Buy himplasia with paypal
Percutaneous liver biopsy may be helpful in diagnosing liver disease kan herbals relaxed wanderer order discount himplasia online, but some common causes of liver disease (eg, M avium complex, lymphoma) can be determined by less invasive measures (eg, blood culture, biopsy of a more accessible site). Paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir/ dasabuvir can be used safely with raltegravir, enfuvirtide, tenofovir, emtricitabine, lamivudine, and atazanavir. Simeprevir can be used safely with raltegravir, rilpivirine, maraviroc, enfuvirtide, tenofovir, emtricitabine, lamivudine, and abacavir. It is important to be extremely cautious about discontinuing these medications in coinfected patients as sudden discontinuation could lead to a fatal flare of hepatitis B infection. Because there are no data to support one regimen over another, the least expensive regimen may be preferred. At the moment, all are very expensive, but it is hoped that competition between the regimens will ultimately reduce the price. Acid-reducing medicines should be avoided with ledipasvir and paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir/dasabuvir. Biliary disease-Cholecystitis presents with manifestations similar to those seen in immunocompetent hosts but is more likely to be acalculous. Typically, the syndrome presents with severe nausea, vomiting, and right upper quadrant pain. Liver enzymes generally show alkaline phosphatase elevations disproportionate to elevation of the aminotransferases. Although dilated ducts can be seen on ultrasound, the diagnosis is made by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, which reveals intraluminal irregularities of the proximal intrahepatic ducts with "pruning" of the terminal ductal branches. Stenosis of the distal common bile duct at the papilla is commonly seen with this syndrome. Relapses of enterocolitis following adequate therapy have been reported with both Salmonella and Shigella infections. Because of the wide range of agents known to cause enterocolitis, a stool culture and multiple stool examinations for ova and parasites (including modified acid-fast staining for Cryptosporidium) should be performed. Although frank deficiency of cortisol is rare, an isolated defect in mineralocorticoid metabolism may lead to saltwasting and hyperkalemia. Management-To date, no consistently effective treatments have been developed for Cryptosporidium infection. The diarrhea can be treated symptomatically with diphenoxylate with atropine (one or two tablets orally three or four times a day). Patients with a negative stool examination and persistent symptoms should be evaluated with colonoscopy and biopsy. Upper endoscopy with small bowel biopsy is not recommended as a routine part of the evaluation. Options for suppressive therapy include acyclovir (400 mg orally twice daily), famciclovir (250 mg orally twice daily), and valacyclovir (500 mg orally daily). Acyclovir can also be used, but it requires very frequent dosing (800 mg orally four or five times per day for 7 days). Vesicular lesions should be cultured if there is any question about their origin, since herpes simplex responds to much lower doses of acyclovir. Bacillary angiomatosis-It is caused by two closely related organisms: Bartonella henselae and Bartonella quintana. The epidemiology of these infections suggests zoonotic transmission from fleas of infected domestic cats. The most common manifestation is raised, reddish, highly vascular skin lesions that can mimic the lesions of Kaposi sarcoma. Fever is a common manifestation of this infection; involvement of bone, lymph nodes, and liver has also been reported. The infection responds to doxycycline, 100 mg orally twice daily, or erythromycin, 250 mg orally four times daily. Therapy is continued for at least 14 days, and patients who are seriously ill with visceral involvement may require months of therapy. Bacillary angiomatosis presenting with facial tumor and multiple abscesses: a case report. Interventions for molluscum contagiosum in people infected with human immunodeficiency virus: a systematic review. While particularly common in the inguinal region, they may occur anywhere on the body. Fungal rashes generally respond well to topical clotrimazole (1% cream twice a day) or ketoconazole (2% cream twice a day). Scrapings of seborrhea have revealed Malassezia furfur (Pityrosporum ovale), implying that the seborrhea is caused by this fungus. Consistent with the isolation of this fungus is the clinical finding that seborrhea responds well to topical clotrimazole (1% cream) as well as hydrocortisone (1% cream). Folliculitis is initially treated with topical clindamycin or mupirocin, and patients may benefit from regular washing with an antibacterial soap such as chlorhexidine. Intranasal mupirocin has been used successfully for staphylococcal decolonization in other settings. Recommendations for empiric treatment are either (1) trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (one doublestrength tablet orally twice daily) with or without clindamycin (500 mg orally three times daily); or (2) doxycycline (100 mg orally twice daily) with close follow-up. Treatment is with emollients (eg, absorption base cream) and antipruritic lotions (eg, camphor 9. The increase in incidence of malignancies is probably a function of impaired cell-mediated immunity. How I treat classical Hodgkin lymphoma in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Presentation-Lesions may appear anywhere; careful examination of the eyelids, conjunctiva, pinnae, palate, and toe webs is mandatory to locate potentially occult lesions. In light-skinned individuals, Kaposi lesions usually appear as purplish, nonblanching lesions that can be papular or nodular. In the mouth, lesions are most often palatal papules, though exophytic lesions of the tongue and gingivae may also be seen. Kaposi lesions may be confused with other vascular lesions such as angiomas and pyogenic granulomas. In this situation, Kaposi sarcoma is likely to be an immune reconstitution reaction (see Inflammatory Reactions below). An anal Papanicolaou smear is performed by rotating a moistened Dacron swab about 2 cm into the anal canal. However, there is no evidence that screening for anal cancer with Papanicolaou smears decreases the incidence of invasive cancer. Systematic review of racial disparities in human papillomavirus-associated anal dysplasia and anal cancer among men who have sex with men. The malignancies are usually of B cell origin and characterized as diffuse large-cell tumors. Management-The prognosis of patients with systemic non-Hodgkin lymphoma depends primarily on the degree of immunodeficiency at the time of diagnosis. Vaginal candidiasis may be treated with topical agents or a single dose of oral fluconazole (150 mg) (see Chapter 36). For women younger than age 30 years, a Papanicolaou smear should be performed within a year of the onset of sexual activity but no later than age 21 years. For women age 30 and older, screening should continue beyond age 65 unlike the general population.
