Generic fulvicin 250mg fast delivery
None of the three sets of items of the criteria (questionnaire antifungal powder discount fulvicin 250 mg mastercard, clinical, and laboratory) is absolutely needed for classification, and this represents an advantage. Ischemia caused by hyaline thrombi that occlude the small blood vessels is related to higher cryocrit levels. Stochastic oncogenetic events are implied to select partially or fully deregulated B-cell clones and then to facilitate the progression of lymphoid malignancy. The irreversible organ damage caused by parenchymal fibrosis after vasculitis requires supportive therapy. In life-threatening manifestations, early diagnosis and prompt treatment are mandatory. Prophylaxis and early recognition and treatment of infectious complications are needed. Acute motor neuropathy and rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis also deserve an aggressive approach. Colchicine, antimalarials, a low-antigencontaining diet, and low-dose glucocorticoids may be helpful for purpura, constitutional, and milder articular manifestations,16 and low-dose glucocorticoids should be avoided long term. The management of pain (nociceptive, neuropathic, and mixed)50 and of weakness is of pivotal importance in certain patients. The cornerstone of therapy remains the targeting of the underlying B-cell disorder: alkylating agents, rituximab, thalidomide, lenalidomide, and bortezomib are used. The novel antiviral regimens, without the antiproliferative effects of interferon, might be also effective. Mycophe, nolate mofetil may be an alternative in some patients with milder renal disease. In about half of patients, the duration of the response to a single cycle of rituximab may be quite long (median, 1 year), and a retreatment at relapse regimen appears convenient. Because the clinical picture may be highly variable based on disease chronicity or the frequency of relapses, the age and activity of the patient, the concomitant liver disease, and comorbidities, the treatment must be individualized. Prevalence of, mixed cryoglobulinaemia syndrome and circulating cryoglobulins in a population-based survey: the Origgio study. Mixed cryoglobulinemia: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 231 patients. The spectrum of type I cryoglobulinemia vasculitis: new insights based on 64 cases. Life-threatening cryoglobulinemic patients with hepatitis C: clinical description and outcome of 279 patients. Recommendations for the management of mixed cryoglobulinemia syndrome in hepatitis C virus-infected patients. A randomized controlled trial of rituximab for the treatment of severe cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. Impact of cryoglobulinemic syndrome on the outcome of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a 15-year prospective study. Involvement of chemokines and type 1 cytokines in the pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia vasculitis neuropathy. Efficacy of rituximab in severe and mild abdominal vasculitis in the course of mixed cryoglobulinemia. Performance of the preliminary classification criteria for cryoglobulinaemic vasculitis and clinical manifestations in hepatitis C virus-unrelated cryoglobulinaemic vasculitis. The development of mixed cryoglobulinemia in Capillaria hepatica-infected mice is associated with the capillaria antigen-induced selective proliferation of splenic B-1a cells in response to interleukin-5 stimulation. Somatic hypermutations confer rheumatoid factor activity in hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia. Low-grade malignant lymphoma, hepatitis C virus infection, and mixed cryoglobulinemia. Importance of cellular microenvironment and circulatory dynamics in B cell immunotherapy. A randomized controlled trial of rituximab following failure of antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus-associated cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. Safety and efficacy of rituximab in patients with hepatitis C virus-related mixed cryoglobulinemia and severe liver disease. Pegylated, interferon-alpha, ribavirin, and rituximab combined therapy of hepatitis C virus-related mixed cryoglobulinemia: a long-term study. Rituximab plus Peg-interferon-alpha/ribavirin compared with Peg-interferon-alpha/ribavirin in hepatitis C-related mixed cryoglobulinemia. Treatment of hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia with direct-acting antiviral agents. Regression of, splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes after treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. Headache, seizure, and cognitive impairment are the predominant symptoms, although various multifocal or diffuse neurologic symptoms with a remitting or progressive course may be present, including ischemic stroke and hemorrhage. Angiographic changes indicating an irregular course of vessels with characteristic segmental narrowing can be observed, but angiographic findings are normal at times and may not predict the pathologic findings. Cerebral angiography demonstrating segmental arterial narrowing and vessel occlusion affecting many cerebral vessels in the absence of proximal vessel atherosclerosis 3. Exclusion of systemic inflammation, cerebral arteriopathy, malignancy, and infection 4. The clinical syndrome is rare, with poorly defined risk factors and varied clinical symptoms that may be identical to those produced by infection; atherosclerotic, occlusive vascular disease; and malignancy. Rapidly progressive presentation is associated with multiple bilateral vessel lesions and is often associated with fatal outcome. The typical manifestation consists of nonfocal symptoms such as headache and intermittent confusion and focal neurologic symptoms such as hemiparesis. Ataxia of limbs or gait, focal cortical dysfunction (including aphasia), and seizures are less frequent. It was difficult to distinguish between polyarteritis and syphilitic endarteritis because of the occasional presence of similar pathologic findings of vascular necrosis, giant cells, and epithelioid cells in these disorders. In addition, the heterogeneity of their clinical features and the lack of accurate and sensitive diagnostic tests have made categorization of these disorders uncertain. Virus (varicella-zoster virus, West Nile virus, cytomegalovirus, hepatitis B and C viruses) b. Stroke occurs in approximately 15% of patients at one point during the illness and is mainly caused by intracerebral hemorrhage. Progressive paraparesis, acute transverse myelitis, and subdural hemorrhage secondary to multiple microaneurysms have been recorded. The histopathologic findings of the mass lesion are described as being those of granulomas, granulomatous angiitis, lymphocytic angiitis, and amyloid-related angiitis. Even though excision of the mass lesion may be curative, aggressive immunosuppressive therapy is associated with a favorable outcome. High field strength (7 T) offers the possibility of directly evaluating small vessels. Although the restriction of diffusion seen with acute infarction is a marker of loss of tissue integrity, an the histopathologic patterns of granulomatous and necrotizing vasculitis are associated with rapidly progressive disease and fatal outcome, but a lymphocytic pattern is associated with mild disease with favorable outcome. Granulomatous vasculitis, a common pattern, is characterized by vasculocentric destructive mononuclear inflammation associated with well-formed granulomas, multinucleated giant cells, or both. Lymphocytic vasculitis is characterized by lymphocytes with occasional plasma cells, typically in multiple layers, extending through the vascular wall and causing vascular distortion or destruction. Necrotizing vasculitis involves predominantly small muscular arteries and is associated with disruption of the internal elastic lamina. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system involves medium-sized arteries and small vessels, including arterioles, capillaries, veins, and venules. The inflamed vessels may become narrowed, occluded, and thrombosed and are associated with tissue ischemia and necrosis in the territories of the involved vessels. The presence of aneurysms should raise suspicion for a mycotic inflammatory reaction, and an infectious etiology needs to be identified. General medical laboratory data are unremarkable, including acute-phase reactants such as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein. The presence of oligoclonal bands with an elevated immunoglobulin G index is reported. Mural thickening, hemorrhages, leukoencephalopathy, and gadolinium-enhanced lesions in the cortex, deep white matter, or leptomeninges can also be demonstrated. High-resolution black-blood contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images may help differentiate intravascular atherosclerosis from cerebral vasculitis.
