Purchase discount toprol xl on-line
Chronic alcohol abuse is a common antecedent arrhythmia bradycardia purchase online toprol xl, because a diet that predominantly consists of alcohol provides only "empty" calories without significant nutritive value. Thiamine deficiency can cause beriberi; clinical findings include polyneuropathy ("dry" beriberi) or cardiac dilation and peripheral vasodilation with edema ("wet" beriberi). His Apgar score is 5 at 5 minutes, but he is in respiratory distress, with grunting and retractions. Pink hyaline membranes and thick interstitium are consistent with hyaline membrane disease. Maternal diabetes retards fetal lung maturity as a result of compensatory fetal hyperinsulinemia. The infant is likely to be larger than normal, because insulin acts as a fetal growth factor. Shortly after delivery, the infant has a PaO level of 60 mm Hg (nl 90 mm Hg) and a blood glucose level of 31 mg/dL (nl 70 to 125 mg/dL). These lead to reflex pulmonary vasoconstriction, hypoperfusion that causes endothelial and epithelial damage, and plasma protein leakage into airspaces. There is extensive fluid collection, particularly in the soft tissues, which is characteristic of hydrops fetalis. These identical twins should be similar in size, but a twin-twin transfusion syndrome has occurred. The recipient twin becomes hydropic from volume overload and congestive heart failure; the donor twin receives too little blood and is growth retarded. An abnormal vascular connection across the monochorionic placenta allows blood from the donor (anemic) twin to overload the circulation of the recipient (plethoric) twin. Reduced or absent synthesis of all four -globin chains results in -thalassemia major. What is the name for a grossly similar process in which just interstitial fluid is present Vaginal group B streptococcal infection led to ascending infection with inflammation, the release of prostaglandins, and premature labor. Fetal distress led to the release of meconium into the amniotic fluid, where it stained the skin and placental surfaces. Gasping respirations in utero led to meconium aspiration, with flattened squames and balls of meconium seen within the alveoli. Hemorrhage beneath the scalp is a cephalhematoma, which is caused by the rupture of small veins that perfuse the periosteum. Caput succedaneum is a common finding with little significance, because the fluid is quickly resorbed. A skull fracture would suggest intracranial injury, such as subdural hematoma or contusion. Large-for-gestational age infants commonly occur when their mothers are diabetic as a result of the growth-promoting effects of insulin produced by fetal islets of Langerhans. He subsequently has failure to thrive as a result of malabsorption, and he experiences recurrent episodes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Note the consanguinity in generation 3, which brought two recessive alleles together. The sweat chloride level is elevated, as are the sodium (to maintain electroneutrality) and water (as a result of the osmotic load) levels. Abnormal pancreatic secretions led to inspissated meconium with intestinal obstruction caused by meconium ileus during the first few days of life. This opened ileum shows inspissated green meconium; the unopened colon at the upper left and the appendix at the lower left beyond the ileocecal valve are not dilated, and little or no meconium has passed via the rectum. This is a small round blue cell tumor, so-called because it is a monotonous, uniform collection of cells with round nuclei and little cytoplasm. However, depending on the primary site, they have different cells of origin, cytogenetic alterations, and marker expression. Typical childhood small round blue cell tumors: (A) Neuroblastoma (B) Retinoblastoma (C) Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor (D) Leukemia/lymphoma (E) Wilms tumor (F) Medulloblastoma 10. What would your diagnosis be if the primary site for the neoplasm is: (A) Adrenal The history and the large mass in the left adrenal gland are most consistent with a neuroblastoma. During childhood, approximately 40% of neuroblastomas arise in the adrenals; the remainder can occur anywhere along the sympathetic chain. Individuals with neuroblastomas detected during infancy (1 year old) tend to do well even if these tumors are metastatic, and many spontaneously regress. What gene mutation is associated with this tumor plus (a) a niridia, g enital anomalies, and mental retardation; (b) adrenal cytomegaly, hemihypertrophy, macroglossia, and omphalocele This Wilms tumor has a blastema component of small blue cells and a stromal component of spindle cells. Wilms tumor microscopically resembles the primitive nephrogenic zone of the fetal kidney and likely arises from nephrogenic rests. The histology of his right renal mass is shown, with adjacent compressed normal kidney. This Wilms tumor arising in the kidney is the most common childhood primary renal tumor and the fourth most common pediatric malignancy in the United States. The left leaf of the diaphragm did not completely form posteriorly, thereby allowing abdominal contents to herniate into the chest cavity. This defect reduces the amount of space that the lungs have for development, so they are too small (hypoplastic), with inadequate oxygenation after birth. The constellation of abnormalities in this case strongly suggests Edwards syndrome, which is caused by trisomy 18. Additional anomalies include a small face with micrognathia, overlapping fingers, and a horseshoe kidney. This bilateral cleft lip is one of the most common birth defects with or without an associated cleft palate (approximately 1 in 1000 births). The failure of midline facial fusion has multiple potential causes; these include the teratogen retinoic acid as well as alterations in the expression of transforming growth factor or fibroblast growth factor or mutations in their receptors (or downstream targets). Although environmental factors contribute, there is a genetic component; if either parent has a cleft lip, the chance of a child being born with such a deformity is approximately 5%. If neither parent has a cleft lip, the chance of such a deformity in a second child is also approximately 5%. This gastroschisis is a large lateral abdominal wall defect that does not involve the umbilical cord and that is not covered by a membrane. Bowel, stomach, and liver are herniated outside of the abdominal cavity. A disruption is an extrinsic disturbance that destroys the morphogenesis of otherwise normal body parts. Amniotic bands (caused by the rupture of the amnion) are a common cause of disruptions. This omphalocele is a large midline ventral abdominal wall defect that involves the umbilical cord and that is covered by a thin membrane. Bowel developing outside of the abdominal cavity is malrotated, and the cavity is too small. Some cases occur with chromosomal abnormalities such as trisomy 18; others are part of syndromes, and some are sporadic. Polyhydramnios, or increased amniotic fluid, often occurs when a gastrointestinal tract abnormality prevents fetal swallowing and resorption of this fluid. Why are premature, low-birth-weight infants at increased risk for this hemorrhage Gut ischemia can result from systemic hypotension or the selective reduction of blood flow to the intestines to preserve central nervous system perfusion. Local inflammation (potentially in response to feeding) can increase mucosal permeability and allow transluminal migration of gastrointestinal flora that eventually culminates in sepsis. At 1 week of age, he develops abdominal distention, bloody stool, and hypotension, and a radiograph shows bowel wall gas.
