Buy robaxin cheap
Patients at increased risk include those who have poor oral hygiene muscle relaxant japan order robaxin online now, preexisting dental or periodontal disease, wear ill-fitting dentures, or require an invasive dental procedure. Patients are also at increased risk if they have a cancer diagnosis, concomitant therapy such as 29 patient teaching chemotherapy or corticosteroid therapy, or other illnesses, such as pre-existing dental or periodontal disease, anemia, coagulopathy, or infection. After the effervescence stops, tell the patient to wait 5 minutes and then stir the solution for about 10 seconds and ingest. Teach patient to remain upright for 30 minutes after taking alendronate and until she has eaten the first food of the day. Orthostatic hypotension (with or without symptoms such as dizziness) may occur within hours after alfuzosin administration. If symptoms of angina pectoris occur or worsen, notify prescriber immediately and expect drug to be discontinued. Selectively blocks alpha1-adrenergic receptors in smooth muscle of the bladder neck and prostate, causing relaxation, and blocks postsynaptic alpha1 adrenoreceptors in the bladder base and neck, prostate, prostatic capsule, and urethra, preventing further action at these sites. These actions improve urine flow and bladder emptying and reduce urinary hesitancy, frequency, and nocturia. Some patients may need infusion once every other day; others may need it once every 4 wk. Peak Duration aliskiren Tekturna Class and Category Chemical class: Hemifumarate salt Therapeutic class: Antihypertensive (direct renin inhibitor) Pregnancy category: D To treat hypertension tablets Up to 60 min Unknown Variable Mechanism of Action Catalyzes hydrolysis of glucocerebroside to glucose and ceramide in membrane lipids. By inhibiting renin release, aliskiren impairs the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Use aliskiren cautiously in patients whose renal function may depend in part on the activity of this system such as those with renal artery stenosis, severe heart failure, post-myocardial infarction, or who are elderly or experiencing volume depletion because aliskiren therapy increases the risk of renal dysfunction in these patients that could lead to acute renal failure. If hypotension occurs during aliskiren therapy, place patient in a supine position and give normal saline solution intravenously, as needed and prescribed. Advise patient to change positions slowly and, if lightheadedness develops, to notify prescriber. To prevent uric acid nephropathy tablets 33 during vigorous treatment of neoplastic disease A Adults. To treat recurrent calcium oxalate tablets calculi allopurinol Apo-Allopurinol (can), Lopurin, Purinol (can), Zyloprim Adults. To treat increased serum and urine uric allopurinol sodium Aloprim Class and Category Chemical class: Hypoxanthine derivative, xanthine oxidase inhibitor Therapeutic class: Antigout Pregnancy category: C To treat gout and hyperuricemia tablets i. Mechanism of Action caused by neoplastic disease To prevent gout attack tablets Children ages 6 to 10. Inhibits uric acid production by inhibiting xanthine oxidase, the enzyme that converts hypoxanthine and xanthine to uric acid. By activating these receptors, almotriptan selectively constricts inflamed and dilated cranial blood vessels and inhibits production of proinflammatory neuropeptides. Because it may cause peripheral vasospastic reactions, such as ischemic bowel disease, watch for abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. In its most severe form, serotonin syndrome can resemble neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which includes a high fever, muscle rigidity, autonomic instability with possible fluctuations in vital signs, and mental status changes. Know that in moderate to severe renal dysfunction, dosage will need to be reduced. If abnormalities are present, monitor patient closely for signs and symptoms of liver dysfunction. If patient develops fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine, or becomes jaundiced during therapy, notify prescriber and expect liver enzymes to be assessed. If present, notify prescriber, expect alogliptin to be discontinued, and provide supportive care, as ordered. If suspected, notify prescriber and expect alogliptin to be discontinued, if confirmed. For patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance is less than 30 ml/min but equal to or greater than 15 ml/min), dosage decreased to 6. Mechanism of Action Inhibits the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme to slow inactivation of incretin hormones. When blood glucose level is increased, incretin hormones increase insulin synthesis and release from pancreatic beta cells. Also watch for evidence of ischemic colitis, such as rectal bleeding, bloody diarrhea, or new or worsening abdominal pain. Replaces the enzyme alpha1-antitrypsin, which normally inhibits the proteolytic enzyme elastase in patients with alpha1antitrypsin deficiency. Without alpha1proteinase inhibitor, elastase attacks and destroys alveolar membranes and causes emphysema. Tell her to stop taking alosetron immediately and to notify prescriber if evidence of ischemic colitis or constipation arises. After stoppers are dry, remove protective cover from diluent end of transfer device and insert into center of upright diluent vial. Then remove protective cover from drug end of transfer device, invert diluent vial with attached transfer device, and using minimal force, insert drug end of transfer device into center of rubber stopper of upright drug vial. Make sure flange of transfer device rests on stopper surface so that diluent flows into drug vial. If adverse reactions occur, slow infusion rate or stop infusion until symptoms subside. Inform patient that drinking a liquid beverage is not necessary after taking this form of alprazolam. No more than 2 doses, separated by 1 hr, should be given on a single day during initial titration phase. If no response, dosage increased in increments to 500 or 1,000 mcg until erection suitable for intercourse (not exceeding 1-hr duration) is achieved. A naturally occurring prostaglandin, alprostadil interacts with specific membrane-bound receptors in the corpora cavernosa cells of the penis. These chemical reactions cause the trabecular smooth muscles to relax and the cavernosal arteries to dilate. Blood flow to the penis is then increased, which distends the penile lacunar spaces and compresses the veins, trapping blood in the penis and causing it to become enlarged and rigid. Be aware that this device uses a superfine 29 gauge needle, so care must be taken to prevent needle breakage. In addition, patient must be assessed closely for drug effectiveness, as device malfunction or failure has occurred with this product. Notify prescriber, and be prepared to treat patient for priapism if erection lasts longer than 4 hours. Teach him how to correctly administer intracavernous injections or urethral suppositories. Inform him that the goal of treatment is to produce an erection that lasts no longer than 1 hour. Inform patient using urethral suppositories not to exceed two doses in a 24-hour period. Also inform him that if the desired effect is not achieved, he should have the device checked, as device malfunction or failure has been reported. If needle breaks during injection and he can see and grasp broken end, he should remove it and contact prescriber. Tell patient to hold penis upright after insertion and to roll it firmly between his hands to distribute drug. Urge him to use a condom to decrease risk of blood-borne disease, because injection can cause minor bleeding at injection site. To avoid acute bleeding complications, treatment for acute ischemic stroke must begin within 3 hr after onset of stroke symptoms and only after computed tomography or other diagnostic imaging method excludes intracranial hemorrhage.
