Best buy for zudena
There is a single case report Considerations of a child with cleft lip/palate and hypoplastic toes born to a woman who ingested multiple agents during pregnancy erectile dysfunction treatment natural cheapest generic zudena uk, including bisoprolol, naproxen, and sumatriptan. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions Bisoprolol should not be combined with other -blocking agents. Women taking catecholamine-depleting drugs, such as reserpine or guanethidine, should be closely monitored, as the added -adrenergic blocking action may produce an excessive reduction of sympathetic activity. In women receiving concurrent therapy with clonidine, it is suggested that bisoprolol be discontinued for several days before the clonidine if therapy is to be discontinued. Women with a history of anaphylactic reaction may be more reactive to repeat challenge while taking -blockers. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat allergic reactions. References Summary Bleomycin Drug Class Indications Mechanism - (Blenoxane) International Brand Names Log on to ExpertConsult. Long-term effects of bleomycin on reproductive function are insufficiently studied. Several studies concluded that subsequent fertility is clinically unaffected after treatment. Bleomycin is associated with lung injury although the mechanism(s) remains unclear. Side effects include impairment of the pulmonary function (pulmonary fibrosis), rash, urticaria, alopecia, and stomatitis. Bleomycin is teratogenic in rodents (skeletal malformations, hydroureter, vascular disruptions). For that reason, it is usually recommended the drug be discontinued in nursing women. Pregnancy Category: D Lactation Category: U Bleomycin should be used during pregnancy and lactation only if the benefit justifies the potential perinatal risk. B Fetal Considerations Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Bretylium Drug Class Indications Mechanism - (Bretylol) International Brand Names Log on to ExpertConsult. The pressor effects of catecholamines such as dopamine or norepinephrine are enhanced by bretylium. Thus a new patient will receive 120 mg/ kg of potassium bromide each day for 5 d and then return to 30 mg/kg qd. Side effects include sedation, ataxia, increased urination, and rare skin disorders. It is unlikely the maternal systemic concentration will reach a clinically relevant level after topical application. It is unlikely the breastfed neonate would ingest clinically relevant amounts after topical application. The American Academy of Pediatrics considers bromides compatible with breastfeeding. Maternal Considerations Fetal Considerations Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary 78 Bromocriptine International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Parlodel; Volbro) B Log on to ExpertConsult. For this indication, bromocriptine has an extensive record of safety and is preferred by some clinicians. Indeed, most information regarding bromocriptine during pregnancy comes from women treated for infertility with an average duration of exposure of 28 d. However, there are no reports of associated malformations after first-trimester exposure. Multicenter surveillance programs suggest no adverse effect of intrauterine exposure to bromocriptine on postnatal development. Bromocriptine reduces lactation, and its use is generally considered contraindicated during breastfeeding. When combined with droperidol, bromodiphenhydramine has been advocated as effective in hospital treatment of severe hyperemesis. It is inferior to nalbuphine for the relief of pruritus associated with intrathecal morphine. Bromodiphenhydramine crosses the human placenta, but the kinetics remain to be detailed. Maternal drug ingestion during rodent pregnancy may alter physical and reflex development. Maternal Considerations Fetal Considerations Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Budesonide International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism - (Budecort; Budeflam; Pulmicort; Rhinocort; Rhinocort Aqua) Log on to ExpertConsult. Corticosteroids; Corticosteroids, inhalation Asthma, rhinitis Antiinflammatory by an unknown mechanism; potent glucocorticoid, weak mineralocorticoid 80 Dosage With Qualifiers Asthma-0. Inhaled corticosteroids should generally be considered the prophylactic medication of choice in pregnant women with persistent asthma, unless well controlled by either cromolyn or nedocromil. Although there are no adequate reports or wellcontrolled studies of budesonide during pregnancy, it is considered a first-line agent along with beclomethasone. Side effects include allergic reaction, stridor, eczema, purpura, back pain, fracture, and myalgia. Epidemiologic study suggests budesonide is not a clinically significant teratogen. Budesonide is secreted in human milk, though <20% of the inhaled dose reaches the systemic circulation; it is unlikely clinically relevant concentrations will enter the breast milk and be absorbed by the breastfeeding newborn. B Maternal Considerations Fetal Considerations Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Bumetanide International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism - (Bumex; Pendock; Segurex) Log on to ExpertConsult. Parenterally administered bumetanide should be avoided when aminoglycoside antibiotics are being used, especially in the presence of impaired renal function, except in life-threatening conditions. Lithium should generally not be given with diuretics because they reduce renal clearance and create a high risk of lithium toxicity. Probenecid should not be administered, as it reduces both the natriuresis and hyperreninemia produced by bumetanide due to its inhibitory effect on renal tubular secretion of bumetanide. Indomethacin should not be co-prescribed because it blunts the increases in urine volume and sodium excretion and inhibits the bumetanide-induced increase in plasma renin activity. May potentiate the effect of various antihypertensive drugs, necessitating a reduction in the dose of these drugs. Bupivacaine crosses the human placenta, with transfer ratios (agent/antipyrine) in vitro approximating 0. Bupivacaine and its major metabolite are found at clinically irrelevant levels after epidural administration. Though it has not been studied after local infiltration, one-time use is unlikely to pose a clinically significant risk to the breastfeeding neonate. B Fetal Considerations Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Buprenorphine International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Buprenex; Subutex) Log on to ExpertConsult. Buprenorphine, methadone, and morphine have been used to treat women seeking recovery from opioids, and closely monitored neonatal outcomes have been reassuring. Moderately strong evidence indicates a lower risk of preterm birth, greater birth weight, and larger head circumference with buprenorphine treatment of maternal opioid addiction during pregnancy compared with methadone treatment, and no greater harms. Side effects include respiratory depression and/or arrest, hypotension, bradycardia, N/V, sedation, miosis, euphoria, hallucinations, dysphoria, dry mouth, pruritus, blurred vision, sweating, and constipation. Buprenorphine crosses the human placenta poorly by a mechanism that does not involve P-glycoprotein. The majority of newborns born to opioid-dependent women show signs of opioid withdrawal. Some exposed children may present with transient motor abnormalities, though most probably resolve completely in 85% of cases.
