly in Southeast Asia and is known as recurrent pyogenic cholangitis or Oriental cholangitis. Most patients have stones in the bile ducts and/or gallbladder, and many cases are associated with the presence of parasites within the ducts. Many researchers believe that they are just coincidental, and have nothing to do with the stones or infection. Diagnosis the symptoms mentioned previously are alone very suggestive of cholangitis; however, it is important to determine the exact cause and site of possible obstruction. This is because attacks are likely to recur, and different causes require different treatments. An elevated white blood count suggests infection, but may be normal in 20% of patients. Abnormal or elevated tests of liver function, such as bilirubin and others are also frequently present. The most common cause of cholangitis is infection of the bile ducts due to blockage by a gallstone. Strictures (portions of ducts that have become narrow) also function in the same way. Strictures may be due to congenital (birth) abnormalities of the bile ducts, form as a result of injury to the bile duct (such as surgery, trauma), or result from inflammation that leads to scar tissue and narrowing. The bacterium most commonly associated with infection of the bile ducts is Escherichia coli (E. Bilirubin-A pigment produced by the liver that is excreted in bile which causes a yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes when it accumulates in those organs. Bilirubin levels can be measured by blood tests, and are most often elevated in patients with liver disease or a blockage to bile flow. The procedure is of greatest value in diagnosing the complications of gallstones (such as abscesses, pancreatitis) rather than documenting the presence of a stone. Endoscope-An endoscope as used in the field of gastroenterology is a thin flexible tube which uses a lens or miniature camera to view various areas of the gastrointestinal tract. When the procedure is performed to examine certain organs such as the bile ducts or pancreas, the organs are not viewed directly, but rather indirectly through the injection of x-ray dye into the bile duct. Endoscopy-The performance of an exam using an endoscope is referred by the general term endoscopy. Primary sclerosing cholangitis-A chronic disease in which it is believed that the immune system fails to recognize the cells that compose the bile ducts as part of the same body, and attempts to destroy them. The inflammation of the ducts eventually produces formation of scar tissue, causing multiple areas of narrowing (strictures) that block bile flow and lead to bacterial infection.
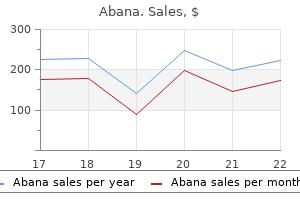
Purchase abana on line amex
Prognosis Early diagnosis and prompt treatment is essential to prevent chronic infection cholesterol control diet order abana from india. Prevention There is no human vaccine for brucellosis, but humans can be protected by controlling the disease in livestock. After checking to make sure an animal is not already infected, and destroying those that are, all livestock should be immunized. Butchers and those who work in slaughterhouses should wear protective glasses and clothing, and protect broken skin from infection. Some experts suggest that a person with the disease refrain from engaging in unprotected sex until free of the disease. The sexual partners of an infected person should also be closely monitored for signs of infection. Around the eighth or ninth day, the skin over the bruised area will have a brown or yellowish appearance, and it will gradually diminish back to its normal color. Long periods of standing will cause the blood that collects in a bruise to seep through the tissues. Bruises are actually made of little pools of blood, so the blood in one place may flow downhill after awhile and appear in another. For instance, bruising in the back of the abdomen may eventually appear in the groin; bruising in the thigh or the knee will work its way down to the ankle. Turkington Brugian filariasis see Elephantiasis Causes and symptoms Bruises Definition Bruises, or ecchymoses, are a discoloration and tenderness of the skin or mucous membranes due to the leakage of blood from an injured blood vessel into the tissues. These often appear as many tiny red dots clustered together, and could indicate a serious problem. Description Bruises change colors over time in a predictable pattern, so it is possible to estimate when an injury occurred by the color of the bruise. Healthy people may develop bruises from any injury that does not break through the skin. Vigorous exercise may also cause bruises due to bringing about small tears in blood vessels walls. In a condition known as purpura simplex, there is a tendency to bruise easily due to an increased fragility of the blood vessels. Bruises also develop easily in the elderly, because the skin and blood vessels have a tendency to become thinner and more fragile with aging, and there is an increased use of medications that interfere with the blood clotting system. In the condition known as purpura senilis, the elderly develop bruises from minimal contact that may take up to several months to completely heal. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen (Advil) and naproxen (Aleve) may lead to increased bruising. Aspirin, antidepressants, asthma medications, and cortisone medications also have this effect. The anti-clotting medications known as blood thinners, especially the drug Warfarin (Coumadin), may be the cause of particularly severe bruising. There are a number of diseases that cause excessive bleeding or bleeding from injuries too slight to have consequences in healthy people. An abnormal tendency to bleed may be due to hereditary bleeding disorders, certain prescription medications, diseases of the blood such as leukemia, and diseases that increase the fragility of blood vessels. If there are large areas of bruising or bruises develop very easily, this may herald a problem. However, faced with extensive bruising, bruising with no apparent cause, or bruising in certain locations, a physician will pursue an evaluation that will include a number of blood tests. Prevention Vitamin K promotes normal clotting in the blood, and therefore may help reduce the tendency to bruise easily. Green leafy vegetables, alfalfa, broccoli, seaweed, and fish liver oils are dietary sources of vitamin K. Other good foods to eat would be those containing bioflavonoids, such as reddish-blue berries. These can assist in strengthening the connective tissue, which will decrease the spread of blood and bruising. It is often recommended that ice packs be applied on and off during the first 24 hours of injury to reduce the bruising. After that, heat, especially moist heat, is recommended to increase the circulation and the healing of the injured tissues. Rest, elevation of the affected part, and compression with a bandage will also retard the accumulation of blood. Rarely, if a bruise is so large that the body cannot completely absorb it or if the site becomes infected, it may have to be surgically removed. The Doctors Book of Home Remedies: Quick Fixes, Clever Techniques, and Uncommon Cures to Get You Feeling Better Fast. The homeopathic remedy, Arnica montana, can be applied as a cream or gel to unbroken skin. Arnica montana, at 30 mL (1 oz), taken one to two times per day is highly recommended. It is an unconscious behavior, perhaps performed to release anxiety, aggression, or anger. Description Bruxism is one of the oldest disorders known, and approximately one in four adults experiences it. Prognosis the blood under the skin that causes the discoloration of bruising should be totally reabsorbed by the body in three weeks or less. Less commonly, the body may develop calcium deposits at the injury site in a process called heterotopic ossification. Symptoms of bruxism include: dull headaches; sore and tired facial muscles; earaches; sensitive teeth; and locking, popping, and clicking of the jaw. High spot-An area of a tooth or restoration that feels abnormal or uncomfortable because it hits its opposing tooth before other teeth meet. Night guard-A removable, custom-fitted plastic appliance that fits between the upper and lower teeth to prevent them from grinding against each other. Rolfing-Based on the belief that proper alignment of various parts of the body is necessary for physical and mental health, a technique that uses deep tissue massage and movement exercises in an attempt to bring the body into correct alignment. Stress management and behavior modification techniques may be useful to break the habit of clenching and grinding teeth. Tight jaw muscles may be relaxed by applying warm compresses to the sides of the face. Massage therapy and deep tissue realignment, including rolfing, can assist in releasing the clenching pattern. Prognosis Bruxism may cause permanent damage to teeth and chronic jaw pain unless properly diagnosed and promptly treated. Prevention Increased awareness in patients prone to anxiety, aggression, or anger may prevent the habit of bruxism from developing. Bethany Thivierge Bubonic plague see Plague Treatment To prevent further damage to the teeth, bruxism is treated by placing a removable, custom-fitted plastic appliance called a night guard between the upper and lower teeth. Although the clenching and grinding behavior may continue, the teeth wear away the plastic instead of each other. In some cases, abnormal occlusion may be adjusted and high spots removed so that the teeth fit together in a more comfortable position. Missing teeth may be replaced and crooked teeth may be straightened with orthodontic treatment to eliminate possible underlying causes of bruxism. In cases where jaw muscles are very tight, a dentist may prescribe muscle relaxants. The high pressure of blood in these veins leads to an enlarged liver, and to an accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, called ascites. Biopsy-Surgical removal of a tiny bit of tissue for examination under the microscope. Sickle cell anemia-An inherited disease in which red blood cells take an unusual shape, leading to circulation problems. Diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome can be made by an internist (a specialist in diseases of the internal organs), a gastroenterologist (a specialist in the diseases of the digestive system), or a general surgeon. On physical examination, the doctor will note that the liver is larger than normal. Often an ultrasound scan of the liver will show abnormalities in the size of the liver, an abnormal pattern of the veins in the liver, and other abnormalities. Once these abnormalities are confirmed, the key test is called hepatic vein catheterization.