Diseases
- Hypoparathyroidism familial isolated
- Alopecia mental retardation syndrome
- Transient neonatal arthrogryposis
- 48, XXXX syndrome
- Epitheliopathy (APMPPE)
- Foreign accent syndrome
- Orotic aciduria hereditary
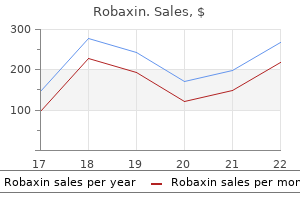
Trusted 500mg robaxin
They can also result in secondary tumor development muscle relaxant use order discount robaxin, even years after the initial therapy. The following chart lists the generic and common trade names of common antineoplastic drugs, which are grouped according to mechanism of action. Usual: 4 to 10 mg/day as a single dose or in divided doses for 3 to 6 wk 1 to 5 mg/kg P. Initially, 50 mg intrathecally (intraventricular or lumbar puncture) over 1 to 5 min every 14 days for two doses (wk 1 and 3); then 50 mg intrathecally every 14 days for three doses (wk 5, 7, and 9), followed by 1 50-mg dose at wk 13; then 50 mg intrathecally every 28 days for four doses (wk 17, 21, 25, and 29) in combination with dexamethasone 4 mg P. Apply generously to cover only lesions every other day on 1st wk; then increased as tolerated to once daily on 2nd wk, twice daily on 3rd wk, three times a day on 4th wk and, finally, four times a day on 5th wk For cycles 1-4:1. For information about the mechanisms of action, interactions, adverse reactions, and nursing considerations related to antihypertensive combinations, review the entries for the specific antihypertensives and diuretics that they contain. Vitamins are classified as one of two types: fat soluble (vitamins A, D, E, and K) and water soluble (vitamin C and all forms of vitamin B). Dosage individualized as part of total parenteral nutrition solution, as prescribed. Dosage Adjustment To reduce or prevent facial flushing, initial dosage reduced to 100 mg/day (tab) or 500 mg/day (E. Be alert to which form is being administered to ensure correct route of administration. Initial: 10 to 100 mg, then individualized based on severity of deficiency, as prescribed. Caused by pernicious anemia; malabsorption disorders (tropical or nontropical sprue, partial or total gastrectomy, regional enteritis, gastroenterostomy, ileal resection); or malignancies, granulomas, strictures, or anastomoses involving the ileum. Dosage Adjustment Recommended daily intake for people who smoke is 100 mg/day because of an increased utilization of vitamin C. Recommended daily intake should be increased to promote wound healing and for those with a chronic illness, fever, hemovascular disorder, or infection; the amount of vitamin C increase depends on the severity of the underlying condition. Initial: 1,000 to 5,000 mcg given in single daily doses of 100 mcg over 2 or more wk. Initial: 1,000 to 5,000 mcg, given in single daily doses of 100 mcg over 2 or more wk. Dosage Adjustment Dosage adjusted, as needed, to maintain normal hematologic morphology and an erythrocyte count greater than 4. They fall into three major categories-alpha, beta, and gamma- which are described below. The table on the following pages lists the trade names, indications, usual adult dosages, adverse reactions, and nursing considerations for these interferons. They also selectively increase the number of cytotoxic T-cells, thereby affecting tumor growth. This delay induces this specific form of interferon is produced by fermentation of genetically engineered Escherichia coli. As monotherapy to treat patients with chronic heptatitis C who have compensated liver disease and have never received an interferon alpha: 180 mcg/wk SubQ for 48 wk. As adjunct to treat patients with chronic hepatitis C who have compensated liver disease and have never received an interferon alpha: 180 mcg/wk SubQ with ribavirin (Copegus) 800 to 1,200 mg/day P. As adjunct treatment of melanoma with microscopic or gross nodal involvement within 84 days of definitive surgical resection: 6 mcg/kg/wk (Sylatron) SubQ for 8 doses followed by 3 mcg/kg/wk (Sylatron) SubQ for up to 5 years To treat hairy cell leukemia: 2 million units/m2 I. To treat condyloma acuminatum: 1 million units (using only the 10-million units/ml strength) intralesionally at base of wart (up to 5 warts/course) 3 times/wk on alternate days for 3 wk. If response is inadequate 12 to 16 wk after initial treatment, repeat course, as prescribed. By enhancing oxidative metabolism, they produce toxic oxygen metabolites in phagocytes, which permits more efficient killing of certain fungi, bacteria, and protozoal microbes. These drugs also stimulate production of cytokines, such as interleukin-1-beta, and regulate the immune system by suppressing the lgE level and inhibiting collagen production. To treat chronic hepatitis B: 5 million units/day or 10 million units 3 times/wk I. Interferon beta drugs interferon alfacon-1 Infergen To treat chronic, active hepatitis C: 9 mcg SubQ 3 times/wk, at intervals of at least 48 hours, for 24 wk. If inadequate response or relapse occurs, 15 mcg SubQ 3 times/wk, for up to 48 wk. As adjunct with ribavirin to treat chronic active hepatitis C: 15 mcg SubQ 3 times/wk at intervals of at least 48 hr, for up to 48 wk. Interferon beta drugs interferon beta-1a Avonex Rebif interferon beta-1b Betaseron, Extavia To treat initial attack or relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis: 30 mcg I. Expect drug to be discontinued if patient develops severe decreases in platelet or neutrophil count. To treat chronic granulomatous disease or to delay progression of severe, malignant osteopetrosis in patients with body surface area of 0. However, keep in mind that drugs listed as compatible when mixed in a syringe may not be compatible when prepared for other routes of administration. Drug combinations prepared for immediate administration usually require a more concentrated solution than those prepared for infusion. Key: C = Compatible; I = Incompatible; n/a = Compatibility information not available; no recommendations can be given. This appendix offers a quick review of ways to calculate the strength of a solution, drug dosages, and I. When a solid form of a drug is used to prepare a solution, the drug must be completely dissolved. Solid drug forms, such as tablets, crystals, and powders, are considered 100% strength. Two of the most common clinical diluents are normal saline solution and sterile water. You can use two formulas to calculate the strength of xa solution, as shown in the examples below. Calculating the Strength of a Solution Most solutions are prepared in the required strength by the pharmacy or medical supply source. Method 1: Calculating percentage and volume Use the following formula: Weaker Solution Stronger Solution Solute Solvent Example: You need to dilute a stock solution of 100% strength to a 5% solution. Method 2: Calculating percentage and volume Use the following formula: (Desired Strength) Total amount of 5 X (amount of undiluted drug (Available strength) needed to make solution) desired solution Example: You need to make 100 ml of a 20% solution, using an 80% solution. How much of the 80% solution must you add to the sterile water to yield a final volume of 100 ml of a 20% solution Calculate as follows: 20 (%)(Desired Strength) 100 ml (Total amount of desired solution) 5 X 80 (%)(Available strength) 0. You should also be prepared to convert various units of measure, such as milligrams (mg) to grains (gr), and dry measurements to liquid. You can use three common methods of ratio and proportion to calculate drug dosages, as shown in the examples below. Method 1: Using labeled amount of drug In this method, true proportions between the drug label and the prescribed dose are used to determine ratio and proportion. The drug label, which states the amount of drug in one unit of measurement-in this case, 0. Method 2: Using an established formula To determine the correct number of digoxin tablets to give using this method, use the following formula: Prescribed dose Quantity (unit of measure) X (unknown quantity to be given) Dose available (continued) 1368 Drug Formulas and Calculations Drug Formulas and Calculations (continued) Calculate as follows: 0. Method 3: Calculating according to proportion size this method uses the same components as method #1, but the ratio is based on proportions according to size. To determine the correct number of digoxin tablets to give using this method, use the following formula: smaller smaller larger larger Substitute 0. Example: You need to administer a prescribed dose of 1 mg morphine sulfate from a unit-dose cartridge containing 4 mg per 2 ml. Method 1: Using labeled amount of drug Using the same ratio as for oral drugs, the drug label-in this case, 4 mg-is the first ratio, and the prescribed dose-in this case, 1 mg-is the second ratio, expressed as follows: 4 mg (the amount of drug): 2 ml (the unit of measure) Calculate as follows: 4 mg: 2 ml 1 mg: X ml 4X 2 2 X 4 X 0. Method 2: Using an established formula Use this formula: Prescribed dose Quantity (unit of measure) X (unknown quantity to be given) Dose available Calculate as follows: 1 mg 4 mg 2 ml X (number of ml) 4 0. Flow Rates 1370 Drug Formulas and Calculations Drug Formulas and Calculations (continued) Example 1: If the physician prescribes 1,000 ml of D5W to infuse over 10 hours, and the drip rate for your administration set is 15 drops (gtt) per ml, calculate as follows: 1,000 ml 15 gtt/ml X gtt/minute 10 hours 60 minutes 1,000 ml 15 gtt/ml X gtt/minute 600 minutes 1.