Syndromes
- Infections, including virus-caused upper respiratory infections, ear infections, and pneumonia
- Eat a healthy diet that is high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fish, and lean meats
- High blood pressure
- Sweet taste in mouth
- Damage to an artery or artery wall from the catheter, which can block blood flow and cause a stroke (rare)
- Polycystic kidney disease
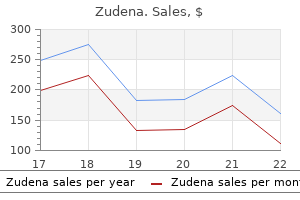
Order genuine zudena line
References Summary Alfentanil Drug Class Indications Mechanism - (Alfenta; Alfentanyl; Rapifen) International Brand Names Log on to ExpertConsult impotence with diabetes generic zudena 100mg on line. As with other lipophilic opioids, alfentanil reduces the total dose of local anesthetic analgesic needed to provide comfort when combined with bupivacaine for epidural analgesia while diminishing the likelihood of an undesired motor blockade. Side effects include respiratory arrest or depression, arrhythmia, seizure, coma, abuse or dependency, muscle rigidity, N/V, dizziness, hypertension, hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia, confusion, sweating, dry mouth, constipation, and urinary retention. Neither human embryo toxicity nor teratogenicity is reported, though first-trimester human data are limited. Lipophilic and hydrophilic characteristics of the drug influence placental transfer, as do fluctuations in maternal flow. Neonatal depression characterized by reduced active and passive tone is reported when alfentanil is given shortly before delivery. There are no reported fetal or neonatal effects after its use for conduction anesthesia. Alfentanil is excreted into human breast milk, though the amount excreted is too small to have any significant effect on the newborn. Erythromycin may inhibit alfentanil clearance and increase the risk of prolonged or delayed respiratory depression. Perioperative administration of drugs affecting hepatic blood flow or enzyme function may reduce plasma alfentanil clearance and prolong recovery. A Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Allopurinol - (Aipico; Alloremed; Alloscan; Alonol; Aloral; Aluline; Aluprin; Apurol; Isanol; Lopurin; Lysuron; Unizuric; Uricemil; Uriconorm-E; Zyloprim; Zyroric) International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers Log on to ExpertConsult. One woman treated for primary gout during pregnancy with allopurinol delivered a healthy child at 35 w. Another documents a woman treated for a gout flare associated with gestational diabetes, also without adverse events. A report documents 13 cases of allopurinol and thiopurine co-therapy used successfully to manage inflammatory bowl diseases during pregnancy without attributable adverse fetal effects. Allopurinol is also used during pregnancy for women undergoing treatment of acute leukemia. Allopurinol was used unsuccessfully in one trial for the treatment of established preeclampsia. Side effects include agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, hepatic dysfunction, urticaria, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, rash, diarrhea, pruritus, nausea, and gout flare. Allopurinol readily crosses the ovine placenta, where it reaches equilibrium within 30 min. It reduces superoxide generation in the brains of fetuses subject to intermittent umbilical cord occlusion. One multicenter randomized placebo controlled trial concluded that maternal treatment with allopurinol during fetal hypoxia lowered neuronal damage markers in female but not male cord blood; developmental outcome was not reported. In 31 prospectively identified pregnancies with allopurinol exposure during at least the first trimester, an overall rate of major malformations (3. Allopurinol and its metabolite oxypurinol are excreted into breast milk to a limited degree and are considered compatible with breastfeeding. Women taking allopurinol require a one-fourth to one-third reduction in their dose of mercaptopurine/azathioprine. The risk of hypoglycemia secondary to this mechanism may be increased in women with renal insufficiency. High doses of allopurinol (300 mg bid) inhibit the clearance of theophylline in normal subjects. Co-administration of allopurinol may increase the plasma concentration of cyclosporine. Fetal Considerations Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary 14 Almotriptan International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Axert) A Log on to ExpertConsult. Similar agents such as sumatriptan are associated with an increased risk of preterm birth. It is likely the metabolism of almotriptan is decreased during pregnancy, thus increasing the risk of toxicity. Maternal Considerations Fetal Considerations Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary 15 A Aloe Vera None identified. However, one study suggested aloe vera may accelerate wound healing by promoting gap junctional intercellular communication and proliferation of human skin fibroblasts. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary There is no published experience in pregnancy. However, considering the topical route, it is unlikely the breastfed neonate would ingest clinically relevant amounts. Alosetron Hydrochloride International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Lotronex) Log on to ExpertConsult. Side effects include ischemic colitis, constipation, hypertension, allergic rhinitis, dyspepsia, and depressive disorders. Maternal Considerations Fetal Considerations 16 Breastfeeding Safety There is no published experience in nursing women. Side effects include physical dependence, syncope, tachycardia, seizures, respiratory depression, coma, drowsiness, light-headedness, dry mouth, depression, headache, constipation, diarrhea, N/V, insomnia, blurred vision, hypotension, increased salivation, and dermatitis. Although there is no evidence that alprazolam is a human teratogen by either case reports or postmarketing surveillance, diazepam has been associated with fetal malformations. There is also concern based on studies with other benzodiazepines that postnatal behavior might be altered by antenatal exposure. Mice exposed to alprazolam demonstrate more individual than group activities and avoid open areas, and the males are more aggressive. Though the risk is reasonably small, alprazolam should be avoided during lactation because of the potential that it might alter neurodevelopment and because of the documented risks of withdrawal. Drugs or diseases that cause dry mouth or raise stomach pH may slow disintegration or dissolution, resulting in slowed or decreased absorption. Drugs that inhibit this pathway can profoundly affect the clearance of alprazolam. Clinical studies of other benzodiazepines suggest a possible drug interaction between alprazolam and diltiazem, isoniazid, macrolide antibiotics such as erythromycin and clarithromycin, and grapefruit juice. In vitro studies of other benzodiazepines suggest possible interactions with ergotamine, cyclosporine, amiodarone, nicardipine, and nifedipine. Side effects include cerebral hemorrhage, arrhythmias, severe bleeding, anaphylaxis, hypotension, N/V, and fever. In light of its high molecular weight, alteplase is unlikely to cross the placenta. Although tissue plasminogen activator is a normal constituent of human breast milk, it is unknown whether alteplase increases that level. There are postmarketing reports of orolingual angioedema associated with alteplase. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Amantadine Symmetrel; Topharmin) International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Contenton; Endantadine; Infectoflu; Mantandan; Shikitan; Log on to ExpertConsult. Though the kinetics and safety are unknown, the unsupplemented term infant would ingest <1 mg/d assuming an M:P ratio of 1. Administration with triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide may increase the plasma amantadine concentration. Administration with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole may impair amantadine renal clearance, causing higher plasma concentrations.
Order 100 mg zudena with mastercard
Not as familiar are the forms of smokeless tobacco erectile dysfunction age 35 discount zudena amex, which include snuff and chewing tobacco (Gritz, Ksir, & McCarthy, 1985). Snuff is powdered tobacco that is mixed with salts, moisture, oils, flavorings, and other additives; a Swedish variant of snuff is called "snus. Chewing tobacco is marketed in loose-leaf form, pressed as a rectangle called a plug, or in a twist or roll. History of Tobacco Use1 the West Discovers Tobacco In the late 15th century, Columbus and other explorers found Native Americans in the New World smoking dried tobacco leaves. The pleasant effects of nicotine caught on like fire, and smoking quickly became popular among the Europeans. They brought home seeds of the tobacco plant and spread them to other parts of the world on their ventures. In these early years, the Spanish held a monopoly on the world tobacco market because Nicotiana tabacum is indigenous to South America. For example, tobacco in England was worth its weight in silver, and people paid that price. By the early 17th century, however, tobacco use had become widespread and even the poor could afford it. By the middle of that century, tobacco use had spread throughout central Europe, and signs of the addictive nature of the drug were evident. If the soldiers were caught smoking, the good sultan punished them by quartering, hanging, beheading, and worse. He punished offending subjects by slitting their nostrils and by imposing other consequences that might discourage them from smoking. Like their Western counterparts, the Japanese quickly took to smoking-so quickly that the emperor had issued an edict against smoking by 1603. In 1639, smoking had become so established in Japan that a person was offered a smoke with a ceremonial cup of tea. When tobacco smokers discovered the pleasures of smoking marijuana or opium, even these drugs did not displace tobacco; they were merely smoked in addition to it. During the 360 years the table covers, some people believed it was literally possible to breathe life into another person as long as that breath carried tobacco smoke. The chemical was named after a man named Nicot, who was the French ambassador to Portugal and who conducted exacting experiments with tobacco as a medicinal herb. The isolation of nicotine was damaging to its medical reputation because the toxic and addictive properties of the compound began to be understood. During the years between 1830 and 1860, the use of tobacco for medicine and pleasure in the United States was subject to a stream of attacks by clergy, educators, and some physicians. For example, perverted sexuality, impotency, and insanity all were attributed to tobacco. Trall denounced the medical use of tobacco and illustrated his argument by describing a case of tobacco addiction. As the United States prepared for a civil war in 1860, the use of tobacco as a medical agent had virtually ended. In the United States today, cigarette smoking is by far the most common way to use tobacco. Congress noted that 94% of all tobacco grown in the United States is used to manufacture cigarettes. Furthermore, cigarette smoking demands the most attention because it is the most toxic way to smoke tobacco, followed in order by cigar and pipe smoking (Blum, 1984). Smoking in the United States Many national surveys of smoking among American adults have been conducted. These studies show that the percentage of men and women who smoke declined in the latter part of the 20th century. Coupled with the decline in smokers is a steady increase in the percentage of adults who identified themselves as former smokers (Molarus et al. That is, increasing numbers of people have said they quit smoking, and most of them did so on their own (Zusy, 1987). Self-quitters are thought to have been "lighter" smokers (smoking fewer than 25 cigarettes a day). Nevertheless, many current smokers say they want to quit but find it difficult to do so. It probably is no coincidence that the peak of smoking among Americans was in 1963. It detailed the health hazards of cigarette smoking in a way then unprecedented in scope and persuasion. You learned in Chapter 1 that the overall prevalence of drug use masks important differences among subgroups of the population. An interesting comparison within this age group is individuals enrolled full time in college versus individuals not enrolled full time in college. On the other hand, there has been a resurgence in popularity among college students and other young people of the "hookah" (or water pipe, among other names). The water pipe, which is a device to deliver nicotine by smoking, is so named because the smoke that is inhaled first passes through water (Maziak, 2008). The water pipe first appeared in Africa and Asia over four centuries ago, but has gained new popularity around the world since the 1990s. A main reason for the reemergence seems to be the perception among young people that the hookah is a harm-free, pleasant way to smoke tobacco. In addition, a proliferation of websites promoting the water pipe and retailing it in ways that are highly appealing have fed what Maziak (2008) called a water pipe use "epidemic" (p. Unfortunately, as with other alternatives to tobacco cigarettes that have been promoted as "safe," smoking from a water pipe is a threat to health, because the smoke from a water pipe contains nicotine, tar, and carbon monoxide (Gathuru, Tarter, & KleinFedyshin, 2015). For example, an experimental study was conducted with 31 young adults who were both regular cigarette smokers and water pipe users. The results showed that water pipe smoking resulted in greater exposure to smoke and carbon monoxide and no difference in nicotine exposure compared to smoking a cigarette (Eissenberg & Shihadeh, 2009). We show later in this chapter that carbon monoxide (and tar) are especially toxic. Although few studies have addressed this question, the prevalence of use of the water pipe among college students in the United States in the past month has been estimated to be in the range of 15% to 20% (Eissenberg et al. Rates of smoking for men and women are less different among individuals 12 to 17 years old and among those 26 and older, compared to individuals 18 to 25 years old. It "I never smoke to excess - that is, I smoke in moderation, only one cigar at a time. The rates of decline in smoking prevalence since that time have been steeper for men than for women, but men started out at a considerably higher rate. Although these variables are correlated, it is of interest to look at them separately. Past month smoking prevalence in 2015 for all respondents 18 years and older consistently was highest for individuals who were unemployed: the prevalence rate for those unemployed was 36. Regarding education among respondents 18 years and older, there was a negative relationship between smoking and education: As years of education went up, prevalence tended to go down, with the difference more than a factor of two between all those who were four-year college graduates and those who were not. Data such as these on education and employment are the bases for arguments that the ills of smoking fall disproportionately on the least advantaged in U. For example, close to 90% of the people who die from smoking-related causes in the United States began smoking when they were adolescents (Primack et al. Moreover, the younger the age at which a person starts to smoke, the harder it seems to be able to quit later (Breslau & Peterson, 1996). A lot of research has been devoted to explaining smoking initiation because of the enormous public health consequences of smoking. Consistent with the approach to understanding human drug use that is taken in this text, the reasons for smoking initiation are a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social/ environmental factors. This finding suggests that certain people not only are more likely to begin smoking, but are also more likely to continue the behavior than are other individuals (Fallon et al. Nicotine 157 Psychological factors also may combine with environmental variables to affect smoking initiation. One study found that adolescents who score high on the characteristic of "novelty seeking" (they tend to be impulsive, to take risks, and to have a high need for stimulation) are more receptive to tobacco company advertisements than are people who score lower on novelty seeking (Andrain-McGovern et al.
