160 mg malegra dxt plus
Acyclovir and prednisolone treatment of acute infectious mononucleosis: a multicenter sleeping pills erectile dysfunction order malegra dxt plus 160 mg fast delivery, double-blind, placebocontrolled study. The effects of short-term corticosteroid therapy on the symptoms of infectious mononucleosis pharyngotonsillitis: a double blind study. Role of steroids in the treatment of infectious mononucleosis in the ambulatory college student. Guidelines for the use of systemic glucocorticosteroids in the management of selected infections. Working Group on Steroid Use, Antimicrobial Agents Committee, Infectious Diseases Society of America. Diagnosis and management of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in solid-organ transplant recipients. Pre-emptive rituximab based on viraemia and T cell reconstitution: a highly effective strategy for the prevention of Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease following stem cell transplantation. Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in solid organ transplant recipients. Induction of the Epstein-Barr virus thymidine kinase gene with concomitant nucleoside antivirals as a therapeutic strategy for Epstein-Barr virus-associated malignancies. Ganciclovir and acyclovir reduce the risk of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in renal transplant recipients. Donor mononuclear cell infusions as therapy for B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder following allogeneic bone marrow transplant. Autologous lymphokine-activated killer cell therapy of lymphoproliferative disorders arising in organ transplant recipients. Rapidly generated multivirus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes for the prophylaxis and treatment of viral infections. Establishment and characterization of a bank of cytotoxic T lymphocytes for immunotherapy of Epstein-Barr virus-associated diseases. Allogeneic T-cell therapy for Epstein-Barr virus-positive posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease: long-term follow-up. Complete responses of relapsed lymphoma following genetic modification of tumor-antigen presenting cells and T-lymphocyte transfer. Adoptive transfer of autologous Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T cells for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Effective treatment of metastatic forms of Epstein-Barr virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma with a novel adenovirus-based adoptive immunotherapy. Efficacy of desciclovir in the treatment of Epstein-Barr virus infection in oral hairy leukoplakia. Retrospective findings of the clinical benefits of podophyllum resin 25% sol on hairy leukoplakia. Identification and isolation of the main component (gp350-gp220) of Epstein-Barr virus responsible for generating neutralizing antibodies in vivo. Rational design of an Epstein-Barr virus vaccine targeting the receptor-binding site. Nonhepatosplenic gammadelta T-cell lymphoma: a subset of cytotoxic lymphomas with mucosal or skin localization. Both viruses infect T cells, are present ubiquitously, and can cause exanthema subitum (or roseola infantum). In addition, both viruses frequently reactivate in highly immunocompromised patients but rarely cause serious disease in these patients. The disease may be accompanied by cough, cervical and occipital lymphadenopathy, erythema of the tympanic membranes, conjunctivitis, eyelid edema, bulging fontanelles, lymphadenopathy, diarrhea, or Nagayama spots (red papules on the soft palate or base of the uvula). Children older than 6 months are more likely to have fever than are younger children. Less common symptoms were upper respiratory tract disease, vomiting, and diarrhea. There are insufficient clinical reports to indicate whether these drugs are effective in vivo. Human herpesvirus-6 infection in children: a prospective study of complications and reactivation. Clinical features of infants with primary human herpesvirus 6 infection (exanthem subitum, roseola infantum). Roseolovirus-associated encephalitis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals. Pathogenic role of human herpesvirus 6B infection in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: what we do and do not know. Clinical characteristics and outcome of human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Risk factors of human herpesvirus 6 encephalitis/myelitis after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Human herpesvirus 6B reactivation and delirium are frequent and associated events after cord blood transplantation. Analysis of five cases of human herpesvirus-6 myelitis among 121 cord blood transplantations. Inherited chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6 as a predisposing risk factor for the development of angina pectoris. Safety of pre-engraftment prophylactic foscarnet administration after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Differentiation between two distinct classes of viruses now classified as human herpesvirus 6. Chromosomal integration of human herpesvirus 6 is the major mode of congenital human herpesvirus 6 infection. Transmission of integrated human herpesvirus 6 through stem cell transplantation: implications for laboratory diagnosis. High incidence of human herpesvirus 6 infection with a high viral load in cord blood stem cell transplant recipients. Selective reactivation of human herpesvirus 6 variant occurs in critically ill immunocompetent hosts. Human herpesvirus-6 entry into the central nervous system through the olfactory pathway. Roseolovirusassociated encephalitis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals. Clinical and virological analyses of 21 infants with exanthem subitum (roseola infantum) and central nervous system complications. Evidence of human herpesvirus 6 infection in 4 immunocompetent patients with encephalitis. Brief report: severe infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome and primary human herpesvirus 6 infection in an adult. Human herpesvirus 6-induced inflammatory cardiomyopathy in immunocompetent children. Clinical outcomes of human herpesvirus 6 reactivation after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Suppressive effects of human herpesvirus 6 on in vitro colony formation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Human herpesvirus 6 viremia in bone marrow transplant recipients: clinical features and risk factors.