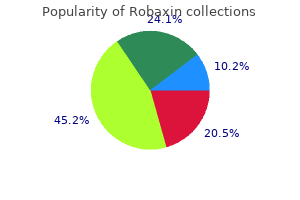
Discount 500 mg robaxin with amex
This condition may be produced artificially by visual (optokinetic nystagmus) or thermal (caloric nystagmus) stimuli muscle relaxant 114 order 500 mg robaxin mastercard. A lesion of the temporal or parietal cortex may abolish visually induced (optokinetic) nystagmus. Congenital nystagmus, which may be familial in origin, is characterized by pendular movement of the eyes at rest, triggered by head or eye movements. It is generally described as having fast and slow phases (phasic or jerk nystagmus). Occasionally, nystagmus may develop in normal individuals when they attempt to maintain extreme gaze to one side. The slow phase of the jerk nystagmus is due to the tonic vestibular stimuli, while the rapid phase (saccadic movement) is the result of the corrective action of the frontal cortex. It may also be observed in individuals with central lesions involving the ascending vestibular pathways. Nystagmus caused by peripheral lesions is generally horizontal, has a rapid phase toward the intact side, and is commonly associated with diplopia and dysarthria. A left turn results in nystagmus in a clockwise direction, whereas a right turn produces nystagmus in a counterclockwise direction. Brainstem lesions may cause gaze-dependent, coarse, and unidirectional nystagmus, which may be horizontal or vertical. The fast saccadic phase of nystagmus is lost in parietal lobe lesions which becomes evident when the striped color in optokinetic test is moved toward the affected side. Central vestibular lesions produce nystagmus with the rapid phase toward the opposite side. Vertical nystagmus with upward gaze is observed in lesions of the tegmentum and ipsilateral cerebellum. Vestibular tests An optokinetic test is performed by observing the displacement of the entire visual field. The fast phase of this nystagmus is in the direction opposite to the movement of the object. A caloric test is based upon initiating a current within the endolymph by cooling or warming the inner ear through irrigation of the external acoustic meatus. Vertical gaze can be tested by rotating the head in the vertical plane, which produces compensatory upward and downward gaze. Instillation of cold water in both ears produces tonic upward movement of the eyes, while bilateral warm water tests produce tonic downward gaze. In comatose patients, with a suppressed reticular activating system, the caloric test elicits tonic deviation of the eye only. Supratentorial lesions produce loss of oculocephalic reflex with preservation of caloric response. Frontal lesions do not interfere with either the caloric test or the oculocephalic reflex. Intactness of the vestibular system is determined by iatrogenic tests, which include optokinetic, caloric, and/or positional tests. The Romberg test determines the integrity of the system that mainly mediates proprioception; however, vestibular dysfunction can produce a positive Romberg test. In this test, the patient is asked by the examiner, who stands close by as a precaution, to stand with the feet together, hands to the sides, looking straight ahead, first with the eyes open and then with the eyes closed, and observe excessive swaying. Fourteen seconds is within normal limits for frail elderly patients; however, the same score in a young individual may suggest that the person is prone to falls. Greater than 20 s and up to 30 s is a normal range for a dependent or disabled patient who needs assistance. This testing modality helps to determine the integrity of the vestibular, visual, and somatosensory systems utilized in postural regulation. An abnormal index is seen in the elderly and patients with stroke and vestibular disorders. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls Vestibular signals of posterior parietal cortex neurons during active and passive head movements in macaque monkeys. The safe zone of posterior semicircular canal resection in suboccipital retrosigmoid sinus approach for acoustic neuroma surgery. Firing behaviour of squirrel monkey eye movement-related vestibular nucleus neurons during gaze saccades. Downbeat nystagmus associated with damage to the medial longitudinal fasciculus of the pons: A vestibular balance control mechanism via the lower brainstem paramedian tract neurons. A geometric analysis of semicircular canals and induced activity in their peripheral afferents in the rhesus monkey. A neural correlate for vestibulo-ocular reflex suppression during voluntary eye-head gaze shifts. Vestibuloocular reflex signal modulation during voluntary and passive head movements. Dissociating self-generated from passively applied head motion: Neural mechanisms in the vestibular nuclei. A score of 7 is found in older adults with a history of falls but without neurologic deficits. The Berg balance scale is a testing modality used to determine the static and dynamic balance, consisting of a set of 14 tasks. The degree of postural control is rated from 0 (unable) to 4 (independent) and also by the final total of all of the scores. Activity of medial vestibulospinal tract cells during rotation and ocular movement in the alert squirrel monkey. The vestibulocortical pathway: Neurophysiological and anatomical studies in the monkey. The vestibuloocular reflex during self-generated head movements by human subjects with unilateral vestibular hypofunction: Improved gain, latency, and alignment provide evidence for preprogramming. The location of the cell bodies in close proximity to the sensory surface is a unique feature that distinguishes them from other receptors, though they do not respond to odorants. The cell body of each receptor appears ellipsoidal with a single apical dendrite that extends to the mucus layer on the epithelial surface and forms rounded extensions receiving centrioles that eventually become the olfactory cilia. Olfactory cilia are unique in that they elicit a strong electrical response upon stimulation by the odorants, contain an abundant amount of actin, and have close resemblance to the microvilli. Due to these characteristics, olfactory cilia maximize the sensory area of each cell for detection of odorants through trailing ends that travel toward the basal layer of the epithelium, where they join other axons to form the olfactory filaments. These glial cells that continue around the olfactory filaments to their termination inside the olfactory bulb are unique cells that gain origin from the olfactory placode. The olfactory filaments pass through the cribriform plate as medial and lateral groups to enter the olfactory bulb and synapse with the mitral, basket, and periglomerular cells in the olfactory glomeruli. Plasma membrane contains concentrations of intramembranous particles that cover the exposed surfaces of the olfactory dendrites. These particles are thought to be the site of olfactory reception and ion channels related to sensory transduction; their concentrations accord with their ability to detect low concentrations of odorants. The path of migration of these cells to the hypothalamus is thought to form the nervi terminalis. These unmyelinated fibers of the bipolar and multipolar neurons extend along the medial sides of the olfactory tracts and pass through the cribriform plate to reach the nasal mucosa. Chemicals that dissolve in liquid stimulate both olfactory and taste receptors in a similar way.
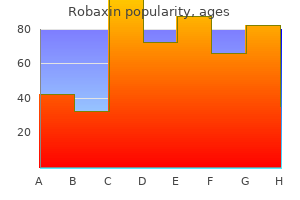
Order on line robaxin
By promoting insulin secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus muscle relaxant 551 cheap robaxin 500 mg visa, nateglinide improves glucose tolerance. Ca++ Mechanism of Action Nateglinide stimulates the release of insulin from functioning beta cells of the pancreas. In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, a lack of functioning beta cells diminishes blood levels of insulin and causes glucose intolerance. Negative chronotropic effects may slow resting heart rate, and negative inotropic effects may reduce cardiac output, myocardial contractility, and myocardial oxygen consumption during stress or exercise. All of these actions may work together to lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Also monitor fluid intake and output and daily weight, and watch for evidence of heart failure, such as dyspnea, edema, fatigue, and jugular vein distention. If patient teaching heart failure occurs or worsens, expect drug to be discontinued. However, monitor patient closely for protracted severe hypotension and difficulty restarting and keeping a heartbeat. Be prepared to administer a beta agonist such as dobutamine or isoproterenol, as ordered, to reverse the effects of nebivolol, if needed. Drug also can decrease blood glucose level, prolong or mask symptoms of hypoglycemia, promote hyperglycemia in patient with diabetes mellitus, or worsen psoriasis. Initial: 100 mg twice daily, increased by 100 to 200 mg daily every wk, as prescribed. Peak Duration Several wk Unknown Unknown Mechanism of Action May inhibit serotonin reuptake at presynaptic neurons, which may increase neuronal level of serotonin, an inhibitory neurotransmitter thought to regulate mood. Monitor patient for signs of hepatic failure, such as the development of anorexia, dark urine, fatigue, jaundice, and malaise during therapy. N O neomycin sulfate Mycifradin, Neo-Fradin Class and Category Chemical class: Aminoglycoside Therapeutic class: Antibiotic Pregnancy category: D 836 neostigmine bromide To suppress intestinal bacterial growth tablets (24-hr regimen) Indications and Dosages Adverse Reactions in preoperative bowel preparation Adults. Onset In 15 min Peak 1 hr Duration 3 hr Mechanism of Action Binds to guanylate cyclase receptor of vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. This action increases intracellular levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate, which leads to arterial and venous smooth muscle cell relaxation. Rock it