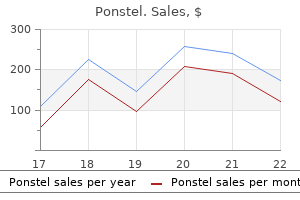
250 mg ponstel amex
Endometriosis occurs in many of these patients quinine muscle relaxant cheap 250mg ponstel with mastercard, presumably secondary to the enforced retrograde menstrual flow. There are many causes of chronic pelvic pain in young women, including psychosomatic factors. It is important to realise that endometriosis should be excluded in chronic pelvic pain that has not responded to simple measures. Re-examination of the age limit for defining when puberty is precocious in girls in the United States: implications for evaluation and treatment. The Drug and Therapeutics and Executive Committees of the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society. Interpreting the continued decline in the average age at menarche: results from two nationally representative surveys of U. Fertility rates in female patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Continuous versus cyclic use of combined oral contraceptives for contraception: systematic Cochrane review of randomized controlled trials. The levonorgestrel intrauterine system (Mirena) for the treatment of menstrual problems in adolescents with medical disorders, or physical or learning disabilities. Uterus didelphys, obstructed hemivagina, and ipsilateral renal agenesis: the University of Minnesota experience. Tests for bleeding disorders should be performed for any girl with moderate to severe menorrhagia. This is mirrored in cyclic endometrial preparation in the uterus for implantation of a pregnancy or cyclic menstruation in the absence of implantation. Understanding the regulation of ovarian and menstrual function is therefore crucial to the rational management of many gynaecological disorders. These include delayed puberty, amenorrhoea, anovulatory infertility, abnormal uterine bleeding and also ovarian stimulation in assisted reproduction treatment. Some of these exert a stimulatory effect, for example leptin, insulin, activin and high levels of oestrogens at ovulation. There is cross-responsiveness of these receptors to the various glycoprotein hormones. The ovary Embryologically ovarian tissue is formed from three main types of cells: 1 Primordial germ cells derived from endodermal cells of the yolk sac which migrate at 6 weeks of intrauterine life the ovarian cycle 545 to the genital ridge. During the 6th to 8th week of development, the primordial germ cells grow and begin to differentiate into oogonia. Until 10 weeks of gestation the germ cells and surrounding sex cord and sex stromal cells are not differentiated, and the gonadal ridges are bi-potential gonads. The primary oocytes are arrested in the prophase stage of the first meiotic division (diploid cell). The few primary oocytes that survive are those that are surrounded by flat, spindle-shaped follicular or pregranulosa cells. At this stage of development, the primary oocyte with its surrounding single layer of pregranulosa cells is called a primordial follicle. The first primordial follicle usually appears around 6 weeks into intrauterine life, and the generation of primordial follicles is complete by about 6 months after birth. The primary follicle forms as the spindle cells of the primordial follicle become cuboidal cells. Thus, the primary follicle contains a larger primary oocyte that is surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal granulosa cells. The secondary follicle contains a primary oocyte surrounded by several layers of cuboidal granulosa cells. The granulosa cells of a primary follicle proliferate and give rise to several layers of cells. In addition, stromal cells differentiate, surround the follicle and become the theca cells. As the developing follicle increases in size, the number of granulosa cells increases to about 600, and the theca cells show increasing differentiation. The progression to secondary follicles also entails the formation of capillaries and an increase in the vascular supply to developing follicular units. The increasingly abundant granulosa cells secrete fluid into the centre of the follicle creating a fluid-filled space called the antrum. In tertiary follicles, gap junctions are formed between