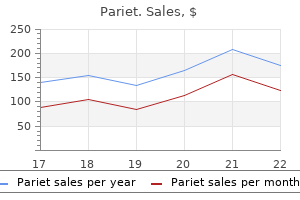
Best purchase for pariet
Other causes of pneumatosis include: post invasive procedure such as colonoscopy gastritis symptoms how long does it last generic pariet 20mg visa, idiopathic, cystic fibrosis, scleroderma, chemotherapeutic agents, and steroid therapy. Teaching Points the incidence of ischemic colitis is not entirely known because the majority of cases are transient and resolve spontaneously. Serum lactate may be elevated, and the patient may also have an increased white cell count and a metabolic acidosis. Possible causes include systemic hypoperfusion, venous thrombosis, arterial occlusion, embolism, and vasculitis. Ischemic colitis tends to occur in the watershed area of the colon: splenic flexure or rectosigmoid junction. Differential Diagnosis Diverticulitis: may show focal colonic wall thickening, but usually associated with diverticulosis and signs of sepsis with acute symptoms. Teaching Points Left-sided and sigmoid colon adenocarcinomas are much more common than right-sided colon cancers. Typical clinical symptoms of left-sided cancers include reduction in stool caliber, bright red blood per rectum, and colonic obstruction. Due to the larger caliber of and the more liquid consistency of stool in the right colon, findings of anemia and weight loss are more common with right than with left colon cancers. Of note, colon cancer may be associated with upstream or downstream colonic wall thickening, which may mimic a primary inflammatory rather than malignant process. For definitive diagnosis, colonoscopy may be required after acute symptoms resolve. However, if colonic obstruction is present, surgery may be required prior to other treatment. There is a polypoid mass along the posterior aspect of the cecal wall that extends in to the cecal lumen (arrow in right image). Differential Diagnosis Perforated inflammatory disorders of the ileocecal region such as appendicitis, cecal diverticulitis, and Crohn disease may be difficult to distinguish from perforated carcinoma, especially when there is a large abscess and marked inflammatory change. For example, associated diverticula, an inflamed appendix, or findings that would suggest Crohn disease. Teaching Points Perforation is one of the major complications of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Perforations may result in abscesses, fistulas to adjacent organs such as the bladder, stomach, and adjacent segments of bowel, pneumoperitoneum, or pneumoretroperitoneum. Perforated carcinomas may be difficult to distinguish from diverticulitis with perforation. Observation of the following features may be helpful to favor carcinoma over diverticulitis: asymmetric wall thickening of the colon, soft tissue mass-like thickening of the colon wall, or the presence of an intraluminal polypoid mass. Inflammatory stranding, lymphadenopathy, and pericolonic fluid may be present in both conditions. Management the management of perforated colon cancer may include diverting colostomy with partial or complete colectomy performed at a single operation or over multiple operations. Percutaneous drainage of the abscess and endoscopic stenting of the colon are adjunctive or alternative options depending upon clinical condition of the patient. Psoas abscess and cellulitis of the right gluteal region resulting from carcinoma of the cecum. Differential Diagnosis Cecal volvulus: the dilated loop of colon directed toward left upper abdomen, often with only one air-fluid level. Rectal gas is usually seen, particularly on a right lateral decubitus or prone lateral view. Large bowel obstruction due to other cause: dilated small bowel and colon proximal to the obstructing lesion. Teaching Points Sigmoid volvulus is the third leading cause of large bowel obstruction after diverticulitis and carcinoma in Western countries. In Western countries sigmoid volvulus is usually acquired from long-standing constipation, Parkinson disease, Alzheimer disease, or chronic debilitation. Radiographic findings include a "coffee bean" or "kidney bean" sign referring to a closed loop of sigmoid distended with gas, with apposed medial walls of dilated bowel forming an oblique line that resembles the cleft of a coffee bean. The dilated sigmoid classically points to right upper quadrant, but may be midline or left ward. Moderate or severe dilatation of the sigmoid with a sigmoid transition point is a more specific finding. Management Endoscopic or fluoroscopic decompression by barium enema is indicated if there are no contraindicating signs of bowel ischemia or perforation. Immediate surgical resection is performed when there is evidence of ischemia, perforation, or if decompression is unsuccessful. Bowel obstruction and perforation occur much less often in patients with colorectal lymphoma than with colorectal adenocarcinoma. Edema from ischemia, inflammatory bowel disease, or infectious proctitis may cause circumferential wall thickening. Teaching Points Primary colorectal lymphoma is a rare type of gastrointestinal lymphoma and may be clinically indistinguishable from colorectal adenocarcinoma. Patients with chronic immunosuppression, including patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection, are at increased risk for colorectal lymphoma. The signs and symptoms are relatively nonspecific, including abdominal pain, weight loss and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Morphologically, colorectal lymphomas may manifest as a polypoid mass, an annular and infi ltrating lesion, or as diff use, multifocal polyps. Management the treatment of primary rectal lymphoma is often surgical resection followed by multiagent systemic chemotherapy. Tumor transgresses the muscularis propria (white arrowheads) and extends in to the mesorectal fat (solid white arrow). Sagittal T2-weighted (right) image shows a distance of 4 cm from the inferior attachment of the rectal mass (asterisks) to the superior aspect of the anal sphincter (solid white line). Numerous lymph nodes with mixed signal intensity and ill-defined margins are present in the mesorectal fat (solid white arrows). Differential Diagnosis Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: are submucosal lesions that often have a prominent extraluminal component. Carcinoid: usually small submucosal masses of polyps when they arise in the rectum. The hypointense mesorectal fascia surrounds the mesorectal fat and is a natural plane for surgical resection. Stage T3 tumors disrupt the muscularis propria and extend in to the mesorectal fat with a nodular or spiculated advancing margin. Tumor extension within 6 mm from the mesorectal fascia has been shown to be associated with a high risk of local recurrence. Mesorectal lymph nodes with irregular borders or mixed signal intensity are suspicious for harboring foci of carcinoma, especially when larger than 5 mm. Punctate rounded calcifications are present in the rectal wall thickening (left) and in the perirectal fat (right) Differential Diagnosis Rectal adenocarcinoma: focal cancers may present with similar rectal wall thickening and associated luminal narrowing. Rectal carcinoma is more likely to demonstrate invasion with extension beyond the rectal wall and perirectal lymphadenopathy. Rectal lymphoma: patients with chronic immunosuppression are at increased risk for colorectal lymphoma. Inflammatory and infectious rectal wall thickening: may have a similar appearance. Teaching Points Colorectal hemangiomas are rare benign lesions that are a potential source of significant lowergastrointestinal bleeding. They commonly affect younger adults and are occasionally associated with Klippel-TrenaunayWeber syndrome, Maff ucci syndrome, blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome, and diff use neonatal hemangiomatosis. Clinically, patients may present with acute, recurrent, or chronic painless rectal bleeding. Enhancement with intravenous contrast may be seen and the mesenteric vasculature may be engorged. Serpentine borders and the presence of phleboliths are helpful distinguishing features. For nonsurgical candidates, alternate therapies reported in the literature include sclerotherapy, polypectomy, electrocautery, angiographic embolization, and irradiation.