Cheap malegra dxt plus 160mg on line
Study participants were peer-trained with the home testing kits and had limited health education and concomitant drug use erectile dysfunction causes high blood pressure discount malegra dxt plus on line, which represented possible correlates for increased frequency of incorrect interpretation, although such limitations do approximate real-world conditions. These new studies will evaluate the utility of self-testing in various settings, ranging from deployment of self-testing kits in villages in Africa and China, to evaluating health approaches to expand home testing in individuals not typically engaged in health care in the United States. These and similar studies are likely to yield important new insights regarding self-testing and linkage to care that may widely expand the numbers of individuals undergoing testing. Patients purchasing a home collection kit must contact the distributor using a toll-free telephone number, register a unique identifier contained in the kit, provide demographic data, and receive an educational pretest counseling session. Packaged material contains consent documents, and consent is implied when the individual registers the test by telephone. Patients prepare the dried blood spot sample, which is shipped for laboratory testing. Evaluation of patients with immunodeficiency will undoubtedly involve testing for known retroviruses, and the possibility of novel infections should be considered. There are, however, numerous distinct retroviruses in primate species, and the sensitivity of currently approved assays for the detection of more distantly related viruses is uncertain but is likely to be low. Spumaviruses of cows, cats, and horses do not infect humans, but simian spumaviruses are readily transmissible to humans. Typically, primate veterinary handlers, bushmeat hunters, and others with occupational or other direct primate contact421,422 may be infected. Concerns for potential retroviral expression with development of zoonotic disease from other porcine and other tissue has prompted debate and recommendations on testing of xenotransplanted tissue for the presence of retroviral sequences and the ability to induce retroviruses in vitro from candidate tissues. Development and use of unique identifiers for patients, especially in key populations, will be useful in linking individuals across clinical and epidemiologic platforms and may address limitations of current data collection strategies. The contribution of infectious disease specialist in diagnosis will be invaluable and should proceed from medical history and physical examination to laboratory diagnostic testing. Prevalence and correlates of point-of-sex human immunodeficiency virus self-testing among human immunodeficiency virus-negative men who have sex with men in China. Comparison of detection of antibody to the acquired immune deficiency syndrome virus by enzyme immunoassay, immunofluorescence, and Western blot methods. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. Evaluation of viral-lysate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits for detecting human immunodeficiency virus (type 1) infections using human sera standardized by quantitative Western blotting. Sensitive assays for viral antibodies in saliva: an alternative to tests on serum. Reduction of diagnostic window by new fourth-generation human immunodeficiency virus screening assays. Fourth-generation enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the simultaneous detection of human immunodeficiency virus antigen and antibody. Multicenter evaluation of a new automated fourth-generation human immunodeficiency virus screening assay with a sensitive antigen detection module and high specificity. Centers for Disease Control perspective on quality assurance for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antibody testing. Quality of laboratory performance in testing for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antibody. Impact of quality control on accuracy in enzyme immunoassay testing for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antibodies. Screening for infectious diseases among newly arrived asylum seekers, Bavaria, Germany, 2015. Laboratory methods in the diagnosis and prognostic staging of infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 population genetics and adaptation in newly infected individuals. Early detection of antibody to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by using an antigen conjugate immunoassay correlates with the presence of immunoglobulin M antibody. Detection of immunoglobulin M antibody in primary human immunodeficiency virus infection. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the measurement of human immunodeficiency virus, type 1 reverse transcriptase antigen and antibodies. False-positive human immunodeficiency virus testing in patients with lupus erythematosus. Viral and immunologic examination of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected, persistently seronegative persons. Performance of the OraQuick rapid antibody test for diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in patients with various levels of exposure to highly active antiretroviral therapy. Comparison of sensitivities and specificities of latex agglutination and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to the human immunodeficiency virus in African sera. Evaluation of a human immunodeficiency virus test algorithm utilizing a recombinant protein enzyme immunoassay. Performance evaluation of a particle agglutination test for antibody to human immunodeficiency virus 1: comparison with enzyme immunoassay. Rapid particle agglutination test for human immunodeficiency virus: hospital-based evaluation. Evaluation of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2, hepatitis B surface antigen, and syphilis in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Essential Medicines and Health Products Information Portal/World Health Organization. Alternative algorithms for human immunodeficiency virus infection diagnosis using tests that are licensed in the United States. Validation of a modified commercial enzyme-linked immunoassay for detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 immunoglobulin G antibodies in saliva. Novel assay for the detection of immunoglobulin G antihuman immunodeficiency virus in untreated saliva and urine. Human immunodeficiency virus antibody testing by enzyme-linked fluorescent and Western blot assays using serum, gingival-crevicular transudate, and urine samples. Detection of antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in oral fluids: a large-scale evaluation of immunoassay performance. Progress toward strengthening blood transfusion services-14 countries, 2003-2007. Detection of human viruses in periodontal pockets using polymerase chain reaction. IgA antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus in serum, saliva and urine for early diagnosis of immunodeficiency virus infection in Ugandan infants. Application of a rapid assay for detection of antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus in urine. Detection of p24 antigen with and without immune complex dissociation for longitudinal monitoring of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Faulty washers and soiled micropipettors may generate false positive serological results. False-positive human immunodeficiency virus seroconversion is not common following rabies vaccination. Testing for antibody to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in a population in which mycobacterial diseases are endemic. Recent experience with human immunodeficiency virus transmission by cellular blood products in Germany: antibody screening is not sufficient to prevent transmission. Current prevalence and incidence of infectious disease markers and estimated window-period risk in the American Red Cross blood donor population. A cluster of human immunodeficiency virus Type 1 recombinant form escaping detection by commercial genomic amplification assays. Standardization of nucleic acid tests: the approach of the World Health Organization. Immunofluorescence assay for detection of antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus type 2.
Discount malegra dxt plus 160 mg on line