Diseases
- Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency
- Cardiomyopathic lentiginosis
- Tutuncuoglu syndrome
- Hyperlipoproteinemia type V
- Soft-tissue sarcoma
- Semmerkrot Haraldsson Weenaes syndrome
- Chemodectoma
- Herpes zoster
Generic abana 60 pills
Corticosteroids cholesterol oxidase buy abana master card, usually inhaled, block inflammation and are most useful for patients with chronic bronchitis with or without emphysema. Services may include general exercise training, administration of oxygen and nutritional supplements, intermittent mechanical ventilator support, continuous positive airway pressure, relaxation techniques, breathing exercises and techniques (such as pursed lip breathing), and methods for mobilizing and removing secretions. The great majority of patients cannot be helped by surgery, and no single procedure is ideal for those who can be helped. In the hands of an experienced team, the one-year survival rate is over 70% Lung transplantation is most often reserved for younger patients. When the operation is successful, patients report significant improvement in symptoms. Therefore, circumcision has become an elective option that parents make for their sons on an individual basis. Families who practice Judaism or Islam may select to have their sons circumcised as a religious practice. Female circumcision (also known as female genital mutilation) is usually performed for cultural and social reasons by family members and others who are not members of the medical profession; it is performed without anesthesia. Not only is the prepuce of the clitoris removed, but often the vaginal opening is sewn to make it smaller. This practice is not universally approved by the medical profession and is considered by many to be a human 1170 rights violation. Some of the medical reasons parents of male infants choose circumcision are to protect against infections of the urinary tract and the foreskin, prevent cancer, lower the risk of getting sexually transmitted diseases, and prevent phimosis (a tightening of the foreskin that may close the opening of the penis). There are also indications that circumcised men are less likely to suffer from penile cancer, inflammation of the penis, or to contract sexually transmitted diseases. Good hygiene usually prevents most infections of the penis and actual incidence of sexually transmitted diseases is low. Education and safe sex practices can prevent sexually transmitted diseases in ways that a surgical procedure cannot because these are diseases acquired through risky behaviors. With these factors in mind, the American Academy of Pediatrics has issued a policy statement that maintains that though there is existing scientific evidence that indicates the medical benefits of circumcision, the benefits are not strong enough to recommend circumcision as a routine practice. Also, infants with a large hydrocele, or hernia, may suffer complications through circumcision. Premature infants and infants with serious infections are also poor candidates to be circumcised, as are infants with hemophilia, other bleeding disorders, or whose mothers had taken anticoagulant drugs. In older boys or men, circumcision is a minor procedure and can be performed on virtually anyone without a serious illness or unusual deformity. Medical circumcisions are performed in the hospital by a pediatrician for an infant or child. For an adult, a general surgeon or urologist may perform a circumcision, especially if there are other urinary tract repairs to be made. A Jewish religious circumcision, a Bris Milah, is performed when an infant male is eight days old. It is conducted by a trained mohel, with family and friends present, in a non-medical setting. In Britain, it is only done for religious practices or to correct a specific medical condition of the penis. Preparation Despite a long-standing belief that infants do not experience serious pain from circumcision, physicians now believe that some form of local anesthesia is necessary. Over 80% of pediatric residents, 80% of family practice residents, and 60% of obstetric/gynecological residents are routinely given instruction on pain control for circumcisions. Local anesthesia is often injected at the base of the penis (dorsal penile nerve block) or under the skin around the penis (subcutaneous ring block). Both anesthetics block key nerves and provide significantly lowered perceived pain. Description the penis consists of a cylindrical shaft with a rounded head called the glans. The foreskin of the penis covers and protects the glans and shields it from irritation by urine, feces, and foreign materials. A retractable foreskin can be pulled back behind the coronal sulcus to expose the glans. In circumcision of infants, the foreskin is pulled tightly into a specially designed clamp, which forces the foreskin away from the broadened tip of the penis. The clamp applies pressure that stops bleeding from blood vessels that supply the foreskin. In older boys or adults, an incision is made around the base of the foreskin, the foreskin is pulled back, and then it is cut away from the tip of the penis. Circumcision should not be performed on infants with certain deformities of the penis that may require a portion of the foreskin for repair. If there is an incision, a wound dressing will be applied and should be changed each time the diaper is changed. Sometimes a plastic ring (ring block with local anesthetic) is applied to the base of the penis instead of a bandage. Infants who undergo circumcision may be fussy for some hours afterward, so parents should be prepared for crying, feeding problems, and sleep problems. Hernia-Bulging of abdominal structures through an abnormal opening in the muscular wall. Hypospadias-A congenital deformity of the penis where the urinary tract opening is not at the tip of the glans. Prepuce-A fold like the foreskin that covers the clitoris; another name for foreskin. Severe penile injuries are rare, but they are serious, and include penile amputation (partial or total), laceration, hemorrhage, and damage to the urinary tract. Other serious complications such as meningitis, penile necrosis, necrotizing fasciitis, and sepsis can occur. These masses usually have no symptoms, but, left untreated, could lead to more serious outcomes. Physicians should examine the penis at every wellbaby checkup during the first year. If a mass is detected, it can easily be removed under a local anesthesia and sent to a pathology lab. If the procedure is performed in a hospital operating room, dorsal penile blocks or caudal (spinal) blocks may be used to lessen pain and avoid use of pain medications. The only alternative to this surgery is to make an informed decision not to have an infant circumcised. Some Jewish parents are even electing not to hold a Bris Milah, a religious circumcision, for their sons, and choosing instead to hold a Brit Shalom, a naming ceremony, similar to that given for their infant daughters. After a period of recovery, an adult male should be able to resume sexual intercourse normally. Infections are rare and occur at the circumcision site, the opening to the bladder, or at the tip of the penis as a result of contact with urine or feces. Infections are indicated by fever and signs of inflammation, and are treatable with antibiotics. Complications as a result of circumcision are usually minor if the physician is experienced and makes 1172 Circumcision Resource Center. The primary risk factors are alcohol and chronic liver infections, such as hepatitis B and C. People at high risk of contracting hepatitis B include those exposed to the virus through contact with blood and body fluids. In most cases, these cannot be prevented or avoided but risk may be reduced with proper treatment of the disease or disorder. Cirrhosis Demographics Cirrhosis is the seventh leading cause of diseaserelated death in the United States. It is the third most common cause of death in adults between the ages of 45 and 65. The disease occurs in more than half of all malnourished chronic alcoholics, and kills about 25,000 people a year. In Asia and Africa, however, most deaths from cirrhosis are due to chronic hepatitis B.