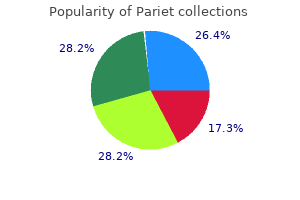
Purchase pariet uk
Because of the age-related decline in renal function symptoms of gastritis in cats order pariet 20 mg online, the use of metformin is often discouraged in patients who are more than 80 years of age. Furthermore, a possible increased risk of bladder cancer in patients taking pioglitazone is a concern. Insulin secretagogues, such as sulfonylureas, can cause hypoglycemia, and elderly patients may be particularly predisposed. Insulin therapy requires good visual and motor skills and cognitive ability of the patient or a caregiver, and it can cause hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia in older patients may be particularly difficult to identify and may be incorrectly diagnosed as irreversible cognitive impairment. Diabetes treatment can be improved in patients with visual impairments through the use of such devices as glucometers with large, easier-to-read screens, audio glucometers, magnifying glasses to help see syringes, or preloaded insulin pens. Estrogen therapy is controversial other than for treatment of severe postmenopausal symptoms, but it may have cardiovascular benefits if therapy is initiated early (near menopause). Testosterone therapy for older hypogonadal men is associated with consistent improvements in body composition (decreased fat and increased fat-free mass), but instituting therapy requires close monitoring especially with regard to cardiovascular status and prostate cancer screening. These changes have not been demonstrated to translate in to functional improvements, and treatment is associated with high rates of adverse events. Weight loss in obese elderly persons is associated with improvements in cardiovascular risk factors, but exercise may be needed to attenuate loss of muscle and bone mass during weight loss and to mitigate against frailty. Adequate calcium and vitamin D are essential for fall and fracture prevention and may improve pain from osteoarthritis. Most hormonal axes are associated with a gradual decline over time, beginning at about age 30 years, with the exception of the relatively rapid decline in estrogen associated with the female menopause. Serum total testosterone decreases with time in men, but numerous other independent health, lifestyle, and secular trends can accelerate the decline. Age-specific reference ranges for thyroid-stimulating hormone may be appropriate and have important implications in defining subclinical hypothyroidism in older adults. Occult hypoglycemia may be much more common in older patients, especially those treated with insulin, and the consequences of this on central nervous system and cardiovascular function must be carefully considered. To a greater or lesser extent, all managed care systems attempt to shift financial risk in one way or another to the providers of care. The panel of providers is published yearly in a directory that goes by a variety of names. However, your presence on the list as a subspecialist does not mean that you will ever receive referrals. When one looks at the managed care system from afar, it is not so different from any other business unit that has to negotiate with vendors to provide services that it cannot provide on its own. Think of a business unit as the cruise ship industry, which negotiates with its own employees, as well as with entertainers, doctors, food suppliers, fuel suppliers, ports, and travel agents, to provide its customers (passengers) a total package for their enjoyment. As pressure was placed on businesses with large numbers of employees who were not happy with the original types of plans and the costs of the yearly premiums of certain plans, many other insurance options were created. Plans can have different deductibles for office visits, hospitalizations, and brand-name versus generic medications. There are many more plans as insurance companies try to provide options to employers that meet the needs of employees but keep the cost down to employers. In some cases, an endocrinologist is employed by a faculty group practice of a large medical center or a large group practice, in which all members are participants in the specific plan. In general, the process of application, review of application, and final approval for participation can be quite long, maybe even more than 6 months. The patient must have in hand some kind of a referral form, either an authorization form or a special slip of paper giving you the specific authority to evaluate and treat the patient. Without the referral form or some kind of definite referral from the center, you will not be compensated for the consultation visit. Each subsequent visit must also be authorized in the same manner, or payment will be withheld. Naturally, the doctor wants to see the patient and has blocked out the time in his or her schedule for the visit. In general, you will be allowed to perform a history and physical examination and order simple diagnostic tests without hassle. This can be a problem because you may not know when or where the study is scheduled or when to have the patient return to discuss the results. Most endocrinologists trust the interpretations by one particular laboratory, often at a university setting. This particular problem is being addressed by the American Thyroid Association and the College of American Pathologists. Sometimes a physician will give the patient a discount to continue their professional relationship. At other times, patients feel so strongly about the opinion of their doctor that they pay the fee out of pocket to the physician, especially if the patient must be seen only once or twice a year. There are movements in Congress to allow the continuation of the patient-physician relationship. Until such time, the physician has to understand that losing patients in this way may be unavoidable. He or she should always welcome the patient back to his or her practice if the insurance situation changes. The doctor then turns the chart and superbill over to a clerical person, thus ending the patient-physician interaction of the day. A secretary or administrative assistant usually enters the charges and the diagnosis in to some type of physician management system, in which an insurance claim is generated and sent electronically or by paper to the insurance carrier. The carrier examines the claim, and eventually a check is cut to cover what the carrier deems appropriate. There was somewhat of an honor system in the past, whereby the insurance company trusted the physician explicitly. This becomes a personal and financial decision that each physician or group practice has to make. Physicians who are in solo practice or small groups must be aware of all the problems so that the decision to begin or continue seeing patients is made for the right economic reasons. Many doctors react out of fear and anger, the worst emotions to invoke when an economic decision has to be made. The practice must monitor collections, be on top of claims, and resubmit claims that were rejected, down-coded, or held for a long time without payment. The doctor must make sure that the collection of claims is not forgotten and that all claims are actively pursued, especially when third-party payment. Doctors or their staff must have a policy in force to ensure that referrals are obtained, claims are submitted on time, and proper payments are received. For those physicians new in practice, it may be worthwhile to see more and more patients, despite the associated problems. In addition, do not make a decision in anger, when a company denies payment or down-codes a series of claims without good reason. Work out the economics associated with leaving, rather than resigning out of anger. Then look at all these issues, and decide whether resignation is appropriate for economic reasons, not emotional ones. The decision to continue should be based on facts, rather than feelings: revenue tracking, handling of claims, and fee schedule. No one can say for sure what the ideal percentage should be, but some physicians use 10% to 15% as the ceiling for the cutoff. How many times did a billing clerk have to call the company before payment was finally received Each time a claim is not paid properly or promptly, administrative costs are associated with collecting these fees. In addition, talk to the secretaries to find out what kinds of hassles are encountered in receiving referrals, scheduling procedures, and getting laboratory tests done promptly. Try not to sign a document that expresses reimbursement in terms of a percentage of Medicare or some other baseline. Try to be specific in providing a list of office visit codes that will be used and agree on criteria for judging what documentation is required for each level.