Syndromes
- MRI of the abdomen
- Abnormally large placenta
- Water therapy
- Have tests to screen for thinning of the bones (osteoporosis)
- If the medication was prescribed for the patient
- Thrombocytopenia purpura
- Mediplast
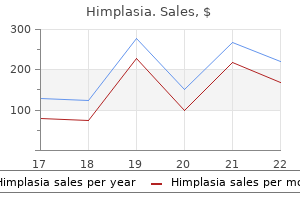
Buy himplasia australia
Also of importance is the measurement of bladder capacity during hydrodistention herbals in tamilnadu generic 30 caps himplasia with mastercard, since patients with very small bladder capacities (less than 200 mL) are unlikely to respond to medical therapy. While men are more frequently affected by urolithiasis than women, with a ratio of 2. Urinary calculi are polycrystalline aggregates composed of varying amounts of crystalloid and a small amount of organic matrix. Stone formation requires saturated urine that is dependent on pH, ionic strength, solute concentration, and complexation. There are five major types of urinary stones: calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate), uric acid, and cystine. The most common types are composed of calcium, and for that reason most urinary stones (85%) are radiopaque on plain abdominal radiographs. Uric acid stones frequently are composed of a combination of uric acid and calcium oxalate and thus are frequently radiopaque, though pure uric acid stones are radiolucent. Areas of high humidity and elevated temperatures appear to be contributing factors, and the incidence of symptomatic ureteral stones is greatest during hot summer months. Persons with sedentary lifestyles have a higher incidence of stones, which have also been associated with higher rates of hypertension, carotid calcification, and cardiovascular disease. High protein and salt intake as well as inadequate hydration appear to be the most important factors in the development of urinary stones. While approximately 50% of calcium-based stones are thought to have a heritable component, other stone types are better characterized genetically. Homozygous individuals have markedly increased excretion of cystine and frequently have numerous recurrent episodes of urinary stones. Distal renal tubular acidosis may be transmitted as a hereditary trait, and urolithiasis occurs in up to 75% of affected patients. Metabolic Evaluation Patients should strain their urine through cheesecloth or a urine strainer during a symptomatic episode to facilitate stone analysis on recovered stones. Patients with uncomplicated first-time stones should undergo dietary counseling as outlined below and can be offered an optional complete metabolic evaluation. General dietary counseling includes encouraging patients to change their diet to reduce sodium intake, reduce their animal protein intake during individual meals, and to ingest adequate fluid to achieve a voided volume of 1. Complete metabolic evaluation is recommended for patients who have recurrent stones or those with a family history of nephrolithiasis. This includes a 24-hour urine collection to ascertain urinary volume, pH, calcium, uric acid, oxalate, phosphate, sodium, and citrate excretion. In patients with either symptomatic or asymptomatic kidney stones, urinalysis usually reveals microscopic or gross hematuria (~90%). Numerous dipstick measurements are valuable in the complete workup of a patient in whom urinary stones are suspected. It is localized to the flank, is usually severe, unremitting, and may be associated with nausea and vomiting. Patients are constantly moving trying to find a comfortable position-in sharp contrast to those with an acute abdomen. As the stone progresses down the ureter, the pain may be referred into the ipsilateral groin. If the stone becomes lodged at the uretero-vesicular junction, patients will complain of marked urinary urgency and frequency and in men, pain may radiate to the tip of the penis. An increased protein load during an individual meal can also increase calcium, oxalate, and uric acid excretion and decrease urinary citrate excretion. Excessive intake of oxalate and purines can increase the incidence of stones in predisposed individuals. In fact, decreased calcium consumption has been found to increase stone recurrence. More than 60% of patients with acute renal colic will have a stone in the distal 4 cm of the ureter; attention should be directed to that region when examining plain radiographs and abdominal ultrasonographic studies. Hypercalciuric-Hypercalciuric calcium nephrolithiasis (greater than 250 mg/24 h; greater than 4 mg/kg/24 h) can be caused by absorptive, resorptive, and renal disorders. There is increased urinary calcium on a regular or even a calcium-restricted diet. Thiazide diuretics decrease renal calcium and result in increased bone density of approximately 1% per year. Thiazides have limited long-term utility (less than 5 years) since they may lose their hypocalciuric effect with continued therapy. It binds to the calcium and impedes small bowel absorption due to its increased bulk. It should be given with meals so it will be available to bind to the dietary calcium. Inappropriate use may result in a negative calcium balance and a secondary parathyroid stimulation and consequent bone reabsorption. However, there is generally no enhanced decline in bone density with long-term use. Long-term use without follow-up metabolic surveillance may result in hypomagnesuria and secondary hyperoxaluria and recurrent calculi. This results in increased vitamin D synthesis and secondarily increased small bowel absorption of calcium. This can be readily reversed by orthophosphates (250 mg orally three to four times per day), presently available without need for a prescription. Orthophosphates do not change intestinal absorption but rather inhibit vitamin D synthesis. Diet To reduce the recurrence rate of urinary stones, dietary modification is important. Additional metabolic evaluation often identifies a modifiable risk factor that can further reduce stone recurrence rates. If no medical treatment is provided after surgical stone removal, stones will generally recur in 50% of patients within 5 years. Some stone types (eg, uric acid, cystine) are more prone to rapid recurrence than others. Absolute volumes are not established, but increasing fluid intake to ensure a voided volume of 1. Patients are encouraged to ingest fluids during meals, 2 hours after each meal (when the body is most dehydrated), and prior to going to sleep in the evening-enough to awaken the patient to void-and to ingest additional fluids during the night. Increasing fluids only during daylight hours may not dilute a supersaturated urine overnight and thus initiate a new stone. Increased sodium intake will increase renal sodium and calcium excretion, increase urinary monosodium urates (that can act as a nidus for stone growth), increase the relative saturation of calcium phosphate, and decrease urinary citrate excretion. Appropriate surgical resection of the parathyroid adenoma cures the disease, although recurrent urinary stones can still occur in 10% of patients after parathyroidectomy. Renal hypercalciuria occurs when the renal tubules are unable to efficiently reabsorb filtered calcium, and hypercalciuria results. Hyperuricosuric-Hyperuricosuric calcium nephrolithiasis is secondary to dietary purine excess or endogenous uric acid metabolic defects. Most cases (85%) can be treated with purine dietary restrictions; those that are not reversed with dietary modification are successfully treated with allopurinol. In contrast to uric acid nephrolithiasis, patients with hyperuricosuric calcium stones typically maintain a urinary pH > 5. Monosodium urates absorb and adsorb inhibitors and promote heterogeneous nucleation. Alternatively, oral lemonade has been shown to increase urinary citrate by about 150 mg/24h. Hyperoxaluric-Hyperoxaluric calcium nephrolithiasis (greater than 40 mg oxalate/24 h urine) is usually due to primary intestinal disorders.
Generic 30 caps himplasia with mastercard
Because of frequent false-positive IgE tests quest herbals himplasia 30caps with amex, especially among atopic patients, oral food challenge remains the gold standard for diagnosis. However, this procedure should only be conducted by an experienced provider in a well-equipped setting. Management involves strict avoidance of the culprit food and guaranteed access to self-administered epinephrine. Other IgE-mediated food reactions include oral allergy syndrome and hypersensitivity to alpha-gal (galactosealpha-1,3-galactose). Oral allergy syndrome, also known as pollen-associated food allergy syndrome, is the result of cross-reactivity between food and pollen proteins. Symptoms and Signs Symptoms and signs typically occur within 30 minutes of initial exposure but may appear up to several hours later. These include (in order of frequency) (1) skin manifestations, typically urticaria but also flushing, blotchy rashes, and pruritus; (2) respiratory distress, including wheezing, stridor, bronchospasm, and airway angioedema; (3) gastrointestinal symptoms, including cramping, emesis, and diarrhea (especially in food allergy); and (4) hypotension, often manifested as lightheadedness, dizziness, or syncope. The condition is potentially fatal, especially if untreated, and can affect both nonatopic and atopic persons. Laboratory Findings Identification of anaphylaxis is clinical as the need for treatment is urgent. Venom Allergy the most common insects causing systemic allergic reactions include honeybees, vespids (yellow jackets, hornets, wasps), and fire ants. Systemic reactions often occur after several unremarkable stinging events and can develop at any age. Patients at highest risk for a severe reaction are those who have had a history of recent and severe reactions. The risk of a systemic reaction appears to decline over time since the last sting. If a systemic allergy is suspected, referral to an allergist for testing and, if appropriate, initiation of venom immunotherapy, is recommended. In the interim, making self-administrated epinephrine available is indicated for those with continuing exposure. In contrast to systemic food allergy, symptoms are limited to the oropharynx and usually do not involve other organ systems or progress to anaphylaxis. Alpha-gal (galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose) is a carbohydrate found in red mammalian meats, including beef, pork and lamb but not in human tissues. Sensitization to this epitope has been linked to tick bites, so nonatopic individuals are at risk. Review article: the diagnosis and management of food allergy and food intolerances. Examples include radiocontrast reactions, opioid reactions (direct mast cell activation), and "red man syndrome" from rapid infusion of vancomycin. Patients with mast cell