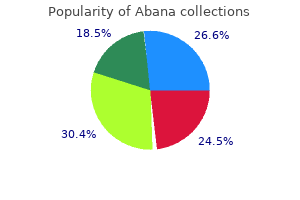
Order abana toronto
Very few individuals ever recovered cholesterol zocor discount 60 pills abana with visa, and the older the patient and the more area of the body burned, the less chance of survival. The widely accepted method for treating burns left the burned skin on the body, allowing the skin to slough off naturally. John Burke, a surgeon and Harvard Medical School professor decided there was a better way. Burke believed that leaving the burned skin on patients actually increased the likelihood of infection, a very common cause of death among these individuals. The Chemical burn treatment Burns from liquid chemicals must be rinsed with cool water for at least 15 minutes to stop the burning process. In cases of burns from dry chemicals such as lime, the powder should be completely brushed away before the area is washed. The burn should then be loosely covered with a sterile gauze pad and the person taken to the hospital for 896 further treatment. A physician may be able to neutralize the offending chemical with another before treating the burn like a thermal burn of similar severity. Electrical burn treatment Before electrical burns are treated at the site of the accident, the power source must be disconnected if possible and the victim moved away from it to keep the person giving aid from being electrocuted. Electrical burns should be loosely covered with sterile gauze pads and the person taken to the hospital for further treatment. Alternatives In addition to the excellent treatment of burns provided by traditional medicine, some alternative approaches may be helpful as well, though major burns should always be treated by a medical practitioner. Supplementing the diet with vitamin C, vitamin E, and zinc also is beneficial for wound healing. Hats, loose clothing, and umbrellas also provide protection, especially between 10 a. Electrical burns may be prevented by covering unused electrical outlets with safety plugs and keeping electrical cords away from infants and toddlers who might chew on them. Persons should also seek shelter indoors during a thunderstorm to avoid being struck by lightning. Chemical burns may be prevented by wearing protective clothing, including gloves and eyeshields. Critical or major burns take more than 14 days to heal and will leave significant scarring. Scar tissue may limit mobility and functionality, but physical therapy may overcome these limitations. In some cases, additional surgery may be advisable to remove scar tissue and restore appearance. Children must be taught never to play with matches, lighters, fireworks, gasoline, and cleaning fluids. Burns by scalding with hot water or other liquids may be prevented by setting the water heater thermostat no higher than 120 F (49 C), checking the temperature of bath water before getting into the tub, and turning pot handles on the stove out of the reach of children. Care should be used when removing covers from pans of steaming foods and when uncovering or opening foods heated in a microwave oven. Bursae cushion the movement between the bones, tendons and muscles near the joints. Diabetes mellitus-A metabolic disease caused by a deficiency of insulin, which is essential to process carbohydrates in the body. Gout-A hereditary metabolic disease that is a form of arthritis and causes inflammation of the joints. Inflammation-Tedness, swelling, heat, and pain, which comprise a reaction of tissue to injury. Inserting a thin needle into the affected bursa and removing (aspirating) some of the synovial fluid for examination can confirm the diagnosis. It can be tested for the presence of microorganisms, which would indicate an infection, and crystals, which could indicate gout. In instances where the diagnosis is difficult, a local anesthetic (a drug that numbs the area) is injected into the painful spot. If the discomfort stops temporarily, then bursitis is probably the correct diagnosis. The application of heat, rest, and immobilization of the affected joint area is the first step. They can be obtained without a prescription and relieve the pain and inflammation. If the nearby muscles have become weak because of the disease or prolonged immobility, then exercises to build strength and improve movement are best. If the bursitis is related to an inflammatory condition like arthritis or gout, then management of that disease is needed to control the bursitis. When bursitis does not respond to conservative treatment, an injection into the joint of a long-acting corticosteroid preparation, like prednisone, can bring immediate and lasting relief. A corticosteroid is a hormonal substance that is the most effective drug for reducing inflammation. The drug is mixed with a local anesthetic and works on the joint within five minutes. Septic bursitis is caused by the presence of a pus-forming organism, usually staphylococcus aureus. This is confirmed by examining a sample of the fluid in the bursa and requires treatment with antibiotics taken by mouth, injected into a muscle or into a vein (intravenously). The bursa will also need to be drained by needle two or three times over the first week of treatment. Each sac contains a small amount of synovial fluid, a clear liquid that acts as a lubricant. The most common site for bursitis to occur is the shoulder (subdeltoid), but it also is seen in the elbows (olecranon), hips (trochanteric), knees, heels (Achilles), and toes. The affected area may be referred to as 'frozen,' because movement is so limited. Causes and symptoms the most common cause of bursitis is repeated physical activity, but it can flare up for no known reason. It can also be caused by trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and acute or chronic infection. If the affected joint is close to the skin, as with the shoulder, knee, elbow, or Achilles tendon, swelling and redness are seen and the area may feel warm to the touch. In the shoulder, it may be difficult to raise the arm out from the side of the body. In acute bursitis symptoms appear suddenly; with chronic bursitis, pain, tenderness, and limited movement reappear after exercise or strain. Diagnosis When a patient has pain in a joint, a careful physical examination is needed to determine what type of movement is affected and if there is any swelling present. Byssinosis Byssinosis Definition Byssinosis is a chronic, asthma-like narrowing of the airways. Also called brown lung disease, byssinosis results from inhaling particles of cotton, flax, hemp, or jute. Alternatives Alternative treatments take into consideration the role of diet in causing bursitis. The faulty use of calcium by the body, magnesium deficiency, and food allergies may have a role. The use of herbs, homeopathy, aromatherapy, and hydrotherapy can help relieve symptoms. Acupuncture has been proven effective in treating hip and shoulder pain caused by bursitis and other conditions. Other therapies that deal effectively with musculoskeletal problems (relating to the muscles and skeleton), may also be helpful, such as body work, magnetic field therapy, naturopathic medicine, chiropractic, and applied kinesiology. Description Although inhaling cotton dust was identified as a source of respiratory disease more than 300 years ago, byssinosis has been recognized as an occupational hazard for textile workers for less than 50 years. More than 800,000 workers in the cotton, flax, and rope-making industries are exposed in the workplace to airborne particles that can cause byssinosis.