Buy generic toprol xl canada
Platelet activation is undesirable because it allows for conformational changes whereby they expose phospholipids allowing procoagulant attachment and further platelet-to-platelet activation blood pressure medication recreational purchase toprol xl, attachment, and clumping. Limiting activation of procoagulant factors circuit surfaces, and to limit activation of procoagulant factors contribute to this goal. Heparin is the primary medication administered to provide anticoagulation for cardiopulmonary bypass. Minimizing circuit exposure Tremendous strides have been made over the past decade in regards to decreasing circuit prime volumes for pediatric perfusion cases. This decrease in prime volume parallels an overall decrease in exposure of the blood to nonendothelial circuit surfaces. Oxygenator and arterial line filter design have played a major role, especially when the two are integrated. Techniques including vacuum-assisted venous drainage, retrograde autologous priming, venous autologous priming, and maximizing the use of smaller tubing diameter lines have also played a part. However, it should be noted that activation of procoagulant systems, and the inflammatory response to bypass, is still primarily due to the use of cardiotomy suction. Procoagulant and anticoagulant factors are normally appropriately balanced in the body. This balance is shifted in favor of anticoagulation by several means, including the presence of heparin. Heparin is normally given in bolus form before bypass with additional doses on bypass as needed. The traditional activated clotting time simply measures the number of seconds required for a blood clot to form when blood is activated in a sampling tube. An activating agent such as celite (silica, glass beads, and kaolin are the bypass plan 37 also used as activators) shifts the hemostatic balance in favor of procoagulation in the sampling tube. An alternate system quantifies clot formation by measuring the impedance of a plunger in a blood sample. Both methods result in a real-time counting of the number of seconds required for organized clot formation. Monitoring the heparin concentration is thought to be more predictive of how well activation of the clotting system has been suppressed. This may be especially true during hypothermia and hemodilution, both of which are common for congenital cardiac surgery patients. The heparin concentration test works off of the principle that heparin is neutralized by protamine in a known ratio with too much or too little protamine resulting in a prolonged clotting time. By exposing blood samples to several different concentrations of protamine and detecting which sample clots first, the heparin concentration can be determined. To note, neonates and infants have immature hemostatic systems and notably lower thrombin and antithrombin levels. Samples are usually drawn after heparin bolus and every 20 min on bypass with an increased sampling rate during rewarming or when values are marginal. Finally, it is important to clarify that while some clinicians equate more heparin with more bleeding, the opposite may in fact be true. Higher heparin doses may better attenuate procoagulant systems and prevent consumption of factors during bypass [8]. The heparin level present theoretically is represented by the difference between point E and point A on the horizontal axis (arrow E). The protamine dose required to neutralize the remaining heparin then may be calculated. The estimate of heparin remaining in the patient may additionally consider the total amount of heparin administered during cardiopulmonary bypass. However, one must account for the potential anticoagulant effects of thrombocytopenia, platelet dysfunction, hypothermia, and the dilution of other procoagulant factors which may be present after bypass. There exists a 1:1 ratio for the complex formed between these two substances (some sources report a ratio of 1. There exist numerous variables when calculating the amount of heparin in the patient which needs to be reversed. This machine estimates the amount of heparin present in a post-bypass sample by exposing it to varying amounts of protamine. The protamine and blood sample that clots first is assumed to best match the heparin concentration. This concentration value, along with an estimated patient circulating blood volume can then be used to determine the amount of heparin present, which must be neutralized. Rapid administration of protamine may cause hypotension, anaphylaxis, pulmonary hypertension, and pulmonary edema. Protamine vials must be kept well away from the medications normally administered by the anesthesiologist and perfusionist. It is a safe practice to draw up the protamine dose only and immediately before administration. Most often, when clinicians refer to "blood gas management," they are talking more specifically about carbon dioxide management and not necessarily oxygenation strategy, which is also important. The various strategies have advantages and disadvantages based on patient diagnosis and age. Adherents to respective strategies cite neurologic and myocardial outcome studies as a basis for their approach. Blood gas management for congenital cardiac surgery must consider the fact that a majority of cardiopulmonary bypass in this population is conducted at some degree of hypothermia. Hypothermia shifts the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the left resulting in oxygen being bound to hemoglobin more tightly and, therefore, less likely to be released at the tissue level. Hypothermia causes vasoconstriction and increases the viscosity of blood, which theoretically may impair microvasculature blood flow. These concerns have increasingly important consequences under deep hypothermia or with low flow bypass. The primary techniques for blood gas management include alpha-stat versus pH-stat and normoxic versus hyperoxic, with crossover options for both. This alkalinity is acceptable since the ratio of hydrogen and hydroxide ions is maintained intracellularly by histidine. Maintenance of this electrochemical neutrality is also important in regards to cerebral blood flow. Preservation of enzymatic function and other cellular and vascular systems additionally maintains cerebral blood flow autoregulation where flow is matched to metabolic need. This may be particular important in older patients with acquired vascular disease who are more prone to embolic events and downstream sequelae on bypass, especially in the cerebral vasculature. Alpha-stat limits cerebral blood flow to that which is necessary to meet metabolic demand and no more. The risk of embolic events is thus kept to a minimum by limiting potential delivery of emboli. This method is most commonly achieved on bypass with air and oxygen delivered through a gas blender and graduated flow meter. The perfusionist adjusts the FiO2 per protocol for independent management of PaO2 on bypass. This is the predominant blood gas strategy for adult cardiac surgery patients with acquired cardiac disease.