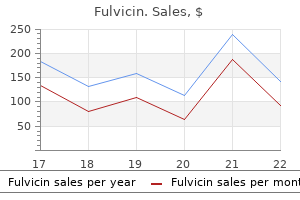
Buy fulvicin online now
Initially fungus gnats egg shells order cheapest fulvicin, the segmental nerve precursors are located at the midportion of each sclerotome, whereas the segmental artery lies at the junction between two adjacent levels. Ater resegmentation, the nerve lies at the level of the disc and the artery lies at the mid-centrum, where one would expect to ind them in the fully developed specimen. With the use of this model, it has been shown that the centrum does arise from the caudal and cranial halves of adjacent sclerotomes. In other words, a single somite was genetically altered so that its cells would produce the lacZ gene product-the protein -galactosidase. When the investigators evaluated the developed embryo, they detected -galactosidase in the caudal and cranial halves of two adjacent vertebrae, suggesting that cells from the labeled somite were incorporated into two neighboring vertebrae. Intervening segments of loosely packed cells are present between the regions of densely packed cells. Ossiication Stage: Week 8 and Beyond Primary ossiication centers develop in utero. At about the ninth week, the preparation for ossiication of the centrum is heralded by anterior and posterior excavations of the cartilaginous centrum produced by the invasion of pericostal vessels. Ossiication of the centra starts irst at the lower thoracic spine working craniad and caudad from that point. Starting in the sixth week, cartilage-producing centers, or chondriication centers, form within each developing vertebra. A hemivertebra is formed because of a failure of chondriication in one half of the vertebral body. Chondriication centers also form within each half of the vertebral arch and eventually fuse with each other in the midline and to the posterior aspect of the centrum. Next, primitive cartilaginous transverse processes and spinous processes develop from the vertebral arch. Ossiication of the centra starts irst at the lower thoracic spine, working craniad and caudad from that point. The centers at the tips of the spinous and transverse processes appear at 16 years and fuse at approximately 25 years. The ring apophysis of the centrum ossiies at around 14 years and fuses at about 25 years. A pair of embryologic joints, known as neurocentral joints, is not present in the fully developed spine. Although not true "joints," they allow expansion of the vertebral arch and spinal canal along with growth of the vertebral body. It is commonly thought that isthmic spondylolysis occurs because of a stress-type fracture within the pars interarticularis of the lower lumbar vertebrae, most commonly L5. Speciic anatomic features of the adult lumbar spine, such as variation of the dimensions of the "lateral buttress" within the lumbar spine, have been described. Sagi and colleagues5 analyzed histomorphologically the lumbar spines of fetal spines aged 8 to 20 weeks to determine the sequence and location of ossiication of the pars interarticularis of the various levels. The contributions of the vertebral arches to the dorsolateral parts of the bodies are apparent. The deinitive vertebral body includes more than just the bone derived from the ossiication center of the centrum, so that the terms body and centrum are not accurately interchangeable. In contrast, the pars of the lower lumbar levels begins within the center of the pars itself, extending from this point to connect to the neighboring structures. Fate of the Notochord In the early embryo, the notochord serves as a rigid template around which the future vertebral column develops. Normally, costovertebral synchondroses develop a true diarthrodial joint only in the thoracic region. A chordoma is abnormal neoplastic growth of notochord cells that remain within the spine in adult life. As a theme of development of the spine, the region of the previous notochord lies anterior to the center of the fully developed vertebral body. Patients with this syndrome, irst described in 2005, may have cervical osseous deformity and instability. Segmentation leads to areas of fusiform enlargements in the region of the intervertebral disc, while the notochord is slowly obliterated in the region of the developing On the twentieth day, ectodermal tissues on either side of the neural plate become thick and "pucker up. As the folds grow toward the midline, the two neural crests meet and fuse on day 22. On the twenty-sixth day, the fused neural crest cells invaginate into the embryo and divide into right and let globules. A sulcus limitans forms between its anterior (basal) and posterior (alar) halves, which are destined to become motor and sensory tracts. During the sixth week, the sulcus limitans disappears, and the basal and alar halves join together, while keeping their Chapter 1 Development of the Spine 9 respective motor and sensory functions. Ventral horns form in the basal portion, which appear as gray matter because they are composed of motor cell bodies. In the seventh to eighth week, white matter inally develops within the spinal cord, representing myelin formation along axon sheaths; this occurs in ascending and descending tracts. Development of the Costal Elements he costal elements persist only in the thoracic spine of the fully developed normal spinal column. During the ith week, costal processes are formed and project from either side of the centrum. By the seventh week, they become sequestrated, or separated, from the centrum, by forming costovertebral and costotransverse joints. In the cervical spine, the primordial costal processes fuse with transverse processes to form the costotransverse bar. Eventually, the unique cervical transverse processes form, which contain the transverse foramen for the vertebral artery. In the sacrum, the costal processes fuse with the embryonic transverse processes and merge to become the anlage of bone of the lateral sacral mass. Development of the Intervertebral Disc he intervertebral disc warrants special attention because it is the pathologic focus of many spinal conditions. In the early stages of embryonic development, there are an increasing number of cells in the peripheral portion of the disc and a decreasing number adjacent to the notochord. As the embryo grows beyond a crown-rump length of 10 mm, the cells in the peripheral zone become elongated and are arranged in a lamellar pattern. When it reaches a length of 20 to 40 mm, collagen ibers begin to be synthesized and are exported from the cells, forming a collagen-rich extracellular matrix. No fully continuous ibers span the entire periphery of the disc; rather, multiple strands interdigitate to create a highly tensile structure. By the start of the fetal period, the disc has three distinct regions: (1) an external ibrous zone, (2) an internal hyaline zone surrounding the notochord, and (3) a ibrocartilaginous zone. Appositional growth refers to growth that occurs longitudinally between the vertebra and the disc. Lamellar ibers form attachments to the cartilaginous endplates in the region of the nucleus pulposus, which completely encases the gel-like structure. As the endplate ossiies, forming the ring apophysis, the inserted annular ibers become tightly ixed. Taylor and Twomney35 found that a plexus of vessels around the circumference of the disc sent branches deep within the anulus. In contrast, Whalen and colleagues36 reported that these vessels entered only the outermost lamellae of the anulus ibrosus. Each tuft consists of a central artery entwined by recurrent veins that end in a chondrous lacuna as a terminal arteriovenous anastomotic sinusoid (cul-de-sac). Inluence of Fetal Movement Development of the human skeleton seems to be strongly inluenced by the interaction of its immature moving parts. In the appendicular skeleton, the opposing surfaces of the femoral head and acetabulum are codependent on each other for normal development into a highly mobile, but stable, weightbearing joint. In the spine, the development of facet joints is thought to be inluenced by torsional loading. It is commonly thought, however, that these demands are placed on the spine only postnatally during upright posture. Boszczyk and colleagues38 used ultrasonography to study the movements of 52 normal fetal spines in utero. Eight rootlets of the hypoglossal nerve can be discerned rostral to the hypoglossal artery, and these usually unite into four, but no less than three, main roots.
Syndromes
- If you smoke, you need to stop. Ask your doctor or nurse for help. Smoking will slow down wound and bone healing. Your recovery may not be as good if you keep smoking.