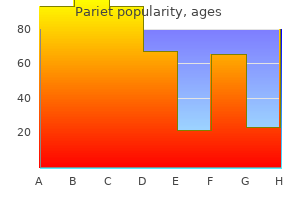
Buy genuine pariet on line
Difficulty in processing information as quickly and accurately as others Hyperactive behavior Inattentive behavior l gastritis and gas order pariet canada. Most symptoms (6 or more) are in the hyperactivity-impulsivity categories, and less than 6 symptoms of inattention are present. The majority of symptoms (6 or more) are in the inattention category and less than 6 symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity are present, although hyperactivity-impulsivity may still be present to some degree. These children have six or more symptoms each of inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity. Diagnosis is primarily clinical, using thorough clinical interview of parents and use of behavior rating scales. Neuropsychological evaluation using standard tests of general intelligence and edu cational achievement help to exclude learning disorders or mental retardation. Adverse effects are mild and include abdominal discomfort, loss of appetite, headache and sleep distur bances. Atomoxetine, a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, and extended-release preparations of selective a. Learning Disabil ities Learning disabilities arise from specific neurodevelop mental dysfunctions that prevent expected learning in one or more academic areas. The important defining principle is that such disabilities are unexpected when considering the overall intellectual functioning of the child. These disorders are not the result of global developmental delay, major vision or hearing handicap or consequences of major social or emotional stress. Others are dysgraphia (difficulty in writing), reading comprehension difficulty (inability to comprehend what is read) and dyscalculia (difficulty in performing mathe matical operations). Word decoding is the ability to apply principles of phonetics to sound the words, i. Secon dary consequences include reduced reading experience that can impede growth of vocabulary, written expression and background knowledge. They also have difficulty in spelling because of underlying problem with word decoding. The difficulty in reading impairs their ability to cope up with the academic syllabus and is often associated with low self-confidence and feeling of frustra tion, which increases the risk of developing psychological and emotional problems. Diagnosis of dyslexia is clinical, based on presence of unexpected difficulties in reading at the level of phono logic processing of words. Standardized tests are used to test speed, accuracy and comprehension in reading and spelling ability, in relation to the age and school grade. Affected children are best taught in small groups by teachers trained in the principle of phonics. Usually these programs improve the reading accuracy significantly and fluency to a lesser extent. For older children, the management stresses more on accommodation rather than remediation. There is difficulty in pronouncing the initial consonants caused by spasm of lingual and palatal muscles. Parents of a young child with primary stuttering should be reassured that stuttering between the age of 2-5 yr usually resolves on its own. Making the child conscious of his stutter or pressurizing him to repeat the word without stuttering will further increase the stress and the stutter. Children who continue to have significant stuttering require referral to a speech therapist. In older children with late onset of stuttering, the help of a child psychologist should be sought. Intelligence is variable, although most children fall in the functionally retarded category by conventional psychological testing. Testing for associated neurological disorders such as tuberous sclerosis and fragile X is recommended. Older children and adolescents with relatively higher intelligence but poor social skills and psychiatric symptoms. Factors associated with better prognosis are early diagnosis, intensive behavioral therapy, higher intelligence level and presence of functional speech. Children with better prognostic factors may grow up to be self-sufficient and employed, though socially isolated. On the other hand, those with poor prognosis remain dependent on family or require placement in facilities outside home. Data from developed countries suggest that 1 in 150 children is affected by such disorders. To meet full criteria for diagnosis, a child must demonstrate the following symptoms: (i) qualitative impairment in social interaction as manifested by two of the following: impairment in the use of multiple nonverbal behaviors. In Munchausen by proxy, the abusing caregiver gains attention from the relation ships formed with health care providers, or her own family as a result of the problems created. Apnea, seizures (which may be induced by suffocating the child or injecting insulin), fever, diarrhea and skin conditions are the common symptoms. Confirmation of diagnosis needs careful history and reviewing of past and current hospital records. Once the diagnosis is made, the offending caregiver should be confronted, separated from the child and provided psychotherapy. The overriding feature is the repetitive and persistent pattern of behaviors that violate societal norms and the rights of other people, for a period of at least one year. The diagnosis of conduct disorder is made if three or more of the above behaviors are present, with at least one having taken place in the previous six months. Various child behavior management techniques, such as positive reinforcement to increase desirable behavior, and extinction and time out to decrease problem behavior, are taught to the parents. The children are taught anger coping, peer coping and problem-solving skills, so that they are able to deal better with problematic interpersonal situations. Oppositional Defiant Disorder Oppositional defiant disorder is a repetitive and persistent pattern of opposition, defiant, disobedient and disruptive behaviors towards authority figures persisting for at least 6 months. Although the disorder does not include the more aggressive aspects of conduct disorder, many children go on to be later diagnosed with conduct disorders. The management should focus on alleviating known risk factors or stresses that might be contributing to the development of oppositional behavior. Juvenile Delinquency Children who show oppositional defiant behavior or conduct disorder and come in to conflict with the juvenile justice system because of such behavior are called juvenile delinquents. The term refers to a person under 18 yr who is brought to the attention of the juvenile justice system for committing a criminal act or displaying a variety of other behaviors not allowed under the law, such as, truancy, use of alcohol or illicit drugs. Family and parenting interventions have been shown to reduce the rate of re-incarceration and criminal behaviour by juvenile delinquents. In some cases, placement in foster care is recommended with similar interventions being administered by the foster family. Godbole, Vijayalakshmi Bhatia Adolescence is a stage of transition from childhood to adulthood. During this stage of life, a youth undergoes rapid changes in body structure, mediated by the sex hormones. The appearance of sexual characters is coupled with changes in cognition and psychology. Whereas adolescence refers to this entire process, puberty refers to the physical aspect. The age group 10-19 yr is considered as the period of adolescence, and puberty marks the early half of adolescence. Though it is a continuous process, for convenience sake, adolescence is generally divided in to three phases: early (10-13 yr), mid (14-16 yr) and late (1719 yr) puberty. Mild degree of breast enlargement is normally seen in more than half of boys in early puberty which subsides spontaneously over several months. Physical Growth and Nutritional Requirements During puberty, boys gain about 20-30 cm and girls about 16-28 cm. Peak growth velocity in girls occurs before attainment of menarche (stage 3) in girls whereas boys have their peak growth velocity during later stages of puberty (stages 4-5). The growth spurt affects the distal skeleton first, hence enlargement of limb and extremities is followed by increase in trunk size.