The pathogenesis and natural history of chronic hepatitis B are covered in more detail in Chapter 145 erectile dysfunction humor buy malegra dxt plus 160 mg fast delivery. Decompensated cirrhosis may be accompanied by fatigue, jaundice, loss of muscle mass (weight loss), ascites, edema, bruising (coagulopathy), gastrointestinal bleeding (gastroesophageal varices or portal hypertensive gastropathy), and hepatic encephalopathy. As is the case for acute hepatitis B and its associated serum-sickness-like prodromal syndrome, chronic hepatitis B may be complicated by immune-complex manifestations, including cutaneous vasculitis, arthritis, glomerulonephritis, and generalized vasculitis. The biochemical hallmark of chronic hepatitis B is elevation of serum aminotransferase activity, with normal to near-normal alkaline phosphatase activity. In severe, progressive, and decompensated chronic hepatitis B, bilirubin levels can increase (hepatic excretory dysfunction); albumin can fall, and prothrombin time can become prolonged (hepatic synthetic defect); and hypersplenism can occur (primarily thrombocytopenia and leukopenia). Histologic features of chronic viral hepatitis vary from absence of necrosis and inflammation to architectural distortion and fibrosis characteristic of cirrhosis. In general, histologic injury (grade) and fibrosis (stage) are categorized as mild, moderate, or severe. The level of necroinflammatory activity or injury is based on periportal necrosis, portal inflammation, and intralobular necrosis. Mild activity is confined to portal tracts, and necrosis and inflammation spilling beyond the limiting plate of periportal hepatocytes (interface hepatitis) signify a more severe injury with increased potential for progression. The degree of fibrosis is based on the localization and extent of scar tissue; fibrosis confined to portal areas is mild, and fibrosis that reaches beyond the portal tract (septal or bridging fibrosis), especially that which links portal tracts to other portal tracts or to central veins, connotes a more advanced and progressive process (see Table 117. Successful antiviral therapy with any agent is likely to have a beneficial impact on the long-term natural history of chronic hepatitis B. If these milestones are not achieved, therapy will be ineffective and can be stopped. Side effects are usually manageable but limit therapy in those with marked hypersplenism and severe psychiatric disorders. Although lamivudine has been superseded by newer, more effective oral agents, many important lessons gleaned from experiences with lamivudine apply to antiviral therapy with other nucleoside analogues. Moreover, in patients with compensated cirrhosis treated for 3 years cumulatively, regression of cirrhosis has been documented histologically to occur in two-thirds of patients. In this subgroup of patients treated for a year, biochemical responses are achieved in approximately 60% to 80% and histologic responses in two-thirds. In contrast, among 23 patients referred to the same center in the period immediately before the availability of lamivudine, all patients for whom donor livers were not available died within just over a year. As the first oral antiviral introduced for hepatitis B, lamivudine has been studied extensively and has an excellent safety record. On the other hand, its poor resistance profile and the subsequent availability of newer, more potent, more effective, and less resistance-prone agents (see subsequent discussions) have reduced dramatically the current use of lamivudine and rendered it almost obsolete; it is no longer recommended as first-line therapy. The histologic efficacy of adefovir is similar in patients with both mild and advanced fibrosis. Although no resistance occurs during 48 or 60 weeks of adefovir therapy,178 adefovir resistance does begin to emerge during the second year of treatment and can reach 30% at 5 years. At doses of 30 mg or more a day of adefovir, however, nephrotoxicity is encountered. At a dose of 10 mg, adefovir has a high therapeutic index, and creatinine elevations of 0. Creatinine monitoring is recommended when adefovir is used, and reductions in dose frequency are mandated for patients with reduced creatinine clearance (CrCl; for CrCl 20 to 49 mL/min, every other day; for CrCl 10 to 19 mL/min, every third day; for patients undergoing hemodialysis, once a week after dialysis). Although adefovir filled an important niche when it was introduced, providing effective therapy for lamivudine resistance, the drug has several limitations. Although entecavir is cross-resistant with lamivudine, the blood levels achieved with daily doses of 0. Although entecavir was found in preclinical toxicity testing to be associated with hepatic, pulmonary, and brain tumors in rodents, similar toxicity has not been detected in other animal species or in humans. Because of its high potency; high efficacy in achieving biochemical, serologic, virologic, and histologic endpoints; high barrier to resistance; beneficial impact on the natural history of chronic hepatitis B; and excellent short-term and long-term tolerability and safety profile, entecavir is recommended as first-line antiviral treatment for chronic hepatitis B. Despite its high potency, telbivudine has not been widely embraced as therapy for hepatitis B because of its poor resistance profile and its inferiority to other available drugs; it is no longer recommended as a first-line agent for hepatitis B, and its production and distribution were discontinued after December 2016. In clinical trials, such monotherapy is as effective as combination therapy, without the emergence of resistance during 3 to 5 years of observation. Clevudine, a pyrimidine nucleoside analogue that was approved for use in Korea, was being evaluated in clinical trials versus adefovir as comparator. Potentially, combination therapy with high-potency, low-resistance agents could achieve even more limited resistance and treatment synergies, such as improved antiviral kinetics. Moreover, therapy with entecavir or tenofovir has been shown to be associated with histologic evidence of regression of fibrosis and cirrhosis after 3 to 5 years of therapy. Additional details for the antiviral drugs for hepatitis B are presented in Chapter 47. In addition, resistance to the newest oral agents, entecavir and tenofovir, is absent to negligible even after several years of therapy. When resistance to lamivudine emerged, adefovir as a second drug that is not cross-resistant was added; however, because of its higher potency and barrier to resistance, tenofovir monotherapy ("switch" rather than "add") suffices. Although entecavir at double the regular dose is approved for treatment of lamivudineresistant hepatitis B,188 the frequency of emergent entecavir resistance in this population is unacceptably high. For pregnant women who meet routine criteria for antiviral treatment, guidelines are the same as for nonpregnant women. Therefore, currently, the outcome of liver transplantation for hepatitis B is comparable with that of the procedure for nonviral types of end-stage liver disease. Chronic hepatitis C contributes to approximately 25% to 40% of all chronic liver disease283 and accounts for up to 40% of all patients undergoing liver transplantation. Progression to cirrhosis among those with chronic hepatitis C has been observed even in patients with asymptomatic and otherwise clinically, biochemically, and histologically mild disease. An analysis of 57 adequately sized and documented published studies showed that, among adults (mean age of infection, 42 years) with transfusion-acquired chronic hepatitis C, progression to cirrhosis occurred in approximately 25% over the course of 20 years. In addition, patients with normal aminotransferase activity respond as well as those with elevated aminotransferase activity to antiviral therapy and are not excluded as treatment candidates (see subsequent discussion). Variability in progression of chronic hepatitis C remains a confounding clinical feature of the disease. In contrast, in a tertiary-care hospital with a liver-transplantation program, referrals that funnel in primarily the sickest patients along the spectrum of disease activity333 bias hepatologists and transplant surgeons to the view that hepatitis C is an invariably progressive and fatal disease. Among patients with compensated cirrhosis resulting from chronic hepatitis C, long-term studies of the natural history of the disease have shown a very good prognosis, a 10-year survival rate of 80%. Overall, clinical features of chronic hepatitis C, and of decompensated cirrhosis associated with hepatitis C, are similar to those of chronic hepatitis B. In patients with compensated cirrhosis associated with hepatitis C, laboratory indicators of hepatic synthetic function- prothrombin time and serum albumin-remain normal, but these markers become abnormal in decompensated cirrhosis. Impaired hepatic excretory function tends to be maintained before the emergence of severe, end-stage cirrhosis, when bilirubin increases. Histologic features of chronic hepatitis C are similar to those observed in chronic hepatitis B (see previous discussion). Hepatitis C has also been linked with insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis (metabolic syndrome), and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The smaller, 12-kDa molecule has a much larger (20-L) volume of distribution and is administered on the basis of weight (1. This observation supported the trend to improve outcomes by tailoring antiviral therapy based on patient characteristics. In addition, many authorities preferred to treat patients with cirrhosis who had genotypes 2 and 3 for a full 48 weeks. As might be anticipated, tolerability was lower in the group receiving higher doses of both drugs. Confidence in the conclusions of these studies is also minimized by other subject selection biases; incomparability of subjects, treatment, and monitoring among trials; inadequately addressed confounding variables (such as alcohol use); and lower publication frequency of studies with negative results. Data in relapsers with cirrhosis were too limited for a definitive recommendation about the duration of therapy. Careful review of coadministered medications was paramount before initiation of treatment.