Generic toprol xl 100 mg
Treatment typically involves long-term phlebotomy blood pressure young female order 50mg toprol xl overnight delivery, with a median survival of 10 years. The neoplastic pleuripotent stem cells infiltrate many organs, particularly the spleen, which results in splenomegaly. The markedly elevated peripheral counts can lead to abnormal blood flow; with platelet dysfunction, there is a significant risk of either thrombotic or hemorrhagic complications. Polycythemia vera tends to evolve to a burnt-out phase with myelofibrosis, but it can also proceed to acute myelogenous leukemia. Imatinib (a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor) induces remission in more than 90% of patients. Hemoglobin A and fetal hemoglobin increase in the absence of an adequate number of chains to complex with the chains. Ineffective erythropoiesis leads to increased iron absorption and increased iron stores, which are reflected by the markedly increased serum ferritin level. His hemoglobin electrophoresis is shown; the hemoglobin A value is about 5% of the total hemoglobin (nl 2. Sickle cell crises can occur with reduced oxygen tension, infection, dehydration, or temperature change, but often no precipitating event can be found. Vaso-occlusive crises result when "sticky" sickled cells clog capillaries and cause tissue ischemia. A positive blood culture grows the organisms that are shown here with Gram staining. The hemoglobin electrophoresis shows a large hemoglobin S peak, with smaller hemoglobin A and hemoglobin F fractions. A single nucleotide mutation results in a valine-for-glutamic acid substitution at the sixth position in the hemoglobin chain. Chest, abdominal, and back pain are common, and there is also risk for cerebrovascular accident ("stroke") involving the brain. The Gram stain shows short, slightly curved gram-negative rods that are consistent with Haemophilus influenzae. For unclear reasons, patients with sickle cell disease are also prone to Salmonella infections, typically either osteomyelitis or cholecystitis. By late childhood, multiple autoinfarctions of the spleen have led to markedly reduced spleen size (autosplenectomy) so that the splenic immune function, which is particularly useful for encapsulated bacteria, is diminished. Anemia of chronic disease has a low serum iron level and abundant stored iron, typically in phagocytes. Note the ringed sideroblast ; bone marrow macrophages should also be substantially iron replete. The serum ferritin level reflects intracellular stores of iron, which are elevated. Chronic inflammatory states lead to increased liver synthesis of hepcidin, which reduces the expression of ferroportin necessary for the release of intracellular iron stores. Her serum iron and transferrin levels are low, but her serum ferritin level is elevated. Glossitis, esophageal webs (which can impede swallowing), and microcytic hypochromic anemia constitute the triad of Plummer-Vinson syndrome. Name a (rare) disorder with the same assay but that involves abnormally large platelets. The arteriole contains a hyaline thrombus that is composed of aggregated platelets. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome caused by Shiga-like toxin that damages endothelium is classically associated with infection caused by Escherichia coli strain O157:H7. She is anemic and thrombocytopenic, with a serum creatinine level of 5 mg/dL (nl 1. Bleeding occurs because there is abnormal platelet adhesion via the glycoprotein Ib receptors, and a primary hemostatic plug fails to form. Autosomal-recessive Bernard-Soulier syndrome results from defective or deficient glycoprotein Ib receptors. Pancytopenia is caused by a marked reduction in erythroid, myeloid, and megakaryocytic cell lines. Aplastic anemia can result from a stem cell defect in the marrow, from a toxin, or from immunologically mediated marrow suppression. He is also profoundly anemic, neutropenic, and thrombocytopenic, although his absolute lymphocyte count is roughly normal. Aside from an acquired intrinsic mutation of the stem cell, what could be the pathogenesis of these findings At this age, the bone marrow should contain at least 50% hematopoietic cells; in this case, it is composed mainly of adipocytes. Despite the name of this condition, all major hematopoietic cell lines are reduced. Thrombocytopenia results in easy bruising; reduced myelopoiesis leads to neutropenia with a risk for infection, and reduced erythropoiesis causes anemia with fatigue. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated cytokine production induces monocytes and endothelial cells to release tissue factor, which initiates the widespread activation of the coagulation cascade. The large gram-negative bacilli are typical of Enterobacteriaceae such as Escherichia coli with urinary tract infection. The fever and flank pain with hypotension and positive blood culture suggest acute pyelonephritis with septicemia. Reticulocytosis is a bone marrow response to anemia; it is prominent after blood loss in a healthy person and in those with hemolytic anemias. Spontaneous pneumothorax in a young adult suggests the rupture of a bulla caused by distal acinar (paraseptal) emphysema. A panic attack is a discrete period of intense fear or discomfort with multiple central nervous system, respiratory, cardiac, or gastrointestinal symptoms that peak after 10 minutes. There is increased lucency on the right, with a shift of the mediastinum to the left. Air trapping with long-standing emphysema or acute asthma can predispose an individual to pneumothorax. This patient has uncompensated respiratory alkalosis from the hyperventilation and mild hypoxemia from the collapsed right lung. What organisms are most likely in the setting of such a community-acquired infection A sputum Gram stain shows gramnegative coccobacilli; these organisms grow on chocolate and nutrient agars with X and V factors. Extensive, right upper lobe consolidation is seen, which is consistent with lobar pneumonia. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common causal organism in this setting, followed by Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Staphylococcus aureus, Legionella pneumophila, and the Enterobacteriaceae. The consolidation represents acute inflammatory cells (neutrophils) exuding into and filling the alveoli, along with transudated fluid and proteins. He requires intubation and mechanical ventilation with increasing positive end-expiratory pressures and Fi. Hyaline membranes and thickened alveolar walls diminish compliance and require increased positive end-expiratory pressures. High levels of inspired oxygen are required to maintain arterial oxygen saturations; these high levels are themselves toxic, and they promote alveolar injury. The end result is a vicious cycle of ongoing injury and worsening ventilation and perfusion. Infection can stimulate Toll-like receptors of the innate immune system that upregulate nuclear factor expression, which results in locally increased proinflammatory cytokine production. When bound IgE is cross-linked by allergen, mast cells release vasoactive substances. Nonatopic forms of asthma occur with hyperreactive airways that are triggered by respiratory pathogens such as viruses, inhaled air pollutants, chemical exposure, or aspirin. Charcot-Leyden crystals are whorls of sloughed epithelium, and Curschmann spirals are crystalloids of eosinophil membrane proteins. Note an expanded edematous submucosa that has been infiltrated with inflammatory cells, mainly eosinophils ; the lumen is filled with mucus. The lipoxygenase pathway produces leukotrienes, and the cyclooxygenase pathway produces prostaglandin D, thereby causing bronchoconstriction. Peripheral bronchial dilation and extensive consolidation are consistent with bronchiectasis complicated by pneumonia. Abnormal chloride ion transport results in pancreatic exocrine duct malfunction with pancreatic exocrine atrophy and a loss of enzyme output.
Order 25mg toprol xl with mastercard
The standard resection approach is pancreaticoduodenectomy arteria 90 obstruida order cheap toprol xl on-line, referred to as the Whipple procedure. Too few pediatric patients have been treated with radiation therapy for pancreatic carcinoma or pancreatoblastoma to allow meaningful conclusions. Studies to evaluate the use of adjunctive conventional or intraoperative radiation therapy are under way in adults. Localized Tumors Chemotherapy for pancreatic carcinoma differs from that given for pancreatoblastoma and is usually ineffective. The reported rates of response to these agents range from 7% to 36%,215,216,217 although gemcitabine is the only cytotoxic agent that has even a modest impact on survival or disease-related symptoms. Symptomatic tumors can present with abdominal pain, ulceration, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, bleeding, perforation, or an externally palpable abdominal mass. A lobulated hyperdense mass (arrow) is seen arising from the superior aspect of the gastric antrum. About 85% of tumors arose in the stomach, and the most common histologic subtype was epithelioid or a mix of spindle and epithelioid cells. In the presence of symptoms or progression, surgical resection should be performed when feasible. Thus, it is seen more frequently in Europe and North America than in Africa or Asia, with the exception of Japan, where the incidence approaches that in other developed countries. In general, an increased intake of red meats and fats and decreased intake of vegetables and fruits is characteristic of diets in more developed countries. Red meat, especially when cooked at high temperatures, has an increased content of carcinogens such as heterocyclic amines,251,252 and a relatively low-fiber diet is thought to prolong the transit time of fecal material containing these carcinogens. However, the geographic variation is likely to reflect a complex interaction of lifestyle, environmental and dietary factors, and genetic factors. In children and adolescents, these tumors may occur at any site in the large bowel and are not usually associated with a family history of large-bowel cancer. They surmised that mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor gene occur early in the development of polyps, followed by Ki-ras mutations during the adenomatous stage. This model has been confirmed by other investigators, and the specific cellular pathways perturbed by these changes are increasingly being elucidated. Individuals with the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome may develop cancers in the stomach, duodenum, or small bowel as well as the large bowel, because the hamartomatous polyps characteristic of this syndrome may occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract. A change in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea, and a change in the caliber of stools may be observed before the development of tarry stools, rectal bleeding, or other changes. Abdominal pain is usually the most common presenting symptom and is frequently severe enough to suggest an acute abdomen. Tumors involving the cecum and descending colon, which may be associated with familial colon carcinoma, may become bulky before symptoms appear. Tumors of the rectum and sigmoid colon may be associated with changes in the caliber of the stool, dyschezia, hematochezia, and anemia. Additional polyps were removed the following year, and a colon resection to the peritoneal reflection was performed during the succeeding year. Acute bowel symptoms necessitate immediate abdominal exploration, at which time perforation of the large bowel with multiple metastatic deposits may be observed. They may spread throughout the peritoneal cavity to involve the omentum, peritoneum, mesenteric lymph nodes, liver, and ovaries, and they may spread through the bloodstream to the lungs and eventually the brain, bones, or both. Peritoneal seeding in female patients frequently involves the ovaries, which may become extremely enlarged. More than half of the reported neoplasms of the colon in younger patients, but only approximately 15% of those in adults, are mucinous adenocarcinomas. Test results of hepatic and renal function are rarely abnormal initially, although metastatic involvement of the liver may cause abnormal liver function test results. A concentration greater than 5 ng per mL in adults has been associated with advanced stage and poorer prognosis. Tumor may extend into the muscularis area to the serosa, perforate the serosa, and penetrate the omental fat, lymph nodes, liver, ovaries, and other loops of bowel. There also may be implants along the abdominal scar, at the anastomotic site, or throughout the peritoneum. The gross appearance of colonic lesions depends on the extent of involvement of the lumen and the extent of the disease outside the bowel wall. Because these tumors are derived from endoderm, all of their cytologic characteristics will be those of carcinoma, yet they may be well differentiated or poorly differentiated and contain