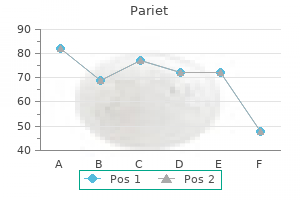
Order 20 mg pariet fast delivery
The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends treatment at $ 5 mg daily of prednisone gastritis diet vanilla pariet 20 mg low cost. No clinical finding, laboratory test, or other radiographic examination is able to reliably identify individuals with osteoporosis. Conventional radiographic techniques are not sensitive enough to diagnose osteoporosis as they do not reliably detect bone loss until 30% to 40% of bone mineral is lost. Although bone densitometry may determine low bone mass, it cannot identify the etiology of the bone loss. Thus, bone densitometry must be used with a complete clinical evaluation, laboratory testing, and other diagnostic studies to determine the cause of and the most appropriate treatment for osteoporosis. Although decreased bone mass is the primary determinant of whether a bone will fracture, bone architecture and geometry are also important factors contributing to bone strength. The relationship between bone mass and fracture risk is more powerful than the relationship between serum cholesterol concentration and coronary artery disease. All bone densitometry techniques determine the amount of calcium present in bone by utilizing an ionizing radiation source (either from a radionuclide or from an x-ray tube) and a radiation detector. Bone densitometry is based on the principle that bone absorbs radiation in proportion to its bone mineral content. The bone mineral content of the bone (or a region of interest within a bone) is then divided by the measured area. The more complex and denser the bone structure, the greater will be the attenuation of the ultrasound wave. It has the best correlation with fracture risk, requires relatively short scanning times (, 5 minutes), determines bone mass in all areas of the skeleton with high accuracy and reproducibility (precision), and is associated with a small radiation exposure. Printout of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan of the hip (personal data deleted). Because the T-score is a good predictor of future fractures, it is used to diagnose osteoporosis. This finding should prompt a search for associated medical or lifestyle conditions (current or in the past) that may have accelerated bone loss or prevented the patient from reaching peak bone mass. Thus, these definitions should be applied to other ethnic groups or to men with caution. The clinician needs to understand which database is being used to generate the T- and Z-scores. Vertebral fractures are the most common of all osteoporotic fractures, occurring in 15% of women 50 to 59 years of age and in 50% of women 85 years or older. The majority of these vertebral fractures are classified as mild, with a reduction in height of not more than 20% to 25%. They may be asymptomatic, often occur in the absence of specific trauma, and frequently do not come to clinical attention or are underreported when radiographic studies are performed. Treatment guidelines that rely exclusively or predominantly on a densitometric diagnosis of osteoporosis to select patients for treatment will miss many patients with T-scores greater than 22. Therefore, it is recommended that this tool be used for untreated postmenopausal women or men older than 50 years who have T-scores between 21. The tool has not been validated in patients currently or previously treated with medications for osteoporosis. Measurement of bone mass at any skeletal site has value in predicting fracture risk. However, the bone density of the hip is the best predictor of hip fractures (the osteoporotic fracture with the greatest mortality and morbidity). The bone mass of the hip also predicts fractures at other sites, as well as do bone mass measurements at those sites. Although there is significant concordance between skeletal sites in predicting bone mass, there is still enough discordance in bone mass at various sites that single bone mass measurements should not be relied on to diagnose osteoporosis. Thus, bone mass should be measured at both the hip and the spine, and the diagnosis of osteoporosis should be based on the lowest T-score. Images of several skeletal sites scanned by a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry bone densitometer. However, the forearm appears to be the best site to assess the effects on bone of excess parathyroid hormone associated with primary hyperparathyroidism. Peripheral bone mass measurements have not been shown to be useful for monitoring the effects of therapy for osteoporosis because changes in bone density occur very slowly at this site. In contrast, the average amount of early postmenopausal bone loss from the spine is 1% to 2% per year. Degenerative changes, oral contrast agents used for other radiographic studies, and osteophytes all falsely elevate the measured spine bone density. Anatomic distortions such as lumbar disc disease, compression fractures, scoliosis, prior surgical intervention, and vascular calcifications in the overlying aorta also affect the accuracy of spine measurements. No clinical finding, laboratory test, or other radiographic examination can reliably identify people with low bone mass. Blake G, Fogelman I: Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry and its clinical applications, Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 6:207, 2002. Hamdy R, Petak S, Lenchik L: Which central dual x-ray absorptiometry skeletal sites and regions of interest should be used to determine the diagnosis of osteoporosis Lenchik L, Kiebzak G, Blunt B: What is the role of serial bone mineral density measurements in patient management Miller P: Bone mineral density-clinical use and application, Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 32:159, 2003. Osteomalacia is a disorder of mature (adult) bone, whereas rickets occurs in growing bone. Although rickets and osteomalacia were initially viewed as distinct clinical entities, the same pathologic processes may result in either disorder. In both conditions, mineralization of newly formed osteoid (the bone protein matrix) is inadequate or delayed. In individuals with rickets, defective mineralization occurs in both bones and cartilage of the epiphyseal growth plates and is associated with growth retardation and skeletal deformities that are not typically seen in adults with osteomalacia. In the United States at the beginning of the 20th century, rickets due to a deficiency of vitamin D was common in urban areas. In the 1920s, rickets was virtually eliminated by an appreciation of the antirachitic properties of sunlight and the use of cod liver oil (which contains vitamin D). However, with the development of effective treatments for previously fatal diseases that affect vitamin D metabolism (such as chronic renal failure) and with an improved understanding of both vitamin D and mineral metabolism, many additional syndromes with osteomalacia or rickets as a feature have emerged. Many later studies have demonstrated that undiagnosed vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency is common in the United States, and for a significant number of adult women with osteoporosis, vitamin D insufficiency may be an unsuspected component of their bone loss. Thus, any disease that results in decreased availability to bone of either calcium or phosphorus may result in osteomalacia or rickets (Table 11-1). Causes of osteomalacia and rickets fall in to three categories: (1) disorders associated with abnormalities of vitamin D metabolism or action that limit the availability of calcium for mineralization of bone, (2) disorders associated with abnormalities of phosphorus metabolism, and (3) a small group of disorders in which there is normal vitamin D and mineral metabolism. Studies have now suggested possible other roles for vitamin D in cardiovascular and neurologic diseases, insulin resistance and diabetes, malignancies, autoimmune conditions, and infections. However, many elderly Americans are at risk for occult vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency because of sun avoidance, sunscreen use, an age-related decrease in dermal vitamin D synthesis, impaired hepatic and renal vitamin D hydroxylation, and diminished intestinal responsiveness to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Celiac disease or sprue, regional enteritis, intestinal bypass surgery, partial gastrectomy, chronic liver disease, primary biliary cirrhosis, pancreatic insufficiency, chronic renal failure, and certain medications have also been associated with the development of osteomalacia. Hypophosphatemic rickets, which is transmitted as an X-linked dominant trait, is the most common inherited form of rickets. Chronic renal failure is associated with several bone diseases: osteomalacia or rickets, adynamic bone, osteitis fibrosa cystica (due to long-standing secondary hyperparathyroidism), and a combination of both osteomalacia and osteitis fibrosa cystica (termed mixed renal osteodystrophy). Rickets or osteomalacia is usually a late finding in the course of the kidney disease and is rarely seen before patients begin dialysis. When symptomatic, osteomalacia may manifest as diffuse skeletal pain (often aggravated by physical activity or palpation), muscle weakness, and sometimes muscle wasting.