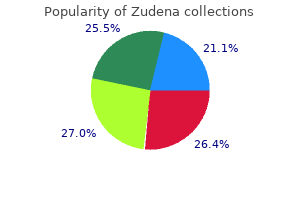
Cheap zudena 100 mg
Better testing methods are needed erectile dysfunction doctors naples fl generic zudena 100mg on-line, but perhaps more important would be regular tests. Many current procedures allow athletes to discontinue the drugs prior to an important event to avoid a positive urine test. But what of the thousands of young men (and women) who are not Olympic-calibre athletes who are taking steroids to improve their performance at the high school or college level or just to "get big" Steroids can cause major problems, and many drug education programs do not even discuss them. Clearly, there is a need to make the public aware of the potential dangers of steroid abuse. Over-the-counter drugs are considered safe enough to dispense without prescription. Many effective painkillers are available over the counter, and aspirin is the most widely known and used. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) is closely related to a chemical found in the bark of the willow and other trees (salicylic acid). The ancient Greeks and Native Americans used willow bark in the treatment of painful conditions and fever. Salicylic acid was isolated and used as a pain reliever in Europe, but it causes severe stomach distress. Not until the late 19th century did the Bayer Company of Germany synthesize acetylsalicylic acid and name it aspirin. It is marketed under the brand names Anacin, Bufferin, and Excedrin, to name just a few, and between 10,000 and 20,000 tons of aspirin are consumed in the United States every year (Julien, Advokat, & Comaty, 2011). Aspirin is analgesic (produces pain relief without unconsciousness), antipyretic (reduces fever), and anti-inflammatory (reduces swelling). It is thought to work by means of a mechanism quite different from opiate analgesia. It is, however, very effective with muscle aches, headaches, and soreness due to inflammation such as arthritis (Grogan, 1987). It frequently causes stomach irritation and bleeding and is contraindicated in people who have stomach problems. Aspirin is also an anticoagulant and may prolong bleeding under certain circumstances. However, this same mechanism may be useful in the prevention of strokes and heart attacks (Advokat, Comaty, & Julien, 2014). An effective analgesic drug useful for people with stomach problems is acetaminophen. This drug, marketed under brand names such as Tylenol, reduces fever and produces analgesic effects but does not cause stomach irritation. Acetaminophen is not a potent anti-inflammatory drug, however, and may cause liver problems in high doses. Acetaminophen-related overdoses are fairly common and account for over 56,000 emergency room visits and nearly 500 deaths every year. These drugs have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects that are similar to aspirin but are generally better tolerated. Because pseudoephedrine is one ingredient used to produce illicit methamphetamine, such products are now sold behind the counter (see Chapter 6). Cold remedies also may include expectorants, which help to break up phlegm so that it may be coughed up. Antitussive agents actually suppress coughing and are often included in cold and cough formulations. One popular antitussive ingredient in many cough formulations is a powerful psychoactive drug, dextromethorphan. Like these dissociative anesthetics, dextromethorphan in sufficiently high doses can produce Copyright 2019 Cengage Learning. Other Prescription and Over-the-Counter Drugs 377 hallucinogenic effects but can also be quite toxic with side effects including psychotic reactions (Meyer & Quenzer, 2013). Of course, the dose of dextromethorphan received when taking cough medicine as recommended on the label does not produce such effects, but dextromethorphan has become a drug of abuse (Wilson et al. An additional problem posed by this high-level use is that it can lead not only to overdose of dextromethorphan but also exposes users to excessive doses of the other ingredients in cough syrup, which may also produce adverse reactions (Meyer & Quenzer, 2013). These compounds actually are more effective in the treatment of hay fever and related allergic reactions. Many allergic symptoms are caused by the release of a naturally occurring chemical called histamine. Commonly used antihistamines include diphenhydramine, chlorpheniramine maleate, and loratadine (Claritin). Other side effects include thickening of mucus secretions, blurred vision, dizziness, dry mouth and nose, and sweating (Grogan, 1987). They certainly will induce mild central nervous system stimulation, but most contain about as much caffeine as one to three cups of coffee, so users should expect about that effect. Because fatigue is a common side effect of antihistamines, they sometimes can help people who are suffering from insomnia. However, other side effects associated with antihistamines (for instance, dry mouth, dizziness, and nausea) may limit their use as sleeping aids. In addition, the problems associated with using prescription sleeping pills may apply to these drugs, too, as discussed in Chapter 13. Herbal Products, Hormones, and Dietary Supplements In 1994, the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act was passed. The new law changed the definition of a dietary supplement to extend beyond vitamins and to include herbs, amino acid preparations, and even some hormones. As such, herbal and other chemical preparations labeled Copyright 2019 Cengage Learning. Now, as long as the packaging for the supplement makes no specific claims with respect to treating a disease, the supplement is not considered a drug, and a company may market it freely (Spinella, 2001). So the label on a dietary supplement may read "improves mood" or "calms the spirit" but not "relieves depression" or "treats anxiety. One view is that because such products are obtained directly from natural sources, they are somehow safer and more in harHerbal/natural health supplements. Many of the drugs we have already considered are also obtained directly from plants, however, including the likes of cocaine, mescaline, morphine, nicotine, and scopolamine. Clearly, a chemical found in natural plant material is not guaranteed to be risk-free. Supporters of the 1994 act argue that valuable remedies are now more readily available to people at low prices. But most herbal preparations have not been well studied, so in many cases, there is little evidence of effectiveness. Even more problematic, in many cases, little is known about possible dangers that might be associated with an herb. An herbal preparation that produces serious side effects may remain on the market until enough evidence accumulates to remove it. Areca (Betel) Areca catechu is a palm tree cultivated in Southeast Asia, India, and Africa. The nuts of this palm, often referred to as betel nuts, are chewed by more than 200 million people to produce a mildly stimulating effect. Chewing areca or betel is a practice similar to chewing tobacco in the United States, and, like nicotine, the active chemical in areca, arecoline, affects the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Heavy use stains the mouth and lips red and damages the mouth and teeth, but users are often unable to quit chewing despite these problems (Spinella, 2001). It is offered as a miracle drug in health food stores with claims that it prevents heart disease, cancer, obesity, and diabetes. The bad news is that virtually no evidence supports any of these claims, although the hormone may have some moodenhancing effects. Ephedra/Ma Huang A number of plant species from the genus Ephedra have been used for their stimulant effects for many years. Ephedra sinica is native to Asia and is frequently sold under its Chinese name, ma huang. Ephedrine is a potent stimulant with effects much like those reviewed in Chapter 6. It is sympathomimetic and produces behavioral effects similar to those of other stimulants (Karch, 2000). Until 2004, ephedrine products were marketed through stores or by mail order to increase energy, prevent drowsiness, suppress appetite, and in high-dose formulations, as an "herbal" alternative to Ecstasy (see Chapter 12).