- Cracked lips
- Fast or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- Death
- Heart failure
- Repeated ear infections
Purchase fulvicin 250 mg without a prescription
The reliability of musculoskeletal ultrasound in the detection of cartilage abnormalities at the metacarpo-phalangeal joints fungus gnats facts safe 250mg fulvicin. Atlas-based knee osteophyte assessment with ultrasonography and radiography: relationship to arthroscopic degeneration of articular cartilage. The development of a preliminary ultrasonographic scoring system for features of hand osteoarthritis. Bone scintigraphy in chronic knee pain: comparison with magnetic resonance imaging. Prediction of the progression of joint space narrowing in osteoarthritis of the knee by bone scintigraphy. Severity mapping of the proximal femur: a new method for assessing hip osteoarthritis with computed tomography. Comparison of 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in evaluating early-stage osteoarthritis of the hip. Quality of life and radiographic severity of knee osteoarthritis predict total knee arthroplasty: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Eighty percent of patients with surgical hip dislocation for femoroacetabular impingement have a good clinical result without osteoarthritis progression at 10 years. Hawker clinical practice or in clinical research, should ideally incorporate the evaluation of all these factors. In clinical practice and research, the need to perform quantitative assessments is driven by requirements to describe current clinical status, including consequences of living with osteoarthritis. An understanding of the current clinical status facilitates a personalized approach to therapeutic decision making. Quantification of response to therapy facilitates decision making as to whether the therapeutic objective has been achieved and whether further intervention is required. Quantification of the symptom state attained with therapy facilitates decision making as to whether the therapeutic objective has been achieved, whether the patient has reached an acceptable level of symptom severity, and whether further intervention is required. Thus, higher standards of reliability are required to ensure that measurement error is minimized relative to clinical research, in which the focus is most often on comparisons of groups of patients. Furthermore, one or more aspects of the condition may be the focus of assessment. Therefore, a battery of measures, used in combination, often provides the most robust evaluation. The latter has the additional advantage of simplifying data management (no data entry is required), improving data quality. Activity limitation is referred to as function or physical disability in arthritis measures. Variability in the timing or order of questionnaire administration and in physical assessments may affect the results obtained. Examination of physical signs of osteoarthritis the skill, knowledge, and ability to conduct a thorough interview and physical examination are generic requirements in rheumatology (see Chapter 32). Through a combination of verbal, tactile, and visual cues, an impression is gained regarding the nature, severity, and consequence of the condition. As in the clinic, in clinical research, the following features should be assessed: bony enlargement, tenderness on palpation, passive crepitus, pain with motion, presence of erythema, and effusion or soft tissue swelling. Increasingly, point-of-care ultrasonography is also being used to assess for the presence and severity of synovitis. Importantly, training of joint assessors before study initiation improves standardization of the assessment. Separate homunculi may be used to indicate tender or painful joints versus those that are swollen. Thus, careful attention is warranted to selection of the measure most appropriate to the research. Many of these measures incorporate a cutpoint score that may be used to discriminate individuals with "poor sleep" or possible underlying sleep disorders from those without. Thus, these measures generally require supplementation with specific measures of activity limitations and participation restrictions. Although many of these measures have been developed with the idea that the content reflects functioning of a specific joint and hence are considered to be joint-specific measures, the items often reflect activities that involve the entire extremity or functional unit. Results of such assessments generally correlate only moderately with assessment of similar constructs using self-report measures. In the case of paired observations, this effect size is called a standardized response mean. The essence of the issue in interpreting change relates to whether measured change reflects meaningful change to patients. Anchor-based methods rely on determining the amount of change in relation to one or more external indicators of change, usually a patient global rating of how much better or worse he or she is from "slightly" to "a great deal" better or worse. This approach considers that small or large change may occur but that it is not important change if it has not reached a critical threshold value or "state. Use of these criteria requires that the patient has a certain minimum score before intervention; otherwise, it is impossible for the patient to improve sufficiently to be designated as a "responder," even if improvement does occur. Changes in patient status over time can be monitored over an extended period using a combination of responder and state attainment criteria. The relationship between responder criteria and state attainment criteria can be best exemplified by the statement, "It is good to be better but better to be good. Standardized, valid, and reliable measures exist to evaluate these constructs, and depending on the intent of the research, these factors may also warrant evaluation to aid in interpretation of research findings. Differentiating real change from change occurring within measurement error can also be difficult. It is critical to remember that responsiveness and the interpretation of change, such as reliability and validity, are a function of the measure score and context interaction. For this reason, the responsiveness metrics and interpretation for a measure are represented by a range of values based on the varying contexts. Central nervous system mechanisms of pain in fibromyalgia and other musculoskeletal disorders: behavioral and psychologic treatment approaches. Determinants of pain severity in knee osteoarthritis: effect of demographic and psychosocial variables using 3 pain measures. Measurement properties of the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index: a systematic review. Pain mechanisms in osteoarthritis: understanding the role of central pain and current approaches to its treatment. Existence of a neuropathic pain component in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Daily fatigue in women with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and fibromyalgia. Validation of the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy Fatigue Scale relative to other instrumentation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Extended-release tramadol in the treatment of osteoarthritis: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. A longitudinal study to explain the pain-depression link in older adults with osteoarthritis. A new look at the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index using Rasch analysis. Construct validity and reliability of the disability of arm, shoulder and hand questionnaire for upper extremity complaints in rheumatoid arthritis. Reliability, validity, and sensitivity to change of the Cochin hand functional disability scale in hand osteoarthritis. Measurement, properties of performance-based measures to assess physical function in hip and knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Health promoting effects of friends and family on health outcomes in older adults. The relationship of gender to pain, pain behavior, and disability in osteoarthritis patients: the role of catastrophizing. Self-efficacy for arthritis pain: relationship to perception of thermal laboratory pain stimuli.
Fulvicin 250 mg amex
Rostrally antifungal eo fulvicin 250 mg without a prescription, the 12th rib may obstruct access from T12 to L2, which may require rib excision or manipulation. Patients are taped carefully; at times, the table may be bent to level the iliac crest away from the disc space. With the lateral skin incision marking, center it over where you palpate your inger in the retroperitoneal space. Allow your inger to sweep the retroperitoneal fat anteriorly for a safer corridor. Blunt dissection through the oblique muscles and transverse abdominal fascia is made with two Kocher clamps at the same time. It is recommended at this point to take the nerve probe to ind the lumbar plexus and determine if the anterior and posterior blades are a safe distance from it. Perform the same task with the Cobb retractor angled toward the superior endplate. Anatomic Considerations Lumbar Plexus A thorough understanding of the regional anatomy is essential to avoid complications with the lateral approach. Multiple studies have attempted to map out the relationship of the lumbar plexus within the psoas and identify safe corridors or "safe zones" for accessing each disc space to avoid injury to the plexus and the genitofemoral nerve. Meticulous preoperative planning, judicious dissection without excessive pressure or manipulation of the psoas, direct visualization of the surgical ield, and the use of electrophysiologic monitoring are essential for success. Additionally, the amount and duration of retraction used and operative time per level should be taken into consideration in order to decrease the likelihood of traction injury to nerves. Our preference is to minimize "breaking" of the table to a degree that is necessary to access the operative level(s). If breaking the table is required for lateral disc space access, we have found that "unbreaking" the table ater only the inner dilator and wire are in can substantially decrease psoas tension while maintaining safe access with little anatomic distortion. Real-time, directionally stimulated neuromonitoring is employed intraoperatively to determine the proximity of the exiting and traversing neural elements. The surgical vascular anatomy of the minimally invasive lateral lumbar interbody approach: a cadaveric and radiographic analysis. Identify abnormal displacement of vascular structures with severe rotational deformity and approaching from the convex side because the approach angle is more rostral. However, this must be weighed against the increased tension and traction placed on the psoas and lumbar plexus. Sometimes a transdiaphragm approach is required for the thoracolumbar junction since the diaphragm cannot be mobilized suiciently to gain access to the disc. With signiicant diaphragm dissection, the diaphragm should be repaired prior to closure. Thoracic Spine Partial rib resection can be commonly performed in anterolateral thoracic approaches with little morbidity. If that technique is performed, expansion of the lateral access retractor should be minimized to prevent prolonged compression of the neural elements on the rib underside for risk of postoperative radicular/rib pain. However, it should be noted that these rates are signiicantly lower than other smaller series reported in the literature. If no clinical recovery is observed, some surgeons perform a limited electromyographic test monthly over the subsequent 3 months to evaluate for reinnervation. Reported complications include bowel perforation,37,72 incisional hernias,12,59 pleural efusions,37 kidney lacerations,47 retrocapsular hematoma,73 abdominal wall paresis,59,74 and pseudohernia. When operating in the thoracolumbar spine, the pleural space can be violated, leading to pleural efusion and requiring careful intraoperative evaluation to evaluate whether a chest tube is needed. Wang and Mummaneni reported a mean coronal correction of 20 degrees (63%) in 23 patients with a solid fusion at all interbody levels. Addressing anterior column pathology in the thoracic spine is technically challenging and a thoracotomy can lead to poor