pools of mucin. These tumors may grow to remarkable sizes, and in females, ovarian involvement may be massive and may complicate the differential diagnosis of bowel cancer versus ovarian cancer. The differential diagnosis includes malignant carcinoid tumor, leiomyosarcoma, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, and metastatic tumor from other sites. All may have similar presentations; metastases may be identified only by histology or metastatic site. When patients present with an acute abdomen, associated pain, and possible perforation, the diagnosis of acute appendicitis is most often considered. A biopsy may be obtained during colonoscopy or laparotomy, at which time definitive surgery may or may not be feasible. In fact, if patients cannot be rendered surgically free of disease, they are rarely cured. The basic surgical principles are removal of the major vascular pedicle supplying the tumor and its lymphatics and en bloc resection of any organs or structures attached to the tumor. A margin of at least 5 cm of normal bowel should be removed on either side of the tumor to minimize the possibility of anastomotic recurrence. A minimum of 12 negative lymph nodes should be examined to define node-negative disease. In these cases, reexploration of the abdomen, with the goals of radical resection of tumor with adequate margins and adequate lymph node sampling, should be done at a center experienced in this type of surgery. Other surgical staging procedures include biopsy of the ovaries in female patients, resection of the omentum, and examination and possible biopsy of the liver. Complete excision is the goal of surgery, whereas secondary aims are related to palliation by resection of bulky tumors or metastases. Debulking provides little benefit for the patient with extensive metastatic disease. However, removal of single or multiple hepatic metastases may be a life-saving procedure for patients whose other sites of disease have been successfully resected. Localized, completely resected tumors (Tis, T1, T2, N0, M0 lesions) are usually cured by surgery alone. Complications of Therapy Complications of therapy and disease are sometimes difficult to distinguish; they may be nutritional or obstructive or may be related to the effects of metastatic disease on other organ systems. Patients who have survived colon carcinoma experience a relatively high quality of life although some have reported ongoing problems with diarrhea and depression. Surgery is the only modality known to be curative, although adjuvant chemotherapy extends life. Few patients with extensive metastatic disease are cured, although options for their treatment have improved with the approval of several new agents, including irinotecan, oxaliplatin, and the monoclonal antibodies cetuximab and bevacizumab. Screening of pediatric patients for fecal occult blood has not proved to be of significant value. These patients were more likely than others to be in a young age group at diagnosis, have poorly differentiated or right-sided tumors, have a higher risk of metachronous tumors, and have a favorable prognosis. It is conceivable that continued research will allow the molecular characterization of tumors and the customized tailoring of therapy in the near future. Inhibition of the cyclooxygenase enzyme pathway is thought to be responsible for these effects, although the exact mechanism is still the subject of intense research. For example, in a prospective mortality study of 662,424 adults, death rate from colon cancer decreased as the frequency of aspirin use increased in both men and women. Celecoxib reduced the rate of advanced adenomas detected through 3 years compared with those who received placebo (5. Other agents being evaluated include polyamine inhibitors, bile salts, statins, complex dietary interventions, and micronutrients such as organoselenium, calcium, and vitamins E, C, and D. The tumor rarely affects adolescents and resembles papillary carcinoma of the ovaries in adults. The differential diagnosis includes mesothelioma of the peritoneum and surface carcinoma of the ovary. Carcinoma Of the Bladder Bladder cancer is an occupationally acquired industrial disease and cigarette smoking is associated with two- or threefold excess risk.
Discount 100 mg toprol xl
Vegetables arteria3d full resource pack order toprol xl 25 mg on line, such as broccoli, can also be a good source if grown in selenium-rich soils. Milk thistle (Silybinum marianum) is an herbal remedy that has been shown in some adult studies to protect the liver and kidneys from chemotherapy toxicity. Milk thistle is generally well tolerated; the most commonly adverse effects are a mild laxative effect and gastrointestinal upset. Panax ginseng is usually well tolerated, but insomnia, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea have been reported; it may also increase the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and sulfonylureas, and possibly antagonize the effects of anticoagulants and interact with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Parts of the noni tree have long been used as herbal remedies for various conditions, and noni juice is a relatively popular complementary cancer therapy. Similarly, mangosteen juice is currently marketed as an effective health-promoting product, but no data exist regarding its use in the oncology setting. Many products from developing countries, such as Ayurvedic medicines and traditional Chinese herbal combinations may be contaminated by other ingredients such as lead, mercury, arsenic, pesticides, and insecticides. In one study of pediatric oncology patients, almost half of all respondents implemented dietary changes including increasing fruit and vegetable consumption, switching to organic foods, reducing fat intake, eliminating red meat, and adding specific foods to the diet. It has been estimated that approximately 30% of adult cancers in developed counties are associated with dietary factors. In particular, obesity and excess alcohol consumption increase the risk of many adult cancers. In contrast, a diet rich in fruits and vegetables is almost certainly protective for some cancers. Generally, the diets are just one part of comprehensive lifestyle programs for adult cancer patients. Four such programs are the Block nutritional program, Gerson therapy, Livingston-Wheeler regimen, and macrobiotics. The Gerson and LivingstonWheeler regimens also include coffee enemas and dietary supplements. Nearly all of these diets are low in fat; high in