disorders may be more prone to these reactions due to more easily triggered mast cell degranulation. In contrast to IgE-mediated reactions, these can often be prevented by prophylactic medical regimens. With the exception of beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillins and some intraoperative drugs, in vivo skin testing for lowmolecular-weight drugs is largely unvalidated, and interpretable only if the test is positive at a nonirritating concentration. Testing for IgE-mediated allergy to penicillin is available because the immunochemistry has been delineated and appropriate skin testing reagents are available. Skin testing with the major and minor metabolic determinants of penicillin has a very high (more than 98%) negative predictive value. Referral of individuals who relate histories of acute penicillin reactions to an allergist for skin testing is worthwhile because more than 90% have negative testing, indicating loss of allergic sensitization. If a patient has had an anaphylactoid reaction to conventional radiocontrast media, the risk for a second reaction upon reexposure may be as high as 30%. The use of the lower-osmolality radiocontrast media in combination with the pretreatment regimen decreases the incidence of recurrent reactions to less than 1%. First described as a vancomycin infusion reaction, it is related to the rate of drug administration resulting in direct activation of mast cells. In patients who have previously experienced a vancomycin infusion reaction, premedication with an H1-antagonist (eg, diphenhydramine) and H2-antagonist (eg, cimetidine) is recommended 1 hour prior to the infusion. Although rare, IgE sensitization to vancomycin does occur and should be suspected in patients who have received multiple courses of the drug. Skin testing is helpful because vancomycin, as a "complete allergen," can elicit positive skin tests. Desensitization to vancomycin is possible for patients with positive skin tests and no acceptable alternative antibiotic. Anaphylactoid reactions to the nonvascular administration of water-soluble iodinated contrast media. Delayed adverse reactions to the parenteral administration of iodinated contrast media. Patients selected for testing include those with moderate to severe disease, those who are potential candidates for allergen immunotherapy, and those with strong predisposing factors for atopic diatheses, eg, a strong family history of atopy or ongoing exposure to potential sources of allergen. Since the development of rhinitis precedes the presentation of asthma in over half of cases, early intervention may decrease the risk of more severe clinical illness. For example, IgE antibody causes allergic rhinitis but not allergic contact dermatitis. Clinical history-driven diagnosis of allergic diseases: utilizing in vitro IgE testing. Reactions outside of the respiratory system can also occur, including ocular, cutaneous, and gastric symptoms. Desensitization and long-term aspirin therapy have also been shown to reduce the need for nasal polypectomy and asthma therapy. Referral to an allergy specialist is appropriate for consideration of such desensitization. Management of patients with nonaspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease aspirin hypersensitivity reactions. A common example is allergic contact dermatitis, which develops when a low-molecular-weight sensitizing substance serves as a hapten for dermal proteins, becoming a complete antigen. Another common expression of delayed hypersensitivity is drug allergy that occurs after a similar process and that often results in maculopapular or morbilliform exanthems. In addition, subsequent inflammation and tissue damage occurs via various effector cell types, including monocytes, eosinophils, and neutrophils. Given the range of cutaneous findings, the differential diagnosis is broad and includes miliaria, lichen planus, folliculitis, pityriasis rosea, tinea corporis, and mycosis fungoides. Physical examination of rash characteristics, dermatologic consultation, and biopsy findings can help narrow the differential. While a whole spectrum of drugs can result in exanthems, there are no commercially available laboratory or other diagnostic tests to reliably identify the culprit drug. Systemic corticosteroids may be indicated for extensive dermatitis or other organ involvement. In vitro diagnosis of delayed-type drug hypersensitivity: mechanistic aspects and unmet needs. Laboratory Findings Laboratory abnormalities include leukocytosis with eosinophilia (greater than 1. The most common skin biopsy findings are a dense, perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate in the papillary dermis with eosinophils and dermal edema. Although the entire skin surface can be involved, the face, trunk, and upper and lower extremities are the commonly affected areas. The most common systemic findings involve the lymphatic (lymphadenopathy), hematologic and hepatic systems, although renal, pulmonary and cardiac involvement is also documented. Most notably, B*57:01 confers risk for reactions to abacavir; B*15:02, for carbamazepine; B*58:01, for allopurinol; and B*13:01, for dapsone.
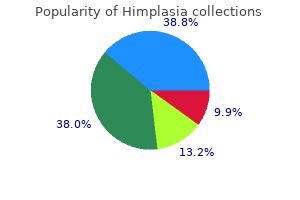
Generic himplasia 30 caps with amex
Sulfonamides herbals on express buy himplasia 30caps with visa, imidazole medications, antituberculous medications, pentamidine, clarithromycin, and didanosine have also been associated with hepatitis. All nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors cause lactic acidosis, which can be fatal. Clinicians should aggressively treat conditions that result in increased risk of heart disease, especially smoking, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and sedentary lifestyle. These inflammatory reactions may present with generalized signs of fevers, sweats, and malaise with or without more localized manifestations that usually represent unusual presentations of opportunistic infections. Tuberculosis may paradoxically worsen with new or evolving pulmonary infiltrates and lymphadenopathy. Therapeutics targeting inflammation in the immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Younger adolescents and older adults who are at increased risk should also be screened. For persons whose test results are positive, it is critically important that they be connected to ongoing medical care. They should be made familiar with the use of condoms, including, specifically, the advice that condoms must be used every time, that space should be left at the tip of the condom as a receptacle for semen, that intercourse with a condom should not be attempted if the penis is only partially erect, that men should hold on to the base of the condom when withdrawing the penis to prevent slippage, and that condoms should not be reused. Women as well as men having sex with men should understand how to use condoms to be sure that their partners are using them correctly. However, for a variety of reasons, people do not always use condoms even when taught to do so. Taking one pill right before sex would not be expected to offer protection because the medicine would not have adequate drug levels in the body. Maximum concentrations are achieved in various locations in the body at different treatment intervals: in blood, maximum levels are achieved after 20 days of daily dosing; in rectal tissue, after 7 days; in cervicovaginal tissue, after 20 days. Study participants who took at least 4 daily doses in a week were protected almost as well as those who took the drug every day, indicating that missed doses do not render the treatment ineffective; however, adherence to daily dosing is the safest method. Compassionate use programs are available from the medication manufacturer for low-income uninsured persons. Pre-exposure prophylaxis: a useful tool to prevent human immunodeficiency virus infection In addition, because the psychosocial issues involved with postexposure prophylaxis for sexual and drug use exposures are complex, it should be offered with prevention counseling. Integrating antiretroviral strategies for human immunodeficiency virus prevention: post- and pre-exposure prophylaxis and early treatment. Although there is no proof that administration of antiretroviral medications following a sexual or parenteral drug use exposure reduces the likelihood of infection, there is suggestive data from animal models, perinatal experience, and a case-control study of health care workers who experienced a needle stick. The choice of antiretroviral agents and the duration of treatment are the same as those for exposures that occur through the occupational route; the preferred regimen is tenofovir 300 mg with emtricitabine 200 mg daily with raltegravir 400 mg twice a day. Recommended regimens are zidovudine and lamivudine with either ritonavir-boosted lopinavir or ritonavir-boosted atazanavir. Because reports have noted hepatotoxicity due to nevirapine in this setting, this agent should be avoided. Use of blood and blood products should be judicious, with patients receiving the least amount necessary, and patients should be encouraged to donate their own blood prior to elective procedures. Because transmission of tuberculosis may occur in health care settings, all patients with cough should be encouraged to wear masks. Epidemiologic studies show that needle sticks occur commonly among health care professionals, especially among surgeons performing invasive procedures, inexperienced hospital housestaff, and medical students. Efforts to reduce needle sticks should focus on avoiding recapping needles and use of safety needles whenever doing invasive procedures under controlled circumstances. The risk is higher with deep punctures, large inoculum, and source patients with high viral loads. Providers who have exposures to persons who are likely to have antiretroviral medication resistance (eg, persons receiving therapy who have detectable viral loads) should have their therapy s errs ook e ook e/eb e/eb /t. Those with a normal cerebrospinal fluid evaluation are treated as having late latent syphilis (benzathine penicillin G, 2. Some clinicians take a less aggressive approach to patients who have low titers (less than 1:8), a history of having been treated for syphilis, and a normal neurologic examination. With currently available treatment, progression of disease has been markedly decreased. In addition to antiretroviral treatment, prophylactic regimens can prevent opportunistic infections and improve survival. Prophylaxis and early intervention prevent several infectious diseases, including tuberculosis and syphilis, which are transmissible to others. Patients with an infiltrate in any location, especially if accompanied by mediastinal adenopathy, should have sputum sent for acidfast staining. Patients with latent tuberculosis infection who have not been previously treated for (active or latent) tuberculosis should receive isoniazid (300 mg orally daily or twice weekly) with pyridoxine (50 mg orally daily) for 9 months. Patients without evidence of hepatitis B surface antigen or surface antibody should receive hepatitis B vaccination, using the 40 mcg formulation; the higher dose is to increase the chance of developing protective immunity. If the patient does not have immunity 1 month after the three-shot series, then the series should be repeated. However, it is not known if it is efficacious in preventing herpes zoster in this population. However, supplementation is unlikely to be as effective in well-nourished populations. Substance abuse treatment should be recommended for persons who are using recreational drugs. They should be warned to avoid consuming raw meat, eggs, or shellfish to avoid infections with Toxoplasma, Campylobacter, and Salmonella. To reduce the likelihood of infection with Bartonella species, patients should avoid activities that might result in cat scratches or bites. Clarithromycin (500 mg orally twice daily) and azithromycin (1200 mg orally weekly) have both been shown to decrease the incidence of disseminated M avium complex infection by approximately 75%, with a low rate of breakthrough of resistant disease. The azithromycin regimen is generally preferred based on high compliance and low cost. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (one double-strength tablet daily) offers good protection against toxoplasmosis, Dose Side Effects Limitations One double-strength tablet three times a week to one tablet daily Rash, neutropenia, hepatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome Anemia, nausea, methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia Rash, diarrhea, nausea Hypersensitivity reaction is common but, if mild, it may be possible to treat through. Less effective than suspension trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; equal efficacy to dapsone, but more expensive. Treating patients with repeated episodes of the same opportunistic infection can pose difficult therapeutic challenges. For example, patients with second or third episodes of Pneumocystis pneumonia may have developed allergic reactions to standard treatments with a prior episode. Fortunately, there are several alternatives available for the treatment of Pneumocystis infection. Trimethoprim with dapsone and primaquine with clindamycin are two combinations that often are tolerated in patients with a prior allergic reaction to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and intravenous pentamidine. Patients in whom second episodes of Pneumocystis pneumonia develop while taking prophylaxis tend to have milder courses. As zidovudine is rarely used now, especially at high doses, the use of epoetin alfa has also decreased. An erythropoietin level greater than 500 milli-units/mL should be demonstrated before starting therapy. The starting dose of epoetin alfa is 8000 units subcutaneously three times a week. Because of the high cost of this therapy, the dosage should be closely monitored and minimized, aiming for a neutrophil count of 1000/mcL. Once a decision to initiate therapy has been made, several important principles should guide therapy. Therapy that achieves undetectable viral load has been shown to provide a durable response to the therapy. To achieve this and maintain virologic control over time, combination therapy with at least three medications from at least two different classes is necessary. Although two drug regimens containing integrase inhibitors are under study, partially suppressive combinations such as dual nucleoside therapy should be avoided. Similarly, if toxicity develops, it is preferable to change the offending medication rather than reduce individual doses. Common Side Effects Special Monitoring1 Didanosine (ddI) (Videx) es kerrs oo k eb oo e//eb /t.
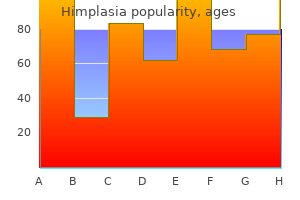
Generic himplasia 30 caps line
Tolvaptan yak herbals pvt ltd generic 30caps himplasia with visa, lixivaptan, and satavaptan are oral selective vasopressin-2 receptor antagonists; conivaptan is an intravenous agent. Desmopressin to prevent rapid sodium correction in severe hyponatremia: a systematic review. Efficacy and safety of vasopressin receptor antagonists for euvolemic or hypervolemic hyponatremia: a metaanalysis. All patients with hypernatremia have hyperosmolality, unlike hyponatremic patients who can have a low, normal, or high serum osmolality. The hypernatremic patient is typically hypovolemic due to free water losses, although hypervolemia is frequently seen, often as an iatrogenic complication in hospitalized patients with impaired access to free water. Hypernatremia in primary aldosteronism is mild and usually does not cause symptoms. An intact thirst mechanism and access to water are the primary defense against hypernatremia. The hypothalamus can sense minimal changes in serum osmolality, triggering the thirst mechanism and increased water intake. In response to increases in plasma osmolality, brain cells synthesize solutes called idiogenic osmoles, which cause intracellular fluid shifts. If hypernatremia is rapidly corrected, the osmotic imbalance may cause cerebral edema and potentially severe neurologic impairment. Fluids should be administered over a 48-hour period, aiming for serum sodium correction of approximately 1 mEq/L/h (1 mmol/L/h). There is no consensus about the optimal rates of sodium correction in hypernatremia. Because water shifts from the cells to the intravascular space to protect volume status, these symptoms may be delayed. Hyperthermia, delirium, seizures, and coma may be seen with severe hypernatremia (ie, sodium greater than 158 mEq/L). Symptoms in older adults may not be specific; a recent change in consciousness is associated with a poor prognosis. Osmotic cerebral demyelination is an uncommon but reported consequence of severe hypernatremia. Hypernatremia with euvolemia-Water ingestion or intravenous 5% dextrose will result in the excretion of excess sodium in the urine. Hypernatremia with hypervolemia-Treatment includes 5% dextrose solution to reduce hyperosmolality. Loop diuretics may be necessary to promote natriuresis and lower total body sodium. In severe rare cases with kidney disease, hemodialysis may be necessary to correct the excess total body sodium and water. Urine osmolality greater than 400 mOsm/kg-Renal water-conserving ability is functioning. Nonrenal losses-Hypernatremia will develop if water intake falls behind hypotonic fluid losses from excessive sweating, the respiratory tract, or bowel movements. Renal losses-While severe hyperglycemia can cause translocational hyponatremia, progressive volume depletion from glucosuria can result in hypernatremia. Calculation of Water Deficit Fluid replacement should include the free water deficit and additional maintenance fluid to replace ongoing and anticipated fluid losses. Acute hypernatremia-In acute dehydration without much solute loss, free water loss is similar to the weight loss. Chronic hypernatremia-The water deficit is calculated to restore normal sodium concentration, typically 140 mEq/L. Hyperosmolality of effective osmoles such as sodium and glucose causes symptoms, primarily neurologic. The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of hyperosmolality and rapidity of development. Approach to the evaluation of a patient with an increased serum osmolal gap and high-anion-gap metabolic acidosis. Urea is an ineffective osmole with little effect on osmotic water movement across cell membranes. Alcohol quickly equilibrates between the intracellular and extracellular compartments, adding 22 mOsm/L for every 100 mg/dL (or 21. Other toxic alcohols such as methanol and ethylene glycol cause an osmol gap and a metabolic acidosis with an increased anion gap (see Chapter 38). The combination of an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis and an osmol gap exceeding 10 mOsm/kg (or 10 mmol/kg) is not specific for toxic alcohol ingestion and may occur with alcoholic ketoacidosis or lactic acidosis (see Metabolic Acidosis). Acid-base disturbances in intensive care patients: etiology, pathophysiology and treatment. Recommendations for the role of extracorporeal treatments in the management of acute methanol poisoning: a systematic review and consensus statement. Cellular uptake of potassium is increased by insulin and beta-adrenergic stimulation and blocked by alpha-adrenergic stimulation. Aldosterone is an important regulator of total body potassium, increasing potassium secretion in the distal renal tubule. The most common cause of hypokalemia, especially in developing countries, is gastrointestinal loss from infectious diarrhea. The potassium concentration in intestinal secretion is ten times higher (80 mEq/L) than in gastric secretions. Hypokalemia in the presence of acidosis suggests profound potassium depletion and requires urgent treatment. In patients with heart disease, hypokalemia induced by beta-2-adrenergic agonists and diuretics may substantially increase the risk of arrhythmias. Magnesium is an important cofactor for potassium uptake and maintenance of intracellular potassium levels. Loop diuretics (eg, furosemide) cause substantial renal potassium and magnesium losses. Flaccid paralysis, hyporeflexia, hypercapnia, tetany, and rhabdomyolysis may be seen with severe hypokalemia (less than 2. In such cases, plasma renin and aldosterone levels are helpful in differential diagnosis. Dietary potassium is almost entirely coupled to phosphate-rather than chloride-and is therefore not effective in correcting potassium loss associated with chloride depletion from diuretics or vomiting. Intravenous potassium is indicated for patients with severe hypokalemia and for those who cannot take oral supplementation. For severe deficiency, potassium may be given through a peripheral intravenous line in a concentration up to 40 mEq/L and at rates up to 10 mEq/h. Avoid glucose-containing fluid to prevent further shifts of potassium into the cells. However, the higher the serum potassium concentration, the smaller the excess necessary to raise the potassium levels further. Mineralocorticoid resistance due to genetic disorders, interstitial kidney disease, or urinary tract obstruction also leads to hyperkalemia. Measurement of plasma potassium level differentiates potassium leak from blood cells in cases of clotting, leukocytosis, and thrombocytosis from truly elevated serum potassium. Rule out extracellular potassium shift from the cells in acidosis and assess renal potassium excretion.