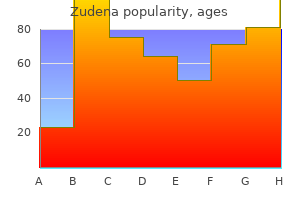
Buy genuine zudena line
Additionally impotence 24 discount zudena online, note the presence of multiple thickened loops of small bowel throughout the left hemiabdomen and portions of the pelvis, likely representing mesenteric ischemia caused by venous occlusion. These patients are critically ill, are almost always found in the acute care or intensive care settings, and nearly always have a history of hypotension or shock physiology. Certain segments of bowel may demonstrate features of arterial ischemia, including bowel wall hypoenhancement, whereas other segments of bowel may demonstrate features of venous occlusion, with prominent bowel wall edema/hemorrhage and mesenteric edema/hemorrhage. It is critical in these cases for a radiologist to differentiate these complex bowel obstructions from simple, routine bowel obstructions. Closed-loop obstructions often demonstrate a unique tethered, radiating appearance of the dilated small bowel loops, quite different from the configuration of the bowel in conventional obstructions. This constellation of findings is compatible with a closed-loop obstruction and bowel ischemia, findings which were confirmed at surgery. Other features that have been described as most specific for bowel ischemia in the setting of a strangulated bowel obstruction include diminished bowel wall enhancement and immediately adjacent mesenteric fat stranding. In rare instances, trauma to the bowel can also result in pneumatosis without necessarily indicating underlying ischemia. Nevertheless, although these findings can theoretically be benign, the presence of pneumatosis or portal venous gas in any patient should be considered indicative of ischemia until proven otherwise and should prompt urgent clinical evaluation for potential mesenteric ischemia. Pneumatosis, which represents the presence of gas truly within the wall of the bowel. There is also extensive pneumatosis involving multiple small bowel loops in both the right and left hemiabdomen, compatible with mesenteric ischemia. The patient was asymptomatic, and this finding was determined to represent benign pneumatosis related to the previous procedure. These findings were determined to reflect benign pneumatosis in this asymptomatic patient who was receiving steroids for another medical condition. Computed tomography evaluation of gastrointestinal bleeding and acute mesenteric ischemia. Arteriography for lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage: role of preceding abdominal computed tomographic angiogram in diagnosis and localization. Comparison of ischemic and nonischemic bowel segments in patients with mesenteric ischemia: multidetector row computed tomography findings and measurement of bowel wall attenuation changes. For many patients with cirrhosis, portal hypertension represents the clinical manifestation of liver disease-the actual signs and symptoms that patients with end-stage liver disease experience. Portal hypertension is the final common pathway of many forms of chronic liver disease, and its development is the turning point in the course of a chronic liver disease, a threshold event that signifies the transition from asymptomatic liver disease to decompensated cirrhosis. Portal hypertension can also occur in patients with acute severe liver disease, and the signs and symptoms in these cases may be indistinguishable from those in cases of chronic liver disease. Clinically, portal hypertension is recognized by the development of variceal bleeding, ascites, or hepatic encephalopathy. In early clinical studies, the prognosis of patients who presented with these forms of decompensation was invariably grim. Liver disease, however, is more intuitively thought of as a spectrum, with implications for patients with advanced liver disease who are asymptomatic-classified as chronic liver failure or acute-on-chronic liver failure in patients who have developed acute decompensation (ascites, hemorrhage, encephalopathy, and/or bacterial infections). Thus, patients with cirrhosis may be further subclassified more discretely into separate stages of disease. These cases can be classified by the site of blood flow obstruction (prehepatic, hepatic, or posthepatic). For instance, this condition is very common among men in their second and third decades of life in India and is possibly responsible for almost one-third of all variceal bleeding episodes in this population,10 whereas in Japan it is more common among women in their fourth decade of life. A number of etiologies for noncirrhotic portal hypertension have been proposed, including chronic infections, exposure to certain medications or toxins, the presence of a hypercoagulable condition such as thrombophilia, and the presence of immunological or genetic disorders. This was derived from the long-term follow-up of almost 500 patients with various stages of cirrhosis who were diagnosed between 1981 and 1984, broken down by clinical stages. The arrows represent the progression of liver disease, and the numbers the percentage of patients progressing to the stage over 5 years of follow-up. Clinicians must be able to distinguish between cirrhotic and noncirrhotic portal hypertension, as the approaches to treatment and prognosis are different for each entity. For example, patients with portal vein thrombosis (a presinusoidal cause of portal hypertension) are at high risk of developing bleeding but tend to have entirely preserved hepatic synthetic function; as a result, these patients tend to have a much better chance of surviving a variceal bleed than patients with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis. The liver receives approximately 25% of the total resting cardiac output and has a dual blood supply: the hepatic artery supplies approximately 25% of the total and the portal vein supplies the remainder. This blood is passed to the sinusoids, composed of one discontinuous layer of fenestrated endothelial cells, which are meant to function as low-pressure vascular channels, allowing blood to percolate across the hepatocytes before being delivered to the central veins. The total hepatic blood flow from both sources is typically 800 to 1,200 mL/min, or approximately 100 mL/min per 100 g of liver weight. Because of the presence of fenestrae between the sinusoidal endothelial cells, there is free flow of sinusoidal blood into the space of Disse. However, in case of cirrhosis, the obstruction to flow results in overaccumulation of lymph, which presents as ascites. The stellate cells, which are typically quiescent cells that store vitamin A, may respond to injury by transforming into an activated form, proliferating and causing contraction and secretion of collagen. These stellate cells are therefore central to the development and maintenance of portal hypertension. A close estimate, however, can be obtained by measuring the wedged hepatic venous pressure, which estimates the sinusoidal pressure. The gradient that exists between the wedged hepatic venous pressure and the free hepatic venous pressure, reflected in the intra-abdominal vena caval pressure, represents the resistance to flow across the liver. In patients with suspected advanced liver disease, this approach is helpful not only in establishing a histologic diagnosis but also in assessing prognosis. Some have described this technique as a "splanchnic sphygmomanometer" that can be used to monitor the effect of therapy and assess the risk of bleeding. The first event that occurs in the pathway to portal hypertension is an increase in resistance to flow, in part as a result of the disruption of the normal venous channels with the accumulation of progressive fibrosis. As pressure increases across the portal venous system, an extensive network of portosystemic collaterals develops, diverting a large fraction of portal blood to the systemic circulation and bypassing the liver. Cirrhosis also tends to be accompanied by an increase in the presence of vasodilators. These vasodilators perpetuate a hyperkinetic systemic circulation, with reduced arterial pressure and peripheral resistance and increased cardiac output. This was first described in detail by Kowalski and Abelmann,31 who reported that patients with cirrhosis typically presented with the signs and symptoms of "warm extremities, cutaneous vascular spiders, wide pulse pressure, and capillary pulsations in the nail beds. A secondary event that occurs in all forms of portal hypertension is the emergence of an expanded plasma volume. This expansion of plasma volume is caused by renal sodium retention, which precedes the increase in cardiac output. The expanded blood volume represents a negative feedback loop and serves to further increase portal pressure. Splanchnic vasodilatation itself can be explained by the combination of increased local vasodilator production and increased systemic vasodilators in the circulation, both of which lead in turn to a decreased response to vasoconstrictors. Cirrhosis is often thought of as a fixed obstruction, based on deposition of scar and development of regenerative nodules that distort normal patterns of blood flow. In support of this concept, histologic studies that have compared the extent of fibrosis with measurements of portal hypertension have demonstrated specific features, including small nodularity and septal thickness, to be independently predictive of clinically significant portal hypertension. The extent of vasodilatation, moreover, is substantial and therefore has clinical implications, accounting for as much as 40% of the total resistance across the liver. Because of the contractile properties and perisinusoidal location of these cells, they may regulate sinusoidal blood flow and resistance and thus may serve as a potentially modifiable target in portal hypertension. The microenvironment that regulates hepatic stellate cell contractility is a control point that determines the relative degree of relaxation or constriction. Each of these is modified by a number of mechanisms and agents that interact with these pathways (Table 3. Many of these same mediators are also involved in angiogenesis,37 which plays a major role in the development of portal systemic shunts but also contributes to the progression of fibrosis within the liver. Glucagon levels in turn are relatively high because of overproduction and decreased clearance. Preliminary studies have found that patients with portal hypertension had significantly lower serum H2S concentrations and that disease severity and the portal vein diameter (a proxy for the degree of portal hypertension) were inversely correlated with H2S concentration.