pulmonary function postoperatively, with major complications reported in up to 12% of patients. Although deformity correction was less pronounced than with the traditional open thoracolumbar approach, no major complications occurred. Short-term mortality and its association with independent risk factors in adult spinal deformity surgery. Anterior excision and vertebral body fusion operation for intervertebral disk syndromes of the lower lumbar spine: three-to ive-year results in 244 cases. A review of diagnostic level testing, with operative results in more than seven hundred cases. Minimally invasive lateral lumbar interbody fusion and transpsoas approach-related morbidity. Anterior column reconstruction through the lateral approach provides equivalent sagittal plane correction as pedicle subtraction osteotomy with signiicantly less blood loss. Lateral interbody fusions limit infection rates compared to open posterior fusions with the obese population. Last, minimally invasive lateral interbody fusion is cost-efective and provides health care savings compared to other lumbar fusion options. A radiographic assessment of the ability of the extreme lateral interbody fusion Chapter 21 Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion 14. Two-year clinical and radiographic success of minimally invasive lateral transpsoas approach for the treatment of degenerative lumbar conditions. Extreme lateral interbody fusion approach for isolated thoracic and thoracolumbar spine diseases: initial clinical experience and early outcomes. Fusion rates of instrumented lumbar spinal arthrodesis according to surgical approach: a systematic review of randomized trials. Clinical outcomes following sublaminar decompression and instrumented fusion for lumbar degenerative spinal pathology. Extreme lateral interbody fusion for unilateral symptomatic vertical foraminal stenosis. Morphologic changes in contralateral lumbar foramen in unilateral cantilever transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using kidney-type intervertebral spacers. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion-systematic review and meta-analysis. Transforaminal versus anterior lumbar interbody fusion in long deformity constructs: a matched cohort analysis. Minimally invasive multilevel percutaneous correction and fusion for adult lumbar degenerative scoliosis: a technique and feasibility study. Two-year radiographic and clinical outcomes of a minimally invasive, lateral, transpsoas approach for anterior lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis. Sagittal alignment ater lumbar interbody fusion: comparing anterior, lateral, and transforaminal approaches. A change in lumbar sagittal alignment ater single-level anterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis with normal sagittal balance. Minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion followed by percutaneous pedicle screw ixation for isthmic spondylolisthesis. Minimally invasive surgery versus open surgery spinal fusion for spondylolisthesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. First report of major vascular injury due to lateral transpsoas approach leading to fatality. Minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas interbody fusion for L4-5 spondylolisthesis: clinical outcomes. Minimally invasive lateral lumbar interbody fusion: clinical and radiographic outcome at a minimum 2-year follow-up. Direct lateral lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative conditions: early complication proile. An analysis of postoperative thigh symptoms ater minimally invasive transpsoas lumbar interbody fusion. Clinical outcome and fusion rates ater the irst 30 extreme lateral interbody fusions. Mid-term to long-term clinical and functional outcomes of minimally invasive correction and fusion for adults with scoliosis. Minimally invasive surgery in adult degenerative scoliosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of decompression, anterior/lateral and posterior lumbar approaches. Perioperative complications of posterior lumbar decompression and arthrodesis in older adults. Predicting morbidity and mortality of lumbar spine arthrodesis in patients in their ninth decade. Minimally invasive surgery compared to open spinal fusion for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spine pathologies.
Purchase fulvicin 250mg without a prescription
For women not at high risk after 3 to 5 years of therapy and drug holiday of 2 to 3 years fungus gnats in potting soil generic fulvicin 250mg on-line, bisphosphonate therapy can be considered. If a fracture occurs off therapy or bone density declines, treatment should be restarted. For denosumab, the off time is much more rapid than bisphosphonates; markers of bone resorption will increase to levels higher than pretreatment values 9 to 12 months after the last dose. The implications of discontinuation of denosumab are very different from those for discontinuation of a bisphosphonate. Histomorphometric analysis based on iliac crest biopsies shows increased trabecular bone volume, connectivity, and cortical thickness. Bone formed during therapy has a lower mineral content as seen with new bone, with mineralization occurring over a several-month period. Strontium competes with calcium for intestinal absorption and, once absorbed, for incorporation into bone and dental tissues. At low doses, strontium ranelate results in uncoupling of bone turnover by stimulating osteoblastic activity and decreasing osteoclastic activity. This would appear to make it different from other antiresorptive agents by increasing formation and reducing resorption of bone. Human and animal studies of strontium ranelate demonstrate that it is an effective therapy for osteoporosis treatment. A post hoc analysis demonstrated a significant 36% reduction in the risk for hip fracture in those considered to be at high risk: age older than 74 years and femoral neck T-score of -3. Standard measures of pain relief are used, including analgesics, muscle relaxants, calcitonin, short periods of bed rest, and physical therapy. Spinal orthotics are three-point hyperextension contact braces (sternum, pubic symphysis, lumbar spine;. Postural training support devices are designed to decrease kyphosis, move the center of gravity backward, and encourage use of the extensor muscles of the back. Studies show that the procedures may restore vertebral height, especially if performed within 6 to 12 weeks of the fracture, and that treated vertebral bodies have increased stiffness and load-bearing capacity, all mechanical advantages that could relieve pain and reduce the risk for additional fracture. The mechanism of pain relief is not known, but reduction in the micromotion of fractured vertebral bodies after the procedure has been hypothesized. Some, but not all, studies have shown an increased rate of adjacent fractures, and one suggested an increased incidence of subsequent fractures in patients with steroid-induced osteoporosis but not in those with primary osteoporosis. Although kyphoplasty appears to be most effective if performed soon after fracture, a nonrandomized trial in patients with painful vertebral fractures longer than 12 months in duration showed increased vertebral height, reduced pain, and improved mobility when compared with medical management alone. This has resulted in a recommendation by the European Medicines Agency to restrict use to patients with severe osteoporosis in whom other treatments are not possible. Patients with a history of ischemic heart disease, peripheral artery disease, and uncontrolled hypertension appear to be at high risk for cardiovascular side effects with strontium. Guidelines for the duration of treatment have recently been published and depend on the initial bone mass, prevalent and incident fractures, other factors that contribute to fracture risk, and the drug used for treatment. This is not the case with denosumab, raloxifene, and estrogen because their skeletal half-life is short, and bone loss would be likely to occur immediately after discontinuation. Lumbar spine, and proximal femur bone mineral density, bone mineral content, and bone area: United States, 2005-2008. Reduced bone mineral density in male rheumatoid arthritis patients: frequencies and associations with demographic and disease variables in ninety-four patients in the Oslo 7. Prevention of postmenopausal bone loss by a low-magnitude, high-frequency mechanical stimuli: a clinical trial assessing compliance, efficacy, and safety. Low-Magnitude Mechanical Stimulation to Improve Bone Density in Persons of Advanced Age: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. A comparative study of exercise, calcium supplementation, and hormone-replacement therapy. Vitamin D with or without calcium supplementation for prevention of cancer and fractures: an updated meta-analysis for the U. Prevention of nonvertebral fractures with oral vitamin D and dose dependency: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Effect of calcium supplements on risk of myocardial infarction and cardiovascular events: meta-analysis. Calcium Intake and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Effects of smoking cessation or reduction on hormone profiles and bone turnover in postmenopausal women. Association between alcohol consumption and both osteoporotic fracture and bone density. The effects of Tai Chi Chuan on physiological function and fear of falling in the less robust elderly: An intervention study for preventing falls. A multifactorial intervention to reduce the risk of falling among elderly people living in the community. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of hormone replacement therapy in treating and preventing osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Hormone replacement therapy and prevention of nonvertebral fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Menopausal estrogen and estrogen-progestin replacement therapy and breast cancer risk. Menopausal hormone treatment cardiovascular disease: another look at an unresolved conundrum. Reduction of vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated with raloxifene: results from a 3-year randomized clinical trial. Update on raloxifene: mechanism of action, clinical efficacy, adverse effects, and contraindications. Raloxifene: a selective estrogen-receptor modulator for postmenopausal osteoporosis - a clinical update on efficacy and safety. Efficacy of bazedoxifene in reducing new vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from a 3-year, randomized, placebo-, and active-controlled clinical trial. Endometrial effects of a tissue selective estrogen complex containing bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens as a menopausal therapy. Analgesic effect of intranasal salmon calcitonin in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Bisphosphonates: an update on mechanisms of action and how these relate to clinical efficacy. Molecular targets of the nitrogen containing bisphosphonates: the molecular pharmacology of prenyl synthase inhibition. Safety and efficacy of risedronate in patients with age-related reduced renal function as estimated by the Cockcroft and Gault method: a pooled analysis of nine clinical trials. Alendronate increases degree and uniformity of mineralization in cancellous bone and decreases the porosity in cortical bone of osteoporotic women. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture risk reduction with alendronate in women with osteoporosis: the Fracture Intervention Trial. Effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with low bone density but without vertebral fractures: results from the Fracture Intervention Trial. Effects of risedronate treatment on vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. Randomized trial of the effects of risedronate on vertebral fractures in women with established postmenopausal osteoporosis. Long-term efficacy of risedronate: a 5-year placebo-controlled clinical experience. Effects of oral ibandronate administered daily or intermittently on fracture risk in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Intravenous ibandronate injections in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: one-year results from the dosing intravenous administration study.