complex carbohydrates, fruits, and vegetables; and devoid of sugar, fats, and oils. Severe dietary restrictions run the risk of vitamin and mineral deficiencies, caloric deprivation, and reduced quality of life. For example, the restrictive forms of macrobiotic diets have been associated with cases of scurvy, anemia, and hypoproteinemia. Although there are numerous testimonials and case reports about the effectiveness of these diets in adult oncology patients, they have not been evaluated in pediatric patients. Other diets used to promote cardiovascular health, lose weight, and avoid other adult health problems may also be adopted by families looking for healthy lifestyle approaches and for cancer treatment. These include low-fat (high carbohydrate), low-carbohydrate (high protein/fat), high-fiber, vegetarian, vegan, macrobiotic, and Mediterranean diets. Although the consumption of particular foods has not been shown to reduce this risk, it is prudent to recommend a balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables and little processed food or fast food. Fruits and vegetables provide vitamins, minerals, and fiber that may reduce subsequent cancer risk, and minimizing processed and P. Studies have documented an association between physical activity/exercise and improved psychological outcomes, including reduced depression and anxiety. The interaction between exercise, immunity, and psychological effects are complex. For patients at risk of exercise-associated complications, exercise recommendations should be individualized. For cancer patients in general, however, the benefits of exercise far outweigh the risks. Because these exercises can be done slowly and noncompetitively and can be practiced in a group or individually at home, they may be useful for children in various stages of cancer therapy. Its benefits are far reaching and it can be done with other family members or friends for additive benefits. Boredom and depression commonly follow exposure to isolation and extremely restricted environments. Developing routines and a predictable schedule during hospitalization may help a child feel a greater sense of control in the face of an overwhelming disease. One study highlighted the importance of minimizing noise to help hospitalized patients sleep. Interventions such as closing doors, moving the location of nursing reports, lowering monitor volumes, and using flashlights instead of overhead lights can all promote better sleep. Most of these approaches rely on common sense and attention to individual preferences. The benefits may be significant not only for the patients, but also for their families. For hospitalized adult oncology patients, music therapy reduces pain and mood disturbance, improves relaxation, and reduces anxiety, and for outpatient pediatric oncology patients music promotes relaxation. Although evidence of biologic plausibility is limited, static and electromagnetic therapies have been evaluated for a number of conditions, most of which involve musculoskeletal pain. Results have been mixed to date,116 and trials have not yet been done in pediatric oncology patients. Mind-Body In the past two decades, there has been increasing attention to the interaction between psychological states and somatic function. In addition to the patient, support groups for parents and siblings of children with cancer may enhance their own psychological well-being and indirectly aid the sick child. Biomechanical Therapies Massage Nearly every cultural group in the world has a historical tradition of massage therapy. There are many different types and variations of massage including Swedish, deep tissue, medical/orthopedic, sports, aromatherapy, shiatsu, reflexology, and Rolfing. Massage is often provided informally by parents and is one of the most commonly used complementary therapies. Massage can be provided alone or in conjunction with guided imagery, music therapy, aromatherapy, or Healing Touch. Massage has proved useful for infants, children, and adolescents with diverse health conditions including cancer. Randomized trials support its use in reducing symptoms such as nausea, anxiety, pain, depression, anger, stress, and fatigue. Individual adjustments are required for children who are restless or dislike being touched. Chiropractic Therapy: Spinal and Cranial Adjustment Chiropractors are licensed in all 50 states in the Unites States, and nearly all chiropractic schools now offer courses in pediatric care. Acute significant adverse effects from chiropractic adjustments are very rare, and the rate of malpractice claims against chiropractors is much lower than that against medical doctors. When the flow of chi is blocked or disrupted, disease occurs; when the flow is balanced, harmonized, and restored, the patient experiences health. The flow of chi can be affected by stimulating specific points along the energy meridians. Acupuncture is sometimes used as an adjunctive therapy to minimize nausea, anxiety, breathlessness, fatigue, and pain experienced by cancer patients. Although it appears safe, its efficacy for most symptoms is still largely unproven. Side effects from acupuncture treatment, such as infections, broken or retained needles, pneumothorax, and cardiac tamponade, are rare. It has been shown to reduce nausea in adult cancer patients receiving radiation therapy,137 and a pilot study has shown it to be safe and well accepted in pediatric cancer patients. Although these kinds of energy healing techniques seem farfetched to many physicians, they can be profoundly meaningful to children and families. These therapies are rarely used as a replacement for mainstream medicine, and they are safe. All of these therapies are provided with the patient fully clothed, and they may be provided in any clinical setting including outpatient clinics and intensive care units. In some cases, Reiki healers do long-distance healing in which the patient is visualized and energy is sent through intention rather than being transmitted by direct physical contact. There are no national certifying examinations, no state licensure, and no studies evaluating its effectiveness in treating children. Qigong can also refer to a set of exercises (internal Qigong) that are similar to Tai Chi, performed by the patients to enhance overall well-being. Qigong is frequently used in China as a complementary therapy for cancer patients. In adult cancer patients, Qigong may improve quality of life, fatigue, positive mood status, and it may also reduce some side effects.