Asthmaplant (Euphorbia). Zudena.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Euphorbia?
- Asthma, bronchitis, coughs, hayfever, tumors, digestive problems, intestinal worms, gonorrhea, and other conditions.
- How does Euphorbia work?
- Dosing considerations for Euphorbia.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96628
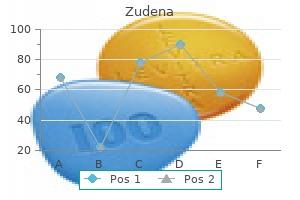
Cheap zudena online american express
A third class of hallucinogens how do erectile dysfunction pills work order zudena 100mg without prescription, called the anticholinergic hallucinogens, is less familiar to most people and includes drugs such as atropine and scopolamine found in plants such as mandrake, henbane, belladonna, and jimsonweed. These drugs produce a dream-like trance in users from which they awaken with little or no memory of the experience. The drugs in this class are antagonists of a subtype of acetylcholine receptors called muscarinic receptors (Prus, 2014). These are often referred to as the dissociative anesthetics because of their ability to produce surgical anesthesia while an individual remains at least semiconscious. Dissociative anesthetics are thought to act through a receptor that influences activity of the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter, glutamate (Meyer & Quenzer, 2013). Almost completely unknown until recently, salvia is not currently a federal controlled substance, although some states have banned it. Relatively little is known about salvinorin A, but it appears to act differently on the brain from any of the previously known hallucinogens by affecting specialized opiate receptors known as kappa receptors, and thus we classify it as a kappa hallucinogen (Prus, 2014). Throughout the world Ayahuasca, Yakee, Yopo Peyote Ololiuqui hallucinogens are found in a wide variety of plants. The hallucinogenic properties of these plants were primarily discovered and used by the Indian peoples of Central and South America (an exception is ibogaine, which tribal peoples of Africa discovered and used). Historians and anthropologists have reconstructed the uses to which these hallucinogenic plants were put and these are worth some consideration here. Early History When the Spanish conquistadores began to explore and colonize Mexico and other parts of Central and South America, they encountered new civilizations with customs and religious practices unfamiliar to Europeans. Among these practices was the use of hallucinogenic plants in religious ceremonies. One of the earliest documentations was by Fernando Hernandez, the royal physician to the king of Spain (Stewart, 1987). In 1577, he studied the plants the Aztecs used and noted the use of peyote cactus (referred to as peyotl), psilocybe mushrooms (called teonanacatl), and morning glory seeds (called ololiuqui). Although each of these plants contains a different drug, all produce vivid visual hallucinations, and the Indians took the visions as oracles that could reveal the future and solve other mysteries, help in decision making, and aid the medicine man or shaman in healing the sick (see the Drugs and Culture Box 12. The Aztec and Mayan peoples called the psilocybe mushrooms teonanacatl, which means "flesh of the gods," and as one might guess from that name, the mushrooms were viewed as sacred. One Spanish writer, de Sahagun in the 1500s, described the use of mushrooms by Aztecs as follows: "Rotating kaleidoscopes. They ate the mushrooms with honey and when they began to feel excited due to the effect of the mushrooms, the Indians started dancing, while some were singing and others weeping. Some Indians who did not care to sing, sat down in their rooms, remaining there as if to think. Others, however, saw in a vision that they died and thus cried; others saw themselves eaten by a wild beast; others imagined that they were capturing prisoners of war; others that they were rich or that they possessed many slaves; others that they had committed adultery and had their heads crushed for this offense. The Aztecs used peyote in their rituals, and de Sahagun noted, "Those who eat or drink it see visions either frightful or laughable. Peyote, like ololiuqui and sacred mushrooms, was forbidden to the Indians by the Spaniards, who regarded its use for religious purposes as blasphemous. Thus, the use of all these agents persisted only "underground," and little is known of them before the 20th century. The peyote religion spread widely during the 18th and 19th centuries, however, to unite most Indian tribes in western Mexico and the United States. The southwestern tribes gathered peyote by cutting the cactus at the soil line, leaving the root intact. The all-night ceremony takes place in a large tepee where the participants sit in a circle around a fire, eating peyote buttons and drinking peyote tea. The night is spent chanting, singing, praying, and later on discussing and interpreting the peyote-induced visions. Some Native Americans still conduct these ceremonies today, much as they did many centuries ago (Stewart, 1987). This may be the first description of hallucinogenic drug effects that captures the range of experiences different individuals may have after taking the drug. The use of sacred mushrooms persists in parts of Mexico in rituals for healing and divination (Schultes, 1976). In South America, a number of different hallucinogenic plants traditionally have been used in much the same way as peyote and psilocybin were used farther north. Perhaps the best known is a concoction called ayahuasca or hoasca used by indigenous people of the western Amazon area of Brazil, Colombia, Peru, Ecuador, and Bolivia. Ayahuasca tea usually contains a second plant, usually a woody vine (Banisteriopsis caapi or B. Sometimes Virola bark is ground into powder and taken intranasally as a snuff that is also effective. Ayahuasca produces a brief (1- to 2-hour) experience characterized by intense visual hallucinations and is traditionally used in healing ceremonies, initiation rites, and other rituals. It is said that the plants provide users with telepathic powers, but this claim has no scientific support (Schultes, 1976), and in fact, the effects are similar to those of the other serotonergic hallucinogens. Despite the long history of hallucinogenic drug use, these drugs had virtually no impact on mainstream European or American culture until the 1960s, when hallucinogen use exploded. The traditional ayahuasca ceremonies and practices have been studied by anthropologists who have noted that these have multiple purposes. The altered state of consciousness and visual hallucinations are seen as a means of communication with a spirit world and of obtaining divine guidance. Shamans use ayahuasca in healing ceremonies to improve physical health and to exorcise evil spirits (de Rios & Rumrrill, 2008). This religion combines features of Christianity with traditional Amazonian beliefs and practices, including ceremonial and spiritual use of ayahuasca. A relatively new phenomenon is the emergence of "ayahuasca tourism," in which European and U. However, a tourist industry has developed around this and the sessions are usually conducted, not by true shamans, but rather, by travel agents who have acquired some knowledge of ayahuasca (de Rios and Rumrrill, 2008). During a laboratory experiment, Hofmann apparently spilled a small Copyright 2019 Cengage Learning. He described his reaction as follows: I was forced to interrupt my work in the laboratory in the middle of the afternoon and proceed home, being affected by a remarkable restlessness, combined with a slight dizziness. At home I lay down and sank into a not unpleasant intoxicated-like condition, characterized by an extremely stimulated imagination. I perceived an uninterrupted stream of fantastic pictures, extraordinary shapes with intense, kaleidoscopic play of colors. After taking the drug, Hofmann (1980) noted in his journal: "Beginning dizziness, feeling of anxiety, visual distortions, symptoms of paralysis, desire to laugh" (p. Everything in my field of vision wavered and was distorted as if seen in a curved mirror. Finally we arrived at home safe and sound, and I was just barely capable of asking my companion to summon our family doctor and request milk from the neighbors. After he recovered and made his report to Sandoz, many other experiments followed. At some point, Leary had stepped out of his role as a scientist and had become the leader of a social and religious movement. It was said to cause insanity, suicide, acts of violence, and homicidal behavior (Stevens, 1987). He crashed around America selling consciousness expansion without ever giving a thought to the grim meat-hook realities that were lying in wait for all the people who took him too seriously. All those pathetically eager acid freaks thought they could buy Peace and Understanding for three bucks a hit. What Leary took down with him was the central illusion of a whole lifestyle that he helped to create. The 2016 high school senior survey found a significant increase in overall use of hallucinogens during the past year (up to 4. The first bit of evidence was suggested by the chemical structures of some of the major hallucinogens.