gently so all surfaces, including the stopper, are in contact with diluent to ensure complete reconstitution. Notify prescriber of abnormal results because nesiritide may decrease renal function. By decreasing the intracellular calcium level, nicardipine inhibits smooth-muscle cell contraction and dilates coronary and systemic arteries. As with other calcium channel blockers, these actions lead to decreased myocardial oxygen requirements and reduced peripheral resistance, blood pressure, and afterload. Also assess for signs of heart failure, such as crackles, dyspnea, jugular vein distention, peripheral edema, and weight gain. Expect elevated liver function test results to return to normal after drug is discontinued. Urge her not to alter niclosamide the amount of grapefruit products in her diet without consulting prescriber. Suggest that she keep a log of blood pressure readings and take it to follow-up visits. Niclosamide causes the scolex (headlike segment) and proximal segment of tapeworm to detach from intestinal wall, which leads to parasite evacuation from intestine through normal peristalsis. Caution against storing in bathroom, near kitchen sink, or in other damp places because heat and moisture break down drug. Indications and Dosages To relieve nicotine withdrawal symptoms, including craving chewing gum Adults. Initial: 2 or 4 mg, as needed, or every 1 to 2 hr, adjusted to complete withdrawal by 4 to 6 mo. By providing a lower dose of nicotine than cigarettes, this drug reduces nicotine craving and withdrawal symptoms. Advise her to chew gum until she detects a tingling sensation or peppery taste and then to place gum between her cheek and gum until tingling or peppery taste subsides. Then direct her to move gum to 846 nifedipine Therapeutic class: Antianginal, antihypertensive Pregnancy category: C a different site until tingling or taste subsides, repeating until she no longer feels the sensation-usually about 30 minutes. Caution against sniffing, swallowing, or inhaling spray because nicotine is absorbed through nasal mucosa. Direct patient to inhale through device like a cigarette, puffing often for 20 minutes. Advise her to apply system to clean, hairless, dry site on upper outer arm or upper body. Instruct her to change systems and rotate sites every 24 hours and not to use the same site for 7 days. Indications and Dosages To manage angina capsules (adalat, apo-nifed, novo-nifedin, nu-nifed, procardia) Adults. Initial: 30 to 60 mg daily, increased or decreased over 7 to 14 days based on patient response. Maintenance: 30 to 60 mg daily, increased or decreased over 7 to 14 days based on patient response. Decreasing intracellular calcium level inhibits smooth-muscle cell contraction and dilates arteries, which decreases myocardial oxygen demand, peripheral resistance, blood pressure, and afterload. The capsule form of nifedipine should not be used to treat hypertension because its effects on blood pressure are not known. Urge her not to alter the amount of grapefruit in her diet without consulting prescriber. Indications and Dosages To treat neurologic deficits associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage capsules, oral solution Adults. Mechanism of Action Inhibits calcium ion transfer into smooth muscle cells, thereby inhibiting contraction of vascular smooth muscle. By relieving or preventing reactive vasodilation, nimodipine may prevent cerebral arterial spasms after hemorrhage. Notify prescriber if edema persists or if patient develops a negative fluid balance. Suggest that she keep a log of weekly measurements and take it to follow-up office appointment. Mechanism of Action May slow extracellular calcium movement into myocardial and vascular smoothmuscle cells by deforming calcium channels in cell membranes, inhibiting ioncontrolled gating mechanisms, and interfering with calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. By decreasing the intracellular calcium level, nisoldipine inhibits smooth-muscle cell contraction and dilates coronary and systemic arteries. Inform her that hot tubs, saunas, and prolonged hot showers may worsen this adverse reaction. Urge her not to alter amount of grapefruit products in her diet without consulting prescriber. Suggest that patient keep a log of weekly measurements and take it to follow-up visits. To treat diarrhea caused by Giardia oral suspension, tablets lamblia Children age 12 and over. N O Mechanism of Action Inactivates or alters bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules.
Mint oil (Japanese Mint). Robaxin.
- What is Japanese Mint?
- Dosing considerations for Japanese Mint.
- How does Japanese Mint work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Irritable bowel syndrome, itching, hives, mouth inflammation, rheumatic conditions, common cold, cough, fever, tendency to infection, nausea, sore throat, diarrhea, headaches, toothaches, cramps, earache, tumors, sores, cancer, cardiac complaints, sensitivity to weather changes, intestinal gas (flatulence), inflammation of the airways such as bronchitis, muscular pain (myalgia), ailments associated with nerve pain, and other uses.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96610
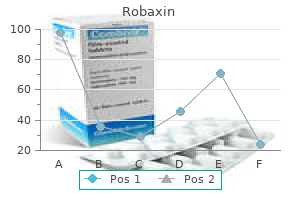
Order robaxin now
It interconnects Brodmann areas 17 and 19 and does not contain the band of Gennari spasms near heart buy generic robaxin 500 mg. Usually, in the dominant hemisphere, the upper lateral portion of Brodmann area 18 deals with memories for inanimate objects, while the lower medial portion is concerned with memories for living parts or individuals. In order for the visual object to be recognized, information must project to Brodmann area 18 of the dominant hemisphere (for fine feature analysis) via the splenium of the corpus callosum. Disruption of the connection between Brodmann areas 18 of both cerebral hemispheres may occur upon excision of the corpus callosum, producing unilateral visual agnosia. Patients with this type of deficit are unable to recognize images received by the right (nondominant) hemisphere of the brain. Bilateral visual agnosia results from a lesion of Brodmann area 18 in the dominant cerebral hemisphere. Visually agnostic patients cannot recognize objects without using tactile, auditory, gustatory, or olfactory clues. Lesions involving the parietal lobe and Brodmann area 19 of the occipital lobe may cause dysfunction similar to astereognosis. Bilateral disruption of the connections between the association visual cortices and the entorhinal cortex (Brodmann area 28) may occur as a result of basilar artery insufficiency that extends to involve the posterior cerebral arteries. This disconnection, which is associated with degeneration of the occipitotemporal area, result in anterograde visual amnesia and difficulty in visually adapting to new and unfamiliar territory despite intactness of the visual apparatus. Visual changes in migraine headaches include blurred vision, flashing lights, wavy lines, and scotoma. It is worth noting that the inferior temporal gyrus serves as a visual association cortex, contains visual memory stores, and receives input from the entorhinal cortex (Brodmann Visual System 339 area 22) and Brodmann areas 7, 18, and 19. These connections may explain the visual hallucination associated with temporal lobe epilepsy, as well as the vivid scenes experienced by patients undergoing brain operation. By the fifth postnatal month, the visual association cortices (Brodmann areas 18 and 19) become involved in stereopsis, a mechanism that enables the brain to measure the incongruity between the two retinal images, thus constructing a complete threedimensional image. Another center that mediates vertical pursuit movement is located in the interstitial nucleus of Cajal. Ocular movements are classified into conjugate (version) movements, where the visual axes of both eyes remain Optic nerve oCular moVemeNts Eye movements provide a significant index of the functional activity of the motor nuclei of the extraocular muscles and the neurons within the brainstem reticular formation. They enable image of the object of interest to be held simultaneously on both fovea centralis despite the head rotation of the observer or movements of the target. Diverting the gaze toward the target to be seen is accomplished through rapid (saccadic) eye movement; stabilization of the moving image on the fovea is mediated by smooth pursuit movements, whereas fixation of gaze during head rotation is performed by the vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic system. Despite the divergence of the neural mechanisms of the ocular movements, the common pathway that links them remains primarily confined to the pons (horizontal movement) and midbrain (vertical movement). Extraneous saccadic movements are prevented by a distinct set of pause neurons scattered in the midline of the caudal pons within the nucleus raphe interpositus that exert tonic inhibitory influence. The projection to the abducens nuclei carries vestibular input that plays a role in the fixation of gaze, but it also conveys signals from the nucleus prepositus hypoglossi through the cerebellum to regulate smooth pursuit movement. Thus the abducens neurons discharge during a horizontal saccadic movement to deviate the eye rapidly to a desired new position (pulse) and also retain this new position (step). Bilaterality of up-and-down movements is maintained by the fibers that run in the posterior commissure and connect the vertical gaze centers on both sides. These movements encompass adduction, abduction, elevation, depression, intorsion, and extorsion. It deals with tracking of approaching (converging) or receding (diverging) objects that require slow movements of the eyes in opposite directions. Conjugate eye movements are further categorized into saccadic, smooth pursuit, and vestibulo-ocular movements. It is the only conjugate movement that could be produced