Trusted fulvicin 250mg
Limited joint mobility in childhood diabetes mellitus indicates increased risk for microvascular disease antifungal nasal irrigation order fulvicin mastercard. Prevalence of symptoms and signs of shoulder problems in people with diabetes mellitus. Correlation of Achilles tendon thickness evaluated by ultrasonography with carotid intima-media thickness in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Safety and tolerability of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin during 5 years in the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study. Atorvastatin decreases the coenzyme Q(10) level in the blood of patients at risk for cardiovascular disease and stroke. Randomized trial of letrozole following tamoxifen as extended adjuvant therapy in receptor-positive breast cancer: updated 19. Practical guidance for, the management of aromatase inhibitor-associated bone loss. Aromatase inhibitor-associated arthralgia and/ or bone pain: frequency and characterization in non-clinical trial patients. Prospective study to assess short-term intra-articular and tenosynovial changes in the aromatase inhibitor-associated arthralgia syndrome. A 10-year, prospective study of primary hyperparathyroidism with or without parathyroid surgery. Parathyroid hormone exerts disparate effects on osteoblastic differentiation depending on exposure time in rat osteoblastic cells. On the mechanism of cancellous bone preservation in postmenopausal women with mild primary hyperparathyroidism. Bone mineral recovery after parathyroidectomy in patients with primary and renal hyperparathyroidism. Primary hyperparathyroidism and hyperuricaemia are associated but not correlated with indicators of bone turnover. The natural history of primary hyperparathyroidism with or without parathyroid surgery after 15 years. Long-term results of total parathyroidectomy without autotransplantation in patients with and without renal failure. Brachydactyly in 14 genetically characterized pseudohypoparathyroidism type la patients. Recurrent hemarthroses can lead to progressive arthropathy, particularly affecting the ankles, knees, and elbows. Prophylactic treatment from a young age is beneficial in preventing hemorrhage and preserving joint function. Chemical or radioactive synoviorthesis is effective treatment of recurrent bleeding and synovitis. Joint replacement or fusion is beneficial for the treatment of chronic, severe arthritis. Viral transmission of bloodborne viruses is virtually eliminated with the use of recombinant factor. Inhibitor development occurs in about 30% of patients with hemophilia A and 5% of patients with hemophilia B and is associated with worse joint outcomes and quality of life. In addition, if an affected male and a carrier female have offspring, 50% of the resultant female children will be homozygous for hemophilia. In secondary hemophilia, factor deficiencies are caused by decreased synthesis, increased clearance, or destruction of clotting factors. Autoantibodies can develop postpartum or can be associated with a range of diseases, most commonly autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and other connective tissue disorders. They can also occur with skin diseases, lymphoproliferative disorders, other tumors, and drugs. It is caused by a deficiency in von Willebrand factor characterized by mucocutaneous bleeding. Severe forms are associated with hemarthroses and arthropathy similar to patients with hemophilia. Albucasis, who documented the deaths of men and boys in a certain Spanish village from uncontrollable hemorrhage after trivial wounds and bleeding, recorded the first published medical recognition of the disorder some 500 years later. Joint disease secondary to chronic intraarticular bleeding was increasingly noted from the early 19th century onward. Elucidation of the underlying coagulation defect and the advent of effective clotting factor replacement during the 20th century revolutionized the management of hemophilia in general and allowed the potential prevention of joint disease and surgical correction of established deformity. Formation of the platelet plug (primary hemostasis) is normal, but stabilization of the plug by fibrin is abnormal because of inadequate thrombin generation. Genetic analysis in all patients is recommended to establish the causative mutation and is shedding much light on the condition. Similarly, molecular characterization of the F9 gene has revealed 1095 unique variants so far. Chorionic villous sampling performed between 11 and 14 weeks or amniocentesis performed after 15 weeks are the current methods of prenatal diagnosis. An alternative to conventional prenatal diagnosis is preimplantation genetic diagnosis, which provides couples with a known transmissible genetic disease the possibility to start a pregnancy with the knowledge that their child will be unaffected. Many of these individuals do not come to clinical attention because they fall into the mild end of the disease spectrum. Hemophilic arthropathy is the most important cause of morbidity in patients with severe hemophilia. Bleeding into muscle occurs at about one tenth of the frequency of joint hemorrhages. Some female carriers of the hemophilia genes have relatively low factor levels and may have problems during menstruation and with hemostasis during surgery and dental extractions, but bleeding into joints rarely occurs. Patients often describe a tingling sensation and tightness in the joint preceding the clinical signs of hemarthrosis. The joint then rapidly loses range of motion and becomes acutely painful, warm, and swollen. Rising intraarticular pressure eventually terminates the bleeding, and resolution occurs slowly, accompanied by bruising. Milder bleeding episodes may manifest less dramatically and be limited to the subsynovium or go unrecognized, as is apparently the case when established arthritis develops in a joint without any history of bleeding. The age at first episode and the frequency of acute hemarthroses depend mainly on the severity of the factor deficiency. Levels of 5% of normal or less are almost invariably associated with recurrent hemarthroses, and established arthritis may occur less frequently with levels up to 20%. The joints traditionally affected in decreasing order of frequency are those of the knees, elbows, and ankles. However, prophylactic treatment induces a changing pattern of joint involvement, with the ankle surpassing the knee as the most common site of bleeding. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head as a result of hemorrhage into the hip joint may also occur, with the clinical and radiologic features resembling those of Perthes disease. Differential diagnosis of acute hemarthroses Occasionally, musculoskeletal hemorrhage is the first indication of the underlying condition, which if not recognized, can result in major morbidity or mortality. In this event, the differential diagnosis includes other causes of hemarthrosis, such as joint trauma with intraarticular fractures, bleeding disorders such as platelet deficiencies or anticoagulant therapy, other blood dyscrasias, villonodular synovitis, acute inflammatory arthritides such as pyrophosphate arthropathy in older patients, and rarely, joint neoplasms. Subacute arthropathy Subacute arthropathy usually follows repeated hemarthroses and often targets one or several joints, in which bleeding is more frequent ("target joint"). A target joint is defined as a joint in which three or more spontaneous bleeding episodes have occurred within a consecutive 6-month period. Some distally situated lesions in children are treated conservatively with immobilization and adequate factor replacement. A 6-week course of treatment with factor is recommended in an attempt to shrink the pseudotumor.
Coptis Chinensis (Goldthread). Fulvicin.
- How does Goldthread work?