Purchase generic zudena canada
Analgesics erectile dysfunction protocol ingredients buy 100 mg zudena free shipping, narcotic agonist-antagonists Labor pain management, anesthesia Binds to opiate receptors producing agonist-antagonist effects Pain-0. Butorphanol provides better initial analgesia than fentanyl during labor, with fewer patient requests for more medication or epidural analgesia. In one well-designed study, it was less effective than meperidine for the relief of affective pain during labor. Side effects include drowsiness, hypotension, respiratory depression, sedation, dizziness, N/V, sweating, headache, euphoria, confusion, nervousness, anorexia, and constipation. Butorphanol crosses the human placenta, achieving an F:M ratio approximating unity. Neonatal respiratory depression may occur after parenteral maternal administration. When used concurrently with such drugs, the dose of butorphanol should be the smallest effective dose and the frequency of dosing reduced as much as possible. The analgesic effect of butorphanol may be diminished if given shortly after sumatriptan nasal spray. It is unknown if the effects of butorphanol are altered by other medications that affect hepatic metabolism of drugs (erythromycin, theophylline, etc. The fraction of butorphanol absorbed is unaffected by the concomitant administration of a nasal vasoconstrictor (oxymetazoline), but the rate of absorption is decreased. Maternal Considerations Fetal Considerations Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary 90 Cabergoline International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Dostinex) Log on to ExpertConsult. Antiparkinson agents; Dopaminergics; Ergot alkaloids and derivatives; Hormones/hormone modifiers Hyperprolactinemia, lactation suppression Stimulates D2 dopamine receptors Hyperprolactinemia-begin 0. Cabergoline Considerations is better tolerated and more effective in inducing a complete biochemical response than bromocriptine. It has been used throughout pregnancy to successfully treat macroprolactinoma; most tumors disappear with therapy. Cabergoline is also effective in women resistant or poorly responsive to bromocriptine. Side effects include N/V, headache, dizziness, constipation, fatigue, abdominal pain, vertigo, hot flashes, dry mouth, depression, and hypotension. Cabergoline suppressed lactation in some studies, with less rebound than bromocriptine. Cabergoline should not be administered with D2 antagonists, such as phenothiazines, butyrophenones, thioxanthenes, or metoclopramide. Cardiac arrhythmias are associated with maternal caffeine use in excess of 500 mg/d. In rodents, high and sustained doses are associated with a small increase in the prevalence of cleft palate. Despite the fact that many epidemiologic studies observed a positive association between maternal caffeine intake and the risk of spontaneous abortion, the evidence is still equivocal given the biases likely present and the fact that most of the potential biases would overestimate any association. Though it enters human breast milk in small amounts, caffeine is generally considered safe for breastfeeding women. The blood levels of ergotamine-containing drugs associated with vasospastic reactions are reported to be increased by the co-administration of macrolide antibiotics. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary 92 Caffeine plus ergotamine International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Cafatine; Cafergot; Cafermine; Cafetrate; Ercaf; Ercatab; Ergo-Caff; Gotamine; Micomp-Pb; Migergot; Secadol; Wigraine) Log on to ExpertConsult. This Considerations combination is contraindicated due to the oxytocic effects of ergotamine. Jejunal atresia was reported in the child of a woman Considerations who ingested caffeine and ergotamine in five consecutive pregnancies. Propranolol may potentiate the vasoconstrictive actions of ergotamine and caffeine by blocking the vasodilating property of epinephrine. Nicotine may provoke vasoconstriction in some patients, predisposing to a greater ischemic response to ergot therapy. Calcifediol is converted in the kidney to an active form of vitamin D, calcitriol. Veiled or dark-skinned pregnant women have an increased risk of vitamin D deficiency, which is associated with disease. Side effects include hypercalcemia, elevated creatinine, polydipsia, nausea, and convulsion. There is a weak Considerations association between vitamin D levels and gestational age and fetal heel length. It is unknown whether calcifediol crosses the human placenta, though the placenta synthesizes active vitamin D. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References There is no published experience in nursing women. It is unknown whether calcifediol enters human breast milk, though vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy increases milk vitamin D levels. Summary Calcitonin Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Calcimar; Miacalcin) International Brand Names Log on to ExpertConsult. There are no adequate reports or well-controlled Considerations studies in pregnant women. Side effects include rhinitis, back pain, epistaxis, nasal irritation, and headache. It is unknown whether calcitonin enters human breast milk, though the high molecular weight argues against it. Drug Interactions References Summary Calcitriol Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Rocaltrol) International Brand Names Log on to ExpertConsult. Vitamins/minerals Hypoparathyroidism, osteoporosis, hypocalcemia, supplementation during pregnancy Active form of vitamin D; stimulates intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus Hypocalcemia-0. Fetal There are no adequate reports or well-controlled studies of the effect of calcitriol in Considerations human fetuses. It is unknown whether calcitriol crosses the human placenta, though the placenta synthesizes active vitamin D. Thiazides are known to induce hypercalcemia by decreasing urine calcium excretion. However, in vivo drug interaction studies of ketoconazole with calcitriol have not been investigated. As calcitriol alters intestinal, renal, and bone phosphate transport, the dose of phosphatebinding agents must be adjusted to reflect the serum phosphate concentration. As calcitriol is the most potent active metabolite of vitamin D3, pharmacologic doses of vitamin D and its derivatives should be withheld during treatment with calcitriol. References Summary Calcium chloride Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers Electrolyte replacements; Vitamins/minerals Hypocalcemia, hypermagnesemia Modulator of cellular events. Calcium chloride reduces the incidence of parturient paresis in cows and transiently increases cardiac output in gravid ewes during hemorrhagic hypotension. Breastfeeding Safety It is unknown whether calcium chloride supplementation increases calcium concentration in breast milk. Calcium salts should not generally be mixed with carbonates, phosphates, sulfates, or tartrates in parenteral admixtures. Considerations There are no adequate reports or well-controlled studies in pregnant women.
Discount zudena 100mg amex
The most lethal complication observed was biliary peritonitis requiring surgical intervention erectile dysfunction essential oil buy generic zudena 100 mg, seen in 3 patients (2%). More recent studies have reported 30-day mortality rates as high as 25%, although only 4% of deaths were attributed to gallbladder-related disease; most were due to preexisting comorbidities. The tract is considered mature if there is no leakage of contrast into the peritoneal cavity, subhepatic, subcapsular, or subdiaphragmatic spaces. In the presence of leakage, a new catheter of equal or greater size should be placed over the wire back into the gallbladder. Cholesterol stones, which are more common in the Western hemisphere, are caused by overproduction of cholesterol by the liver, with associated gallbladder hypomobility. Pigmented stones, which are subclassified into black pigment and brown pigment stones, occur more often in the Eastern hemisphere. Black pigment stones are formed by extremely hard bilirubin polymers, whereas brown pigment stones are polymers of calcium bilirubinate and are often associated with biliary infections. Choledocholithiasis has long been known to be a risk factor for acute biliary pancreatitis and ascending cholangitis. Several studies have been performed to analyze risk factors and predictors for choledocholithiasis,58,59,60,61 and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy has used this information to stratify cases into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk categories based on laboratory, sonographic, and clinical findings (Table 13. Based on the results of the bacterial culture, proper antibiotic therapy should be continued. If an obstructing calculus was present, percutaneous cholecystolithotomy can be considered (discussed later in this chapter). Cholecystostomy tube removal can only be performed when the tract has matured, which typically occurs approximately 3 to 6 weeks after initial placement. Tract maturity can be assessed beginning at 14 days after tube placement via "tractography. Uncomplicated gallstone pain can be controlled with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and/or narcotic analgesics. Decisions regarding when and how to treat are not always clear-cut, as most patients with cholecystitis are asymptomatic. Factors that influence this decision include the presence of symptoms and complications and whether the patient is a surgical candidate. Additionally, complete dissolution of the gallstone can take up to 3 years or longer, and sometimes complete dissolution does not occur. Additionally, 5 to 47% of postcholecystectomy patients experience continued or recurrent dyspepsia and upper abdominal pain, a condition known as "postcholecystectomy syndrome. The drain is then exchanged over the wire for subsequent dilators to at least an 18-Fr sheath. Alternatively, the tract can be dilated with a high-pressure noncompliant balloon. Then, under fluoroscopic and endoscopic guidance, calculi can be removed with graspers or baskets. An 8- to 16-Fr pigtail drain is left in place in the gallbladder to allow for external drainage. Approximately 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure, the drain can be capped to allow for internal drainage. The patient can then return in an additional 1 to 2 weeks for tractography (see above). Kim et al83 suggested a new methodology using a 12Fr sheath under only fluoroscopic guidance. Larger stones may require initial fragmentation with a snare technique or by passing a bent Amplatz Extra-Stiff wire through the sheath. Causes of incomplete stone retrieval included the inability to grasp large stones and loss of the tract due to a decompressed gallbladder. Other potential complications include transient cholangitis, skin site infection, chest infection, and deep vein thrombosis. Tse et al86 used the aforementioned American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk stratification (Table 13. Basket Extraction Burhenne et al93,94 first described biliary tract stone extraction in 1972. If biliary tract calculi were present on a 7-day postoperative cholangiogram, the patient would return to the radiology department as an outpatient 5 weeks later. The authors recommended the use of basket extraction only for T-tubes that were 14 Fr or larger. With this technique, a safety guidewire is placed through the existing T-tube before tube removal. A steerable catheter is then advanced through the tract alongside the safety guidewire with the tip beyond the calculus. A basket is advanced through the catheter, and the basket is retracted to engage the stone. Once the stone and/or its fragments are engaged, the catheter/basket combination is retracted through the sinus tract, leaving the safety guidewire in place. When all of the visualized calculi are removed, the guidewire is removed, and a straight catheter is left in the ductal system for drainage. In a study of 661 patients who underwent this procedure, 95% of cases were technically successful, although approximately one-third of the patients required more than one session. In the absence of a T-tube, transcystic and transhepatic modifications to the Burhenne technique have been reported. Papillary balloon dilation and balloon-push stone clearance can be performed through an existing T-tube, transhepatic tube, or transcystic tube. The tube is then exchanged over the wire for a steerable