Diseases
- Photosensitive epilepsy
- Hemangioma thrombocytopenia syndrome
- Kashani Strom Utley syndrome
- Achalasia-Addisonianism-Alacrimia syndrome
- Contact dermatitis, photocontact
- Woods Leversha Rogers syndrome
- Chromosome 1, monosomy 1q4
- Schizotypal personality disorder
Buy discount pariet 20 mg
For thyroid cancers of medium size bile gastritis diet buy pariet 20mg without prescription, patient-specific selection is indicated for determining whether to use radioiodine therapy. In the absence of other forms of contamination (contrast agents or iodine-containing medications such as amiodarone), 1 week of a strict low-iodine diet is usually adequate to deplete the body of competing nonradioactive iodine. For remnant ablation, recent prospective data demonstrates that a dose of 30 mCi has efficacy similar to 100 mCi. For locally invasive and distant metastatic tumors, larger doses may be indicated. The treatment is designed to eradicate residual thyroid cancer after surgery, but patients should have a scan approximately 3 to 10 days after treatment to visualize radioiodine uptake and rule out or detect metastatic disease. The main acute complications are dry mouth, transient taste alteration, and sialadenitis. Up to 40% of patients will experience at least one side effect, but these effects generally resolve more than 90% of the time. There is a statistically significant, dose-dependent increased risk of secondary malignancy with radioiodine, but the absolute risk is very small (,10 cases/10,000 patient-years). Tg is a precursor protein for thyroid hormone that is released in to the blood by the thyroid gland and by most differentiated thyroid cancer cells. Thus, in the absence of a thyroid gland, Tg is an excellent thyroid cancer tumor marker. It correlates roughly with the mass of thyroid cancer present and can be followed for evidence of tumor growth or stability. Therefore, in the presence of TgAbs, assessment of disease presence based on Tg measurements should be made with caution. Tg can also be measured from lymph node aspirates after washing the needle with saline solution and running the wash in the Tg assay. Even in the absence of cytologically detectable thyroid cancer in a lymph node aspirate, a positive Tg wash indicates thyroid cancer metastasis to that lymph node. In metastatic disease, this is a poor prognostic sign that suggests a need for aggressive therapy, especially when lesions are growing on cross-sectional imaging. Treatment of gross, unresectable residual disease in the neck, painful bone metastases, or other metastases that threaten critical structures. This drug has relatively high toxicity and low efficacy, and in the era of targeted therapies, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, it is rarely prescribed. There is a slight female predominance, and the mean age at diagnosis is approximately 50 years. These should not be monitored more often than every 3 months because fluctuations in these levels can cause false reassurance or panic if they are checked too often. A doubling of the value of these markers in less than or more than 24 months generally predicts progressive disease or general stability of lesions, respectively. A doubling time of less than 6 months indicates a very poor prognosis, with increased mortality and 10-year survival of less than 10%. A doubling time of more than 24 months predicts no or rare deaths in up to 10 years of follow-up. Doubling times between 6 and 24 months have intermediate mortality risks (,25% to 35%). They are multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors that are generally well tolerated and result in stasis of previously progressive lesions in the majority of patients. Standard chemotherapies tend to be relatively toxic with limited efficacy but are reasonable treatment options if vandetanib is ineffective. One-year survival rates range from 10% to 20%, although there are some long-term survivors. The classic presentation is a rapidly expanding neck mass, usually associated with pathologically enlarged lymph nodes, and often with hoarseness, dysphagia, and possibly hemoptysis. Cross-sectional imaging is appropriate for evaluation of distant metastases because these are often evident at initial presentation. In patients who are candidates, complete surgical resection of the primary tumor results in prolonged survival. Frasoldati A, et al: Role of thyroglobulin measurement in fine-needle aspiration biopsies of cervical lymph nodes in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer, Thyroid 9:105-111, 1999. Mallick U, et al: Ablation with low-dose radioiodine and thyrotropin alfa in thyroid cancer. Thornton K, et al: Vandetanib for the treatment of symptomatic or progressive medullary thyroid cancer in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease: U. Today, the prognosis is significantly improved if appropriate therapy is initiated early; however, the mortality rate continues to be approximately 20%. Thyroid storm usually occurs in patients who have unrecognized or inadequately treated thyrotoxicosis and a superimposed precipitating event, such as thyroid surgery, nonthyroid surgery, infection, or trauma. Tachycardia is usually present, and tachypnea is common, but the blood pressure is variable. Cardiac arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, and ischemic heart symptoms may develop. These hormone levels, however, cannot reliably distinguish patients with thyroid storm from those who have uncomplicated thyrotoxicosis. Other common findings include anemia, leukocytosis, hyperglycemia, azotemia, hypercalcemia, and elevated liver enzymes. If the diagnosis is strongly suspected, waiting for the results of tests may cause a critical delay in the initiation of effective lifesaving therapy. The immediate goals are to decrease thyroid hormone synthesis, to inhibit thyroid hormone release, to reduce the heart rate, to support the circulation, and to treat the precipitating condition. Because beta1-adrenergic receptors are significantly increased in patients with this condition, beta1-selective blockers are the preferred agents for heart rate control. Plasma exchange and plasmapheresis can be lifesaving measures in patients with thyroid storm who have not adequately responded to the foregoing standard measures. Myxedema coma is a life-threatening condition characterized by an exaggeration of the manifestations of hypothyroidism. Today, the outlook is much improved for appropriately treated patients; the mortality rate in more recent studies has varied from 0% to 45%. Myxedema coma usually occurs in older patients who have inadequately treated or untreated hypothyroidism and a superimposed precipitating event. Important events include prolonged cold exposure, infection, trauma, surgery, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, pulmonary embolism, stroke, respiratory failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, and administration of various drugs, particularly those with a depressive effect on the central nervous system. The electrocardiogram often shows sinus bradycardia, various types and degrees of heart block, low voltage, and T-wave flattening. The normal total body pool of T4 is about 1000 mg (500 mg in the thyroid, 500 mg in the rest of the body). Thyroid storm is a life-threatening form of severe thyrotoxicosis that usually has a precipitating factor and a high mortality rate if it is not treated promptly and appropriately. When thyroid storm is diagnosed or suspected, treatment with antithyroid drugs, cold iodine, betablockers, and stress doses of glucocorticoids, along with management of any precipitating factors, should be promptly initiated. Myxedema coma is a life-threatening form of severe hypothyroidism that often has a precipitating cause and a high mortality rate if it is not promptly and adequately treated. When myxedema coma is diagnosed or suspected, management should include rapid repletion of thyroid hormones, stress glucocorticoid doses, and treatment of any precipitating causes.