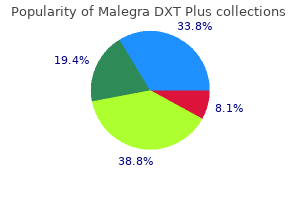
| Comparative prices of Malegra DXT Plus | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | PetSmart | 283 |
| 2 | YUM! Brands | 593 |
| 3 | Tractor Supply Co. | 267 |
| 4 | Price Chopper Supermkts | 360 |
| 5 | Walgreen | 245 |
| 6 | Burlington Coat Factory | 342 |
Buy malegra dxt plus 160 mg overnight delivery
Department of Health and Human Services; Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents erectile dysfunction at 30 order malegra dxt plus american express. Safety and immunogenicity of 4 intramuscular double doses and 4 intradermal low doses vs. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia antigen associated hepatitis. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the major protein of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen: characterization of the lipid components and their association with the viral proteins. Isolation and characterization of the major protein and glycoprotein of hepatitis B surface antigen. Chemically synthesized peptides of hepatitis B surface antigen duplicate the d/y specificities and induce subtype-specific antibodies in chimpanzees. Mapping of the hepatitis B virus attachment site by use of infectioninhibiting preS1 lipopeptides and tupaia hepatocytes. Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein-dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Entry of hepatitis B virus into immortalized human primary hepatocytes by clathrin-dependent endocytosis. A genetic variant of hepatitis B virus divergent from known human and ape genotypes isolated from a Japanese patient and provisionally assigned to new genotype J. Associations between hepatitis B virus genotype and mutants and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatitis B genotypes correlate with clinical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Sequences 5 to the polyadenylation signal mediate differential poly(A) site use in hepatitis B viruses. Characterization of hepatitis B virus major surface antigen gene transcriptional regulatory elements in differentiated hepatoma cell lines. Differential regulation of the hepatitis B virus surface gene promoters by a second viral enhancer. Hepatocyte-specific expression of the hepatitis B virus core promoter depends on both positive and negative regulation. Identification of a promoter element located upstream from the hepatitis B virus X gene. Hepatitis B virus gene function: the precore region targets the core antigen to cellular membranes and causes the secretion of the e antigen. Regulation of Toll-like receptor-2 expression in chronic hepatitis B by the precore protein. Transactivation of viral enhancers including long terminal repeat of the human immunodeficiency virus by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Hepatitis B virus X protein induces cell death by causing loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Transactivation by hepatitis B virus X protein is promiscuous and dependent on mitogen-activated cellular serine/threonine kinases. Hepatitis B virus X protein and p53 tumor suppressor interactions in the modulation of apoptosis. Spontaneous seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B: role of mutations in the precore/core gene. Temporal analysis of early immune responses in patients with acute hepatitis B virus infection. Identification of immunodominant T cell epitopes of the hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid antigen. Noncytolytic control of viral infections by the innate and adaptive immune response. Foxp3+ regulatory T cells protect the liver from immune damage and compromise virus control during acute, experimental hepatitis B virus infection. Natural variants of cytotoxic epitopes are T-cell receptor antagonists for antiviral cytotoxic T cells. Selective killing of hepatitis B envelope antigen-specific B cells by class I-restricted, exogenous antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Antiviral intrahepatic T-cell responses can be restored by blocking programmed death-1 pathway in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus: a prospective study of 22,707 men in Taiwan. Wild-type and e antigen-minus hepatitis B viruses and course of chronic hepatitis. Unexpectedly high proportion of drug users and men having sex with men who develop chronic hepatitis B infection. Acute hepatitis B virus infection: relation of age to the clinical expression of disease and subsequent development of the carrier state. Prevalence of chronic hepatitis B among foreign-born persons living in the United States by country of origin. Incidence and prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and cytomegalovirus among health care personnel at risk for blood exposure: final report from a longitudinal study. Prevention of hepatitis B flare-up during chemotherapy using lamivudine: case report and review of the literature. Chronic active hepatitis B exacerbations in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients following development of resistance to or withdrawal of lamivudine. Etiology and outcome for 295 patients with acute liver failure in the United States. Clinical outcome and virological characteristics of hepatitis B-related acute liver failure in the United States. Trends of acute hepatitis B hospitalizations, comorbidities, fatality rate, and costs associated with the hospitalization in Spain (2001-2006). Mortality secondary to fulminant hepatic failure in patients with prior resolution of hepatitis B virus infection in Japan. Hepatitis B virus reactivation after cytotoxic chemotherapy: the disease and its prevention. Clinical characteristics and molecular analysis of hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatitis B surface antigen-negative patients during or after immunosuppressive or cytotoxic chemotherapy. Multiple viral infection as the most common cause of fulminant and subfulminant viral hepatitis in an area endemic for 133. Hepatitis B virus precore mutation and fulminant hepatitis in the United States: a polymerase chain reaction-based assay for the detection of specific mutation. A prospective study characterizing full-length hepatitis B virus genomes during acute exacerbation. Electron microscopy and immunoelectronmicroscopy of cytoplasmic hepatitis B antigen in hepatocytes. Recurrent hepatitis B in liver allografts: a distinctive form of rapidly developing cirrhosis. Conservation of precore and core sequences of hepatitis B virus in chronic viral carriers. Occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation in western European patients with cirrhosis type B. A long-term follow-up study of asymptomatic hepatitis B surface antigen-positive carriers in Montreal. Causes of death in patients with hepatitis B: a natural history cohort study in the United States. Mortality of hepatitis B surface antigen-positive blood donors in England and Wales. Higher proportion of viral basal core promoter mutant increases the risk of liver cirrhosis in hepatitis B carriers. Role of hepatitis B virus precore/core promoter mutations and serum viral load on noncirrhotic hepatocellular carcinoma: a case-control study. Alcohol and hepatocellular carcinoma: the effect of lifetime intake and hepatitis virus infections in men and women. Hepatitis C virus superinfection in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Influence of hepatitis delta virus infection on progression to cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis type B.