catheter (Multipurpose or Cobra catheters). Through wire/catheter manipulation, the guidewire is advanced past the papilla into the duodenum. The hydrophilic wire can then be exchanged for an Amplatz Super Stiff Guidewire, and the steerable catheter is exchanged for a peripheral balloon angioplasty catheter. The balloon is placed across the papilla and inflated until the waste of the sphincter disappears; inflation should then be maintained for 30 to 60 seconds. The size of the balloon should be equal to or slightly larger than the largest stone. These shock pulses immediately expand the plasma (liquid), creating spherical shock waves that oscillate, leading to pressure waves that fragment the stone. To pass a choledochoscope, a tract of at least 18 Fr is required; the tract should be dilated over the course of a few days to weeks. When the tract is mature, the choledochoscope can be advanced through an 18-Fr sheath or directly into the skin tract. Passing the stone fragments usually requires either endoscopic or transhepatic sphincterotomy. The stone fragments can then be passed into the duodenum with aggressive Table 13. Therefore, this procedure is often performed with the assistance of experts in interventional radiology and endourology. Over the course of several weeks, this catheter should be upsized, usually to between 12 and 16 Fr, to allow passage of a 7-Fr choledochoscope. Only small population studies have been reported for this procedure, as this technique is typically performed endoscopically. The few studies available have reported technical success rates ranging from 92 to 100%, with total stone clearance usually achieved in one to two sessions. While first-line therapy for such conditions includes surgery or endoscopy, interventional radiology plays a large therapeutic role in many circumstances. Endoscopic therapy for choledocholithiasis can be much more technically challenging in patients with altered gastrointestinal anatomy. Therefore, percutaneous procedures, such as antegrade papillary dilation with stone clearance or extraction of stones with a basket, may prove beneficial. Interventional radiology may even collaborate with other specialists to perform intracorporeal lithotripsy. The above procedures have been proven to be effective and practical with little risk of complication, and should be considered as first-line therapy or alternative therapy when appropriate. Flowcharts for the diagnosis and treatment of acute cholangitis and cholecystitis: Tokyo Guidelines. Comparative operative outcomes of early and delayed cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis: a population-based propensity score analysis. Emergency cholecystectomy vs percutaneous cholecystostomy plus delayed cholecystectomy for patients with acute cholecystitis.
Buy zudena 100mg low price
When alcoholsensitizing drugs are used erectile dysfunction 23 years old discount zudena 100 mg, they are applied as part of a rehabilitative program that is concerned with the physical, psychological, and social problems that tend to accompany heavy drinking. A second type of pharmacotherapy for alcohol use disorder is based in biological theories of etiology, which as we saw earlier focus on abnormalities or changes in brain chemistry as causes or consequences of substance use disorder. Such theories imply that a correction of the abnormal brain chemistry is essential to alleviating the substance use problem. From a broader perspective, including a biological component to treatment is entirely compatible with the biopsychosocial approach to drug use and its modification that this text takes. Pharmacological agents also may be applied as part of programs that are not derived from any particular model of alcohol use disorder, simply if it is believed that such agents are effective (Brewer, 1996). In recent years, the major advances that have been made in understanding the biological bases of addiction have resulted in the development and evaluation of pharmacotherapies for alcohol use disorders. You can see that the pharmacological agents have diverse biological actions, and some of the drugs are thought to act on the brain in different ways. Treatment of Substance Use Disorders 405 Effectiveness of Alcohol Treatment After reading about a variety of settings and methods that fall into the category of alcohol treatment, you are probably wondering whether any of the effort is worth it. When we talk about treatment effectiveness, we refer to the relationship between participating in some treatment and achieving some treatment goal. Therefore, treatment effectiveness concerns whether and how treatment participation causes different outcomes. Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment is called treatment outcome research. In this section, we do not cover detoxification services because they are not considered rehabilitation. Rather, they should be viewed as effective in managing safe alcohol withdrawal but not in providing rehabilitation beyond that. When we discuss the effectiveness of treatment aimed at rehabilitation, we must take into account the rate of spontaneous remission of alcohol use disorder (a synonymous term commonly used in the literature is natural recovery). As you might guess, to show that a treatment is worth its cost requires a demonstration that it helps significantly beyond the rate of spontaneous remission. This reasoning is sound, but it is extremely difficult to determine the rates of spontaneous remission. People who resolve their problems without treatment are the ones with whom clinicians and researchers are least likely to have contact. Professionals instead tend to see people who are referred to a formal treatment setting. We noted earlier in this chapter that making a credible effort to determine the prevalence of spontaneous remission of alcohol use disorder would be complex and costly. Despite this problem, estimates of spontaneous remission have been made for alcohol use disorder, mostly through studies of people who entered a formal treatment program but dropped out of it prematurely and could say they received "no treatment. The estimates of spontaneous remission of alcohol problems that have been made vary with the definition of remission, the comparison groups used, and the length of the interval during which functioning is measured. Miller and Hester (1980) suggested that the spontaneous remission (abstinence or improvement in drinking patterns) in one year for individuals not treated for their alcohol use disorder is 19%, and Emrick (1975) calculated 13% for abstinence and 28% for abstinence plus "improved. Overall, a period of research interest in the topic in the late 1990s to early 2000s on individuals who had experienced "natural recovery" from their alcohol or other drug problems yielded data suggesting that it occurs often, just as we observed for nicotine dependence (Sobell et al. Questions about the effectiveness of nonpharmacological professional treatment have been studied for many years. We can offer some general conclusions about the effectiveness of nonpharmacological treatments. Studies have shown that the amount of money saved in, say, health care and business expenses as a result of improvements in people undergoing treatment is greater than the amount of money the treatment costs. Similarly, research that insurance companies completed suggests that substance abusers (and their families) use significantly fewer health care services after treatment than before. Of course, the more important, but more difficult to measure, gains in human welfare are considerable. Although our knowledge about matching and alcohol treatment is still not extensive or particularly sophisticated, there is some clinically informative research on matching patients to treatment settings and services (Carroll & Kiluk, 2016; Finney, Wilbourne, & Moos, 2007). For example, inpatient or residential treatment settings may be best reserved for individuals whose alcohol use disorder is more severe, or who have other drug problems, or who have less social stability. For other individuals, outpatient treatment likely will do just as well as inpatient and at far less cost. It seems that the accumulation of findings such as these would help to take alcohol treatment to a level of more efficient service delivery. These findings were corroborated in the Finney, Wilbourne, and Moos (2007) review. The treatments that have been identified are listed and are briefly described in Table 15. You can see that most of the treatments listed in the table are based broadly on social learning principles. Motivational enhancement therapy also uses principles of social learning theory (also called social cognitive theory) but combines them with psychotherapy methods designed to help clients arrive at their own conclusions about the need to change rather than the therapist imposing change on clients. For example, sessions (individual or group) might be held to educate people about the twelve-step change program. Brief interventions average one to three sessions, and each session lasts up to 45 minutes, but much less time is often spent in a session. Traditional alcohol outpatient, face-to-face individual treatment typically is designed to have considerably more sessions that usually last about an hour. Brief interventions have been applied in several different settings, including college campuses and the general medical care setting, and they may be delivered in-person, provider to patient, face-to-face, or to the patient by some electronic medium such as a smartphone or a computer via the Internet. The general medical setting is such a prominent base for delivery of alcohol brief interventions, because patients in that setting tend to have higher rates than the general population of unidentified alcohol problems of varying degrees of severity due to the correlation between heavy alcohol use and physical problems. Accordingly, if some type of intervention could be done in these settings to thwart the development of more severe alcohol problems, then there is the potential to save society billions of dollars. Furthermore, the success of brief interventions in treating alcohol problems has led more recently to evaluations of their effectiveness in treating people, including adolescents, who have problems with other drugs (Humeniuk et al. Brief interventions can be as simple as feedback about the consequences of heavy alcohol use for a person. They are based on the idea that alcohol problems exist on a continuum of severity and that interventions can occur at any point along that continuum. Who is most helped by brief interventions and why they work are current important clinical and research questions. The findings about brief interventions have great practical implications for alcohol treatment providers and for saving society a lot of money and suffering. For example, what do you think disease or biological model adherents might say about brief interventions Self-Help Treatment What we have said so far about treatment effectiveness was pertinent to professional services. The twelfth tradition, anonymity, "is the spiritual foundation of our traditions, ever reminding us to place principles before personalities. Of course, we do not currently have clear evidence about the effectiveness of participation in these alternative groups. It is essential that matching research be aimed at discovering which individuals fit best with which self-help group participation. Effectiveness of Pharmacological Treatments With the exception of disulfiram, pharmacotherapies for alcohol use disorders have been developed relatively recently, but the amount of research that has been devoted to discovering effective pharmacotherapies for alcohol (and other) drug use disorders has grown almost exponentially in the last two decades. When disulfiram became available, it was thought to be the long-sought answer to alcohol treatment. Unfortunately, the results of many studies show that disulfiram has fallen far short of this mark. One problem in interpreting the research on disulfiram is that often it has not been done well. The clinical trials on disulfiram that have been well controlled show modest effects on number of drinking days, but they also have yielded inconsistent findings (Garbutt et al. One factor to keep in mind when evaluating disulfiram is that its effects may be enhanced considerably if its use is combined with a behavioral program that in part consists of supervised administration of the disulfiram.