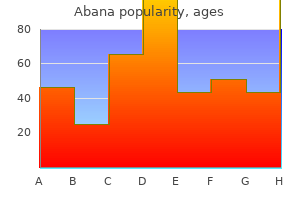
Discount abana 60pills fast delivery
Those who do not have a specific behavioral issue they wish to address and whose goals for therapy are to gain insight into the past may be better served by psychodynamic therapy cholesterol rates best buy abana. Patients must also be willing to take a very active role in the treatment process. Cognitive-behavioral intervention may be inappropriate for some severely psychotic patients and for cognitively impaired patients (for example, patients with organic brain disease or a traumatic brain injury), depending on their level of functioning. Pioneered by psychologists Aaron Beck and Albert Ellis in the 1960s, cognitive therapy assumes that maladaptive behaviors and disturbed mood or emotions are the result of inappropriate or irrational thinking patterns, called automatic thoughts. Instead of reacting to the reality of a situation, an individual reacts to his or her own distorted viewpoint of the situation. For example, a person may conclude that he is 'worthless' simply because he failed an exam or did not get a date. Behavioral therapy, or behavior modification, trains individuals to replace undesirable behaviors with healthier behavioral patterns. Unlike psychodynamic therapies, it does not focus on uncovering or understanding the unconscious motivations that may be behind the maladaptive behavior. In other words, strictly behavioral therapists do not try to find out why their patients behave the way they do, they just teach them to change the behavior. Cognitive-behavioral therapy integrates the cognitive restructuring approach of cognitive therapy with the behavioral modification techniques of behavioral therapy. The therapist works with the patient to identify both the thoughts and the behaviors that are causing distress, and to change those thoughts in order to readjust the behavior. In some cases, the patient may have certain fundamental core beliefs, called schemas, which are flawed and require modification. For example, a patient with depression may be avoiding social contact with others, and suffering considerable emotional distress because of his isolation. When questioned why, the patient reveals to his therapist that he is afraid of rejection, of what others may do or say to him. Upon further exploration with his therapist, they discover that his real fear is not rejection, but the belief that he is hopelessly uninteresting and unlovable. His therapist then tests the reality of that assertion by having the patient name friends and family who love him and enjoy his company. In this case, the person learns to think, 'I am an interesting and lovable person; therefore I should not have difficulty making new friends in social situations. A number of different techniques may be employed in cognitive-behavioral therapy to help patients uncover and examine their thoughts and change their behaviors. Ideally, when the situation arises in real life, the patient will draw on the rehearsed behavior to address it. Patients are asked to keep a detailed diary recounting their thoughts, feelings, and actions when specific situations arise. The journal helps to make the patient aware of his or her maladaptive thoughts and to show their consequences on behavior. In later stages of therapy, it may serve to demonstrate and reinforce positive behaviors. The therapist and patient engage in roleplaying exercises in which the therapist acts out appropriate behaviors or responses to situations. The gold star reinforces and increases the desired behavior by identifying it with something positive. Reinforcement can also be used to extinguish unwanted behaviors by imposing negative consequences. Patients imagine a situation they fear, while the therapist employs techniques to help the patient relax, helping the person cope with their fear reaction and eventually eliminate the anxiety altogether. For example, a patient in treatment for agoraphobia, or fear of open or public places, will relax and then picture herself on the sidewalk outside of her house. In her next session, she may relax herself and then imagine a visit to a crowded shopping mall. The imagery of the anxiety-producing situations gets progressively more intense until, eventually, the therapist and patient approach the anxiety-causing situation in real-life (a 'graded exposure'), perhaps by visiting a mall. Exposure may be increased to the point of 'flooding,' providing maximum exposure to the real situation. By repeatedly pairing a desired response (relaxation) with a fear-producing situation (open, public spaces), the patient gradually becomes desensitized to the old response of fear and learns to react with feelings of relaxation. Patients are asked to test the validity of the automatic thoughts and schemas they encounter. The therapist may ask the patient to defend or produce evidence that a schema is true. If the patient is unable to meet the challenge, the faulty nature of the schema is exposed. Cognitivebehavioral therapists frequently request that their patients complete homework assignments between therapy sessions. These may consist of real-life 'behavioral experiments' where patients are encouraged to try out new responses to situations discussed in therapy sessions. Cognitive restructuring-The process of replacing maladaptive thought patterns with constructive thoughts and beliefs. Maladaptive-Unsuitable or counterproductive; for example, maladaptive behavior is behavior that is inappropriate to a given situation. Psychodynamic therapy-A therapeutic approach that assumes dysfunctional or unwanted behavior is caused by unconscious, internal conflicts and focuses on gaining insight into these motivations. Relaxation techniques are used in cognitive-behavioral therapy to teach patients new ways of coping with stressful situations. Schemas-Fundamental core beliefs or assumptions that are part of the perceptual filter people use to view the world. As such, it empowers the patient by giving him an active role in the therapy process and discourages any overdependence on the therapist that may occur in other therapeutic relationships. Therapy is typically administered in an outpatient setting in either an individual or group session. Treatment is relatively short in comparison to some other forms of psychotherapy, usually lasting no longer than 16 weeks. Many insurance plans provide reimbursement for cognitive-behavioral therapy services. Because coverage is dependent on the disorder or illness the therapy is treating, patients should check with their individual plans. People form illogical, irrational thinking patterns that become the cause of both their negative emotions and of further irrational ideas. Certain people are bad, wicked, or villainous, and should be punished for their sins. People have little or no ability to control their sorrows or to rid themselves of negative feelings. It is right to be terribly preoccupied with and upset about something that may be dangerous or fearsome. It is catastrophic if perfect solutions to the grim realities of life are not immediately found. Maximal human happiness can be achieved by inertia and inaction or by living passively and without commitment. This type of therapy emphasizes teaching patients coping skills that they can use in a variety of situations to help themselves. The technique used to accomplish this is self-instructional inner dialogue, a method of talking through a problem or situation as it occurs. Cold agglutinins test Paula Anne Ford-Martin Preparation Patients may seek therapy independently, or be referred for treatment by a primary physician, psychologist, or psychiatrist. Because the patient and therapist work closely together to achieve specific therapeutic objectives, it is important that their working relationship is comfortable and their goals are compatible. Prior to beginning treatment, the patient and therapist should meet for a consultation session, or mutual interview. The consultation gives the therapist the opportunity to make an initial assessment of the patient and recommend a course of treatment and goals for therapy. In some managed-care clinical settings, an intake interview or evaluation is required before a patient begins therapy. The intake interview is used to evaluate the patient and assign him or her to a therapist.