Discount malegra dxt plus 160mg free shipping
Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent post-abortal upper genital tract infection in women with bacterial vaginosis: randomized controlled trial impotence underwear purchase genuine malegra dxt plus. Association between bacterial vaginosis and preterm delivery of a low-birth-weight infant. Bacterial vaginosis in early pregnancy may predispose for preterm birth and postpartum endometritis. Effect of metronidazole in patients with preterm birth in preceding pregnancy and bacterial vaginosis: a placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Effect of early oral clindamycin on late miscarriage and preterm delivery in asymptomatic women with abnormal vaginal flora and bacterial vaginosis: a randomised controlled trial. Vaginal clindamycin in preventing preterm birth and peripartum infections in asymptomatic women with bacterial vaginosis: a randomized, controlled trial. Indications for therapy and treatment recommendations for bacterial vaginosis in non-pregnant women: a synthesis of data. Evidence on the benefits and harms of screening and treating pregnant women who are asymptomatic for bacterial vaginosis: an update review for the U. Systematic review of randomized trials of treatment of male sexual partners for improved bacterial vaginosis outcomes in women. Recurrence of bacterial vaginosis is significantly associated with posttreatment sexual activities and hormonal contraceptive use. Sexual networks, sex hormones, and recurrent bacterial vaginosis: not such strange bedfellows. Definition of a type of abnormal vaginal flora that is distinct from bacterial vaginosis: aerobic vaginitis. Desquamative inflammatory vaginitis: differential diagnosis and alternate diagnostic criteria. Vulvodynia: the role of inflammation in the etiology of localized provoked pain of the vulvar vestibule (vestibulodynia). Successful treatment of persistent vulvodynia with submucous infiltration of betamethasone and lidocaine. Chapter 108 Vulvovaginitis and Cervicitis 109 Definition Microbiology Infections of the Female Pelvis Richard H. Pelvic infections are commonly polymicrobial, with cultures revealing a mixture of both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. These pathogenic microorganisms frequently originate from the flora of the lower genital tract. The microbial etiology of even hospital-acquired intrapartum, postpartum, and postsurgical infections reflects this because isolation of bacteria resistant to broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy is uncommon. Approximately 75% of infected women require augmentation of labor with oxytocin, and approximately 35% require cesarean delivery, usually because of arrest of progress in labor. Intrauterine infection can also occur after cervical cerclage (a circumferential suture about the cervix to prevent preterm delivery in women with cervical insufficiency) in 1% to 2% of patients, and this risk may be as high as 25% if the cerclage is performed after prolapse of the membranes into the vagina. Practically, clinicians tend to base the diagnosis on the presence of intrapartum fever plus one additional criterion anyway. Although the abdomen should be examined for uterine tenderness, it is often obscured by conduction anesthesia. Furthermore, patients with preterm-premature rupture of the membranes before 32 weeks of gestation are candidates for antenatal steroid therapy to promote fetal lung maturity. Betamethasone leads to an increase in maternal leukocyte count and a decrease in lymphocyte count. Gibbs and colleagues11 documented improved neonatal and maternal outcome when antibiotic therapy is begun intrapartum rather than immediately postpartum. Delivery of the fetus and placenta removes the sites of infection, much like draining an abscess, making this intervention the most significant part of therapy. This regimen is sufficient to treat the mother if the delivery was vaginal, with only one additional dose of the antibiotic regimen needing to be administered postpartum. If cesarean delivery is required, up to 15% of operative patients given only ampicillin and gentamicin experience treatment failure by developing postpartum endometritis. These patients probably require continued broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage, including anaerobic coverage, and accordingly, a drug such as clindamycin and metronidazole should be added to the treatment regimen to decrease the risk for postpartum endometritis by half. This antibiotic regimen should be continued until the patient has been afebrile (temperature < 37. Postpartum infection of the uterus, the most common cause of puerperal fever, is designated endomyometritis. Risk factors for postcesarean endomyometritis include a prolonged duration of labor or rupture of the membranes, presence of bacterial vaginosis, number of vaginal examinations, and use of internal fetal monitoring. All patients undergoing cesarean delivery, either elective or unscheduled, are candidates for antibiotic prophylaxis. Note the potential pathways for contaminated amniotic fluid to infect the postpartum pelvic tissues. These organisms have also been reported to be important pathogens associated with abdominal wound infection after cesarean delivery. The source of a sporadic postpartum group A -hemolytic streptococcal infection is typically unknown, but outbreaks of postpartum and postsurgical group A -hemolytic streptococcal infections have been associated with colonized health care workers. Health care workers who were asymptomatic carriers of group A -hemolytic streptococci have been identified in 15 of 21 outbreaks of postpartum and postsurgical infections reported from 1976 to 2005. These can sometimes also be fatal if unrecognized/ untreated (and even occasionally with appropriate recognition and therapy). Other consistently associated findings are lower abdominal pain, uterine tenderness, and leukocytosis. These patients may also exhibit a delay of the normally rapid postoperative return of bowel function due to an associated local peritonitis. This requires a bimanual pelvic examination in women in whom the uterus is no longer palpable on abdominal examination. The value of transvaginally obtained uterine cultures and the optimal method of obtaining such cultures remain matters of controversy. Although cultures obtained transvaginally are often difficult to interpret because of contaminants, they may be useful for those patients in whom initial therapy fails. Failures of those regimens with poor activity against penicillin-resistant anaerobic bacteria. For this reason antimicrobial regimens used in the treatment of postcesarean endometritis should provide satisfactory coverage of penicillin-resistant anaerobic microorganisms. The carbapenems (imipenem-cilastatin, meropenem, ertapenem) have also proved effective in the treatment of these infections but are generally reserved for more resistant infections not usually found on an obstetric service. It is recommended if this is the chosen treatment route that timely clinical follow-up does occur to assure improvement and/or resolution. Failure to accomplish this goal frequently suggests the presence of an abdominal wound infection (or an alternative source), which occurs in 50% of these patients. This is particularly true if the organism is olated in pure culture or from heavy growth from an endometrial specimen. Uncommonly, failure results from lack of coverage of a drug-resistant anaerobe; this can be corrected by a regimen containing either metronidazole or clindamycin. The importance of endometrial cultures for aerobes, anaerobes, and mycoplasmas will increase as antimicrobial resistance to clindamycin grows among isolates of gramnegative anaerobes. Careful physical examination is the most important to distinguish between pelvic and nonpelvic causes of fever. If present, percutaneous drainage by interventional radiology can be considered, and occasionally open surgery is required for complete management and resolution. All health care workers present at the delivery and those who performed vaginal examinations before delivery should be screened with cultures of the nares, throat, vagina, rectum, and skin. Any health care worker who is culture positive for group A Streptococcus should refrain from patient care for the first 24 hours of antimicrobial therapy. If surveillance identifies additional patients or health care workers with positive cultures for group A Streptococcus, the isolates should be typed by sequencing the variable portion of the M-protein gene or other molecular methods to identify the strain. Brown and colleagues37 studied women who had pelvic infection and fever that persisted after 5 days despite adequate antimicrobial therapy with clindamycin, gentamicin, and ampicillin. Women were randomly assigned to continuation of antimicrobial therapy, either alone or with the addition of heparin, until the temperature was lower than 37.