Order 100 mg zudena with amex
Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Ceftriaxone International Brand Names Drug Class Indications - (Cef-3; Rocephin; Rowecef) Log on to ExpertConsult erectile dysfunction kolkata generic zudena 100 mg on line. However, third- and fourth-generation cephalosporins are not generally recommended for surgical prophylaxis. Side effects include thrombocytopenia, anaphylaxis, diarrhea, pseudomembranous colitis, eosinophilia, and vomiting. Ceftriaxone Considerations rapidly crosses the human placenta, reaching therapeutic concentrations in the fetal compartments. Some studies suggest that intrapartum prophylaxis with ceftriaxone decreases the rates of bacterial colonization and early-onset infection in newborns. However, in vitro, ceftriaxone weakly impairs rat nephrogenesis at all doses studied except 1000 mcg/mL, which blocked kidney development completely. But with a relative infant dose of <5%, it is considered compatible with breastfeeding. Probenecid may decrease renal tubular secretion of cephalosporins, resulting in increased and more prolonged cephalosporin blood levels. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Cefuroxime International Brand Names Drug Class Indications - (Ceftin; Kefurox; Zinacef) Log on to ExpertConsult. Considerations It appears to be safe and effective during pregnancy for the treatment of acute infections, especially pyelonephritis. One investigator suggested it was a first-choice option for the treatment of acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy due to its tolerance, microbiologic activity, and superior clinical effect compared to cephradine. Side effects include thrombocytopenia, anaphylaxis, pseudomembranous colitis, eosinophilia, diarrhea, vomiting, interstitial nephritis, neutropenia, and elevated hepatic enzymes. There is no evidence of teratogenicity after first-trimester exposure, and children of women treated with cefuroxime are normal at 18 mo. With a relative infant dose of <5%, it is considered compatible with breastfeeding. Drugs that reduce gastric acidity may result in a lower bioavailability of cefuroxime compared with that of the fasting state and tend to cancel the effect of postprandial absorption. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Celecoxib Drug Class Indications Mechanism 128 - (Celebrex) International Brand Names Log on to ExpertConsult. In several trials, celecoxib was employed as a tocolytic agent with modest or no effect. Celecoxib (80 and 160 mg/kg/d) significantly reduces fertility, prolongs pregnancy, and inhibits normal cervical ripening in rats. The authors concluded it was similar to indomethacin but with a lower frequency of adverse fetal effects. There is a dose-dependent increase in the frequency of diaphragmatic hernia in rats. There are no adequate reports or well-controlled studies of celecoxib in nursing women. Celecoxib is excreted into human breast milk in low amounts, with a relative infant dose of <1%. Patients on lithium should be closely monitored when celecoxib is introduced or withdrawn. Bleeding events have been reported postmarketing in patients receiving celecoxib and warfarin, predominantly in older adults. Cephalexin - (Alsporin; Biocef; Carnosporin; Cefaseptin; Cephin; Ceporexin-E; Check; Ed A-Ceph; Keflet; Keflex; Lopilexin; Mamlexin; Synecl; Winlex) International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers Log on to ExpertConsult. Cephalexin appears effective and safe during pregnancy for the treatment of acute bacterial infection. Side effects include neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anaphylaxis, pseudomembranous colitis, diarrhea, nausea, and elevated hepatic enzymes. Cephalexin crosses Considerations the human placenta in a carrier-mediated fashion. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions the amount of cephalexin excreted into human breast milk is small with a relative infant dose of <2%. Nephrotoxicity has been reported following co-administration of other cephalosporins and aminoglycosides. References Summary 130 Cephapirin Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Cefadyl) International Brand Names Log on to ExpertConsult. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions the amount of cephapirin excreted into human breast milk is small with a relative infant dose of <1%. References Summary Cephradine International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism - (Anspor; Cefamid; Cefradina; Eskefrin; Nobitina; Velosef) Log on to ExpertConsult. Side effects include anemia, thrombocytopenia, anaphylaxis, pseudomembranous colitis, diarrhea, nausea, and elevated hepatic enzymes. Bacteriostatic agents may interfere with the bactericidal action of cephalosporins in acute infection; other agents. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Cetirizine Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Alltec; Zyrtec) International Brand Names Log on to ExpertConsult. Considerations the product labels state medications for allergic rhinitis should be avoided during pregnancy owing to lack of fetal safety, though the majority of agents have human data that refute this position. Side effects include bronchospasm, hepatitis, hypersensitivity, somnolence, fatigue, dry mouth, pharyngitis, dizziness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. There is a small decrease in the clearance of cetirizine after 400 mg of theophylline; it is possible a larger theophylline dose could have a greater effect. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Chenodiol Chino; Soluston) - (Chebil; Chelobil; Chendal; Chenix; Chenocol; Chenodex; International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers Log on to ExpertConsult. There are no adequate reports or well-controlled studies of chenodiol in pregnant women. Maternal pregnancy outcome may be improved in pregnancies complicated by intrahepatic cholestasis by treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid. Neither fetal liver damage nor fetal abnormalities occurred in reproduction studies in rats and hamsters. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions References Summary Chloral Hydrate International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Aquachloral; Chloralhydrat; Chloralix; Dormel; Kloral; Noctec) Log on to ExpertConsult. There is a case report of successful hemodialysis during pregnancy for the treatment of a chloral hydrate overdose. Side effects include hypersensitivity, leukopenia, dependence, respiratory depression, hyperbilirubinemia, and angioedema. Chronic use Considerations during pregnancy may result in neonatal withdrawal, suggesting placental transfer. Chloral hydrate is excreted into human breast milk with a relative infant dose of <3%. Though it should be safe at this dose, there are scattered reports of neonatal sedation. Breastfeeding Safety Drug Interactions C References Summary Chlorambucil International Brand Names Drug Class Indications Mechanism Dosage With Qualifiers - (Leukeran; Linfolysin) Log on to ExpertConsult. There are many case reports of a successful outcome in women treated with chlorambucil throughout pregnancy. Side effects include bone marrow suppression, N/V, confusion, anxiety, seizures, skin hypersensitivity, and pulmonary fibrosis.