Sussholz (Licorice). Himplasia.
- Dosing considerations for Licorice.
- What is Licorice?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Licorice work?
- Muscle cramps, arthritis, lupus, infections, hepatitis, infertility, cough, stomach ulcers, prostate cancer, weight loss, atopic dermatitis (eczema), chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), and other conditions.
- What other names is Licorice known by?
- Upset stomach (dyspepsia), when a combination of licorice and several other herbs is used.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96849
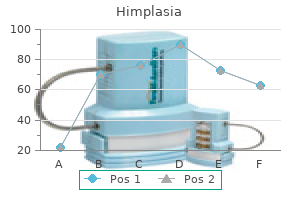
Buy generic himplasia line
Chronic hyperkalemia is best treated with dietary potassium restriction (2 g/day) and minimization or elimination of any medications that may impair renal potassium excretion greenridge herbals discount 30caps himplasia overnight delivery, as noted above. Loop diuretics may also be administered for their kaliuretic effect as long as the patient is not volume-depleted. For very elderly patients, or those with multiple debilitating or life-limiting comorbidities, dialysis therapy may not meaningfully prolong life, and the option of palliative care should be discussed with the patient and family. Conversely, for patients who are otherwise relatively healthy, evaluation for possible kidney transplantation should be considered prior to initiation of dialysis. Hemodialysis-Vascular access for hemodialysis can be accomplished by an arteriovenous fistula (the preferred method) or prosthetic graft; creation of dialysis access should be considered well before dialysis initiation. Because catheters confer a high risk of bloodstream infection, they should be considered a temporary measure. Infection, thrombosis, and aneurysm formation are complications seen more often in grafts than fistulas. Staphylococcus species are the most common cause of soft tissue infections and bacteremia. Results of trials comparing quotidian modalities (nocturnal and frequent home hemodialysis) to conventional in-center dialysis have not thus far shown significant mortality differences, but there may be improvements in blood pressure control, mineral metabolism, and quality of life. Peritoneal dialysis-With peritoneal dialysis, the peritoneal membrane is the "dialyzer. Phosphorus restriction-The phosphorus level should be kept in the "normal" range (less than 4. Foods rich in phosphorus such as cola beverages, eggs, dairy products, nuts, beans, and meat should be limited, although care must be taken to avoid protein malnutrition. Processed foods are often preserved with highly bioavailable phosphorus and should be avoided. Magnesium-containing medications, such as laxatives or antacids, and phosphorus-containing medicines, (eg, cathartics) should be avoided. Peritonitis may present with nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation, and fever. The normally clear dialysate becomes cloudy; and a diagnostic peritoneal fluid cell count greater than 100 white blood cells/ mcL with a differential of greater than 50% polymorphonuclear neutrophils is present. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common infecting organism, but streptococci and gram-negative species are also common. Two-thirds of kidney allografts come from deceased donors, with the remainder from living related or unrelated donors. The 1- and 5-year kidney graft survival rates are approximately 95% and 80%, respectively, for living donor transplants and 89% and 66%, respectively, for deceased donor transplants. Very elderly persons may die soon after dialysis initiation; those who do not may nonetheless rapidly lose functional status in the first year of treatment. The decision to initiate dialysis in patients with limited life expectancy should be weighed against possible deterioration in quality of life. Diuretics, volume restriction, and opioids, as described in Chapter 5, may help decrease the symptoms of volume overload. Use of renin angiotensin system inhibitors in patients with chronic kidney disease. Diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease in advanced and end-stage renal disease. Drug management in the elderly adult with chronic kidney disease: a review for the primary care physician. Practical approach to detection and management of chronic kidney disease for the primary care clinician. There is likely little difference in survival for well-matched peritoneal versus hemodialysis patients. Five-year Kaplan-Meier survival rates vary from 37% for patients with diabetes to 54% for patients with glomerulonephritis. Lesions are most commonly found in the proximal third or ostial region of the renal artery. Fibromuscular dysplasia has a characteristic "beads-on-a-string" appearance on angiography. Approximately 5% of Americans with hypertension suffer from renal artery stenosis. It occurs most commonly in those over 45 years of age with a history of atherosclerotic disease. In addition to hypertension, physical examination may reveal an audible abdominal bruit on the affected side. Unexplained hypertension in a woman younger than 40 years is reason to screen for this disorder. Options include medical management, angioplasty with or without stenting, and surgical bypass. Two large randomized trials have shown that vascular intervention is no better than optimal medical management in typical patients with renal artery stenosis. Angioplasty might reduce the number of antihypertensive medications but does not significantly change the progression of kidney dysfunction in comparison to patients medically managed. However, blood pressure and serum creatinine are similar at 6 months of observation compared with both angioplasty and stents. Treatment of fibromuscular dysplasia with percutaneous transluminal angioplasty is often curative, which is in stark contrast to treatment for atherosclerotic causes. A specific histologic pattern of glomerular injury results from this damage and can be seen on kidney biopsy. According to the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines, one of these should be undertaken if a corrective procedure would be performed when a positive test result is found. Doppler ultrasonography is highly sensitive and specific (85% and 92% respectively in a meta-analysis of 88 studies) and relatively inexpensive. Renal angiography is the gold standard for diagnosis but more invasive than the screening tests above. In the "least severe" end of the nephritic spectrum, the findings of glomerular hematuria (ie, dysmorphic red blood cells with some degree of proteinuria) are characteristic. The nephritic syndrome, comprising glomerular hematuria, subnephrotic proteinuria (less than 3 g/day), edema, and elevated creatinine, falls in the mid-portion of the spectrum. The nephrotic spectrum comprises diseases that present primarily with proteinuria of at least 0. Glomerular diseases present within one of the clinical spectra shown; the exact presentation is determined by the severity of the underlying disease and the pattern of injury. Nephritic diseases are characterized by the presence of an active urine sediment with glomerular hematuria and often with proteinuria. Nephrotic spectrum diseases are proteinuric with bland urine sediments (no cells or cellular casts). Glomerular diseases can also be classified according to whether they cause only renal abnormalities (primary renal disease) or whether the renal abnormalities result from a systemic disease (secondary renal disease).