theca and granulosa cells. Gap junctions may also exist between the oocyte and the granulosa cells closest to the oocyte and may function as channels to transport nutrients and paracrine signals from the granulosa cells to the oocyte and vice versa. The granulosa cells closest to the oocyte also secrete a layer of mucopolysaccharides (the zona pellucida). The latter is produced from the granulosa cells and reaches the systemic circulation in levels proportional to the secondary follicle pool. In the absence of further gonadotrophin stimulation the secondary follicles undergo apoptosis and atresia. This process of gonadotrophin-independent recruitment to secondary follicles and apoptosis in absence of gonadotrophins is continuous during intrauterine, pre-pubertal and reproductive life till depletion of the follicular pool at the age of menopause. Unlike spermatogenesis, the atretic follicles cannot be replenished; therefore the ovarian reserve of follicles is a finite pool. It is believed that natural fertility is lost around 10 years earlier than the age of menopause (fixed-interval hypothesis). The effect of the latter is further proliferation of the granulosa and theca cells with accelerated production of oestrogen and peptide hormones (inhibins, activin, follistatin) and formation of a cavity (antrum) in which the oocyte is surrounded by a few layers of granulosa cells projecting into the cavity. The follicular cavity fluid contains a myriad of growth factors and signalling molecules involved in bidirectional communication between the oocyte and surrounding granulosa. In the luteo-follicular transition and early follicular phase, inhibin B is secreted by the granulosa cells, recruited from the secondary follicles pool, to enter the gonadotrophin-dependent phase. The dominant follicle expands in size with an exponential rise of oestradiol levels. The oocyte with its surrounding corona radiata and cumulus oophorus are bathed within follicular cavity fluid. The resulting effect of these changes is follicular wall rupture with release of follicular fluid and the oocyte and its surrounding cumulus cells. This is usually picked up by the fimbrial end of the tube, and is transported to the ampullary part of the fallopian tube where fertilisation may occur. In a regular 28-day cycle the gonadotrophin-dependent phase (follicular phase of the ovarian cycle) lasts about 14 days. However, this is variable amongst individuals and leads to variable lengths of the follicular phase and subsequent variable menstrual cycle lengths as the corpus luteum lifespan is nearly fixed at about 14 days. It then enters into an apoptosis and regression phase of about 4 days if pregnancy does not occur. In the absence of pregnancy, the corpus luteum has a fairly predictable life span of 14 days. The falling oestradiol and progesterone levels lead to apoptosis and shedding of the endometrium. In the early follicular phase the endometrium is rebuilt from the basalis layer after its superficial layer has been shed in the menses of the previous cycle. The prevailing oestradiol secreted from the ovary leads to active mitosis and proliferation of the endometrial glands and stroma. Following ovulation the prevailing progesterone hormone leads to more functional maturation of the endometrial glands and decidualisation of the endometrial stroma. Histologically these changes are reflected in enlarged tortuous endometrial glands that are full of secretions; hence this phase is called the secretory phase. The stroma appears oedematous with an increased number and coiling of the spiral arteries and pericapillary leukocytic and cellular infiltrates, a process called decidualisation. The effect of the epithelial changes is secretion of adhesion molecules, such as integrins and glycodelins, which mediate the attachment of the blastocyst (in the case of successful fertilisation) that initiates the implantation process. The effect of stromal decidualisation is recruitment of immunological cells (natural killer cells, dendritic cells) that help regulate the trophoblastic invasion and effect changes in the spiral arteries that lead to the development of the early placenta.