Order pariet 20mg
Hence gastritis fatigue order 20 mg pariet free shipping, internationally, fibrinolysis remains the most commonly used reperfusion therapy. Thrombolytic agents have a common goal: the generation of plasmin that lyses the clot. Physiologically, the plasminogen activator system forms plasminogen that binds to the clot surface to lyse the clot,199 opposing thrombus formation. These effects may be important in provoking a thrombotic response in the presence of minor endothelial damage. This process, when chronic, can promote accumulation of intravascular fibrin, which may then be invaded by proliferating vascular smooth muscle cells and circulating progenitor cells gradually to form a cellular neointima in the fibrin-rich clot. These effects could provoke a delayed thrombotic response in the presence of minor endothelial damage. Dramatic reductions in mortality can be achieved if treatment is obtained during the "golden" first hour. Overall, during the first 1-3 hours of symptoms, the time to treatment is critical, whereas later when the patient is on the "flat" part of the curve time is less of a factor and opening the infarct-related artery is the priority. In this later time, a mechanical approach is superior to fibrinolytic agents that have lesser effectiveness on more mature coronary artery clots. Hence it is relatively "clot selective," although in clinical doses some systemic effects do occur. The very short half-life of alteplase mandates co-therapy with intravenous heparin to avoid reocclusion. As with the other fibrinolytics (see later), aspirin 300 mg should be given as soon as possible. Clopidogrel 300 mg followed by 75 mg per day (no loading dose in patients 75 years old or older) should also be commenced. Side effects and hence contraindications relate chiefly to hemorrhage, for example, risk of hemorrhage or hemorrhagic stroke (Table 9-7). Gentamicin sensitivity is a specific exclusion for alteplase therapy because gentamicin is used in the preparation of alteplase. An important disadvantage of alteplase is its cost, which is approximately five times that of streptokinase. Reteplase Reteplase (Retavase) is a deletion mutant of alteplase with elimination of the kringle-1, finger, and epidermal growth factor domains, as well as some carbohydrate side chains. This results in prolonged plasma clearance, so that a double-bolus regimen (10 U110 U intravenously, each over 10 minutes and 30 minutes apart) can be used. Heparin must not be given through the same intravenous line (physical incompatibility). It has no direct effect on plasminogen, but rather works by binding with plasminogen to form a 1:1 complex that becomes an active enzyme to convert plasminogen to plasmin. In addition, streptokinase may increase circulating levels of activated protein-C, which enhances clot lysis. The second and third generation of thrombolytics are superior drugs, but streptokinase is cheap and still widely used in many parts of the world. First, in an analysis of 68,000 patients (all of whom received aspirin, 93% of whom received fibrinolytic therapy and many of whom received streptokinase), the benefits of added heparin translates in to a benefit/risk ratio of five deaths and three infarctions prevented at a cost of three transfusions per 1000 patients treated and a nonsignificant increase in stroke. Contraindications are similar to those against alteplase, with the exception of gentamicin sensitivity. Additional contraindications are (1) major recent streptococcal infection, because antistreptococcal antibodies cause resistance to streptokinase; and (2) previous treatment by streptokinase, because the antibodies diminish efficacy and there is an increased risk of allergy. Several large trials randomizing over 100,000 patients have compared the effects of streptokinase and alteplase. In patients with alteplase and three risk factors, the probability is more than 3%. Trial, there was a 14% relative and a 1% absolute mortality reduction with alteplase infused over 90 minutes compared with streptokinase,211 at the cost of two extra strokes per 1000 patients randomized. Thus when stroke reduction is important (as in older adults), streptokinase may be better (and much cheaper). The bolus agents are more convenient, simpler to use, and help to reduce medication errors. Attention is also switching to improvements that can be achieved by lessening reperfusion injury. Some degree of resistance of thrombi to lysis can be expected in perhaps 10%-15% of patients; the cause may include deep fissuring or rupture of the plaque or platelet-rich thrombus, which is very resistant to lysis. The Western world has established the necessary network to hasten the procedure with ever-shortening pain-to-balloon times. The potential for greater improvements in patient outcomes can be achieved with improved delivery of care rather than by the potential gains achieved by switching therapeutic strategies. Physicians also need to be educated and motivated to participate in community activities to educate patients to not waste the "golden hour. Adherent, activated and aggregated platelets (the three As) form the thrombus by a series of events initiated by tissue factor, which becomes exposed when a plaque ruptures or the endothelium is injured. This well-tested, widely used, and cheap antiplatelet agent is beneficial in a wide variety of vascular disorders, including the prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease. In the past, primary prevention by aspirin was considered only for high-risk patients. Clopidogrel has fewer serious side effects, especially thrombocytopenia, than ticlopidine. There is no complete antidote for overdosing although protamine reverses the antithrombin effect. The chosen regimen may differ between interventional and noninterventional centers. When intervention is likely, bivalirudin has excellent data, whereas if a conservative strategy is employed, fondaparinux is well tested in combination with fibrinolysis. Anticoagulation with warfarin is essential for those with prosthetic mechanical heart valves. Two, major problems with warfarin are, first, the genetically induced large interpatient variation in the dose required, and, second, the serious risk of intracranial hemorrhage as use of warfarin in older adults has increased as world populations age. The risk of brain hemorrhage can be predicted by genetic profiling where available and affordable, and lessened by using the new oral agents. Oral thrombin inhibitors such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban compare well with warfarin in large-scale studies, often giving better outcome reduction. Their major advantage is a fixed oral dose that needs no monitoring, and reduced intracranial bleeding versus warfarin. Increased bleeding is usually not serious, but if it occurs, there is no tested antidote. The next development could be therapy aimed at reduction of reperfusion injury in the ambulance. If this is achieved, overall gain is far greater than the difference between reperfusion regimens. Unfortunately, many patients, including those at highest risk, receive no reperfusion therapy at all. Jessica Opie, Senior Laboratory Haematologist, Groote Schuur Hospital and University of Cape Town, South Africa. Hemostatic therapy in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage associated with the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran. Collaborative meta-analysis of randomized trials of antiplatelet therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction and stroke in highrisk patients. Effects of thrombin inhibition on the development of acute plateletthromubus deposition during angioplasty in pigs. Inflammation, aspirin and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. Aspirin-resistant thromboxane biosynthesis and the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death in patients at high risk for cardiovascular events. Aspirin and clopidogrel drug response in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: the role of dual drug resistance.