voluntarily, for example, when reading or visualizing the items in a room. Saccades occur virtually in all voluntary eye movements with the exception of smooth pursuit eye movements. In contrast to smooth pursuit movement, visual acuity is diminished during saccades. Saccadic movements are used to improve reading speed by increasing the numbers of words read in a single fixation. Several cortical areas are involved in saccadic movements, which include the frontal eye field in the premotor cortex (Brodmann area 8), the supplementary eye field in the rostral part of the supplementary motor cortex (Brodmann area 6) and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which occupies an area rostral to the frontal eye field (Brodmann area 46); and a posterior eye field in the superior part of the angular gyrus (Brodmann area 39). The frontal eye field initiates saccades that predict the appearance of an expected target, when a previously seen target appears, or when scanning is require to search for an image of interest. The posterior eye field in the parietal lobe is associated with the integration of visual and spatial stimuli that triggers saccadic movement in response to the sudden appearance of visual or auditory targets. The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is believed to provide a spatial map for saccadic movements that govern a previously seen target and eliminate misdirected saccades, whereas the supplementary eye field helps to produce the sequence of the saccades. Like the cortical projections, these tectal inputs to the gaze centers discharge very shortly before the saccadic movement begins and is linked to the presentation of the visual image. Thus, through this connection, the ipsilateral abducens nucleus is activated, whereas the contralateral abducens nucleus is inhibited. Visual System 341 Saccadic movements are controlled by the contralateral frontal cortex and are not affected by sedatives or analgesics. Cerebellar diseases may produce overshooting and undershooting of saccadic movements. Damage to the frontal eye field results in loss of ability to produce saccadic movements to the contralateral side and deviations of the eyes toward the lesion side (see also cortical dysfunctions, Chapter 8). Vestibulo-ocular eye movement Vestibulo-ocular movement (reflex) is designed to fixate gaze during rapid head movement. Slow movement, movement with eyes closed or head movement in darkness usually elicits minimal transient vestibulo-ocular response. The latter type of movement activates the optokinetic system, which may follow the vestibulo-ocular reflex when the head movement begins to dissipate. It is a conjugate ocular movement that involves compensatory eye movement the same distance as the head but in the opposite direction, mediated by the frontal eye fields that maintain connections with the parietotemporal cortex, and also with the primary, secondary, and tertiary visual cortices that initiate and guide the smooth pursuit movement. The mechanical stimuli generated in the vestibular receptors are transduced to impulses that travel in the primary vestibular fibers (axons of the bipolar neurons of the Scarpa ganglia) terminating in the cerebellum and the vestibular nuclei. Cerebellar dysfunctions and administration of sedatives and analgesics produce fragmentation of this movement into a series of saccades. DisorDers oF oCular moVemeNts these disorders include nystagmus, conjugate gaze palsy, ocular dysmetria, oculogyric reflex, opsoclonus, ocular flutter, ocular bobbing ocular myoclonus, oscillopsia, and congenital ocular motor apraxia. Nystagmus is an involuntary, rhythmic oscillation of the eye in response to an imbalance in the vestibular impulses (see also the vestibular system). Lateral gaze palsy refers to the inability to look to the side of the lesion resulting from destruction of the abducens nucleus. Vertical gaze palsy is characterized by the inability to look up-or downward and is associated with lesions of the vertical gaze center in the rostral midbrain. Ocular dysmetria denotes an error in ocular fixation, producing overshooting of the intended target followed by oscillation of the eyeball. The oculogyric reflex is characterized by upward or side-to-side rolling movements of the eyes accompanied by abnormal contractions of the facial muscles. This reflex may be the result of metabolic disorders of dopamine and may be alleviated with anticholinergic medications. Opsoclonus (dancing eyes in infants) is another ocular disorder that exhibits a random, conjugate saccadic movement of the eyes in all directions with unequal amplitudes. Ocular flutter, seen in individuals with cerebellar lesions, is characterized by sudden, rapid, and spontaneous to-and-fro oscillations of the eyes. It is associated with blurred vision and may be seen with changes in fixation regardless of the direction of the gaze. Ocular bobbing refers to the fast, spontaneous (not rhythmic) downward deviation of both eyes, followed by slow synchronous return of the eyes to the original position. This phenomenon may be seen in comatose individuals with lesions of the pons, cerebellum, or cerebral cortex. Ocular myoclonus is a term used to describe the rhythmic, rotatory, or pendular movements of the eyes synchronously with similar movements of the palatal, pharyngeal, laryngeal, lingual, and diaphragmatic muscles.
Order robaxin 500 mg with mastercard
Also muscle relaxant guidelines buy discount robaxin 500 mg line, a higher than recommended starting dosage may cause severe vomiting and possibly esophageal rupture. If treatment is interrupted for longer than several days, expect to restart at lowest recommended dosage. Explain that dose may be swallowed directly from the syringe or mixed into a small glass of water, cold fruit juice, or soda; stirred; and then drunk. Tell patient to remove the old patch before applying a new one and to use a new application site daily. If present, instruct patient or family to notify prescriber, as drug will need to be discontinued. Mechanism of Action Binds to selective 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor sites on cerebral blood vessels, causing vessels to constrict. This may decrease the characteristic pulsing sensation and thus relieve the pain of migraine headaches. Rizatriptan may also relieve pain by inhibiting the release of proinflammatory neuropeptides and reducing transmission of trigeminal nerve impulses from sensory nerve endings during a migraine attack. Notify prescriber immediately if the patient exhibits agitation, hallucinations, coma, tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia, hyperreflexia, incoordination, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, as serotonin syndrome can be life-threatening. Detection of peripheral blood cell abnormalities may require a bone marrow examination to identify specific abnormality. Gently swirl and invert vial to dissolve powder, which normally occurs within 2 minutes. For example, a patient starting therapy at 1 mcg/kg who weighs 75 kg will receive 75 mcg. Then, divide ordered microgram dose by concentration of reconstituted drug solution (500mcg/ ml). Initial: 2 mg once daily for 1 to 2 wk, increased, as needed, in increments of 2 mg/day at 1 wk or longer intervals. Directly stimulates postsynaptic dopamine type 2 (D2) receptors within the brain and acts as an agonist at peripheral D2 receptors. Rapid dose reduction may lead to a symptom complex resembling neuroleptic malignant syndrome that includes fever, muscle rigidity, altered level of consciousness, and autonomic instability. Orthostatic hypotension can occur more than 4 weeks after start of therapy or after a dosage reduction because ropinirole may impair systemic regulation of blood pressure. Initial: 4 mg once daily or 2 mg twice daily, increased to 8 mg once daily or 4 mg twice daily. Insulin dosage decreased by 10% to 25% if hypoglycemia occurs, or fasting plasma concentrations decrease to less than 100 mg/dl with combination therapy. This peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist regulates the transcription of insulinresponsive genes found in key target tissues, such as adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and the liver. Notify prescriber about abnormalities, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, and dark urine. If present, notify prescriber, expect to stop rosiglitazone and provide appropriate medical care as indicated and ordered. For patients taking gemfibrozil or combined atazanavir and ritonavir or lopinavir and ritonavir, 10 mg daily. For patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance greater than 30 ml/min/1. Drug may be temporarily withheld if patient develops any condition that may be related to myopathy or that predisposes her to renal failure, such as sepsis, hypotension, major surgery, trauma, uncontrolled seizures, or severe metabolic, endocrine, or electrolyte disorders. He should also tell the prescriber if these symptoms occur even after drug is discontinued. Initial: Apply 2 mg every 24 hr once daily, increased weekly in increments of 2 mg every 24 hr, as needed. Initial: Apply 4 mg every 24 hr once daily, increased weekly in increments of 2 mg every 24 hr, as needed. Initial: Apply 1 mg every 24 hr once daily, increased weekly in increments of 1 mg every 24 hr, as needed. Mechanism of Action Thought to stimulate dopamine receptors within the caudate-putamen in the brain. Know that sulfite sensitivity is more frequent in asthmatic patients than in nonasthmatic patients. Notify prescriber if present because dosage adjustment may be needed or drug discontinued. For patient with restless leg syndrome, daily dose reduced by 1 mg every 24 hours every other day, until complete withdrawal of rotigotine is achieved. Also monitor patient for fluid retention, especially in a patient with a history of congestive heart failure. If applicationsite