Syndromes
- Too much salt in the diet
- Falls
- Recent endoscopy of the bile draining tubes
- PET scan of the brain will show changes in the front of the brain
- Examination of the retina after dilating the pupil
- Caffeine and nicotine use
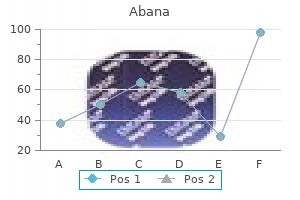
60 pills abana with visa
Compressions should be done on the center of the chest midway between the nipples cholesterol ratio defined discount 60pills abana with mastercard. Chest compressions should continue with two puffs of breath given for every 50 compressions (two puffs per minute) until help arrives or the victim begins breathing spontaneously. If victims appear to be unconscious, they should be shaken or tapped gently to check for any sign of consciousness. If there is no response, the rescuer should call emergency medical services immediately or (preferably) send someone else to call for help. Victims should be placed on their back on a level surface such as the ground or the floor unless there is some sign of neck or back injuries, in which case the individual should not be moved. When a person is deprived of oxygen, permanent brain damage can begin in as little as four minutes and death can follow only minutes later. It is necessary to place the recipient on a flat surface facing up before administering compressions. Precautions Rescuers should follow these rules: Do not leave the individual alone. Arrest-A sudden stopping of the function of a body organ, such as no breathing (respiratory arrest) or no beating of the heart (cardiac arrest). Circulation-The passage of blood and delivery of oxygen through the veins and arteries of the body. Respiratory-Referring to breathing in and breathing out and the function of the lungs. Sometimes chest compressions can result in one or more breaks in the ribs and accompanying damage to internal organs, especially in young children, the elderly, and debilitated persons. Prevention People with serious health conditions can follow these general guidelines: Risk factors that contribute to heart disease should be reduced or eliminated. People can reduce risks if they stop smoking, lower blood pressure and cholesterol, lose excess weight, and reduce stress. Demographics Abnormal heart rhythms are slightly more common in men than in women, and the prevalence of abnormal heart rhythms, especially atrial fibrillation, increases with age. Atrial fibrillation is relatively uncommon in people under age 20 but affects 5% of the American population over 65 and 8% of the population over 80. To find a heart rhythm specialist or an electrophysiologist, patients can contact the Heart Rhythm Society (formerly the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology). It may also be performed in an intensive care unit, recovery room, or other special procedure room. Synchronized electrical cardioversion Elective synchronized electrical cardioversion is usually scheduled ahead of time. During the five or ten minutes of anesthesia, an electric shock is delivered through paddles or patches placed on the exterior of the chest and sometimes on the back. It may be necessary for the doctor to administer the shock two or three times to stop the abnormal heartbeat and allow the heart to resume a normal rhythm. Pharmacologic cardioversion Pharmacologic, or chemical, cardioversion is a less immediate method of restoring normal heart rhythm, and is somewhat less effective than electrical cardioversion, having a success rate between 60% and 80%. The first type is called synchronized electrical cardioversion; the second is called pharmacologic or chemical cardioversion. Purpose Cardioversion is used to treat many types of fast and/ or irregular heart rhythms. When the heart beats too fast, blood no longer circulates effectively in the body. It helps return the heart to its normal rhythm so that the heart can pump more efficiently. Ablation therapy-A procedure used to treat arrhythmias, especially atrial fibrillation. Ambulatory monitors include the Holter monitor, loop recorder, and transtelephonic transmitter. Anticoagulant-A medication, also called a 'blood thinner,' that prevents blood from clotting. Atrial flutter-A rapid pulsation of the upper chambers of the heart that interferes with normal heart function. Atrial flutter occurs most often in people with heart disease and in the first week after heart surgery. Cardiac catheterization-An invasive procedure used to create x-ray images of the coronary arteries, heart chambers and valves. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into an artery in the groin or arm and is guided to the heart. Contrast material (dye) is injected into the catheter to produce the x-ray images. The test uses high-frequency sound waves that come from a hand wand placed on the chest. The test is used to help determine the cause of the abnormal heart rhythm and find the best treatment. During the test, the doctor may safely reproduce the abnormal heart rhythm and give the patient medications to determine which medication works best to control the abnormal heart rhythm. Head-upright tilt table test-A test used to determine the cause of fainting spells. The patient does not need to undergo anesthesia and can receive the drugs immediately after eating; there is no need to fast for several hours. There are two basic groups of drugs given in pharmacologic cardioversion: those given to control the heart rate and those given to normalize the heart rhythm. The first group includes such medications as digoxin (Lanoxin), diltiazem (Cardizem), verapamil (Calan), esmolol (Brevibloc), metoprolol (Lopressor), and propranolol (Inderal). With the exception of 984 digoxin, which takes about 30 minutes to take effect, these drugs begin to work in five to seven minutes. Quinidine (Quinaglute), the oldest drug in this group, is given by mouth, while procainamide, propafenone (Rythmol), flecainide (Tambocor), amiodarone (Cordarone), sotalol (Betapace), dofetilide (Tikosyn), and ibutilide (Corvert) may be given intravenously or orally. Unlike the drugs given to control the heart rate, these medications take longer to work, one hour for procainamide and ibutilide, and three to eight hours for the others. During the procedure, precise incisions are made in the right and left atria to interrupt the conduction of abnormal impulses. Nuclear imaging-Method of producing images by detecting radiation from different parts of the body after a radioactive tracer material is administered. This device sends electrical impulses to the heart to maintain a suitable heart rate and prevent slow heart rates. Pharmacologic cardioversion-The use of medications to restore normal heart rhythm. Ventricular fibrillation-An erratic, disorganized firing of impulses from the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart. Ventricular tachycardia originates from the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). The rapid rate prevents the heart from filling adequately with blood, so less blood is able to pump through the body. Ventricular tachycardia can be a serious type of arrhythmia and may be associated with more symptoms. Dofetilide can be prescribed only by physicians who have had special training in the risks and side effects of the drug. In addition, the diagnosis may be based upon the presence of certain symptoms, including: palpitations (feeling of skipped heart beats or fluttering in the chest) Not everyone with abnormal heart rhythms will experience symptoms, so the condition may be discovered upon examination for another medical condition. Discomfort Some chest wall discomfort may be present for a few days after the procedure. The doctor may recommend that the patient take an over-the-counter pain reliever such as ibuprofen to relieve discomfort. Results About 90% of cardioversions are successful in restoring the normal heart rhythm safely and preventing further symptoms, at least temporarily. Preparation Medication to thin the blood (blood thinner or anticoagulant) is usually given for at least three weeks before elective cardioversion. The patient should take all usual medications as prescribed, unless other instructions have been given.
Purchase abana 60pills free shipping
Cholecystitis Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder cholesterol score of 8 purchase cheapest abana and abana, both acute and chronic, that results after the development of gallstones in some individuals. The most common symptoms and physical findings associated with cholecystitis include: Cholecystectomy Purpose A cholecystectomy is performed to treat cholelithiasis and cholecystitis. In cholelithiasis, gallstones of varying shapes and sizes form from the solid components of bile. The presence of these stones, often referred to as gallbladder disease, may produce symptoms of excruciating right upper abdominal pain radiating to the right shoulder. The gallbladder may become the site of acute infection and inflammation, resulting in symptoms of upper right abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Cholecystectomy is used to treat both acute and chronic cholecystitis when there are significant pain symptoms. The typical composition of gallstones is predominately cholesterol, or a compound called calcium bilirubinate. Cholelithiasis Most patients with cholelithiasis have no significant physical symptoms. When gallstones obstruct the cystic duct, intermittent, extreme, cramping pain typically pain and tenderness in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen nausea vomiting fever jaundice history of pain after eating large, high-fat meals Demographics Overall, cholelithiasis is found in about 20,000,000 Americans. The following groups are at an increased risk for developing cholelithiasis: A surgeon performs a laparoscopic cholecystectomy on a patient. Cholelithiasis-Also known as gallstones, these hard masses are formed in the gallbladder or passages, and can cause severe upper right abdominal pain radiating to the right shoulder, as a result of blocked bile flow. Gallbladder-A hollow pear-shaped sac on the under surface of the right lobe of the liver. Bile comes to it from the liver, and passes from it to the intestine to aid in digestion. Laparoscope-A device consisting of a tube and optical system for observing the inside of the abdomen and its organs. In a conventional or open cholecystectomy, the gallbladder is removed through a surgical incision high in the right abdomen, just beneath the ribs. Diagnosis the initial diagnosis of acute cholecystitis is based on the following symptoms: constant, dull pain in upper right quadrant of abdomen fever chills nausea vomiting pain aggravated by moving or coughing Overall, patients with cholelithiasis have about a 20% chance of developing biliary colic (the extremely painful complication that usually