Diseases
- Phytanic acid oxidase deficiency
- Renal tubular acidosis, distal, autosomal dominant
- Epilepsy, myoclonic progressive familial
- Hernandez Aguire Negrete syndrome
- Amnesia, psychogenic
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- Penta X syndrome
- Arhinia choanal atresia microphthalmia
Cheap ponstel 250 mg mastercard
When the woman is anaesthetised muscle relaxant japan purchase ponstel once a day, it is often possible to palpate the vaginal opening of the fistula tract. The vesical opening may be seen at cystoscopy, usually on the posterior wall or at the bladder base. If the fistula is not related to recent gynaecological surgery for a benign condition, both the vaginal and the vesical openings should be biopsied to exclude the possibility of malignancy. Presentation varies from a mild discharge with small fistulae to continuous urine loss with larger fistulae. The patient is asked to empty her bladder and then an abdominal ultrasound scan can easily be performed to assess the residual urine. In either case, it is very important that the residual volume is measured and accurately recorded. Management It is vital that all clinicians are aware of the complications associated with an episode of acute retention and that all possible steps are taken to avoid it happening. If it does occur, catheterisation should be undertaken as soon as possible and the catheter should be left in for at least two days, after which it is reasonable to undertake a trial without catheter, but only under strict supervision. Aetiology Neurological the aetiology depends on the underlying neurological condition and the level at which the anatomy is affected. Peripheral lesions include lesions at the sacral outflow, for instance a prolapsed intervertebral disc, cauda equina syndrome or herpes zoster. Medical therapy Bethanechol 25 mg twice daily has been shown to enhance bladder emptying providing there is no evidence of outflow obstruction, although it is seldom useful clinically. Surgery If the voiding difficulties are a result of extrinsic compression, this is usually best treated by removing the underlying cause, for example a hysterectomy or myomectomy in the case of fibroids. However, in the case of pregnancy causing obstruction, supportive measures are usually used in the form of a urethral catheter until the uterus has grown a little more and the obstruction relieves itself. If the obstruction is intrinsic, this may be treated by the removal of a foreign body or offending material. Alternatively, if a urethral stricture is suspected, a cystoscopy and an Otis urethrotomy may be required, in which case the patient would need to be counselled about having a urethral catheter on free drainage for two weeks on discharge from hospital and the possibility of post-operative urinary incontinence. In the long term, intractable voiding difficulties may need to be treated with clean intermittent self-catheterisation. The patient needs to be able to perform the technique, and this usually requires a degree of manual dexterity in addition to willingness to undertake it. Myogenic this usually results from ischaemia due to acute retention, for example after an epidural block or spinal shock. Iatrogenic Post-operative retention is relatively common and may be associated with long operation times, epidural anaesthesia, patient-controlled analgesia, high doses of opiates and large volumes of intravenous fluids. It may also be associated with obstructive outflow procedures such as continence procedures. Alternatively, it may be as a result of kinking of the urethra, as can occur with a large prolapse. Inflammatory Any lesion may be sufficiently painful to inhibit the voiding reflex. Appropriate investigation and management allows an accurate diagnosis and avoids inappropriate treatment. Whilst many forms of conservative therapy may be initiated in primary care, continence surgery and the investigation of more Diagnosis Voiding difficulties should be suspected if a pelvic mass that is dull to percussion is palpable on clinical examination. The Conclusion 759 complex and recurrent cases of incontinence should be performed in specialist secondary and tertiary referral units. Distress and delay associated with urinary incontinence, frequency, and urgency in women. A comparison of the long-term consequences of vaginal delivery versus caesarean section on the prevalence, severity and bothersomeness of urinary incontinence subtypes: a national cohort study in primiparous women. Location of maximal intraurethral pressure related to urogenital diaphragm in the female subject as studied by simultaneous urethra-cystometry and voiding urethrocystography. Conservative treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women: a systematic review of randomised clinical trials. Progressive resistance exercise in the functional restoration of the perineal muscles. Pelvic floor muscle training is effective in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, but how does it work Anatomy and mechanics of structures around the vesical neck: how vesical position may affect its closure. Knowledge about and ability to correct pelvic floor muscle exercises in women wit urinary stress incontinence. Pelvic Floor muscle training in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse and sexual dysfunction. Comparisons of approaches to pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women. Feedback or biofeedback to augment pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women. Moore K, Dumoulin C, Bradley C, Burgio K, Chambers T, Hagen S, Hunter K, Imamura M, Thakar R, Williams K, Vale, L. Pelvic floor muscle training for prevention and treatment of urinary and faecal incontinence in antenatal and postnatal women. Effects of Duloxetine, a combined serotonin and norepineephrine reuptake inhibitor, on central neural control of lower urinary tract function in the chloralose-anesthetised female cat. Pharmacological treatment of women waiting surgery for stress urinary incontinence. A randomised controlled trial of duloxetine alone, pelvic floor muscle training alone, combined treatment and no active treatment in women with stress urinary incontinence. Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Clinical Guidelines Panel summary report on surgical management of female stress urinary incontinence. Prospective multicentre randomised trial of tension free vaginal tape and colposuspension as a primary treatment for stress incontinence. Longterm (10-15 years) follow up after Burch colposuspension for urinary stress incontinence. Cost effectiveness analysis of open colposuspension versus laparoscopic colposuspension in the treatment of urodynamic stress incontinence. Clinical outcomes with laparoscopic and open Burch procedures for urinary stress incontinence. An ambulatory surgical procedure under local anesthetic for treatment of female urinary incontinence. A three year follow up of tension free vaginal tape for surgical treatment of female stress urinary incontinence. Seven year follow up of the tension free vaginal tape procedure for the treatment of urinary incontinence. Eleven years prospective follow up of the tension free vaginal tape procedure for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Ward K, Hilton P, United Kingdom and Ireland Tension Free Vaginal Tape Trial Group. Prospective multicentre randomised trial of tension free vaginal tape and colposuspension as primary treatment for stress incontinence. A prospective multicentre randomised trial of tension free vaginal tape and colposuspension for primary urodynamic stress incontinence: two-year follow up. Tension-free vaginal tape versus colposuspension for primary urodynamic stress incontinence: 5 year follow up. A cost utility analysis of tension free vaginal tape versus colposuspension for primary urodynamic stress incontinence. Laparoscopic Burch colposuspension versus tension free vaginal tape: a randomised trial. Tension free vaginal tape procedure for treatment of female urinary stress incontinence. A randomised controlled equivalence trial of short term complications and efficacy of tension free vaginal tape and suprapubic urethral support sling for treating stress incontinence. Trans-obturator urethral suspension: miniinvasive procedure in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women. Transobturator tape (Uratape): a new minimally invasive procedure to treat female urinary incontinence.
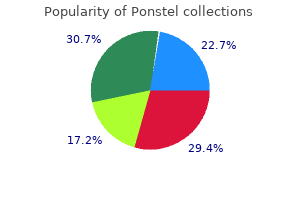
Buy ponstel pills in toronto
Protein classification and fingerprints identification are among the most important tasks in the study of protein 3D-structures spasms synonyms buy 250 mg ponstel. Both tasks can efficiently be performed through mining-discriminative subgraph motifs. The aim is to identify motifs that best discriminate a given family of proteins (for instance, functional or structural family) from other proteins. Motifs that frequently appear in a considered group of proteins and not in others are usually referred to as fingerprints. Such motifs can be used to identify functional sites [20], substructures that characterize a given protein family, and also to identify the function or, in general, the affiliation of an unknown protein [54]. The main aim of this chapter was to review how to bridge the gap between both tasks and both domains of research. The first part of the chapter reviewed existing methods to transform protein 3D-structures into graphs, enabling the usage of graph mining and pattern-recognition techniques to perform protein 3D-structure analysis. The second part of the chapter focused on subgraph discovery from graph databases that can be used to extract motifs from protein 3D-structures in a graph perspective. It presented the context and formalization of frequent subgraph discovery: problem definition, candidates generation, the main approaches proposed in the literature (Apriori and pattern growth-based approaches), and variants of frequent subgraph mining (closed and maximal subgraphs). It also presented the general framework of feature selection and the complexity of adopting the old techniques for frequent subgraphs. The chapter further investigated a panoply of subgraph selection approaches proposed in the literature that can be used easily with protein 3D-structure motifs. Even though great advances have been noticed in recent years in all the reviewed three tasks. It is also worth mentioning some of the other existing techniques for mining protein 3D-structure motifs, such as geometric 3D-motifs as in Reference [46] and 3D-templates as in Reference [3]. The main difference between geometric 3D-motifs and the motifs discussed in this chapter. Mining and matching motifs from graph representations of protein structures allow more flexibility than geometric 3D-motifs and templates. An algorithm for constraint-based structural template matching: application to 3D templates with statistical analysis. A simple topological representation of protein structure: implications for new, fast, and robust structural classification. On effective presentation of graph patterns: a structural representative approach. Smoothing 3D protein structure motifs through graph mining and amino-acids similarities. Boosting with structure information in the functional space: an application to graph classification. Data mining and machine learning techniques for the identification of mutagenicity inducing substructures and structure activity relationships of noncongeneric compounds. Comparing graph representations of protein