Buy malegra dxt plus 160mg on line
Systemic fluconazole (for susceptible strains) or voriconazole (for fluconazole-resistant strains impotence at 19 order cheap malegra dxt plus on-line, such as Candida krusei or some strains of Candida glabrata) is recommended in all cases of exogenous Candida endophthalmitis, in addition to intravitreal antifungal therapy. In cases that occur after corneal transplantation, the infected cornea is often replaced with a new donor cornea at the onset of endophthalmitis. For cases resulting from progression of fungal keratitis, corneal transplantation is almost always required when endophthalmitis is diagnosed, to rapidly debulk the infection. An intravitreal injection of amphotericin or voriconazole is often given in exogenous cases even if there is no apparent vitritis because of concern for occult infection. Intravitreal injections of either amphotericin or voriconazole may be repeated at least 48 hours after the first injection if there is no improvement and may be repeated more than once if necessary. Systemic voriconazole is recommended for all cases of exogenous mold endophthalmitis due to susceptible molds, such as Aspergillus and Fusarium. However, the potential risk of toxicity versus benefit of adjunctive systemic liposomal amphotericin therapy must be weighed for a particular case, and this evaluation must take into account the response to initial vitrectomy and intravitreal amphotericin. Systemic therapy with posaconazole has been used with success in a few case reports. For endogenous cases in patients ill with fungemia, the systemic antifungal chosen should be the one optimal for the systemic infection. Such patients are often too ill for vitrectomy but can tolerate intravitreal injections of antifungal agents. Patients who lose all vision (no light perception) almost never regain it, however. Some predictions can be made based on presenting visual acuity and the causative organism, factors that are related. In contrast, 20/100 or better vision was achieved in only 56% of gram-negative cases, 50% of S. Similar large outcome studies are not available for other types of endophthalmitis, but in general, outcomes reflect the virulence of the predominant organisms. Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis also usually has a poor outcome, although early diagnosis and prompt treatment with vitrectomy and intravitreal antibiotics has saved useful vision even in eyes with virulent organisms. In a review of 36 patients diagnosed with this infection over 22 years, the visual outcome was 20/40 or better in half of the patients but worse than 20/400 in one-fifth of patients. Candida endophthalmitis also may have a good outcome if treated with vitrectomy, intravitreal antifungal therapy, and systemic therapy. The prognosis in mold endophthalmitis in the pre-voriconazole era was poor, with rare salvage of useful vision. Although adoption of intracameral cefuroxime prophylaxis has reduced endophthalmitis rates in some centers, other sites have not seen a benefit. This reaction is labeled "hemorrhagic occlusive retinal vasculitis" and is of unknown etiology, although clearly associated with recent intraocular vancomycin injection. However, ophthalmologists commonly prescribe postoperative topical antibiotics, partly due to the concern about potential contamination postoperatively through a clear cornea incision. In Sweden, where prophylactic intracameral cefuroxime is used but topical postoperative antibiotics are not, endophthalmitis rates are low. As a consequence, use of masks or observing silence in the room during the injection is recommended. A brief course of prophylactic antibiotics at the time of presentation with an open globe appears to be beneficial, based on the results of several series. Real-time polymerase chain reaction test to discriminate between contamination and intraocular infection after cataract surgery. Endogenous fungal endophthalmitis: causative organisms, management strategies, and visual acuity outcomes. Reevaluating intracameral cefuroxime as a prophylaxis against endophthalmitis after cataract surgery in India. Pooled estimates of incidence of endophthalmitis after intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents with and without topical antibiotic prophylaxis. However, the high incidence of postinjection endophthalmitis caused by viridans streptococci has led to the realization that the ocular surface may be contaminated by oral Key References the complete reference list is available online at Expert Consult. Postinjection endophthalmitis rates and characteristics following intravitreal bevacizumab, Ranibizumab, and aflibercept. The 5 year incidence of bleb-related infection and its risk factors following filtering surgeries with adjunctive mitomycin C: collaborative bleb-related infection incidence and treatment study 2. Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis: a 17-year prospective series and review of 267 reported cases. Clinical implications of hypermucoviscosity phenotype in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates: association with invasive syndrome in patients with community-acquired bacteremia. Endogenous endophthalmitis associated with intravenous drug abuse: seven-year experience at a tertiary referral center. Report of the Eye Bank Association of America medical review subcommittee on adverse reactions reported from 2007 to 2014. Laboratory diagnosis of endophthalmitis: comparison of microbiology and molecular methods in the European Society of Cataract & Refractive Surgeons multicenter study and susceptibility testing. An updated estimate of costs of endophthalmitis following cataract surgery among medicare patients: 2010-2014. Incidence of endophthalmitis and the perioperative practices of cataract surgery in Japan: Japanese prospective multicenter study for postoperative endophthalmitis after cataract surgery. A literature review and update on the incidence and microbiology spectrum of postcataract surgery endophthalmitis over past two decades in India. Six-year incidence of endophthalmitis after cataract surgery: Swedish national study. The source of coagulase-negative staphylococci in the endophthalmitis vitrectomy study: a comparison of eyelid and intraocular isolates using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Bacterial contamination of the anterior chamber during phacoemulsification cataract surgery. Acute endophthalmitis following cataract surgery: a systematic review of the literature. Bacterial endophthalmitis after small-incision cataract surgery: effect of incision placement and intraocular lens type. Dynamics of small-incision clear cornea wounds after phacoemulsification surgery using optical coherence tomography in the early postoperative period. Ingress of India ink into the anterior chamber through sutureless clear corneal cataract wounds. Laser-assisted cataract surgery versus standard ultrasound phacoemulsification cataract surgery. Endophthalmitis after cataract surgery: a nationwide prospective study evaluating incidence in relation to incision type and location. Results of the endophthalmitis vitrectomy study: a randomized trial of immediate vitrectomy and of intravenous antibiotics for the treatment of postoperative bacterial endophthalmitis. Acute-onset endophthalmitis after clear corneal cataract surgery (1996-2005): clinical features, causative organisms, and visual acuity outcomes. Spectrum and clinical profile of postcataract surgery endophthalmitis in north India. Pathological findings in the lens capsules and intraocular lens in chronic pseudophakic endophthalmitis: an electron microscopy study. Treatment strategies and visual acuity outcomes in chronic postoperative Propionibacterium acnes endophthalmitis. Meta-analysis of infectious endophthalmitis after intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents. Ocular complications after anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in medicare patients with age-related macular degeneration. Incidence of late-onset bleb-related complications following trabeculectomy with mitomycin. Prophylaxis of acute posttraumatic bacterial endophthalmitis: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial of intraocular antibiotic injection, report 2.