- Digestive problems and other uses.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Goldthread?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96480
Cheap fulvicin 250 mg with amex
For components such as ligaments antifungal and antibacterial cream order 250mg fulvicin amex, the experimental test data are required to deine the true mechanical behavior as well as failure modes and hysteresis characteristics of the corresponding element in the model. Ligaments can be modeled either as a bundle with appropriate crosssection or as a combination of individual truss elements with cross-section of unity. Intervertebral Disc he intervertebral disc was modeled as the anulus ibrosus and nucleus pulposus. Experimental and Theoretical Investigations Into the Efects of Artiicial Disc Implantation. Chapter 11 Finite Element Analysis 171 only tension; also, the iber thickness and stifness increased in the radial direction. An overall collagenous iber content of 16% of the annular volume was distributed in the anulus. Apophyseal (Facet) Joint Simulation of the facet joints is crucial for the spine model since it drastically afects the outcome of the analysis. Force is transmitted by using the Abaqus "sotened contact," which exponentially adjusts the force transfer as the gap is closed. Ligaments All seven major ligaments-interspinous, supraspinous, intertransverse, capsular, posterior longitudinal, anterior longitudinal, and ligamentum lavum-were simulated in the model. Hypoelastic material properties were assigned to each of these ligaments, allowing a "neutral zone" to be incorporated in which the ligament provided little stability under minimally applied external loads. Although the ligamentum lavum and the longitudinal ligaments experience a prestress at rest, all ligaments were assumed to be unstressed initially. Surface processing of the reconstructed geometry is conducted in Geomagic Studio 2014. Ater importing the geometry, there are various functions that allow the surface to be precisely smoothed and edited. Multiple mesh densities are created of each body to then perform mesh convergence. Abaqus has the capability of assigning a variety of material types and constitutive models to accurately simulate the linear elastic, plastic, and hyperelastic properties of bones, implants, and sot tissue. Interactions are then generated to tie surfaces together, such as the vertebral endplate to the intervertebral disc. Interactions are also used to generate contact deinitions, such as the articulation between a cage and endplate, to accurately simulate the contact force, contact area, stress, displacement, and so on. Loading and boundary conditions are then applied to simulate various clinically relevant conditions. Complex subroutines are available to simulate growth and deformities of the spine. Last, both static and dynamic loading scenarios are available to fully capture all studies of interest. Axial compressive preload afects the load displacement characteristics of the joint. In addition to the axial preload, motion was predicted for all six degrees of freedom with a moment of 10 Nm. Although these values are somewhat low, the values were in the range reported by Dooris et al. Using a large number of elements is known to reduce error, and the mesh should be reined until a stage is reached at which the results from the current reinement iteration are similar to the results obtained by the previous reinement iterations. Such a mesh would be an optimized mesh, which enables the model to predict correct results. Specimens were potted in a rigid base secured to the sacrum and a loading frame likewise was secured to the L1 vertebral body. Finite element model predictions fall within one standard deviation of in vitro results. Smoothing, wrapping, and iltering functions were executed to obtain good-quality geometry. Finally, the mesh quality module in the sotware was used to evaluate, and thus develop, the high-quality mesh for the model. Ligament insertion points and material properties of all of the sot and hard tissues were extracted from literature. Left rotation L3-S1 L3-L4 L4-L5 L5-S1 Facet Joints A contact formulation was used to deine the contact pattern between articulating surfaces in facet joints with an initial gap of 0. The left image depicts the three-dimensional C3 vertebra, the center image shows the constructed building blocks, and the right image depicts the meshed vertebra, respectively. Brick elements were used to model ground substance and the nucleus pulposis was deined as incompressible luid. Numerous studies have simulated diferent spinal injuries and compared various biomechanical parameters, such as angular motion and stress distribution across degenerated and adjacent segments, between intact and injured spine models. Implants are useful in treatment of spinal injuries when conservative therapies fail to reduce the pain and restore the patient to a normal daily routine. Invasive surgeries aim to remove the pain-causing structures, stabilize the segment, and correct bone failure due to trauma or disease. For example, spinal stenosis is a progressive degenerative condition that occurs when the articulating facet joints become arthritic and no longer provide necessary stability to the spine. Decompression is a surgical procedure, which is performed to alleviate pain caused by pinched nerves (neural impingement). Although clinical studies have shown that decompression surgery enhances neurologic recovery, pain relief, and mobility, signiicant destabilization of the spinal motion segment is seen ater decompression, especially if the facet joint is removed. Addition of a posterior fusion system, including pedicle screws interconnected with a rigid rod, is a common procedure to restore the stability of the afected segment. While useful, the model is not without limitations due to the constraints of a biologic system and its associated properties being modeled by a digital representation. It can be inferred that the data used to generate the models can be thought of as an "average" of the normal population, just as reference ranges are for determining the upper and lower threshold of certain markers in routine bloodwork. Just as individual patients may have variations in their spine anatomy, the rate of degeneration and the impact of degenerative processes may vary from patient to patient, making generalizations about the "best" treatment for a particular type of spinal pathology far from simple. Oten in clinical practice, patients with a similar degree of degenerative pathology may have widely diferent clinical manifestations or, in some cases, may be completely asymptomatic. Additionally, the patients that are seen in practice oten are far down the degenerative cascade, at which point surgery may only temporarily alleviate their symptoms before their recurrence due to scarring, nociceptor hypersensitivity, and/or further degeneration. By isolating these segments and subjecting them to biomechanical analysis, they do not address global spinal parameters, such as sagittal and coronal balance, which have become increasingly important in treating spinal pathology. Many studies have been conducted with the goal of accounting for intersubject variability as a result of aging and anatomic deformities. In current clinical practice, a signiicant proportion of spine procedures are centered around removing ofending pathology (laminectomy, facetectomy, corpectomy, and so on) and fusing the levels of interest using implants such as rods and pedicle screws. Over time, the inlammatory cascade that promotes healing fuses the operated levels while placing stress on the adjacent motion segment. More recently, nonfusion-based spinal implants are being used as an alternative to stabilizing the spine ater decompression. Unlike fusion, nonfusion stabilizing systems allow for angular motion, shear stability, and adjusting to the instant axis of rotation of the motion segment during movement. To simulate the physiologic loading condition on the spine, once the implanted model was created, both implanted and intact models were loaded with 400 N of compressive follower preload plus 10 Nm of moment to simulate lexion, extension, let/right bending, and let/right rotation. Some require an anterior surgical approach for replacement as opposed to others that are placed from the posterior side of the spine. Chapter 11 Finite Element Analysis 179 and thus are well suited to characterize the complex biomechanical behavior of the spine and its anatomic structures, including internal stresses/strains of the intervertebral disc, facet joints, and any ligaments of interest. For example, they do not account for variations in the geometry of the specimens, such as facet orientation and material properties that vary from specimen to specimen. But, for a given model geometry, the predicted data are in reasonable agreement with the results from the in vitro investigations. The authors were able to demonstrate marked diferences in intervetebral motion in a inite element model of the degenerative lumbar spine that closely mimics the reported in vitro behavior as a function of degeneration. The mildly degenerated segment showed an increase in motion in all loading cases with further degeneration resulting in decreases in motion.