structure for mining family-specific residue-based packing motifs. The European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases; Lyon, France; 2000. Lazar C, Taminau J, Meganck S, Steenhoff D, Coletta A, Molter C, de Schaetzen V, Duque R, Bersini H, Nowe A. A survey on filter techniques for feature selection in gene expression microarray analysis. Computational Methods of Feature Selection, Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Series. A geometric algorithm to find small but highly similar 3D substructures in proteins. The model of most informative patterns and its application to knowledge extraction from graph databases. GraphSig: A scalable approach to mining significant subgraphs in large graph databases. Drug-target interaction prediction from chemical, genomic and pharmacological data in an integrated framework. A protein is an organic compound, made entirely from different combinations of amino acids; proteins provide a gamut of functions to the organisms that use them. At a very basic level, a protein is a linear chain of amino acids, ranging from a few tens up to thousands of amino acids. Proteins derive their structure from folding of this chain; under the influence of several chemical and physical factors, proteins fold into three-dimensional structures, which determine their biological functions. The application for the determination of protein structure has given rise to many advances in the field of the biotechnology, for example, the design of new proteins and folds [5], disease study [36], drug design projects [17], refinement of theoretical Pattern Recognition in Computational Molecular Biology: Techniques and Approaches, First Edition. Furthermore, the function of a protein is a consequence of its structure, and predicting the native structures of proteins would help to take advantage of the large amount of biological information that is being generated by genome-sequencing projects. Determining the protein structure, the functional conformation of a protein, is viewed by many as one of the most interesting challenges of modern computational biology [3]. Not only has determining protein structures from their respective amino acid sequence remained a central problem in computational biology but this determination has also found its way into computer science and machine learning because of the scope and complexity of the problem. The common methodologies that are used are either comparative modeling or ab initio methods; these methodologies present different complexities and, in many cases, different solutions. In comparative modeling, databases of known structures are referred to for the development of the protein structure. Comparative modeling methods include homology modeling, threading, and fold recognition. Ab initio methods are those that use the amino acid sequence and the interactions between them to determine structure. In ab initio methods, correct structure is generally calculated by determining the overall energy of the structure; the lower the energy, the more stable the structure, which increases the probability of its being in the correct conformation and structure. The major goal when developing protein structure development strategies is to develop more reliable ways to determine correct and incorrect structure and the creation or improvements of methods that find functional conformations from those correct structures. Physically, it is understood that conformations with the lowest Gibbs free energy are the most stable structures and are, by definition, the natural conformations. Protein folding may be altered by outside factors such as chaperones and electrostatic conditions of the environment, and therefore isolated and refolded proteins may be nonnative. This mimicry comes into play with the major steps of this type of algorithm: fitness test, crossover, and mutation. Chromosomes are written as strings of information (in basic cases, binary string where each bit represents a specific value). In each generation, including the initial population, every individual is evaluated and ranked by their respective fitness. The mutation operation represents the random and slight genetic changes that happen in nature, while the crossover operations represent the transfer of information in reproduction. In mutation, the algorithm is given percentage likelihood to select random bits of information to be changed. This step usually happens in one of the following three ways: single-point mutation (bit inversion), segment mutation, or order-changing mutation. In single-point mutation, only a random bit of information is changed to another possible value. In segment mutation, a block of information is mutated; sometimes, this presents itself as a single bit being mutated and the rest of the gene adjusting to make it a valid solution. In crossover, the algorithm is given a percentage likelihood that crossover will occur in the current generation of individuals; the determination of which individuals will be paired to perform a crossover is usually influenced by the ranking provided by the fitness function. Crossovers usually occur in one of the four following ways: single-point crossover, multipoint crossover, uniform crossover, and arithmetic crossover. In the single-point crossover, a point is selected in both individuals; this point is called the crossover point; the new genes are created by separating both individuals at the crossover point and combining those halved genes with the opposite half of the other individual. Currently, the types of models one has to choose are cubic lattice models and all-atom models. The cubic lattice model is a discretization of the conformational space of the protein, because of which predicting the exact protein structure is impossible [16].