Buy 30 caps himplasia with amex
If the chest radiograph is suggestive of a community-acquired pneumonia (consolidation) biotique herbals purchase cheapest himplasia and himplasia, therapy for outpatient pneumonia is begun with a third-generation cephalosporin, such as ceftriaxone, 1 g intravenously every 24 hours, plus azithromycin, 500 mg orally or intravenously every 24 hours, or doxycycline, 100 mg orally or intravenously twice daily. If the chest radiograph is normal and no focal site of infection can be found, endocarditis is presumed. While awaiting the results of blood cultures, empiric treatment with vancomycin is started. If blood cultures are positive for organisms that frequently cause endocarditis in drug users (see above), endocarditis is presumed to be present and treated accordingly. If blood cultures are positive for an organism that is an unusual cause of endocarditis, evaluation for an occult source of infection should go forward. In this setting, a transesophageal echocardiogram may be quite helpful since it is 90% sensitive in detecting vegetations and a negative study is strong evidence against endocarditis. In every patient, careful examination for an occult source of infection (eg, genitourinary, dental, sinus, gallbladder) should be done. From a diagnostic and therapeutic standpoint, it is helpful to classify infectious diarrhea into syndromes that produce inflammatory or bloody diarrhea and those that are noninflammatory, nonbloody, or watery. In general, the term "inflammatory diarrhea" suggests colonic involvement by invasive bacteria or parasites or by toxin production. Patients complain of frequent bloody, small-volume stools, often associated with fever, abdominal cramps, tenesmus, and fecal urgency. Tests for fecal leukocytes or the neutrophil marker lactoferrin are frequently positive, and definitive etiologic diagnosis requires stool culture. Noninflammatory diarrhea is generally milder and is caused by viruses or toxins that affect the small intestine and interfere with salt and water balance, resulting in large-volume watery diarrhea, Acute diarrhea: lasts less than 2 weeks Chronic diarrhea: lasts longer than 2 weeks. Moderate diarrhea: 4 or more stools per day with local symptoms (abdominal cramps, nausea, tenesmus). Severe diarrhea: 4 or more stools per day with systemic symptoms (fever, chills, dehydration). Abrupt onset of profuse diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea; vomiting occasionally. Treatment requires clear airway, ventilation, and intravenous polyvalent antitoxin (see text). Clostridia grow in anaerobic acidic environment eg, canned foods, fermented fish, foods held warm for extended periods. Associated with antimicrobial drugs; clindamycin and beta-lactams most commonly implicated. Undercooked beef, especially hamburger; unpasteurized milk and juice; raw fruits and vegetables. Abrupt onset of diarrhea, often with blood and pus in stools, cramps, tenesmus, and lethargy. Therapy depends on sensitivity testing, but the fluoroquinolones are most effective. No antimicrobials unless high risk (see text) or systemic dissemination is suspected, in which case give a fluoroquinolone. Nausea, vomiting (more common in children), diarrhea (more common in adults), fever, myalgias, abdominal cramps. Common causes of this syndrome include viruses (eg, rotavirus, norovirus, astrovirus, enteric adenoviruses), vibriones (Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus), enterotoxin-producing E coli, Giardia lamblia, cryptosporidia, and agents that can cause food-borne gastroenteritis. In developed countries, viruses (particularly norovirus) are an important cause of hospitalizations due to acute gastroenteritis among adults. The term "food poisoning" denotes diseases caused by toxins present in consumed foods. Examples include intoxication from S aureus or Bacillus cereus, and toxin can be detected in the food. When the incubation period is longer- between 8 hours and 16 hours-the organism is present in the food and produces toxin after being ingested. Vomiting is less prominent, abdominal cramping is frequent, and fever is often absent. The inflammatory and noninflammatory diarrheas discussed above can also be transmitted by food and water and usually have incubation periods between 12 and 72 hours. Cyclospora, cryptosporidia, and Isospora are protozoans capable of causing disease in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. If symptoms persist and a pathogen is isolated, it is reasonable to institute specific treatment even though therapy has not been conclusively shown to alter the natural history of disease for most pathogens. Uncomplicated gastroenteritis due to Salmonella does not require therapy because the disease is usually self-limited and therapy may prolong carriage and perhaps increase relapses. Ciprofloxacin, 500 mg orally every 12 hours for 5 days, is effective in shortening the course of illness compared with placebo in patients presenting with diarrhea, whether a pathogen is isolated or not. However, because of concerns about selecting for resistant organisms (especially Campylobacter, where increasing resistance to fluoroquinolones has been documented and erythromycin is the drug of choice) coupled with the fact that most infectious diarrhea is self-limited, routine use of antibiotics for all patients with diarrhea is not recommended. Their use should be limited to patients without fever and without dysentery (bloody stools), and they should be used in low doses because of the risk of producing toxic megacolon. Postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome can follow infection and is approached in a similar fashion as in noninfectious irritable bowel syndrome. Therapeutic recommendations for specific agents can be found elsewhere in this book. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Health Organization estimates of the global and regional disease burden of 22 foodborne bacterial, protozoal, and viral diseases, 2010: a data synthesis. Cost-effectiveness of competing strategies for management of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection: a decision analysis. General Measures In general, most cases of acute gastroenteritis are selflimited and do not require therapy other than supportive measures. Treatment usually consists of replacement of fluids and electrolytes and, very rarely, management of hypovolemic shock and respiratory compromise. In more severe cases of dehydration (postural light-headedness, decreased urination), oral glucose-based rehydration solutions can be used (Ceralyte, Pedialyte). Less than 3 weeks following exposure may suggest dengue, leptospirosis, and yellow fever; more than 3 weeks suggest typhoid fever, malaria, and tuberculosis. Meningoencephalitis Etiologies include N meningitidis, leptospirosis, arboviruses, rabies, and (cerebral) malaria. Jaundice Consider hepatitis A, yellow fever, hemorrhagic fever, leptospirosis, and malaria. The evaluation is best done by identifying whether a particular syndrome is present, then refining the differential diagnosis based on an exposure history.