Best order for fulvicin
A set of classification criteria has been newly developed for children and may help pediatricians in making the diagnosis fungus weevil buy discount fulvicin 250 mg. Evidence-based data are desperately needed for the treatment of kidney involvement, although this is one of the most common childhood vasculitides. A seasonal distribution of the disease, a frequent history of a preceding upper respiratory tract infection, and a higher incidence in childhood point to an infectious etiology. Although group A streptococci have been studied the most, other viral and bacterial pathogens have been postulated, such as parvovirus B19, Bartonella henselae, Helicobacter pylori, varicella, rubella, rubeola, hepatitis A and B, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. According to these criteria, palpable purpura is a mandatory feature, age as a criterion has been removed, arthritis or arthralgia was added, and the finding of granulocytes in biopsy specimens was replaced by IgA deposition. The cutaneous lesions progress in color from red to purple to brown before fading. In children, the eruption is characterized by its polymorphism, but in adults, it is frequently monomorphic. The joint disease is nonmigratory and transient and resolves without residual abnormalities. Intussusception develops in 1% to 5% of children and is mostly ileoileal in location. Clinical findings range from the more common transient, isolated microscopic hematuria and mild proteinuria to the less common nephrotic syndrome, nephritic syndrome, rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, and renal failure. Clinical symptoms of pulmonary hemorrhage include hemoptysis, dyspnea, chest pain, and anemia. Serologic tests such as antinuclear antibodies and rheumatoid factor are negative, and C3 and C4 are normal and need not be studied for diagnosis. Skin biopsy is helpful if the rash is atypical; it reveals leukocytoclastic vasculitis involving the capillaries and venules of the mid and upper dermis and, with direct immunofluorescent studies, shows perivascular deposition of IgA, C3, and fibrinogen in the affected vessel wall. In patients with renal disease and urinary abnormalities, the degree of proteinuria should be defined, and renal function tests should be performed. Prednisone is generally taken at dose of 1 mg/kg/day for 2 weeks, with weaning over the subsequent 2 weeks. However, in patients who need to be admitted to the hospital, steroids must be administered intravenously. Furthermore, it is difficult to interpret the efficacy of treatment because spontaneous recovery can occur in patients with severe initial findings. More important, long follow-up is required because late progression to chronic kidney disease can be seen in patients with mild symptoms. We have a good level of evidence that the use of steroids early in the course of the disease does not prevent the development of nephritis. Moderate nephritis this group would include patients with less than 50% crescents on renal biopsy, no renal failure, and the presence of heavy proteinuria. Corticosteroids have been advocated for these patients either alone or in combination with immunosuppressive agents. Although we lack well-designed controlled studies for such patients, intensive therapy should be considered, including steroids and cyclophosphamide with or without plasma exchange. The disease status of the recipient and other factors may affect IgA production and its deposition in the newly grafted kidney. The actuarial risk for recurrence in a first graft was 11%, and the risk for graft loss as a result of recurrence was 7. The duration of the disease is less than 14 days in approximately one third of patients, 2 to 4 weeks in one third, and longer than 4 weeks in the remaining third. Recurrence develops in around one third of cases, generally within 4 months of resolution of the symptoms. On the other hand, Narchi57 reviewed 12 studies that included 1133 children, which provided important data on the subject. Thus, patients with nephrotic proteinuria need to be treated and monitored closely. Patients with microscopic hematuria should be assessed annually because of the possibility of late renal deterioration. Narchi57 recommended that because no long-term renal impairment occurred if the findings on urinalysis were normal, there is no need for follow-up after the first 6 months in those whose urinalysis results remain normal. It has been recommended that patients with normal findings on urinalysis undergo follow-up for at least 1 year. Patients who have had clinical nephritis should be monitored closely for at least 5 years, and those with significant proteinuria or deteriorating renal function should undergo biopsy. Incidence, of vasculitis in children in the Czech Republic: 2 year prospective epidemiology survey. Circulating immune complexes in IgA nephropathy consist of IgA1 with galactose deficient hinge region and antiglycan antibodies. Recent understanding on diagnosis and management of central nervous system vasculitis in children. Anaphylactoid purpura nephritis in childhood: natural history and immunopathology.
Best 250 mg fulvicin
Diagnosis of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease: ultrasonographic criteria proposed kill fungus gnats uk purchase fulvicin canada. Distinguishing Gouty Arthritis from Calcium Pyrophosphate Disease and Other Arthritides. Detection and characterization of crystal suspensions using single-source dual-energy computed tomography: a phantom model of crystal arthropathies. Assessment of diffraction-enhanced synchrotron imaging for cartilage degeneration of the human knee joint. Enzymic and electron-microscopic analysis of extracellular matrix vesicles associated with calcification in cartilage. Histologic localization of lipid in the articular tissues in calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease. Chondrocytes that accumulate proteoglycans and inorganic pyrophosphate in the pathogenesis of chondrocalcinosis. An ultrastructural study of articular chondrocalcinosis in cases of knee osteoarthritis. Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease: a review of the literature and a light and electron microscopic study of a case of the temporomandibular joint with numerous intracellular crystals in the chondrocytes. Release of pyrophosphate by normal mammalian articular hyaline and fibrocartilage in organ culture. Revisiting spatial distribution and biochemical composition of calcium-containing crystals in human osteoarthritic articular cartilage. Articular cartilage vesicles generate calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate-like crystals in vitro. Characterization of an additional articular cartilage vesicle fraction that generates calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in vitro. Autophagy Modulates Articular Cartilage Vesicle Formation in Primary Articular Chondrocytes. Promotion of articular cartilage matrix vesicle mineralization by type I collagen. Transglutaminase activity in aging articular chondrocytes and articular cartilage vesicles. Phosphocitrate blocks calcification-induced articular joint degeneration in a guinea pig model. Characterization and membranolytic effects of triclinic calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals. Calcium crystal effects on the cells of the joint: implications for pathogenesis of disease. Release of collagenase, neutral protease, and prostaglandins from cultured mammalian synovial cells by hydroxyapatite and calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals. Phosphocitrate inhibits a basic calcium phosphate and calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade signal transduction pathway. Comparison of the acute inflammation induced by calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate, apatite and mixed crystals in the rat air pouch model of a synovial space. Efficacy of anakinra for various types of crystal-induced arthritis in complex hospitalized patients: a case series and review of the literature. Methotrexate in chronic-recurrent calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease: no significant effect in a randomized crossover trial. Double blind, placebo controlled trial of magnesium carbonate in chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy. Probenecid inhibits transforming growth factor-beta 1 induced pyrophosphate elaboration by chondrocytes. Inhibition of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal formation in articular cartilage vesicles and cartilage by phosphocitrate. In calcific periarthritis, the shoulder is the main site affected, but deposits have been described near many other joints. Deposits can rupture and cause local acute, crystal-induced inflammation; they may also be associated with local chronic pain and functional impairment. No comparable epidemiologic data have been reported subsequently, although a number of smaller pathologic or radiographic studies have documented the relatively high frequency of periarticular calcification. Calcific periarthritis has been reported in children as young as 3 years but appears to be uncommon in older adults. This suggests that many of the deposits seen in young adults must disappear spontaneously. Thirty years later, renewed interest in periarthritis of the shoulder led to further descriptions of the phenomenon, as well as recognition of periarticular calcifications at other sites. All early descriptions stress the involvement of older females and localization to the shoulder joint. The most striking clinical finding is acute calcific periarthritis, which most commonly involves the shoulder but can occur in almost any joint. The episode may be preceded by mild trauma or overuse, but most cases have a spontaneous onset. Patients report sudden onset of severe pain, and within hours the affected part is usually swollen with redness and warmth of the overlying skin. The pain is most marked around the subacromial region and radiates down the outside of the arm. Severe pain may last for several days, but the symptoms then generally resolve slowly over a period of 2 to 3 weeks. Calcific periarthritis is thought be caused by rupture of a calcific deposit into an adjacent soft tissue space or bursa along with initiation of an acute inflammatory reaction. The deposit is dense, homogeneous, and well defined, findings characteristic of inert periarticular deposits of calcific material. Aspiration revealed a large amount of blood-stained fluid (b) that contained numerous particles of basic calcium phosphate. Moderate to severe pain is described, with varying degrees of tenderness and restriction of motion. Pain usually radiates to the insertion of the deltoid and sometimes beyond to the forearm. In some patients, recurrent acute attacks around the shoulder, separated by pain-free periods lasting months or years, are followed by the development of chronic pain. Damage to the tendons and muscles of the rotator cuff may result and lead to total disruption of the cuff apparatus. The shoulder is the most commonly affected site followed by the hip, knee, elbow, wrist, and ankle joints. The joints of the feet and toes are less commonly involved (<1% of all reported cases), as are those of the hands and fingers. This manifestation can cause diagnostic confusion and may even mimic a seronegative polyarthritis. The deposit has become indistinct and ill defined as the crystals have been shed into the surrounding tissues. In this older adult patient, communication between the shoulder joint and the subacromial bursa led to a large effusion in the glenohumeral joint and a huge extension of the bursa into the upper part of the arm, as shown by the soft tissue swelling seen on the radiograph. With the onset of an attack, however, these calcific deposits appear fluffy with poorly defined margins. Ultimately, there is a reduction in the size of the deposit seen radiographically, and it may disappear completely. Calcific deposits in periarticular tissues are also associated with chronic pain syndromes without a history of a previous acute episode. The dominant side is usually involved initially, although 60% have bilateral involvement. Examination shows extensive damage to periarticular soft tissues, as well as to cartilage and subchondral bone on both sides of the joint. Active range of motion is reduced in all affected joints, sometimes associated with pronounced joint instability. Crepitation and pain may be noted, especially when the humerus is grated passively against the glenoid. Joint effusion is typically present and may be massive and extend into the subdeltoid region. Rupture of the effusion can lead to massive extravasation of blood and synovial fluid into the surrounding tissue.