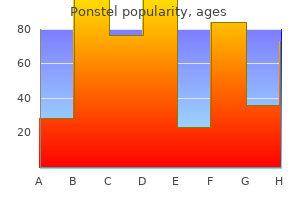
Ponstel 500 mg low price
Current research on information retrieval goes beyond this primary goal and deals with several other tasks such as modeling muscle relaxant properties of xanax 500mg ponstel with visa, object categorization or classification, information visualization, user interfaces, high-performance computing, and natural language processing. In this manner, it intersects with several other research fields such as data mining, machine learning, and pattern recognition. A key distinction should be made between data retrieval and information retrieval. Data, information, and knowledge are three encompassing terms to explain the flow of concepts in representing and understanding things. Knowledge, on the other hand, is a more structured and high-level representation of information that is used for reasoning and inference. Data retrieval is the process of finding and reporting all objects that satisfy clearly the defined conditions. These conditions are usually given to describe the data in terms of regular or relational algebra expression. On the other hand, the information retrieval task is concerned with the relevance, not correctness, of the objects retrieved from the collection. Information retrieval systems can be distinguished into Boolean retrieval and ranked retrieval systems. In Boolean systems, the user is allowed to specify his information need in more complex queries in order to get a single best-fit solution. In ranked retrieval, on the other hand, the system returns a list of relevant results ordered by their confidence level on the relevance between query and the outcome. How to score this confidence is another challenging question in information retrieval. Another issue in distinguishing between information retrieval systems is the scale at which they operate. A web retrieval system has to search over a tremendous collection of objects in millions of computers. In addition to the crucial need for very efficient indexing techniques, web retrieval systems should deal with the hierarchy and linked structure of the documents. The second class, personal information retrieval systems target the documents contained in personal computers. The third class can be referred as domain-specific retrieval systems in between the former two. Here, the retrieval is performed over a specified collection, either in a local computer or remote locations such as the web or a distributed system. Therefore, such systems require building of domain-specific index structures and matching strategies. It is used to traverse a collection to locate the relevant object to the queried one in a faster way than a brute-force approach. In its naive form, an index is a data structure containing the terms or concepts with which are associated pointers to the related object. In traditional information retrieval for text documents, each term corresponds to a word appearing in at least one of the documents in the collection. Since it is not an efficient way to include all possible words in the collection, an appropriate index should include a representative set of keywords that can be deduced by various operations such as stemming, compression, and feature selection. In a trade-off between efficiency and representativeness, creating an optimal index is one of the challenging questions in the information retrieval field. A good indexing is expected to improve the quality of the answer set of an information need. Current studies on information retrieval focus also on human interaction and try to develop strategies to enhance the tools for better understanding user behavior. This trend had been tandem with the happenings and developments in the Internet world. Along with the immense accumulation of other types of data over the Internet, the main focus of information retrieval researchers has shifted from text data to other formats, such as image, audio, and video [21]. It has been, of course, inevasible to develop additional domain-specific models that fit into the nature of new data types. Multimedia information retrieval is the most attractive field of study as opposed to traditional information retrieval studies. Here, a document is replaced by a multimedia object and the methods used in document information retrieval are transplanted into the new object by redefining the concept of term appearing in these sorts of files. These annotations, also called meta-data, may contain brief information about the object content or its environment, which are usually provided by the people producing or uploading the file. If the user having a retrieval request is interested in this brief information, the retrieval task is analogous to typical document retrieval as the meta-data annotation can simply be regarded as a text document. The user may ask to find details inside the multimedia object just the way he/she perceives when he/she looks or hears. This term is used for the tasks that retrieve the objects using its actual content rather than meta-data annotations. There is no straightforward way of vectorizing a multimedia file to an index using a set of terms. Even if a term concept is abstracted to represent some part of the multimedia content using some domain-specific data exploration techniques, the information need of a user cannot be adopted to a query by these abstract definitions. In this approach, the user query is maximally abstracted by requesting an example that would resemble the object to be retrieved. The information retrieval