reactions become severe, tell patient to notify the prescriber. Initial: 200 to 400 mg twice daily, increased in daily increments of 200 to 400 mg twice daily, every 2 days until reaching 1,600 mg twice daily. Initial: 5 mg/kg twice daily, increased in daily increments of 5 mg/kg twice daily. For patients also receiving valproate, initial dosage reduced to less than 400 mg daily. Although uncommon, it may cause serious adverse effects, such as urticaria, facial edema, fever, elevated eosinophils or liver enzymes, hematuria, stupor, lymphadenopathy and severe hepatitis, in addition to rash. Notify prescriber at once if such changes appear, and expect to stop drug and provide supportive care. Know that salmeterol should salsalate not be used in patients whose asthma is adequately controlled on low- or mediumdose inhaled corticosteroids and it should only be used as additional therapy for patients with asthma who are currently taking but are not adequately controlled on long-term asthma control medication, such as an inhaled corticosteroid. Expect adults with poor compliance and children and adolescents who require the addition of a long-acting beta agonist such as salmeterol to be prescribed a combination product containing both an inhaled corticosteroid and a long-acting beta agonist to increase compliance. Advise him to exhale immediately before using the diskus and then to place mouthpiece to his lips and inhale through his mouth, not his nose. Then he should remove mouthpiece from his mouth, hold his breath for at least 10 seconds, and exhale slowly. Initial: 10 mg/kg daily with dosage increased or decreased after 1 wk based on response and then periodically adjusted, as needed. Expect to discontinue drug if levels fail to increase after 1 mo of therapy at 20 mg/kg/day. This improves the oxidative metabolism of phenylalanine, which decreases blood phenylalanine. If there are particles left in glass after administration, add more water or apple juice and have patient drink again to ensure a complete dose. Advise him to stir or crush tablets to hasten process and to drink solution within 15 minutes of dissolving. Explain that tablets may not completely dissolve and that he can drink solution with particles floating in it. After drinking solution, tell him to add more water or apple juice if any particles are clinging to glass and drink again. Upon arrival at the pancreas, they stimulate pancreatic beta cells to release insulin. Incretin hormones become inactivated within minutes of release by the enzyme, dipeptidyl peptidase-4.
Order discount robaxin
However quad spasms after acl surgery discount 500 mg robaxin otc, the managerial implications of this diagnosis in the setting of less than 20% blasts is unknown. Additional clinically significant disease subgroups other than those mentioned earlier likely exist and may emerge from future studies. T-Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma T-lymphoblastic tumors constitute approximately 15% of pediatric lymphoblastic leukemia and 85% to 90% of cases that present as lymphoblastic lymphoma. Morphologically, it is not possible to reliably distinguish precursor T-lymphoblasts from precursor B-lymphoblasts, and thus immunophenotyping is required. Detection of these aberrations at diagnosis may be useful for disease monitoring, but distinct prognostic disease groups defined by recurring cytogenetic abnormalities, as are identified in the precursor B-cell tumors, are not yet part of any major classification scheme for risk group stratification. Improved survival is associated with abnormal karyotype or with t(10;14)(p13;q11). Eosinophils, which are morphologically normal, are often increased in number in the marrow, and maturing granulocytes may show pinker cytoplasm or mild nuclear irregularities than is seen in uninvolved marrows. The large number of cytoplasmic granules in the neoplastic cells of this leukemia subtype may cause some P. Large blasts display perinuclear clearing and large pink or salmon-colored cytoplasmic granules. Rare cases will have numerous eosinophils and maturing monocytes, making the blast cell count less than 20%. Blast cells contain folded or "monocytoid" nuclear features; abnormal eosinophils contain large, dark-staining granules. These patients are at risk for intracerebral hemorrhage, and recognition of the unique diagnostic features is essential for initiation of rapid therapy. In addition, numerous Auer rods are present in individual blasts (so-called faggot cells). The blasts characteristically have folded or bilobed nuclei with very fine to undetectable cytoplasmic granules. A: the hypergranular type shows abundant cytoplasmic granules as well as blasts with numerous Auer rods. B: the hypogranular variant shows blasts with basophilic, agranular cytoplasms and characteristic folded nuclei. Promonocytes are frequently present, with more mature-shaped nuclei but retaining immature nuclear chromatin. Occasionally they may lack differentiation or rarely demonstrate megakaryocytic differentiation. The blasts are large with folded, monocytoid nuclei, basophilic cytoplasms, and cytoplasmic vacuoles. Dyspoiesis of all three lineages may be evident on the peripheral smear and bone marrow aspirate. Basophilia (>2% marrow or blood basophils) is present in roughly half of reported cases, and many cases show an erythroid hyperplasia. The bone marrow blasts may show multiple morphologies, including meeting criteria for megakaryoblastic leukemia. Megakaryocytes may be normal or increased in number, frequently with small unilobated and bilobated forms or other dysplastic features. Some patients present with bone pain, lytic lesions, and bilaterally symmetric periostitis. The megakaryoblasts show typical morphologies on blood smears and aspirates with a small amount of blue cytoplasm showing P. Micromegakaryocytes may be seen in the marrow, but dyserythropoiesis and dysmyelopoiesis are not common. Megakaryoblasts may clump on core biopsies, mimicking metastatic small round blue cell tumor. The blasts have basophilic, finely granular cytoplasms with a suggestion of cytoplasmic blebbing, similar to mature megakaryocytes. These features are not specific for t(1;22), and a diagnosis of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia requires immunophenotypic or electron microscopic confirmation of megakaryocyte lineage. The prognosis of therapy-related myeloid neoplasms is very poor in general, with overall survival reported at less than 10% for adults. Treatment is limited by toxicities of prior treatment as well as drug resistance mechanisms in the neoplastic cells. The blasts have scant, agranular cytoplasms and can be easily mistaken for lymphoblasts. Most of the older literature contained cases with genetic abnormalities now recognized to be of more importance than the morphology. In addition, 20% or more of the nonerythroid cells must be myeloblasts for this diagnosis. Positive nonspecific esterase staining in virtually every blast cell confirmed the diagnosis. Of note, some presentations in the newborn may warrant a more conservative approach with observation. Myeloid sarcoma may be confused with other small round blue cell tumors of childhood. Despite these morphologic features, immunophenotypic studies are necessary to confirm the diagnosis, and repeat biopsy with flow cytometry may be necessary. Cytogenetic analysis is necessary for optimal classification and risk stratification. Repeat biopsy of the lesion for cytogenetics may be warranted when the blood or bone marrow lacks significant involvement. In vitro studies of trisomy 21 fetal liver hematopoietic stem cells show enhanced proliferation and survival. A gene array study identified three transcriptional differences between the two entities. Confirmation of these transcriptional differences may provide useful molecular markers that distinguish these related but prognostically distinctive diseases. In children younger than 4 years, the prognosis appears good despite the presence of additional karyotypic abnormalities, some of which are myelodysplasia associated. The blasts have features similar to acute megakaryoblastic leukemia, and it is not possible to predict the transient nature of this process by morphology. Acute Leukemias of Ambiguous Lineage Rare acute leukemias express both myeloid- and lymphoid-associated antigens to a degree that no single lineage can be assigned. Ambiguous lineage may be assigned because one blast population expresses markers definitive for more than one lineage (biphenotypic acute leukemia) or there are two distinct blast populations present: one myeloid and one lymphoid (bilineal acute leukemia). The proliferations typically present in the skin and subsequently rapidly disseminate to the bone marrow. Nucleoli can be prominent, and some cases may exhibit cytoplasmic "tail" extensions. Some cases may show weak TdT, and exclusion of T- or B-lymphoblastic lineage by other markers is imperative. Cytogenetic studies may show complex karyotypes, with abnormalities of 5q, 12p, 13q, 6q, 15q, and loss of chromosome 9 most frequently observed. The diagnostic criteria for the rare childhood cases are the same as those used in adults. Algorithms have been proposed to help navigate the complexity of initial diagnosis. The diagnosis of refractory anemia with excess blasts is the same in children as in adults. B: the marrow of refractory cytopenia of childhood is often hypocellular and shows characteristic micromegakaryocytes (arrow). Dysplastic changes must be present in two or more lineages or in more than 10% of the elements of any one lineage. Dysmegakaryopoiesis is evidenced by micromegakaryocytes, forms with separated nuclei, or mature forms with round nuclei. Patients are typically diagnosed before age 3, with symptoms related to infiltration of organs by the malignant cells (hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy), pallor, and skin lesions.