Buy cheap fulvicin 250mg on-line
This is consistent with injury to the left lower lumbar and sacral nerve roots (L5 trichophyton fungus definition buy fulvicin 250 mg, S1, S2). Relative contraindications include epilepsy, cortical lesions, convexity skull deicits, raised intracranial pressure, cardiac disease, intracranial electrodes or shunts, cardiac pacemakers, and other implantable biomedical devices. In two patients there were some signiicant changes in the motor potentials that correlated with postoperative neurologic deicits. None of these patients had new postoperative deicits or worsening of preexisting deicits. Some of the suppressant efects of balanced anesthesia can be overcome with higher stimulation intensities and repetitive stimulation. Pedicle Screw Stimulation Intraoperative assessment during pedicle screw insertion can be used to avoid nerve root trauma from a misdirected screw. Absence of a myogenic response up to 10 mA is thought to be indicative of an intact pedicle. Presence of a highly skilled and experienced technical and neurophysiologic team that will ensure for optimal technical recordings and accurate interpretation of any changes that may occur 3. Rapid communication between the neurophysiologic team and the surgical/anesthesia teams 4. One key to the success of intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring is a good understanding of the capabilities and limitations of the neurophysiologic tests being monitored. One of the irst issues to address when planning for intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring is to determine the types of neurophysiologic tests to perform on a particular patient undergoing surgery. Summary Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring of the spinal cord can be used to help detect the early occurrence of neurophysiologic changes, thereby allowing corrective action to reduce the incidence of neurologic injury to patients undergoing spine surgery. There has been recent evidence to suggest that these spinally elicited neurogenic responses are generated through activation of the sensory pathways and retrograde activation of the alpha motor neurons. The role of intraoperative neurophysiology in the protection or documentation of surgically induced injury to the spinal cord. Safety of intraoperative transcranial electrical stimulation motor evoked potential monitoring. Postoperative neurological deicits may occur despite unchanged intraoperative somatosensory evoked potentials. A new technique for intraoperative monitoring of spinal cord function: multichannel recording of spinal cord and subcortical evoked potentials. Sensory nerve conduction in the human spinal cord: epidural recordings made during scoliosis surgery. Considerations for safety in the use of extracranial stimulation for motor evoked potentials. Evaluation of conduction in central motor pathways: techniques, pathophysiology, and clinical interpretation. Comparison of human transcallosal responses evoked by magnetic coil and electrical stimulation. The aim of most spinal cord monitoring is to prevent intraoperative injury that results in irreversible paraplegia or quadriplegia. The term signiicant change is used in reference to the degree of changes seen in the neurophysiologic recordings. Changes termed signiicant have been shown to correlate well with intraoperative injury to the nervous system. A variety of methods have been used to monitor spinal motor pathways during surgery. The second method involves recording responses directly from the spinal cord with use of an epidural catheter electrode that records a direct D wave and a volley of indirect I waves. This combination of techniques is considered safe, reliable, and accurate and may obviate the need for the wake-up test. Intraoperative assessment during pedicle screw insertion can be used to minimize the risk of nerve root trauma from a misdirected screw. The integrity of pedicle screw placement can be assessed by directly stimulating the screw and by simultaneously recording myogenic responses from the appropriate myotomes. Somatosensory evoked potential spinal cord monitoring reduces neurologic deicits after scoliosis surgery: results of a large multicenter survey. Comparison of transcranial motor evoked potentials and somatosensory evoked potentials during thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Somatosensory evoked potential spinal cord monitoring reduces neurologic deicits ater scoliosis surgery: results of a large multicenter survey. Evaluation of various evoked potential techniques for spinal cord monitoring during scoliosis surgery. Motor evoked potential monitoring during spinal surgery: responses of distal limb muscles to transcranial cortical stimulation with pulse trains. Myogenic motor-evoked potential monitoring using partial neuromuscular blockade in surgery of the spine. Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation in children using simultaneous motor and somatosensory evoked potential monitoring. Isolurane-induced attenuation of motor evoked potentials caused by electrical motor cortex stimulation during surgery. Isolurane plus nitrous oxide versus propofol for recording of motor evoked potentials ater high frequency repetitive electrical stimulation. Noninvasive intraoperative monitoring of motor evoked potentials under propofol anesthesia: efects of spinal surgery on the amplitude and latency of motor evoked potentials. Efects of nitrous oxide on motor evoked potentials recorded from skeletal muscle in patients under total anesthesia with intravenously administered propofol. Low concentrations of isolurane abolish motor evoked responses to transcranial electrical stimulation during nitrous oxide/opioid anesthesia in humans. Corticospinal volleys evoked by electrical stimulation of human motor cortex ater withdrawal of volatile anesthetics. Efect of nitrous oxide on myogenic motor potentials evoked by a six pulse train of transcranial electrical stimuli: a possible monitor for aortic surgery. Within-patient variability of myogenic motor-evoked potentials to multipulse transcranial electrical stimulation during two levels of partial neuromuscular blockade in aortic surgery. Spine pain with a signiicant recurrence has lifetime prevalence estimated between 24% and 80%,1,2 an annual prevalence of 15% to 45%, and a point prevalence of 18% to 30%. From 1992 to 2006, the prevalence of patients presenting with chronic impairing low back pain increased from 4% to 10%. Much of the epidemiologic data on low back pain are nonspeciic, meaning that a cause cannot be found in most cases. Despite evidence to the contrary in the 21st century, these older, inaccurate epidemiologic studies continue to be quoted by current authors. One of the oldest epidemiologic studies commonly quoted was published more than 40 years ago by Dillane and colleagues8 and was based on a retrospective practice audit of data gathered more than 50 years ago. Dillane and colleagues8 reported that they could not detect a cause for low back pain in approximately 80% of female and 90% of male patients with acute back syndrome. In perhaps the most frequently quoted epidemiologic study on the cause of chronic low back pain, he reported that in only 15% of cases could a pathoanatomic explanation be found for patients with chronic low back pain (>3 months). As stated in the study, "probably very little can be done at our present state of ignorance to treat these patients and to improve their natural histories. In acute cases of low back pain, this nonspeciic diagnosis usually suices because most cases of acute, irst-time low back pain resolve with minimal intervention. However, when low back pain becomes chronic, recurrent, and disabling, the clinician must diagnose the source of the pain so that an appropriate treatment plan may be devised. When a source of pain is not obvious, diagnosis oten depends on who makes the diagnosis and sets the reference standards by which the diagnosis is "proven. For that matter, can anyone reliably diagnose the cause of chronic benign spinal pain Many authors argue that chronic benign spinal pain is largely due to exaggerated functional complaints and irreversible central nervous system sensitization,11 making pain self-perpetuating and diagnosis all but impossible. Fluoroscopically guided block procedures are now considered the reference standard to conirm a tissue diagnosis. Chronic spinal pain may originate from one or more spinal levels and diferent anatomic structures in the anterior, middle, and posterior columns.