Discount malegra dxt plus 160 mg with visa
Initial symptoms are usually subtle and include difficulty with memory erectile dysfunction doctor toronto cheap malegra dxt plus 160mg with mastercard, slowness of thought, and trouble concentrating. A loss of interest in social and professional activities soon follows, and such apathy and social withdrawal may be mistaken for depression. Although cognitive and behavioral symptoms are prominent in most patients, some mainly present with motor dysfunction, which includes decreased coordination, altered handwriting, loss of balance, and gait instability. The mental status examination reveals minor psychomotor slowing, inattention, decreased short-term memory, inability to perform simple calculations, and frontal release signs. Other frequent findings are brisk reflexes, mild postural tremor, slowing of rapid alternating movements, and gait instability when performing half-turns. If untreated, dementia becomes more global, profoundly impairing orientation, memory, and cognition. Confusional or psychotic episodes have been reported, but seizures are a rare occurrence. Despite the extent of the cerebral involvement, there is usually no aphasia, apraxia, or other signs of discrete cortical dysfunction, except in terminal stages. The severity of global brain atrophy and signal changes in basal ganglia correlates with cognitive impairment. Postmortem examination reveals encephalitis with multinucleated giant cells and microglial nodules, as well as astrocytosis and perivascular mononuclear cell infiltrates. These findings are sometimes related to microinfarcts and are postulated to give rise to increased vascular permeability. Therefore quantitative neuronal loss, decrease in cell size, or dendritic injury found in the cortex of demented patients71 may only be secondary to infection of other cells and associated immune activation. The T2-weighted image (A) shows bilateral, ill-defined hyperintense signal in the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale, which does not enhance with gadolinium injection on the T1-weighted image (B). Seroprevalence can vary widely between countries and even within a country depending on factors such as country of birth, climate, and socioeconomic status. The seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis in the United States for individuals ages 12 to 49 years decreased from 14. The clinical presentation is usually subacute, ranging from a few days to a month (see Chapter 278). On enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, only 7% of patients known to be seropositive for T. Lesions are multiple in two-thirds of the cases, and 90% of them display ring enhancement after administration of contrast material. The T1-weighted image after gadolinium injection shows a large enhancing lesion in the left frontal lobe (A), surrounded by edema, as demonstrated on the T2-weighted image (B). Additional smaller enhancing lesions can be seen on coronal cuts in the right thalamus and at the left convexity (C) and in the right cerebellum and right temporal lobe (D). Histologic examination shows mainly necrotic abscesses with blood vessel thrombosis and necrosis. Treatment consists of a combination of pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine, which cause a synergistic and sequential block on the folic acid metabolism necessary for the development of the parasite. Side effects, which consist of cytopenia, rashes, diarrhea, and increased liver enzymes, have been reported in 40% to 70% of patients receiving pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine and in 36% of those receiving pyrimethamine and clindamycin. Neurologic improvement is clinically apparent in more than half the cases by day 3 of therapy and in most cases by day 7. Because dormant cystic forms may rupture and reinitiate the infectious process at any time, maintenance therapy is necessary to prevent a relapse, which is likely to occur after a delay of 6 to 8 weeks of interruption of treatment. Flow cytometry immunophenotyping has at least 25% higher sensitivity than conventional cytomorphologic methods for the detection of malignant cells. Lesions are frequently located in the corpus callosum, the periventricular white matter, or the cortex. The macroscopic appearance of these tumors is generally that of a multifocal, diffusely infiltrating, and expanding nonhemorrhagic mass, without well-demarcated borders, simulating the appearance of an infiltrating glioma. Microscopic analysis reveals a variety of patterns, including large cells, small noncleaved cells, and immunoblastic or mixed cellular components. A study of 51 patients treated with this regimen demonstrated a median overall survival of 5. As the disease progresses, hemiparesis, aphasia, seizures, and cranial nerve palsies occur. Results were influenced by the performance status at presentation, with patients with good performance status having a 100% 3-year overall survival versus 38% in those with poor performance status. Additionally, whole-brain radiation therapy is associated with worsened cognitive function and white matter disease. These generally do not enhance after administration of contrast material, and they are not surrounded by edema, and, hence, substantial mass effect on surrounding structures is absent. Lesions are usually bilateral, asymmetrical, well demarcated, and localized preferentially in the periventricular areas and the subcortical white matter. One such case showed multiple small foci of demyelination disseminated among the cortical U fibers at autopsy. Demyelinating lesions may be entirely circumscribed within the cortical gray matter. However, approximately 10% of patients had a protracted course and survived more than a year. Focal necrotizing lesions associated with periventricular and meningeal enhancement or hydrocephalus may be seen on brain imaging studies. Maintenance therapy can include a low dose combination of ganciclovir and foscarnet, foscarnet monotherapy, ganciclovir monotherapy, and valganciclovir monotherapy. Blood levels of oral valganciclovir at a dose of 900 mg are equivalent to those of intravenous ganciclovir at a dose of 5 mg/kg. Cidofovir may be used in patients in whom ganciclovir or foscarnet has failed or who have become intolerant to these drugs. This drug is nephrotoxic and should be given with intravenous hydration and high doses of probenecid before and after cidofovir injection (see Chapter 137). In addition, this procedure is not without significant risks in this patient population. The elements in italics represent data that contribute to the decision-making process (see text for details). The evolution is usually progressive and leads to severe paralysis of the legs and loss of sphincter control. Neurologic signs include spastic paraparesis, hyperreflexia, extensor plantar responses, and mild sensory impairment, with vibratory and position sense being disproportionately affected. However, this examination is useful to rule out an extradural or intradural mass lesion or an epidural abscess. These lesions are usually symmetrical and more frequent at the middle to lower thoracic levels. Ultrastructural studies indicate both axonal and myelin injury,196 although axonal destruction is seen only in areas of intense vacuolation. Macrophage activation might generate substrates that are metabolized by methylation and therefore trigger a local deficit of methyl group donors in the spinal cord, leading to myelin vacuolization. Finally, the peripheral nervous system can also be affected by antiretroviral treatment toxicities. Sensory symptoms such as paresthesias may precede an acute, progressive weakness of distal and proximal muscles of two or more limbs, associated with areflexia. Respiratory muscles may be involved, and patients sometimes require assisted ventilation. Demyelination is demonstrated by decreased motor nerve conduction velocities or prolonged distal latencies and minimum F-wave latencies in two or more nerves. Sural nerve biopsy generally demonstrates the presence of a perivascular and endoneural mononuclear cell infiltrate with macrophage-mediated segmental demyelination. Plasmapheresis is indicated if the illness is sufficiently severe to warrant treatment. The pain is often described as an aching or burning sensation and is worse on the soles of the feet.