requires surgery) over a 20-year period. Acute cholecystitis develops most commonly in women between the ages of 40 and 60 years. Some ethnic groups, such as Native Americans, have a dramatically higher incidence of cholecystitis. Description Cholecystectomy, including the laparoscopic approach, is usually performed by a general surgeon who has completed a five-year residency training program in all components of general surgery and, in particular, proper techniques involving the use of the laparoscope. If surgery is being considered, it is a good idea to find out how many laparoscopic cholecystectomies the surgeon performs on a yearly basis. Laparoscopic cholecystectomies are often performed in the specialized department of a general hospital, but they are also performed in specialized gastrointestinal clinics or institutes for gastrointestinal disorders. The laparoscopic cholecystectomy involves the insertion of a long, narrow cylindrical tube with a camera on the end, through an approximately 0. Three smaller incisions allow for insertion of other instruments to perform the surgical procedure. A laser may be used for the incision and cautery (burning unwanted tissue to stop 1132 Most patients have elevated leukocyte (white blood cells) levels. Ultrasonography of the gallbladder usually provides evidence of gallstones, if they are present. This type of imaging cannot identify gallstones, but it can provide evidence of obstruction of the cystic and common bile ducts. Cholelithiasis is initially diagnosed based on the following signs and symptoms: history of biliary colic or jaundice nausea vomiting sudden onset of extreme pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen fever chills Laboratory blood analysis often finds evidence of elevated bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, or aminotransferase levels. Preparation As with any surgical procedure, the patient will be required to sign a consent form after the procedure is explained thoroughly. If nausea or vomiting are present, a suction tube to empty the stomach may be used, and for laparoscopic procedures, a urinary drainage catheter will also be used to decrease the risk of accidental puncture of the stomach or bladder with insertion of the trocar (a sharp, pointed instrument). Some patients undergoing elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy will require conversion to an open procedure. The primary complication with the open technique is infection, whereas bile leak and hemorrhage are the most common complications associated with the laparoscopic technique. The overall mortality rate associated with cholecystectomy is less than 1%; however, the rate of mortality in the elderly is higher. In a small minority of cases, symptoms will persist in patients who receive cholecystectomy. This has been named the post-cholecystectomy syndrome, and usually results from functional bowel disorder, errors in diagnosis, technical errors, overlooked common bile duct stones, recurrence of common bile duct stones, or the spasm of a structure called the sphincter of Oddi. Cholecystectomy Aftercare Postoperative care for the patient who has had an open cholecystectomy, as with those who have had any major surgery, involves monitoring of blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and temperature. The patient is shown how to support the operative site when breathing deeply and coughing and is given pain medication as necessary. Fluid intake and output is measured, and the operative site is observed for color and amount of wound drainage. The patient is generally encouraged to walk eight hours after surgery and discharged from the hospital within three to five days, with return to work approximately four to six weeks after the procedure. Care received immediately after laparoscopic cholecystectomy is similar to that of any patient undergoing surgery with general anesthesia. A unique postoperative pain may be experienced in the right shoulder related to pressure from carbon dioxide used in the laparoscopic tubes. This pain may be relieved by lying down on the left side with right knee and thigh drawn up to the chest. The patient is usually discharged the day after surgery and allowed to shower on the second postoperative day. The patient is advised to gradually resume normal activities over a three-day period, while avoiding heavy lifting for about ten days. Results the prognosis for cholecystitis and cholelithiasis patients who receive cholecystectomy is generally good. Alternatives Acute cholecystitis usually improves following conservative therapy in most patients. This conservative therapy involves the withholding of oral feedings, the use of intravenous feedings, and the administration of antibiotics and analgesics. Most of these patients should receive cholecystectomy within a few days to prevent recurrent attacks. In the short term, patients often receive narcotic analgesics such as meperidine to relieve the intense pain associated with this condition. Patients who have evidence of gallbladder perforation or gangrene need to have an immediate cholecystectomy. In patients with cholelithiasis who are deemed unfit for surgery, alternative treatments are sometimes effective. These individuals often have symptom improvement after lifestyle changes and medical therapy. Lifestyle changes include dietary avoidance of foods high in polyunsaturated fats and gradual weight loss in obese individuals. Patients with three or fewer gallstones of cholesterol composition and with a 1133 Risks Potential problems associated with open cholecystectomy include respiratory problems related to location of the incision, wound infection, or abscess formation. Possible complications of laparoscopic cholecystectomy include accidental puncture of the bowel or bladder and uncontrolled bleeding. Other nonsurgical alternatives include using a solvent to dissolve the stones and using sound waves to break up small stones. A major drawback to medical therapy is the high recurrence rate of stones in those treated, as well as the possibility of successfully removing stones, but leaving an infected gallbladder behind, requiring a later operation for its removal. The disorder can occur a single time (acute), or can recur multiple times (chronic).
Buy abana mastercard
It is not reliable for detecting smaller polyps (less than 1 cm) cholesterol levels 70 year old order 60pills abana with mastercard, which account for 80% of growths. Cancer screening guidelines Cancer screening guidelines for at least some people have also been established for skin, lung, ovarian, and endometrial (uterine lining) cancers. In contrast, stool testing is usually performed at home using a simple kit that is sent to a laboratory for developing. African Americans should be screened by colonoscopy every ten years beginning at age 45, and those at higher risk should be screened more frequently. They also have more right-sided polyps and cancers, which are especially dangerous. Medicare provides for surveillance colonoscopy every two years for those at high risk. However, people with second-degree (aunts, uncles, grandparents) and third-degree (nieces, nephews, cousins, great-grandparents) relatives with adenomas were also at increased risk, and screening guidelines may therefore miss 10% of colon cancers. Skin cancer People at higher risk for melanoma, including those previously diagnosed with melanoma or with a strong family history of melanoma, should have their skin examined regularly by a physician. They do not recommend screening asymptomatic patients with chest x rays or sputum cytology. Women are at increased risk for breast cancer if they have had previous breast cancer, have a family history of breast cancer, or have a known genetic predisposition. Breast cancer caused by these mutations tends to occur at an earlier age and in both breasts. Genetic screening also may identify mutations in other genes associated with breast cancer. Women with particular medical histories also may need to consider yearly endometrial biopsies. Men of African descent or with a father or brother diagnosed with prostate cancer at an early age (before 65) are considered at increased risk. Men with more than one firstdegree relative affected at an early age are considered to be at high risk. Women over 65 who have had regular normal test results should no longer be tested. Women with a history of serious cervical precancerous conditions should be tested for at least 20 years after diagnosis, regardless of whether they turn 65. Women who have had their uterus and cervix removed and have no history of cervical cancer or serious pre-cancer should not be tested. Men at high-risk because of multiple family members diagnosed with prostate cancer before age 65 should discuss screening with their doctors beginning at age 40. For men who decide to be screened, routine screening at intervals of two years or more is preferable to annual screening, since this interval appears to preserve the majority of screening benefits while reducing false positives and over-diagnoses. Colonoscopy-An examination of the rectum and colon with a long flexible instrument passed through the anus that can remove polyps and cancerous lesions. Melanoma-A malignant skin tumor that originates in melanocytes (pigmented cells) of normal skin or moles. Pap test-Pap smear; examination of cervical cells for the early detection of cancer. Sigmoidoscopy-An examination of the rectum and lower colon with a flexible instrument passed through the anus that can remove polyps. Invasive procedures, such as sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, carry a small risk of tissue damage or infection and a very small risk of significant bleeding or puncture of the colon or rectum that, rarely, may require surgical repair. Colonoscopy carries more risk of complications than sigmoidoscopy because it examines the entire large intestine. Mammography sometimes fails to detect cancerous tissue or detects lumps that are normal breast tissue or would never cause problems but can result in overtreatment. Some prostate cancers may never cause symptoms or become life-threatening, yet treatment can result in harmful side effects. Detection of prostate cancer may not improve health or life expectancy if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. National Institutes of Health that is concerned with research and education on prevention, diagnoses, treatments, and cures for cancer. It develops and disseminates state-of-the-art cancer care guidelines for clinicians and patients, including screening guidelines for lung cancer. The size of a tumor and where its cancer cells spread can indicate its stage and how it should be treated. It relies on laboratory testing, diagnostic imaging, and biopsy