Purchase pariet 20 mg with visa
Second gastritis diet in telugu generic pariet 20 mg on line, this term avoids confusion with airways diseases, namely bronchiolitis obliterans. This is a nonspecific finding, but in a smoker with chronic symptoms, desquamative interstitial pneumonia is the favored diagnosis. Peripheral and peribronchovascular consolidation, often with a nodular or mass-like appearance, and irregular margins, is seen bilaterally. This manifests as a ring or partial ring of consolidation surrounding a central region of clearing or ground glass opacity. Organizing pneumonia typically presents with consolidation as the predominant abnormality. A peripheral rim of consolidation (yellow arrows) surrounding a central area of clearing or ground glass opacity (red arrows) is called the atoll or reversed halo sign. Patchy subpleural and peribronchovascular mass-like regions of irregular consolidation are present. There are multiple possible causes of organizing pneumonia, one of which is drug toxicity. If imaged early in its course, the abnormalities may have a peripheral distribution, but then quickly become diffuse in nature. Patchy, bilateral mass-like regions of consolidation and ground glass opacity are seen in a patient with chronic symptoms and no contributing history or exposures. The clinical presentation is usually that of the underlying systemic disorder, although chronic dyspnea and dry cough may be present. Although this appearance is nonspecific, in this clinical setting, lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia is a possible diagnosis. These findings are quite nonspecific, and thus, the clinical history is important in diagnosis. Nodules, when present, may be more suggestive of the diagnosis in the appropriate clinical setting and are usually centrilobular or perilymphatic in distribution. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia manifesting as multiple large nodules or masses. Respiratory bronchiolitis, respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease, and desquamative interstitial pneumonia: different entities or part of the spectrum of the same disease process Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: report of an American Thoracic Society project. While patients tend to present with a single pattern, an overlap of more than one pattern is sometimes seen. These include pulmonary edema, vasculitis, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary hemorrhage, pleural or pericardial effusion, lung nodules, bronchiectasis, constrictive bronchiolitis, and esophageal dilatation. For instance, the serology Scl-70 is relatively specific for a diagnosis of scleroderma. While this may be seen with any connective tissue disease, it is most common with rheumatoid lung disease. Basilar predominant fibrosis is present with irregular reticulation and traction bronchiectasis. Cysts are typically thin walled and limited in number and vessels may be seen in association with their walls. Follicular bronchiolitis represents localized lymphoid infiltration of bronchioles. Lung cysts are thought to reflect the presence of air trapping associated with follicular bronchiolitis. Cysts are seen in association with ground glass opacity in a patient with polymyositis. Small areas of ground glass opacity appear to have a centrilobular distribution (arrow). Centrilobular nodules of ground glass opacity are noted, associated with mild bronchial dilatation. Note that the nodules are located at a distance from the pleural surfaces (arrow) and are evenly spaced from one another. Ground glass opacity is less common and typically seen in immunosuppressed patients. Smooth interlobular septal thickening as an isolated finding suggests pulmonary edema. The combination of ground glass opacity and interlobular septal thickening, the crazy paving pattern, may be seen with any of these patterns. The severity of constrictive bronchiolitis may vary from patchy and lobular to diffuse lung involvement. Consolidation, ground glass opacity, nodules, and tree-in-bud opacities are typically absent. Image through the lung bases (B) shows bronchiectasis in association with mosaic perfusion. Airways and vascular causes of mosaic perfusion are often distinguishable by their morphology. The mosaic perfusion associated with airways disease often involves smaller lung regions, is patchy in distribution, and may show lobular regions of decreased lung attenuation. Mosaic perfusion from vascular disease is typically more extensive, peripheral, and non-lobular in appearance. Mosaic perfusion from airways disease (A) appears as sharply demarcated, lobular areas of decreased lung attenuation (arrows). Vascular disease, such as chronic pulmonary embolism (B) appears as larger, peripheral, non-lobular areas of decreased lung attenuation. Enlargement of the main pulmonary artery (yellow arrows) is present in a scleroderma patient with pulmonary hypertension. The degree of pulmonary hypertension is out of proportion to the severity of lung findings, suggesting vasculitis. Pulmonary Hypertension Pulmonary hypertension is a relatively common manifestation of collagen vascular disease. Pulmonary hypertension may be due to parenchymal lung fibrosis or pulmonary vascular disease. The vascular disease may be due to vasculitis, arterial fibrosis, chronic pulmonary emboli, or in situ thrombus. This is particularly true during the initial presentation of a patient with diffuse lung disease. Effusions are not typical of other causes of diffuse lung disease such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma) Progressive systemic sclerosis, or scleroderma, is a systemic disorder with primary manifestations of skin thickening and tightening. Pathologically this patient with mixed connective tissue disease had more than one interstitial pneumonia pattern present. Patchy, bilateral ground glass opacity and cysts correspond to lymphoid interstitial pneumonia. Pulmonary hypertension may also be seen in scleroderma patients due to either the parenchymal lung disease or vascular disease. Late disease with severe fibrosis shows extensive traction bronchiectasis and irregular reticulation. Rheumatoid nodules are a rare manifestation and patients are typically asymptomatic. As with any cause of cavitary nodules, rheumatoid nodules may be complicated by bronchopleural fistula. Disorders involving the renal, neurologic, and hematological systems are common as well. Honeycombing (A, yellow arrow) and mild traction bronchiectasis (B, red arrow) are seen in the subpleural lung regions. Patients with multiple episodes of pulmonary hemorrhage may eventually develop fibrosis. Pleural or pericardial effusions may be seen in isolation or associated with lung disease. Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis the features of myositis include muscle weakness, arthritis, and constitutional symptoms.