Order cheapest malegra dxt plus
For preterm hospitalized infants top 10 causes erectile dysfunction generic 160mg malegra dxt plus free shipping, guidelines for use have been recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics Red Book Committee. A vaccine was licensed for the prevention of chickenpox in immunocompetent individuals in 1995. In immunocompromised children, serologic evidence of host response after vaccination has been achieved in 89% to 100% of vaccinated individuals. However, vaccine-induced rash is not uncommon and occurs in variable percentages of patients from approximately 6% to 47%. The factor most predictive of the appearance of rash is the degree of immunosuppression. Specifically, for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the likelihood of rash can be 40% to 50%. The subsequent occurrence of natural varicella after community exposure was decreased in larger control studies and averaged 8% to 16%. Vaccination did not appear to increase the likelihood of subsequent herpes zoster during the period of follow-up. Vaccine-induced rash was far less common in these individuals and occurred at a frequency of 0. First, the incidence of herpes zoster was 50% lower in the vaccine group than in placebo recipients (5. In addition, the median duration of pain among subjects in whom herpes zoster developed was shorter in the vaccine group, albeit of marginal clinical value (21 days vs. Third, vaccination significantly decreased the burden of illness overall for patients who developed zoster (as assessed by an area under the curve evaluation, P =. Vaccination was more effective in preventing herpes zoster among the younger elderly group versus the older elderly group. The risk of subsequent development of herpes zoster does not appear to be increased in vaccine recipients. The two-dose regimen of Shingrix resulted in frequent mild-to-moderate local and systemic reactions, although serious adverse reactions were no more frequent than in patients receiving placebo, and administration of Shingrix to previous recipients of Zostavax was shown to be well tolerated and immunogenic. Additional follow-up studies of Shingrix are planned, including administration to immunocompromised individuals. Latency of varicella zoster virus in dorsal root, cranial, and enteric ganglia in vaccinated children. Early vidarabine therapy to control the complications of herpes zoster in immunosuppressed patients. Phase specific analysis of herpes zoster associated pain data: a new statistical approach. A randomized trial of acyclovir for 7 days or 21 days with and without prednisolone for treatment of acute herpes zoster. Uber den atiologischen zusammenhang der varizellen mit ewissen fallen von herpes zoster. Experimentelle ubertragungen von herpes zoster auf menschen und die beziehungen von herpes zoster zu varicellen. The etiologic agents of varicella and herpes zoster: serologic studies with the viruses as propagated in vitro. Untersuchugen uber die atiologie der krankheiten der herpesgruppe (herpes zoster, herpes genitalis, and herpes febrilis). Serial propagation in vitro of agents producing inclusion bodies derived from varicella and herpes zoster. Fluorescent antibody studies with agents of varicella and herpes zoster propagated in vitro. Intranuclear inclusion bodies in cultures of human tissue inoculated with varicella vesicle fluid. Observation on the fine structure and replication of varicella virus in cultivated human amnion cells. Varicella-zoster virus infections: biology, natural history, treatment, and prevention. Spread of zoster virus in human embryonic lung cells and the inhibitory effect of idoxyuridine. Infectiousness of communicable diseases in the household (measles, chickenpox, and mumps). Modification of chickenpox in family contacts by administration of gamma globulin. Communicable diseases transmitted chiefly through respiratory and alimentary tracts. Herpes zoster: demonstration of virus in trigeminal and nerve ganglion by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. Cellular and humoral immunity in the pathogenesis of recurrent herpes viral infection in patients with lymphoma. Viremia is present in incubation period in nonimmunocompromised children with varicella. The neurological complications of varicella: a clinical and epidemiological study. Polymerase chain reaction detection and clinical significance of varicella-zoster virus in cerebrospinal fluid from human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Varicella pneumonia in adults: report of seven cases and review of the literature. Association between the initiation of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy and the risk of herpes zoster. Antibody assays for varicella-zoster virus: comparison of enzyme immunoassay with neutralization, immune adherence hemagglutination, and complement fixation. Valaciclovir compared with acyclovir for improved therapy for herpes zoster in immunocompetent adults. Famciclovir for the treatment of acute herpes zoster: effects on acute disease and postherpetic neuralgia. Antiviral resistance in herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus infections: diagnosis and management. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Collaborative Antiviral Study Group. The lidocaine patch 5% effectively treats all neuropathic pain qualities: results of a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, 3-week efficacy study with use of the neuropathic pain scale. Varicella zoster immune globulin for the prevention of chickenpox: recommendations of the immunization practices advisory committee. Evaluation of varicella-zoster immune globulin: protection of immunosuppressed children after household exposure to varicella. Chickenpox vaccination of healthy children: immunological and clinical responses and protective effect in 1978-1982. Immune response of elderly persons four years after receiving a live attentuated varicella vaccine. Use of a live attenuated varicella vaccine to boost varicella-specific immune responses in seropositive people 55 years of age and older: duration of booster effect. Immunization to reduce the frequency and severity of herpes zoster and its complications. Vaccination of immunocompetent elderly subjects with a live attenuated oka strain of varicella zoster virus: a randomized, controlled, dose-response trial. Recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices for use of herpes zoster vaccines. Increasing risk of disease in this population is associated with increasing suppression of T-lymphocyte responses. Next-generation sequencing has demonstrated multiple viral genotypes (quasispecies) in infected individuals. Nonstructural viral proteins provide a large number of functions required for efficient replication of the viral genome and assembly of progeny virions. This includes immediate-early genes, expressed shortly after infection, that have been shown to regulate intrinsic host cell responses to infection as well initiating the transcription of viral genes essential for genome replication and virus assembly. Early viral genes represent the second class of viral genes expressed during productive infection.