information to examine three main factors about cancers. The staging system assigns a number to each grouping that may indicate a finding such as the size of a tumor, then a number to the final stage, which is determined by combining specific information from the T, N, and M groupings. The tumor (T) category measures the size and behavior of the primary tumor, or original site of the cancer, according to: Cancer staging L. Tumors that become too large begin to invade healthy tissues and organs nearby and cause symptoms, pain, or health problems. If it spreads into nearby tissues, doctors may call it regional spread or local-regional spread. Uncontrolled cell growth also can affect the balance of cancer cells to healthy cells in the body, such as in blood cancers. The term restaging is used, however, to refer to describing cancer after treatment or cancer that returns, or recurs. As researchers and doctors learn more about cancer cells and genetics, other information is used in cancer staging as well. Some cancers involve different types of cells that affect treatment and outcome for patients. Doctors arrived at the stage by determining that the patient had any T, combined with N3 and M0. This means that the patient had a breast tumor of any size, cancer cells that had spread to particular lymph nodes around the collarbone or underarm area that are not the closest lymph nodes to the tumor, and possible in some lymph nodes inside breast tissue. Based on the staging, the patient would receive a combination of breastconserving surgery, lymph node removal, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy. Origins In the 1760s, a Scottish surgeon named John Hunter had described 'movable tumors' and compared them to those that were immovable, or more advanced. He advised that doctors only remove movable tumors because immovable ones were beyond treatment. A German researcher named Theodor Schwann first recognized the role of multiplying cells in cancer, and put a description to metastasis in the mid-nineteenth century. He also recognized that the early and widespread forms of the disease should be treated differently. Family members, friends, and caregivers are also impacted by the survivorship experience and are therefore included in this definition. Sixty-four percent survived five years or more after diagnosis, with 41% living 10 years or longer and 15% living 20 years or more. Within the next decade, the number of cancer survivors is expected to increase by 37%, to 11. The most common types of cancer represented among cancer survivors in the United States are cancers of the female breast (22%); the prostate (21%); colorectal cancer (9%); and gynecologic cancers (7%). Historical background Cancer survivorship is a relatively recent issue because survival rates were quite low until the 1980s. As recently as 1960, only 25% of cancer patients lived 937 Cancer survivorship issues five years or longer post diagnosis; in the 1980s the figure approached 50% and was close to 65% as of 2014. When survival rates were low, however, little attention was paid to the minority of patients who did survive. Fitzhugh Mullin, a physician, wrote the article that is often credited with starting the survivorship movement. Mullan was then in his mid-30s, and the article was published in the New England Journal of Medicine in July 1985.
Effective abana 60pills
Placental abruption-Separation of the placenta from the uterine wall cholesterol lowering foods oatmeal discount abana 60 pills without a prescription, cutting off blood flow to the fetus. Preeclampsia-A pregnancy-related condition that causes high blood pressure and swelling. Prolapsed cord-Pushing of the umbilical cord into the vagina ahead of the baby, cutting off its blood flow. Transverse presentation-A baby laying sideways across the cervix rather than head first. Of the hundreds of thousands of women in the United States who undergo c-sections each year, about 500 die from serious infections, hemorrhaging, or other complications of the procedure. Two-thirds of maternal deaths following cesareans are related to other conditions, including those that made the c-section necessary. Very rarely, a woman may develop a wound hematoma at the site of either incision or blood clots elsewhere in the body. The risk for developing deep vein thrombosis is three to five times higher with a cesarean than with vaginal delivery. C-sections sometimes cause psychological distress that extends beyond hormonal mood swings and postpartum depression (the 'baby blues'). Mothers may feel disappointment and a sense of failure at not experiencing a vaginal delivery. They may feel isolated if the father or birthing coach is not with them in the operating room or if an unfamiliar doctor delivers the baby. Women may feel that they have lost control over their labor and delivery with no opportunity to actively participate. The mother is at risk for increased bleeding from the two incisions, the placental attachment site, and possible damage to a uterine artery. Approximately 7% of women develop infections of the incision, urinary tract, or tissue lining the uterus. Less common is injury to the surrounding organs such as the bladder and bowel, occurring in approximately 0. Strategies for the C-Section Mom: A Complete Fitness, Nutrition, and Lifestyle Guide. It involves damage to the nerves that control the heart, digestive and other organs, and eventually leads to damage to these organs. Researchers believe that the parasite that causes the disease is only found in the Americas. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Committee on Obstetric Practice. Endoscopy-Exam using an endoscope (a thin flexible tube which uses a lens or miniature camera to view various areas of the gastrointestinal tract). When the procedure is performed to examine certain organs such as the bile ducts or pancreas, the organs are not viewed directly, but rather indirectly through the injection of x ray. Parasite-An organism that lives on or in another and takes nourishment (food and fluids) from that organism. Regurgitation-Flow of material back up the esophagus and into the throat or lungs. Inability to eat, weight loss, and malnutrition become a significant factor in affecting survival. Involvement of the large intestine (colon) causes constipation, distention, and abdominal pain. The reduviids, in turn, become infected with the parasite by biting infected animals and humans. There are three phases related to infection: Acute phase lasts about two months, with non-specific symptoms of low grade fever, headache, fatigue, and enlarged liver or spleen. Chronic phase is the stage when symptoms related to damage of major organs (heart, esophagus, colon) begin. The best way to diagnose acute infection is to identify the parasites in tissue or blood. Occasionally it is possible to culture the organism from infected tissue, but this process usually requires too much time to be of value. Present medications can reduce the duration and severity of an acute infection, but are only 50% effective, at best, in eliminating the organisms. Esophageal complications require either endoscopic or surgical methods to improve esophageal emptying, similar to those used to treat the disorder known as achalasia. Constipation is treated by increasing fiber and bulk laxatives, or removal of diseased portions of the colon. In the chronic phase, irregularities of heart rhythm, heart failure, and blood clots cause weakness, fainting, and even sudden death. Because the esophagus does not empty properly, food regurgitates into the lungs causing cough, bronchitis, and repeated 1060 Prognosis Those patients with gastrointestinal complications often respond to some form of treatment. Cardiac problems are more difficult to treat, particularly since transplant would rekindle infection. Mosquito nets and insect repellents are useful in helping to avoid contact with the bugs. Blood screening is not always effective in many regions where infection is common. It is necessary to carefully screen people who have emigrated from Central and South America before they make blood donations. Common locations for chancroid sores (ulcers) in men are the shaft or head of the penis, foreskin, the groove behind the head of the penis, the opening of the penis, and the scrotum. In women, common locations are the labia majora (outer lips), labia minora (inner lips), perianal area (area around the anal opening), and inner thighs. In about 50% of the patients with chancroid, the infection spreads to either or both of the lymph nodes in the groin. Demographics Chancroid is most commonly found in developing and third world countries. In the United States, the most common cause of genital ulcers is genital herpes, followed by syphilis, and then chancroid. There are about 1,500 cases of chancroid in the United States per year and it occurred primarily in African Americans, Hispanic Americans, and Native Americans. In addition, the practice of exchanging sex for drugs has lead to a link between crack cocaine use and chancroid. Description Chancroid is an infection of the genitals that is caused by the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi. Chancroid is a sexually transmitted disease, which means that it is spread from person to person almost always by sexual contact. Uncircumcised men are about three times more likely than circumcised men to become infected following exposure to Haemophilus ducreyi. Having unprotected sex, exchanging sex for drugs, and having unprotected sex with a prostitute are other risk factors. Many cases of chancroid in the United States occur in persons who had traveled to countries where the disease is more common. Chancroid occurs when Haemophilus ducreyi penetrates the skin through an injury, like a scratch or cut. The first sign of chancroid is a small, red papule that occurs within three to seven days following exposure to the bacteria, but may take up to one month. The chancroid ulcer is painful, bleeds easily, drains a grey or yellowish pus, and has sharply defined, ragged edges. Sometimes 'kissing' ulcers occur when one ulcer spreads the bacterial infection to an opposite skin surface. Alternatively, women may not have any external sores but may experience painful urination, intercourse, and/or bowel movements and may have a vaginal discharge or rectal bleeding. Signs that the infection has spread to the lymph node appear about one week after the formation of the genital ulcer. Lymph nodes are small organs in the lymphatic system that filter waste materials from nearly every organ in the body. This lymph node infection is called 'lymphadenitis' and the swollen, painful lymph node is called a 'bubo. For a clear-cut diagnosis of chancroid, Haemophilus ducreyi must be isolated from the ulcer.