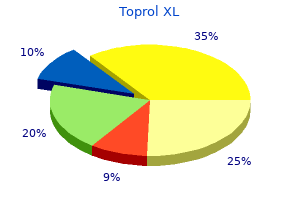
Generic toprol xl 25mg with mastercard
Note the variations in the size of the muscle fibers and the markedly diminished dystrophin blood pressure drops after eating buy toprol xl 50mg lowest price. This is a different mutation of the dystrophin gene than that seen with Duchenne muscular dystrophy; there is diminished (or dysfunctional) dystrophin, but it is not absent. The onset of the disease is delayed into adult life, and symptoms typically progress more slowly. Additional myopathic changes seen in striated muscle include the degeneration and regeneration of muscle fibers. The microscopic appearance of his muscle biopsy specimen with immunohistochemical staining for dystrophin is shown. Dystrophin is absent; it is responsible for linking sarcomeric contraction to the extracellular matrix. This is an X-linked disorder; one third to one half of cases represent new spontaneous mutations. Female carriers may exhibit mild weakness and some elevation in their creatine kinase levels; they also may develop dilated cardiomyopathy later in life. Muscle with inflammation is progressively replaced by fat and fibrous connective tissue. Death from progressive muscular weakness, which eventually affects the diaphragm and the myocardium, often occurs by age 20. Chains of central nuclei are seen in this longitudinal section, with fibrous replacement of the muscle fibers. Why are individuals in his family affected at an earlier age and more severely in successive generations The histology is confirmatory, showing a ragged red fiber with subsarcolemmal aggregates of mitochondria. With electron microscopy, these often show characteristic paracrystalline "parking lot" inclusions in the cristae. Her serum creatine kinase level is elevated, and her muscle biopsy specimen is shown. There is variation in fiber size and fibrous replacement, which is typical for a myopathic disease. Filamentous inclusions that contain amyloid and hyperphosphorylated tau proteins are seen. Intracellular -amyloid deposits, amyloid fibrils, and hyperphosphorylated tau suggest an aging phenomenon. There is marked lymphocytic infiltration with necrosis as well as the regeneration of muscle fibers. She has no focal neurologic signs, but she cannot remember three objects after 5 minutes, and she cannot count backward from 100 by 7s. She falls and sustains a hip fracture; subsequently, she dies of a pulmonary embolism. What neurodegenerative condition would involve a vertical gaze palsy and truncal rigidity A characteristic but nondiagnostic radiographic feature of dementias is cortical atrophy, which is shown here as prominently involving the frontal and parietal regions. The clinical history and severity of the atrophy suggest a form of frontotemporal lobar degeneration known as Pick disease. Tau filaments accumulate within Pick bodies; the latter are round to oval inclusions found in residual neurons. What paired helical filaments are present in round cytoplasmic inclusions in patients with this disorder The gross and clinical findings suggest a frontotemporal dementia such as Pick disease. Any condition that reduces or alters consciousness, including any condition that reduces the gag reflex, increases the risk of aspiration pneumonia. Progressive supranuclear palsy with neuronal loss in the globus pallidus, colliculi, and periaqueductal gray is present. In contrast with Pick disease, mutations in tau proteins have not been identified with this type of condition. Less than 20% of patients with epidural hematoma exhibit a "lucid" interval after injury. Unless the blood is expeditiously evacuated, the expanding hematoma within the closed intracranial cavity can cause herniation. He initially loses consciousness, but he then remains alert (albeit with a bad headache) for 2 hours, when he again becomes unconscious. At that time, his pulse is 55 beats/min, his respiratory rate is 10 breaths/min, and his blood pressure is 160/100 mm Hg. The large, lens-shaped epidural collection of blood on the left is bounded by parietal bone suture lines. The middle meningeal artery can be torn in association with a skull trauma, with or without fracture. Plaques of demyelination appear as pale tan to gray areas as compared with normal white matter. This is putatively an autoimmune disorder that involves cellular immunity directed against the oligodendroglial cells responsible for synthesizing myelin. The oligoclonal antibodies reflect increased B-cell proliferation, but these immunoglobulins are directed against multiple epitopes rather than myelin or other oligodendroglial antigens. Her newer symptoms are attributable to transverse myelitis (bladder and bowel dysfunction). Cerebellar findings (ataxia), intranuclear ophthalmoplegia, and sensory paresthesias are also common. Most patients have a relapsing-remitting course with acute exacerbations followed by partial to full remissions; one third of patients have complete recovery within 2 months of onset. This is a highly cellular neoplasm with vascular proliferation and densely packed malignant cells arranged around areas of necrosis (pseudopalisading). The large right cerebral mass infiltrates across the midline and impinges on the cerebral ventricles. Because it is difficult to eradicate such large neoplasms surgically, most patients survive less than 1 year. This meningioma is composed of whorled nests of cells with abundant pink cytoplasm (psammoma bodies may also be seen in this kind of neoplasm). She has also developed obsessive anxiety about her health and her children, and she is calling the school that they attend several times per day. If she had other similar lesions and an acoustic neuroma, what syndrome would you suspect There is a circumscribed mass in the parasagittal region that is impinging on the frontal lobe; this is consistent with meningioma. Meningiomas often express progesterone receptors, so their growth is stimulated during menstrual cycles or pregnancy. Most are benign lesions; approximately 10% are atypical (having more aggressive growth) or frankly malignant. Neurologic examination shows impairment of his attention span, verbal and nonverbal memory, spatial skills, and judgment. Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease has an incidence of 1 in 1 million, with a mean age at onset of 62 years and survival of less than 1 year. The rarer variant CreutzfeldtJakob disease is presumed to be related to bovine spongiform encephalopathy, which has a mean age at onset of 28 years and a longer course. He is no longer able to perform any activities of daily living, and he exhibits myoclonic jerks of his entire body whenever anyone touches him. This is spongiform encephalopathy with numerous clear vacuolar spaces in the neocortex, which is consistent with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. The accumulated abnormal protein drives the loss of neuronal cell function, vacuolization, and death, thereby leading to the extensive and rapid destruction of the brain. In the United States, 20% of strokes are intracerebral hemorrhages; most of these result from hypertension, and most occur in the basal ganglia and the thalamus. Intracerebral hemorrhage accounts for approximately 15% of mortality in patients with chronic hypertension.