Order pariet 20 mg
Systematic review of trials using vasodilators in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Why a new approach is needed gastritis dieta order cheap pariet on line. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research Network: a controlled trial of sildenafil in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pharmacology of macitentan, an orally active tissue-targeting dual endothelin receptor antagonist. Impact of first-line sildenafil monotreatment for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Fasudil reduces monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension: comparison with bosentan and sildenafil. Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulation prevents fibrotic tissue remodeling and improves survival in salt-sensitive Dahl rats. Antiserotonergic properties of terguride in blood vessels, platelets, and valvular interstitial cells. Hemodynamic predictors of survival in scleroderma-related pulmonary arterial hypertension. Fenfluramine-induced gene dysregulation in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Delayed recovery in peripartum cardiomyopathy: an indication for long-term follow-up and sustained therapy. Current status on knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy on peripartum cardiomyopathy: a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on peripartum cardiomyopathy. Evaluation of bromocriptine in the treatment of acute severe peripartum cardiomyopathy: a proof of concept pilot study. Although hypertension is easy to treat, it is often difficult to manage optimally, as most patients will require lifestyle modification plus combination therapy with two, three, or more antihypertensive drugs of different mechanisms of action (Table 7-1). Asymptomatic patients often will not stay on therapy, particularly if it makes them feel weak, sleepy, forgetful, or impotent. It must constantly be considered that hypertension is usually multifactorial in cause, that different drugs act on different mechanisms. In the future such matching should be much more efficient, especially if genetic profiling ever becomes feasible. Note major mechanisms: 1, Increased adrenergic drive as found especially in younger hypertensives. As will be noted, prevention should be our primary goal but, lacking that, effective treatment can slow if not stop its insidious damage to the heart, brain, and kidneys. Therefore more than a few measurements in the office are almost always needed to establish its level and range. Because hypertension is frequently multifactorial in origin, it may be difficult to find the ideal drug for a given patient and drug combinations are often used. Hypertension also kills by renal failure and cerebral complications such as stroke. The diagnosis has been made in 10% to 20% of unselected patients and is associated with an eventual risk comparable to that of sustained hypertension. Thus the emphasis must be on lifestyle changes (aerobic exercise, no smoking, no stimulant drugs, reduced caffeine and alcohol). Arterial stiffness is an independent predictor of cardiovascular events and mortality in hypertensive patients, especially in older adults. Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity is now considered the gold standard for arterial stiffness assessment in daily practice. Use of blood pressure lowering drugs in the prevention of cardiovascular disease: metaanalysis of 147 randomised trials in the context of expectations from prospective epidemiological studies. Although its short-term danger is minimal, it eventually poses a hazard with the likelihood for cardiovascular events that is 68% of that seen with sustained hypertension. Contrariwise, a more radical view is that prehypertension may warrant drug therapy, as supported by the epic metaanalysis by 147 studies on nearly 1 million people. With knowledge of overall risk, appropriate therapy for hypertension and the need for additional treatments for other risk factors can be determined (Table 7-2). The presence of target organ damage generally mandates faster and more intensive therapy. Lifetime Risk versus Current Risk In a very large study, 61,585 American men and women were followed from age 55 for 700,000 person-years. Currently available medications should cause little if any bother (except financial) to the patient, but there remains uncertainty regarding how to provide maximal protection. Based on and modified from recommendations of European Societies of Cardiology and Hypertension. Associated clinical conditions: cerebrovascular disease including transient ischemic attack, angina or myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, renal impairment, proteinuria, peripheral vascular disease, and advanced retinopathy. In patients with diabetes or renal damage 130/80 is a generally accepted goal that should be upheld27 even though disputed. Counseling of those who are overweight is of minimal value over time48 and, for the increasing number who are markedly obese, bariatric surgery may be the only hope. Intermittent external counseling by itself does not seem to work to prevent weight gain50 or to increase physical activity,51 and perhaps only a program that integrates home, school, and community would work. The ideal diet is low in calories, rich in fresh rather than processed foods, and high in fruits and vegetables (and hence high in potassium) besides being low in fat and sodium. Other measures include increased aerobic exercise, cessation of smoking, and moderation of alcohol. Smoking is an independent risk factor for coronary heart disease and stroke, besides increasing the risk of malignant hypertension. Whereas in low-risk groups, many hundreds of patients must be treated to prevent one stroke, in very high-risk groups, such as older adults, only 20 to 25 patients need to be treated for 1 year to prevent one cardiovascular event, including stroke. The well-known Framingham tables and several websites aid the assessment of risk factors. The new European guidelines show color-coded tables, with the highest risk of 10-year fatality being in red and the lowest in green. The evidence for additional protection in hypertensive patients by improvements in blood lipids and other features of the metabolic syndrome is presented in Chapters 11. Overall Aims of Treatment Reducing cardiovascular risk safely is the sole aim of therapy. In other studies of older adults with isolated systolic hypertension, a decrease of diastolic pressure to less than 65 mm Hg increased the risk of stroke and coronary heart disease. Patients with concomitant renal disease seem particularly susceptible to systolic levels less than 130 mm Hg. Unexpectedly, factors that contribute to albuminuria may contribute to cognitive decline, suggesting that both conditions share a common microvascular pathogenesis. For many years, a great deal of attention, energy, and money has been spent in deciding which drug is the best choice for initial therapy and which combination is best for eventual therapy. Central sympatholytics are limited by their side effects, and outcome trials have shown that a- and b-blockers are inferior in lowering the incidence of heart failure and strokes, respectively, compared with other drugs. The expectation is that the eighth report due soon will support chlorthalidone as the low-dose diuretic of choice. The European Hypertension Society39 recommends whatever class seems most appropriate for the patient, whereas the World Health Organization29 states that any class may be used but a diuretic is preferred. Thus two out of the three major guidelines suggest a low-dose diuretic as the first choice for uncomplicated patients; this recommendation is reinforced when cost is factored in to the equation. However, in most developed countries, including the United States, diuretics are used in only approximately 30% of patients. Although the details vary somewhat, the tabulation based on the 2007 European guidelines fits most situations very nicely (Table 7-3). If these various guidelines are followed, the use of low-dose diuretic therapy should markedly increase. Thus adherence and excellent physician-patient relationships become essential, as repeated studies show that as the number of drugs that should be taken increases, the number of drugs actually taken decreases. Serum potassium levels should be measured before initiating eplerenone and then monitored regularly to avoid hyperkalemia. However, it should be noted that in the overall hypertensive population, the response rate. Compliance and Adherence There are two different yet complementary approaches, the first to target known high-risk patients, and the second to achieve better adherence of the wider population with less severe but more common hypertension levels in the community.