Purchase generic abana online
Chest x rays are often used to assess lung damage cholesterol test kit order abana 60pills without a prescription, but alone cannot lead to a definitive diagnosis of coccidioidomycosis because other diseases can produce similar results on the x ray. Alternatives Alternative treatment for fungal infections focuses on creating an internal environment where the fungus cannot survive. This is accomplished by eating a diet low in dairy products, sugars, including honey and fruit juice, and foods like beer that contain yeast. Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium will replenish the good bacteria in the intestines. Antifungal herbs, like garlic (Allium sativum), can be consumed in relatively large does and for an extended period of time in order to increase effectiveness. Chronic and disseminated coccidioidomycosis, however, are serious diseases that require treatment with prescription drugs. Patients with intact immune systems who develop chronic coccidiodomycosis are treated with the drug ketoconazole (Nizoral) or amphotericin B (Fungizone). Patients with suppressed immune systems are treated with amphotericin B (Fungizone). Amphotericin B is a powerful fungistatic drug with potentially toxic side effects. Because of the high cost of fluconazole, Pfizer, the 1202 Prognosis Most people who are infected with coccidiodomycosis only suffer from the mild, acute form of the disease and recover without further complications. Patients who suffer from chronic coccidiodomycosis and who have no underlying lung or immune system diseases also stand a good change of recovery, although they must be alert to a relapse. Untreated disseminated coccidiodomycosis is almost always fatal within a short time. Prevention Because the fungus that causes coccidioidomycosis is airborne and microscopic, the only method of prevention is to avoid visiting areas where it is found in the soil. In males, the coccyx curves downward, and in females, it is straighter to allow a baby to pass through the birth canal without impediment. Coccydynia presents a range of symptoms associated to a variety of underlying causes and conditions. Coccyx injuries Causes and symptoms Causes Coccydynia can be caused by a number of factors. Usually, patients report pain after a fall onto their buttocks, as occurs when going down stairs or while skating. Some experience repetitive strain from rowing or cycling, and some cite anal intercourse as the cause of pain. Sometimes bony spurs appear on the coccyx, but only seem to be painful in thin patients who do not have the padding to protect the region from the spur. Other causes of coccydynia include cancer or damage to the sacrum that generates referred pain, meaning pain that appears in one region but originates from another. Muscle strain or tension, pinched nerves or damaged nerves, or dislocation of the coccyx due to gross obesity are other causes. Symptoms the most common symptom of coccydynia, irrespective of the cause of the condition, is pain when sitting, or when rising from a sitting position. If the condition lasts long enough, the patient may even experience pain when standing or lying down. Some patients will experience pain during bowel movements, sexual intercourse, or menstruation. Secondary symptoms include back pain from sitting in odd positions in order to relieve pain, and painful feet from standing too much, because patients avoid sitting. Coccyx injuries Definition the coccyx-or tailbone-is the last bone of the vertebral column, and usually consists of three to five fused vertebrae that connect with the sacrum, a part of the pelvis. Description the coccyx consists of fused vertebrae, which are not flexible like the other vertebrae of the vertebral column which are all interspaced by intervertebral disks and joined together by elastic ligaments. Since the spinal cord ends just before the coccyx begins, coccygeal vertebrae also lack a central foramen (hole). Coccyx-The last bone of the spinal column, consisting of three to five fused vertebrae that connect with the sacrum, a part of the pelvis. Sacrum-The triangle-shaped bone located between the fifth lumbar vertebra and the coccyx that consists of five vertebrae fused together. Spinal cord-Elongated nerve bundles that lie in the vertebral canal andfrom whichthespinal nerves emerge. Vertebrae-Bones in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions of the body that make up the vertebral column. Vertebral column-The vertebral column, also called the spinal column or spine, consists of a series of vertebrae connected by ligaments. Pain control may be dangerous if an underlying condition exists of which the pain is a warning sign. This is done through careful diagnosis and the application of manual treatments, corticosteroid injections into the coccyx vertebrae, or surgery. Injections into the fourth and fifth sacral nerves and coccygeal nerves often bring relief, but are considered more as a pain control measure than as curative treatment. Surgery is a radical procedure whose indications are inconsistent and dependent on the subjectivity of the physician. Prognosis With current treatment, prognosis is good and patients usually are able to live pain free. Some women may choose to give birth through caesarian section instead of vaginally after an episode of coccyx pain from a previous delivery. Some models include a small headpiece that is worn just behind the ear and contains all the external parts, while other models also use body-worn modules that are placed in a shoulder pouch, in a pocket, or worn on a belt. The convenience of the all-in-one headpiece is balanced by shorter life for the batteries used in the smaller units, although systems using rechargeable batteries do solve some of these issues. Although a cochlear implant cannot restore hearing completely, it can provide sufficient hearing so these people can better understand the speech of themselves and others. It delivers useful auditory signals from the environment to the patient by electronically bypassing nonfunctional parts of the ear and directly stimulating the auditory nerve. Although it does not restore normal hearing, the additional input provided by the implant often improves sound detection and increases speech understanding. The content of the generated digital signal is determined by the programming of the processor and is complex. It includes information about the pitch, loudness, and timing of sound signals, and attempts to filter out extraneous noise. The transmitter and the internal parts are kept in correct alignment by using magnets present in both the internal and external parts of the device. It receives the digital signals from the transmitter and converts them into electrical signals. A wire connects the receiver to a group of electrodes that are threaded into the cochlea when the implant is placed. As many as 24 electrodes, depending on the type of the implant, stimulate the ganglion cells in the cochlea. The sounds heard through an implant are different from the normal hearing sounds and have been described as artificial or robot-like. However, as more electrodes are added, electrode placement issues are solved, and the software for the implant speech processor takes into account more and more aspects of sound, the perceived results are moving closer to how speech and other sounds are naturally perceived. Despite the benefits that the implant appears to offer, some hearing specialists and members of the deaf community believe that the benefits may not outweigh the risks and limitations of the device. Because 1205 Description Normal hearing occurs because sound travels from the outer ear into the ear canal and vibrates the eardrum. The vibration is carried through the middle ear by three small bones attached to the eardrum and on to a fluid-filled part of the inner ear called the cochlea. The movement of these hair cells stimulates nerve cells called ganglion cells, which send an electrical current to the auditory nerve. In turn, the nerve carries the electrical current to the brain, where the electrical stimulation is recognized as sound. This kind of deafness, called sensorineural deafness, can often be treated with cochlear implants.