Buy 100 mg toprol xl with mastercard
Separation from the treatment team heart attack keychain toprol xl 25mg visa, on whom the family has depended for so long, also generates fear and uneasiness in parents and the older adolescent who may believe that not actively fighting the disease may make relapse more likely. Physicians must outline reasons for discontinuation of therapy, the possibility of relapse with or without treatment, and the risks of continuing therapy longer than necessary. Families can also be reassured by the knowledge that the child is still a patient and will be monitored closely. Changes and growth that have taken place in each family member should be discussed at this time, encouraging an awareness of achievement while preparing the family for the challenges of long-term cancer survival. Finally, patient, siblings, and parents should be instructed about and given written guidelines for self-care. Family members may, at this point, find it useful to increase their use of available communication resources, including chat rooms, through the Internet Table 45. The anxiety felt when therapy is completed dissipates slowly as months pass and the child remains free of disease. In certain ways, this second crisis can be more devastating than the initial stress of diagnosis. Denial of the illness and fantasies of cure become much more difficult to maintain. After confirmation of a relapse, feelings of shock, anxiety, disbelief, fear, guilt, anger, and sadness are common. Families faced with reinitiating treatment must start over again, but with a smaller chance for successful outcome. The crisis and stress of the diagnosis are reactivated, the threat to life is relived, and new adjustments are required. Families can gain a sense of hope from the knowledge that further action will be taken against the disease. Optimal communication among the child, family, and oncology team is essential at this time. Support must also be given to staff members who have worked most closely with the child and family. Krulik128 refers to the time between the first relapse (recurrence) and second remission as the midstage of illness. Hopes for another treatment response are rekindled when the family is encouraged to begin reinduction or another treatment regimen promptly. Work habits, social activities, friendship patterns, relationships within the family, and expression of feelings are again altered. Within the hospital environment itself, the family may experience a change of identity because they are no longer part of the "successful" remission group. Team members may be struggling with their own feelings of disappointment, frustration, sadness, and possibly defeat. When the disease recurs, relatives and friends may encourage families to seek other treatments or new second opinions or to try an unorthodox method of therapy. Newspapers, magazines, the Internet, fund-raising events, and television talk shows disseminate information about cancer research "breakthroughs" and unconventional treatment in such a dramatic way that it is difficult for the general public to evaluate these reports (see Chapter 51). At this time, the physician may refer the child to another treatment center for participation in a particular randomized clinical trial. The physician needs to reassure the child and family that the relationship that he or she has with the family will not be severed. In most instances, parents continue treatment with their current medical team and refuse to subject their child to unproved methods. Nonetheless, they may experience guilt and anxiety about rejecting a possible "miracle cure. A commitment to care for the emotional needs of the patient and family, to provide pain control, if necessary, and not to abandon the family if the disease progresses, is essential. Each family searches for ways to cope with the renewed threat to life and to emotional equilibrium. As was the case during the first treatment course, coping patterns are influenced by treatment side effects, length of hospitalization, and concurrent stresses. The altered prognosis elicits feelings of sadness and fears of separation and loss; yet, an investment in "going on" persists. Maladaptive coping is manifested by an overly pessimistic attitude about the future that may immobilize parents in their dayto-day functioning. Crisis intervention with individual or family sessions can help the family to alter maladaptive coping. If another remission is achieved, the termination of active treatment often activates a crisis that requires additional education and support from the staff. Some parents do pursue complementary medicine and unproved methods of treatment or faith healing in addition to , or instead of, traditional or conventional care. Regardless of prognosis, the health care team should present to the family all the information regarding the success rate of conventional treatments. Should parents refuse to pursue conventional treatments, one should enlist the help of extended family members as well as clergy, if appropriate, as a way of convincing them not to turn their back on conventional care. Treatment Refusal When the child or adolescent refuses treatment, the underlying motivations may include hopelessness about the outcome, feelings of helplessness, loss of control, distress about the side effects of treatment, or a combination thereof. By refusing treatment, some adolescents are asserting their independence and are demonstrating that they are in charge of their own destiny. This is another situation in which preventive measures are far more effective than trying to intervene in a crisis. While the specific preventive measures should be tailored to the age of the adolescent, it is important to include the adolescent in the discussion and decision-making process from the beginning. Support groups for teenagers may be effective in this regard because the members confront one another when poor decisions are made, just as they share coping skills with one another and general support. In the event that staff and family must intervene during a crisis, the staff needs to calmly sort out which factors are influencing the decision and proceed in an orderly manner to discuss them. This situation can usually be handled directly by encouraging the parents to work collaboratively with the adolescent. For patients and parents who believe that treatment is hopeless, the risk-to-benefit ratio of further treatments must be presented clearly, particularly when the treatment is palliative. The distress and discomfort of side effects are the most common reasons for refusing further treatment. When Treatments are No Longer Effective Although survival of childhood cancer is more prevalent now than in the past, the course of cancer for some children is characterized by a series of treatment responses and relapses leading to a time when curative options are exhausted. There have been recent developments in how care is provided to children who may (or will) die that include consideration of psychosocial factors from earlier in the disease process than has typically been evidenced. The point at which curative treatments are unlikely to be successful is typically a crisis point for the family. This gap has been increasingly recognized, as the discordance among patients, families, and staff can be an obstacle to care. The staff members who have been most intimately involved with the child and family during the course of the disease ideally should be present at these meetings. The child may or may not attend these meetings, depending on his or her age, developmental stage, and other circumstances. If the child is not present, relevant information should be communicated to the child in a developmentally appropriate manner. Staff members who are closest to the child and family should be present at these meetings if the parents wish them to be present. The patient and family should be informed of both physical and emotional expectations and possibilities. Once they understand that treatment is no longer effective, parents begin the process of accepting that their child will die. Many of their thoughts focus on preparing for death (this may include rehearsing the funeral in their imaginations) while continuing to hope for cure or recovery. Guilt can be diminished in parents by simply informing them of the normality of these responses. Comprehensive care for the dying child involves maximizing physical and emotional comfort. Open communication, pain control, involvement with friends and family, distractions, and the maintenance of familiar routines all convey a sense of security that is important in reassuring the dying child. The family itself needs ongoing emotional support as well as specific information and assistance with difficult decisions and preparations.