Cheap himplasia 30caps online
Chemotherapeutic agents that can cause silent thyroiditis include the following: tyrosine kinase inhibitors (eg euphoric herbs cheap himplasia 30 caps visa, sunitinib), denileukin diftitox, alemtuzumab, interferon-alpha, interleukin-2, thalidomide, and lenalidomide. Immune checkpoint inhibitors include pembrolizumab, ipilimumab, tremelimumab, and atezolizumab. This usually starts with hyperthyroidism (often unrecognized) and then progresses to hypothyroidism. Chronic hepatitis C is associated with an increased risk of autoimmune thyroiditis, with 21% of affected patients having antithyroid antibodies and 13% having hypothyroidism. Physical findings can include bradycardia; diastolic hypertension; thin, brittle nails; thinning of hair; peripheral edema; puffy face and eyelids; and skin pallor or yellowing (carotenemia). Less common manifestations-Less common symptoms of hypothyroidism include diminished appetite and weight loss, hoarseness, decreased sense of taste and smell, and diminished auditory acuity. Although most menstruating women have menorrhagia, some women have scant menses or amenorrhea. Physical findings may include thinning of the outer halves of the eyebrows; thickening of the tongue; hard pitting edema; and effusions into the pleural and peritoneal cavities as well as into joints. Psychosis "myxedema madness" can occur from severe hypothyroidism or from toxicity of other drugs whose metabolism is slowed in hypothyroidism. Hypothermia and stupor or myxedema coma, which is often associated with infection (especially pneumonia), may develop in patients with severe hypothyroidism. Some hypothyroid patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis have symptoms that are not due to hypothyroidism but rather to another associated disease. Laboratory Findings Hypothyroidism is a common disorder and thyroid function tests should be obtained for any patient with its nonspecific symptoms or signs. Other laboratory abnormalities can include hyponatremia, hypoglycemia, or anemia (with normal or increased mean corpuscular volume). In patients with autoimmune thyroiditis, titers of antibodies against thyroperoxidase and thyroglobulin are high; serum antinuclear antibodies may be present but are not usually indicative of lupus. Useful in assessing the risk of malignancy (multinodular goiter or pure cysts are less likely to be malignant). However, there is considerable controversy about what represents "normal," such that each laboratory uses a slightly different range. It occurs most often in persons aged 65 years or older, in whom the prevalence is 13%. Patients without such symptoms do not require levothyroxine therapy but must be monitored regularly for the emergence of symptoms. This syndrome can be seen in patients with severe illness, caloric deprivation, or major surgery. An enlarged thymus is frequently seen in the mediastinum in cases of autoimmune thyroiditis. Factors that may cause aberrations in laboratory tests that may be mistaken for primary hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism is a rare cause of infertility, which may respond to thyroid replacement. Preexistent coronary artery disease and heart failure may be exacerbated by levothyroxine therapy. Myxedema crisis refers to severe, life-threatening manifestations of hypothyroidism. Myxedema crisis particularly affects elderly women and can occur spontaneously in severely hypothyroid patients with prolonged exposure to the cold, with resultant hypothermia. It can also be induced by a stroke, heart failure, infection (particularly pneumonia), or trauma. Metabolism of drugs is slowed in hypothyroidism and myxedema crisis is often precipitated by the administration of sedatives, antidepressants, hypnotics, anesthetics, or opioids. The drugs further impair cognition and respiratory drive and can precipitate respiratory arrest. Affected patients have impaired cognition, ranging from confusion to somnolence to coma (myxedema coma). Patients have profound hypothermia, hypoventilation, hyponatremia, hypoglycemia, hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and hypotension. Patients without symptoms of prior brain lesion or hypopituitarism are very unlikely to suddenly develop hypopituitarism during an unrelated illness. Treatment for Hypothyroidism Synthetic levothyroxine has been the overwhelmingly preferred preparation for treating hypothyroid patients. However, some clinicians prescribe mixtures of levothyroxine and triiodothyronine for certain patients. The lower doses are used for very mild hypothyroidism, while higher doses are given for more symptomatic hypothyroidism. Pregnancy usually increases the levothyroxine dosage requirement; an increase in levothyroxine requirement has been noted as early as the fifth week of pregnancy. By midpregnancy, women require an average of 47% increase in their levothyroxine dosage. Postpartum, levothyroxine replacement requirement ordinarily returns to prepregnancy level. Levothyroxine dosage may need to be titrated downward for patients who start taking teduglutide for short bowel syndrome. Myxedema crisis requires larger initial doses of levothyroxine intravenously, since myxedema itself can interfere with intestinal absorption of oral levothyroxine. The hypothermic patient is warmed only with blankets, since faster warming can precipitate cardiovascular collapse. When giving intravenous saline to myxedematous patients, care must be taken to avoid fluid overload. However, before increasing the T4 dosage, it is important to confirm that the patient is taking the levothyroxine as directed and does not have coronary insufficiency. Gastrointestinal disorders can interfere with thyroxine absorption, including celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, lactose intolerance, Helicobacter pylori gastritis, and atrophic gastritis. Women with hypothyroidism may require increased doses of levothyroxine after commencing oral estrogen therapy. For most patients with hypothyroidism, an ideal stable maintenance dose of levothyroxine can usually be found. Such patients must be assessed for concurrent conditions, such as an adverse drug reaction, Addison disease, depression, hypogonadism, anemia, celiac disease, or gluten sensitivity. If such conditions are not present or are treated and hypothyroid-type symptoms persist, a serum T3 or free T3 level is often helpful.

Buy generic himplasia 30caps line
Women with panhypopituitarism have profound androgen deficiency caused by the combination of both secondary hypogonadism and adrenal insufficiency ayur xaqti herbals buy 30 caps himplasia fast delivery. Hormonal replacement in hypopituitarism in adults: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related hypophysitis and endocrine dysfunction: clinical review. Excess mortality associated with hypopituitarism in adults: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Other Treatment Selective transsphenoidal surgery is usually performed to resect non-prolactinoma pituitary masses and Rathke cleft cysts that cause local symptoms or hypopituitarism. Patients with lymphocytic hypophysitis have been treated with glucocorticoid therapy and other immunosuppressants without much response and without reversing hypopituitarism. Spontaneous recovery from hypopituitarism associated with pituitary stalk thickening has been reported. Patients with hypopituitarism have an increased mortality risk, particularly women and those in whom diagnosis was made at a younger age, who have a craniopharyngioma, or who required transcranial surgery or radiation therapy. There is also an increased risk of death from infections with adrenal crisis in patients with untreated secondary insufficiency. In patients who have received pituitary radiation therapy, there is an increased risk of a second intracranial neoplasm and small-vessel stroke. Asymptomatic Rathke cleft cysts may not require surgery but do require endocrine, ophthalmic, and scan surveillance. Functionally, most patients with hypopituitarism do very well with hormone replacement. Women under age 40 years, with infertility due to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, can usually have successful ovulation induction. Familial diabetes insipidus occurs as a dominant genetic trait with symptoms developing at about 2 years of age. Reversible central diabetes insipidus can occur during chemotherapy with temozolomide and in the myelodysplastic preleukemic phase of acute myelogenous leukemia. Metastases to the pituitary are more likely to cause diabetes insipidus (33%) than are pituitary adenomas (1%). Partial diabetes insipidus presents with less intense symptoms and should be suspected in patients with enuresis. Most patients with diabetes insipidus are able to maintain fluid balance by continuing to ingest large volumes of water. However, in patients without free access to water or with a damaged hypothalamic thirst center and altered thirst sensation, diabetes insipidus may present with hypernatremia and dehydration. Diabetes insipidus is aggravated by administration of high-dose corticosteroids, which increases renal free water clearance. It must also be distinguished from vasopressinase-induced diabetes insipidus and from nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Vasopressinase-induced diabetes insipidus may be seen in the last trimester of pregnancy, associated with oligohydramnios, preeclampsia, or hepatic dysfunction, and in the puerperium. A circulating enzyme destroys native vasopressin; however, synthetic desmopressin is unaffected. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by unresponsiveness of the kidney tubules to the normal secretion of vasopressin, and the polyuria is due to unresponsiveness to it. A congenital form is familial and transmitted as an X-linked trait; it is caused by defective expression of renal vasopressin V2 receptors or vasopressin-sensitive water channels. Certain drugs (eg, corticosteroids, diuretics, demeclocycline, lithium, foscarnet, or methicillin) may induce nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. When nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is a diagnostic consideration, measurement of serum vasopressin is done during modest fluid restriction; typically, the vasopressin level is found to be high, distinguishing it from central diabetes insipidus. Patients with an impaired thirst mechanism are very prone to hypernatremia, as are those with impaired mentation who forget to take their desmopressin. Laboratory Findings errs es ook b ook b Diagnosis of diabetes insipidus is a clinical one; there is no diagnostic laboratory test. A urine volume of less than 2 L/24 h (in the absence of hypernatremia) rules out diabetes insipidus. Hyperuricemia occurs in many patients with central diabetes insipidus, since reduced vasopressin stimulation of the renal V1 receptor causes a reduction in the renal tubular clearance of urate. Patients with central diabetes insipidus notice a distinct reduction in thirst and polyuria; serum sodium usually remains normal. If the pituitary stalk is thickened, the cause may be Langerhans cell histiocytosis, sarcoidosis, or lymphocytic hypophysitis. It is also useful in vasopressinaseinduced diabetes insipidus associated with pregnancy or the puerperium, since desmopressin acetate is resistant to degradation by the circulating vasopressinase. Oral desmopressin is particularly useful for patients in whom rhinitis or conjunctivitis develops from the nasal preparation. Gastrointestinal symptoms, asthenia, and mild increases in hepatic enzymes can occur with the oral preparation. Desmopressin may cause hyponatremia, but this is uncommon if minimum effective doses are used and the patient allows thirst to occur periodically. Desmopressin can sometimes cause agitation, emotional changes, and depression with an increased risk of suicide. The term "acromegaly," meaning extremity enlargement, seriously understates the manifestations. Facial features coarsen since the bones and sinuses of the skull enlarge; hat size increases. Macroglossia occurs, as does hypertrophy of pharyngeal and laryngeal tissue; this causes a deep, coarse voice and sometimes makes intubation difficult. Insulin resistance is usually present and frequently causes diabetes mellitus (30%). The skin may also manifest hyperhidrosis, thickening, cystic acne, skin tags, and acanthosis nigricans. Decreased libido and erectile dysfunction are common in men and irregular menses or amenorrhea in women. Women who become pregnant have an increased risk of gestational diabetes and hypertension. Temporal hemianopia may occur as a result of the optic chiasm being impinged by a suprasellar growth of the tumor. Central diabetes insipidus after pituitary surgery usually remits after days to weeks but may be permanent if the upper pituitary stalk is cut. Chronic central diabetes insipidus is ordinarily more an inconvenience than a dire medical condition. Hypernatremia can occur, especially when the hypothalamic thirst center is damaged, but diabetes insipidus does not otherwise reduce life expectancy, and the prognosis is that of the underlying disorder. Pituitary Microsurgery Transsphenoidal pituitary microsurgery removes the adenoma while preserving anterior pituitary function in most patients. Diabetes insipidus can occur within 2 days postoperatively but is usually mild and selfcorrecting. Corticosteroids are administered perioperatively and tapered to replacement doses over 1 week; hydrocortisone is discontinued and a cosyntropin stimulation test is performed about 6 weeks after surgery. Radiographs may also show tufting of the terminal phalanges of the fingers and toes. Medications Acromegalic patients with an incomplete biochemical remission after pituitary surgery may benefit from medical therapy with dopamine agonists, somatostatin analogs, tamoxifen, or pegvisomant.