Order cheapest robaxin and robaxin
This insidious condition is bilateral in the majority of patients and can be inherited (autosomal dominant) and affects males and females to an equal degree spasms movie buy on line robaxin. Drusen is not always visible and may become more prominent after the first decade of life or with atrophy of the optic nerve axons. Presence of these globules may lead to compression of the optic nerve axons and the central retinal vessels, causing retinal scaring. One complication of this condition is the development of choroidal neovascular membrane and abnormal blood vessel growth beneath the retina and subsequent loss of central acute vision. It may be associated with retinitis pigmentosa and Noonan syndrome and can mimic papilledema. Integrity of the optic nerve is determined by examination of the visual fields and visual acuity. In normal individuals, the fingers will be seen at the same time by the examiner and patient. A flashing light beam or a pencil may also be used, and the patient is asked to state the timing of its appearance and direction. Visual acuity may be assessed by using the Snellen eye chart, positioned approximately 20 feet from the patient. Each eye is tested separately, and the first number in the standard ratio 20/20 denotes the actual distance of the patient from the chart, while the second number represents the distance at which a person with normal vision can read the chart. Visual acuity of each eye, which reflects the macular function, should be tested independently with and without glasses. For this purpose, the examiner may use a newspaper article or attempt to present a picture or small objects to be identified by the patient. However, upon moving the light quickly from the intact to the affected eye, the affected eye shows apparent pupillary dilatation due to the lack of afferents to the retina and optic nerve (Marcus Gunn pupil). It is formed inferior and anterior to the third ventricle and superior and rostral to the pituitary gland and sella turcica. It lies medial to the internal carotid and the site of its bifurcation into the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. It is also caudal to the anterior communicating and medial to the posterior communicating arteries. Through this vascular network, the optic chiasma receives its arterial blood supply. Corollary to this, the venous drainage pursues a similar course into the adjacent anterior cerebral vein and also to the basal vein of Rosenthal. The decussating inferior nasal fibers occupy a rostral position to that of the superior fibers within the optic chiasma. Fibers from the lower nasal quadrant form a short loop into the medial part of the contralateral optic nerve prior to joining the optic tract as the anterior knee fibers of von Willebrand. This accounts for superior temporal quadranopsia in the contralateral eye, which accompanies optic nerve lesion. Similarly, the fibers from the superior nasal quadrant of the retina form a short loop backward into the ipsilateral optic tract known as the posterior knee fibers of von Willebrand. Beyond the optic chiasma, the temporal fibers continue caudally to join the ipsilateral optic tract, whereas the crossed fibers join the contralateral optic tract. Observe the course of the optic chiasma and its relationship to the anterior cerebral artery. However, due to the benign nature of the expanding pituitary adenoma and the pattern of arrangement of the crossing nasal fibers, the disruption and the associated visual deficits occur gradually. Initially, the visual deficit is confined to the superior temporal quadrant and visual acuity and color vision, with central vision being spared. As the tumor expands, the inferior temporal quadranopsia develops, and then complete visual loss in the temporal visual half becomes evident. A lesion that affects the posterior chiasma and beginning of the optic tract produces posterior junctional scotoma, which is characterized by incongruous contralateral hemianopsia due to disruption of the nascent optic tract fibers and ipsilateral inferior temporal quadranosia as a result of damage to the crossing superior nasal fibers of the optic chiasma. Binasal heteronymous hemianopsia may be produced by aneurysms of both internal carotid arteries. Unilateral nasal hemianopsia may possibly occur if the aneurysm of the internal carotid artery is ipsilateral, which may mimic a pituitary tumor, producing visual deficits and radiographically detectable sellar enlargement. A chiasmal lesion near its junction with the optic nerve may also produce junctional scotoma, which is characterized by superior temporal quadranopsia (due to disruption of the fibers from the inferonasal part of the retina located in the rostral part of the optic chiasma) and loss of ipsilateral central vision. Based on the pattern of fiber arrangement, a chiasmal lesion also produces superior or inferior bitemporal quadranopsia or monocular temporal hemianopsia. In its anterior onethird, the optic tract is supplied by branches derived from the internal carotid, middle cerebral, and posterior communicating arteries, and in its posterior two-thirds, by a single anterior choroidal artery. The optic tract, lateral geniculate body, and optic radiation are prominently displayed. Visual System 333 Pulvinar Posterior commissure Inferior brachium of the ipsilateral temporal retinal fibers causes upper and lower pole disc atrophy, while disruption of the contralateral nasal fibers and the contralateral nasal papillomacular bundle produces a "band or bowtie" disc characterized by atrophy in the temporal and nasal poles. Partial damage to the optic tract produces the characteristic configuration of wedge-shaped loss of visual field. Cingulate gyrus Optic chiasma provides preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the ciliary ganglion that control the curvature of the lens and the contraction of the sphincter pupillae muscle through the short ciliary nerves. This will be accompanied by a mild afferent pupillary defect in contralateral side as more fibers have entered the optic tract from the opposite than the ipsilateral side. Note the optic nerve, optic chiasma, optic tract, lateral geniculate nucleus, and optic radiation. The relationship of the arterial circle of Willis to the optic nerve, optic chiasma, and optic tract is shown. Layers 1 and 2 form the ventral (magnocellular) subnucleus, and layers 3 to 6 comprise the dorsal (parvicellular) subnucleus. The medial part of this projection terminates in the superior bank of the calcarine fissure, whereas the lateral part projects in a similarly precise manner to the inferior bank of the visual cortex. Individuals with this type of lesion may exhibit pupillary constriction in accommodation but not in response to light (Argyll Robertson pupil. The optic radiation (geniculocalcarine tract), shaped like a crescent, has superior and inferior parts that course within the retrolenticular part of the internal capsule en route to the visual cortex. Fibers derived from the upper retinal quadrant run in the superior part of the optic radiation, and fibers from the lower retinal quadrant are shifted to the lower part of the optic radiation. The superior (upper) fibers of the optic radiation follow a direct path through the parietal lobe to end in the cuneus in the upper bank of the calcarine fissure. The anterior choroidal and, to a lesser degree, the posterior choroidal supply the rostral part of the optic radiation, whereas the mid portion is provided blood supply by the middle cerebral artery. The calcarine artery is the chief source of blood supply to the posterior part of the optic radiation. Similarly, in a parietal lesion that disrupts the entire optic radiation, visual field defects are bilateral and homonymous, and the smooth pursuit ocular movement to the side of the lesion is lost. Ischemic changes due to hypotension, occlusion of the posterior cerebral or basilar arteries, contrecoup head trauma, or cardiac arrest can cause a bilateral occipital lobe infarction with a unique keyhole defect seen in the vertical meridian. This visual field defect resembles a wedge or "slice" removed from the superior visual field and is commonly termed a "pie in the sky. Vascular lesions affecting the optic radiation may also be caused by occlusion of the anterior choroidal and posterior cerebral arteries. Those defects that result from damage to the optic radiation near the visual cortex are congruous (edges of the visual field defect in each eye are identical in shape). Damage to the superior fibers of the optic radiation, which rarely occurs in parietal lobe lesion, produces a contralateral inferior quadranopsia. As a result of this unique visual field representation, a lesion of the most rostral part of the calcarine fissure produces monocular homonymous defect. Visual Cortex Primary Visual corTex the primary visual or striate cortex (Brodmann area 17) is the principal cortical area for visual perception, integration, and formation of a binocular image. It is mainly confined medially to the banks of the calcarine fissure, although part of this cortex also extends slightly around the occipital pole to the lateral surface.