Buy 30 caps himplasia visa
Although most experts recommend application of the same primary prevention guidelines for women as for men herbals 4 play monroe la generic himplasia 30caps with visa, clinicians should be aware of the uncertainty in this area. Estimating the 10-year cardiovascular risk is particularly important in women since a larger percentage of women than men will have estimated 10-year cardiovascular risks below 7. Other measures-including smoking cessation, hypertension control, and aspirin-are also of central importance. In this study, elderly patients with cardiovascular disease (secondary prevention) benefited from statin therapy, whereas those without cardiovascular disease (primary prevention) did not. The guidelines, however, suggest not screening or treating patients over the age of 75 who do not have evidence of cardiovascular disease. Individual patient decisions to discontinue statin therapy should be based on overall functional status and life expectancy, comorbidities, and patient preference and should be made in context with overall therapeutic goals and end-oflife decisions. Thus, the results of diet therapy should be assessed about 4 weeks after initiation. Most Americans currently eat over 35% of calories as fat, of which 15% is saturated fat. In most instances, this approach will also result in fewer total calories consumed and will facilitate weight loss in overweight patients. Other diet plans, including the Dean Ornish Diet, the Pritikin Diet, and most vegetarian diets, restrict fat even further. Several studies have suggested that this approach may also be associated with reductions in endothelial dysfunction, insulin resistance, and markers of vascular inflammation and may result in better resolution of the metabolic syndrome than traditional cholesterol-lowering diets. A clinical trial demonstrated reduced cardiovascular events in persons on a Mediterranean diet supplemented with additional nuts or extra-virgin olive oil compared to persons on a less intensive Mediterranean diet. Nonpharmacological approaches for reducing serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The most common side effects are muscle aches, occurring in up to 10% of patients, and mild gastrointestinal effects. Other serious, but extremely uncommon, side effects include liver failure and muscle disease including myositis and rhabdomyolysis. Some patients experience muscle pain even when the serum creatine kinase levels are normal. Manufacturers of statins recommend monitoring liver enzymes before initiating therapy and as clinically indicated thereafter. As discussed above, the guidelines define four groups of patients who benefit from statin medications. Flushing may also be decreased by initiating niacin therapy with a very small dose, eg, 100 mg with the evening meal. It is not known whether routine monitoring of liver enzymes results in early detection and thus reduced severity of hepatocellular hepatitis with jaundice. Although niacin may increase blood sugar in some patients, clinical trials have shown that niacin can be safely used in diabetic patients. Treatment with these agents reduces the incidence of coronary events in middle-aged men by about 20%, with no significant effect on total mortality. The resultant reduction in the enterohepatic circulation causes the liver to increase its production of bile acids, using hepatic cholesterol to do so. They may interfere with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (thereby complicating the management of patients receiving warfarin) and may bind other drugs in the intestine. Simvastatin at the highest approved dose-80 mg-is associated with a higher risk of muscle injury or myopathy. This dose should be used only in those who have been taking the medication for longer than 1 year without muscle toxicity. Long-term followup of a secondary prevention trial of middle-aged men with previous myocardial infarction disclosed that about half of those who had been previously treated with niacin had died, compared with nearly 60% of the placebo group. This favorable effect on mortality was not seen during the trial itself, though there was a reduction in the incidence of recurrent coronary events. A meta-analysis of 10 randomized trials using niacin has also shown a 27% reduction in cardiovascular events. Niacin will also reduce triglycerides by half and will lower lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]) levels and will increase plasma homocysteine levels. The fibric acid derivatives or fibrates approved for use in the United States are gemfibrozil and fenofibrate. Drug Alirocumab (Praluent) Atorvastatin (Lipitor) Cholestyramine (Questran, others) es kerrs oo k eb oo e//eb /t. The incidence of the latter two conditions may be higher among patients also taking other lipid-lowering agents. Ezetimibe es kerrs oo k eb oo e//eb me Ezetimibe is a lipid-lowering drug that inhibits the intestinal absorption of dietary and biliary cholesterol across the intestinal wall by inhibiting a cholesterol transporter. However, beneficial effects of ezetimibe monotherapy on cardiovascular outcomes have not been demonstrated. Effect of ezetimibe on major atherosclerotic disease events and all-cause mortality. Identification and management of patients with statin-associated symptoms in clinical practice: a clinician survey. Drugs for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: an overview of systematic reviews. The current state of niacin in cardiovascular disease prevention: a systematic review and meta-regression. Comparative tolerability and harms of individual statins: a study level network meta-analysis of 246,955 participants from 135 randomized, controlled trials. Recommendations for management of clinically significant drug-drug interactions with statins and select agents used in patients with cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. At the end of 7 years of study, patients taking ezetimibe-simvastatin had a 2% absolute reduction in cardiovascular events compared to patients taking simvastatin alone. Studies designed to demonstrate a reduction in cardiovascular events have not been published, but analysis of existing studies does suggest a substantial reduction in death from cardiovascular disease and myocardial infarction. However, cost-effectiveness models suggest that these medications, at current prices, are not cost-effective. Although other medications will also have beneficial effects on lipids, there is little evidence demonstrating the desired effects on cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality. The use of extended-release niacin with laropiprant (a prostaglandin antagonist) in high-risk patients taking a statin also did not reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. An increase in adverse events was also seen when niacin plus laropiprant was added to statins. Safety and efficacy of statin treatment alone and in combination with fibrates in patients with dyslipidemia: a meta-analysis. The pathophysiology is not certain, since pancreatitis never develops in some patients with very high triglyceride levels.