Purchase cheap robaxin on-line
Contraindications Bleeding or bleeding tendencies; blood dyscrasias; cerebral or dissecting aneurysm; cerebrovascular hemorrhage; diverticulitis; eclampsia or preeclampsia; history of warfarin-induced necrosis; hypersensitivity to warfarin or its components; malignant or severe uncontrolled hypertension; malnutrition and emaciation; mental state or condition that leads to lack of patient cooperation; pericardial effusion; pericarditis; polyarthritis; pregnancy; prostatectomy; recent or planned neurosurgery spasms treatment quality robaxin 500mg, ophthalmic surgery, or spinal puncture; severe hepatic or renal disease foods propafenone, propoxyphene, quinidine, quinine, quinolones, salicylates, streptokinase, sulfamethoxazoletrimethoprim, sulfinpyrazone, sulfonamides, tamoxifen, tetracyclines, thyroid hormones, urokinase, valdecoxib, vitamin E: Increased anticoagulant effect of warfarin, increased risk of bleeding aminoglutethimide, barbiturates, carbamazepine, cholestyramine, dicloxacillin, estrogens, ethchlorvynol, etretinate, glutethimide, griseofulvin, nafcillin, oral contraceptives, rifampin, spironolactone, sucralfate, thiazide diuretics, trazodone, vitamin C, vitamin K: Decreased anticoagulant effect of warfarin atorvastatin, pravastatin: Increased or decreased anticoagulant effect of warfarin herbal remedies (including bromelains, danshen, dong quai, garlic, ginkgo biloba, and ginseng): Increased anticoagulant effect of warfarin, increased risk of bleeding I. Advise him to continue these precautions for 2 to 5 days after therapy stops, as directed, because anticoagulant effect may persist during this time. This action causes bronchial relaxation and decreases vascular leakage and edema, mucus secretion, eosinophil movement, and bronchial hyper-responsiveness. This binding produces muscle relaxation and sedation as well as antianxiety and anticonvulsant effects. If present, discontinue zaleplon immediately, notify prescriber, and provide supportive care. Instruct patient to report allergic reactions, such as rash or difficulty breathing, to prescriber. If family notices any such behavior or patient sees evidence of such behavior upon awakening, prescriber should be notified. Dorsal horn Pain stimulation Pathway to the brain Dendrites Sensory neuron N-type calcium channel Sensory neuron Ziconotide binds to N-type calcium channels on primary nociceptive afferent nerves in superficial layers of the dorsal horn, as shown below. By blocking these channels, the drug prevents excitatory neurotransmitter release in primary afferent nerve terminals and relieves pain. Then, follow manufacturer guidelines for programming the microinfusion devise and doing an initial pump fill, including zileuton priming using only undiluted 25-mcg/ml solution and rinsing the internal pump surfaces with 2 ml of drug three times. If diluting ziconotide, use only normal saline solution without preservatives, following manufacturer guidelines. Expect device to need refilling about every 40 days if ziconotide is given diluted or about 60 days if given undiluted. If levels become elevated, notify prescriber and expect to decrease ziconotide dosage or stop drug until levels return to normal. Emphasize the need for strict aseptic technique with the microinfusion device and connections and the need to check the site often for problems, such as a disconnected catheter, which increase the risk of meningitis. Onset 2 hr Peak Unknown Duration Unknown Mechanism of Action Inhibits formation of leukotrienes found mainly in neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes, macrophages, and mast cells. X Y Z 1264 zinc sulfate immediately, institute safety measures and expect drug to be discontinued. Normally, leukotrienes augment neutrophil and eosinophil migration, neutrophil and monocyte aggregation, leukocyte adhesion, capillary permeability, and smooth-muscle contraction. By inhibiting leukotriene formation, zileuton causes bronchial relaxation and decreases vascular leakage and edema, mucus secretion, eosinophil movement, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Emphasize need to take drug even during symptom-free periods and acute exacerbations. If present, notify prescriber Indications and Dosages To prevent zinc deficiency based on U. Zinc also helps maintain nucleic acid, protein, and cell membrane structure and is essential for certain physiologic functions, including cell growth and division, sexual maturation and reproduction, dark adaptation and night vision, wound healing, host immunity, and taste acuity. This mineral also provides cellular antioxidant protection by scavenging free radicals. In addition, zinc acetate interferes with intestinal absorption of copper and produces a protein that binds with copper, preventing its transfer to blood. Contraindications Interactions drugs Hypersensitivity to zinc or its components Adults and children. As adjunct to lithium or valproate for capsules maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder Adults. Same dose patient was initially stabilized on that falls within 40 mg to 80 mg twice daily. Caution her not to take zinc within 2 hours of iron or copper supplements or phosphorus-containing drugs. Dizziness, palpitations, and syncope may indicate life-threatening torsades de pointes. If abnormalities occur during ziprasidone therapy, watch for fever and other evidence of infection, notify prescriber, and expect to discontinue drug if severe. Further dilute in 100 ml normal saline solution or 5% dextrose injection, and infuse over no less than 15 minutes. These reactions usually occur within first 3 days after zoledronic acid administration and resolve within 3 days (although resolution may take up to 14 days for some patients). If hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, or hypophosphatemia occurs, expect to give short-term supplemental therapy. If present, notify prescriber and expect drug to be withheld until dehydration has been corrected. If patient develops flulike symptoms such as fever, chills, flushing, bone pain, arthralgias, and myalgias, notify prescriber. If present, notify prescriber and expect to provide supportive care, as ordered, for pain relief. Class and Category Chemical class: Selective 5-hydroxytryptamine agonist Therapeutic class: Antimigraine Pregnancy category: C Indications and Dosages To treat acute migraine headache with or without aura oral disintegrating tablets Adults. Oral disintegrating tablets are not recommended for these patients because the tablet cannot be broken in half. Constricts inflamed and dilated cranial blood vessels in the carotid circulation and inhibits production of proinflammatory neuropeptides by binding to receptors on intracranial blood vessels and sensory nerves in the trigeminal-vascular system to stimulate negative feedback, which halts the release of serotonin. Tell her also not to take more than 10 mg in any 24-hour period, nor should she take drug for 10 or more days a month, because overuse of drug may lead to exacerbation of headache. Tell her to be alert for migraine-like daily headaches developing or marked increase in frequency of migraine headaches that signals overuse may be occurring. Tell her to notify prescriber, as drug may no longer be as effective and drug withdrawal may be needed. Instruct her to peel open pack, let tablet dissolve on her tongue, and then swallow. If present, discontinue zolpidem immediately, notify prescriber, and provide supportive care. Instruct patient to place tablet under his tongue and allow it to dissolve completely before swallowing. She should not perform any hazardous activity such as driving during the morning hours. Mechanism of Action May stop seizures and suppress their foci by blocking sodium channels and reducing voltage-dependent, inward currents from calcium channels. This action stabilizes neuronal membranes and suppresses synchronized neuronal hyperactivity. Systemic absorption may result in life-threatening reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, fulminant hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and other blood dyscrasias. Explain that the registry is collecting information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. When giving rapid-acting insulin via an insulin pump, do not dilute or mix with any other insulin, change the insulin in the reservoir at least every 7days (Apidra at least every 48 hours), and change the infusion sets and insertion site at least every 3 days. Be very careful to use conversion chart if U-500 strength is being administered using U-100 syringes. For an insulin pump, phosphate-buffered insulin is preferred over nonphosphate-buffered insulin. The catheter tubing and reservoir insulin should be changed every 48 hours or as specified by the pump manufacturer. So expect to mix it with a short-acting insulin, as prescribed, for optimum blood glucose control. Inject Humulin-U or Novolin ge Ultralente 30 to 60 minutes before a meal or bedtime snack. Inject Lantus once daily at any time, keeping the daily injection time consistent. Inject Levemir prescribed once daily with the evening meal or at bedtime; inject Levemir prescribed twice daily with the morning meal and with the evening meal, at bedtime, or 12 hours after the morning dose.