framework is then responsible for vectorizing both the query and the objects in the collection. The user is, on the other hand, not aware of what kind of search is being performed behind the system. Visual objects, such as image and video, contain more versatile components in comparison with text data. Content-based image retrieval methods attempt to extract low-level visual characteristics that may be defined by gradient, color, shape, texture, or spatial relationships and combine them with higher level characteristics inferred from semantic analysis of more general conceptual features of data. In spite of a great effort, the field is still considered to be in its infancy as satisfactory performance that is close to human perception is yet to be achieved. The characterization of visual data requires low-level signal processing techniques and the real human perception can only be abstracted by high-level features extracted from low-level signal characteristics. While text documents and multimedia objects dominate the current web content, some other special data types are also subject to information retrieval. Scientific articles, for example, have a special format to be reconsidered for information retrieval purposes. Recommendation systems operate with a strategy of retrieving similar users from the collection of previous user-item rating matrices. Research in biological and biochemical sciences has produced an enormous amount of data accumulated in public databases. While they both need domain-specific treatment for information retrieval studies, we focus on the latter in the following sections. It has become a major platform for wet-lab analysis of gene expression and regulation since its invention. The data typically form a numerical matrix with rows corresponding to the genes under consideration, and columns representing the conditions under which the experiment is done. The analysis of a gene expression matrix is a challenging task owing to numerous reasons. First, data may contain noise or fluctuations because of platform differences, environmental conditions, and biological instability. Therefore, more than one replicate is used in the experiment to get more reliable results. In many situations, only a subset of genes, for example, those that are differentially expressed, contribute to the results inferred from a computational analysis. Third, the biological knowledge inherited in one matrix probably repeats in some others. Therefore, the gene expression matrix has attracted computational scientists to design and develop more reliable and efficient data analysis methods. From an information and computer science point of view, it is defined as partitioning related objects into previously unlabeled groups. For a gene expression matrix, this can emerge in two ways: clustering genes or clustering conditions [26]. Therefore, a clustering may result, for example, with grouping related people on the basis of behavior of their genes. In this case, the genes having similar profiles over a set of subjects or conditions are grouped into coherent sets.
Aster officinalis (Elecampane). Ponstel.
- What is Elecampane?
- How does Elecampane work?
- Coughs, asthma, bronchitis, nausea, diarrhea, worms which infest the gut (hookworm, roundworm, threadworm, and whipworm), and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dosing considerations for Elecampane.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96052
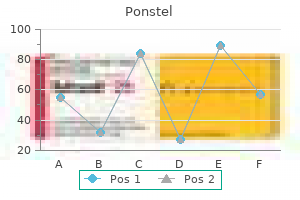
Cheap 250mg ponstel fast delivery
However spasms left side under rib cage purchase 500mg ponstel mastercard, they can develop a number of common problems which, while not necessarily life threatening, may nonetheless cause significant morbidity and parental anxiety. This chapter introduces the reader to the most common problems encountered at or shortly after birth, concentrating in the main on those relating to the term fetus/neonate. At the end of this chapter, there is a brief summary of the more complicated problems associated with prematurity. It is essentially a sign of alveolar disease: the alveoli do not open adequately, hence the infant tries to open them by increasing his or her intrathoracic pressure. More serious conditions, such as sepsis, aspiration, pneumothorax or respiratory distress syndrome, should be excluded. The signs of acute respiratory embarrassment are the same for many aetiologies;1 thus, such infants should be seen by a paediatrician. If this is not successful, or if there are indicators to suggest the infant is unwell, intravenous dextrose may be needed (a 10 per cent solution should be used initially). It is most commonly seen in growth-restricted and preterm small infants, or as part of the clinical picture in the sick infant. Newborn infants are born exposed and wet, and can lose heat very quickly if not dried and covered adequately. Hypothermia can cause significant morbidity; infants are lethargic and feed poorly. More seriously, hypothermia is associated with hypoglycaemia, metabolic acidosis and respiratory distress. Hence, when dealing with the cold newborn, the first concern is to look for the underlying cause. Once this has been dealt with, specific measures to warm the child include a warm environment (this may seem obvious, but it is often found that delivery rooms are environmentally unfriendly for the newborn infant), drying the infant adequately and dressing him or her in warm clothes (including skin-to-skin contact with the mother and warm towels and covers), and the use of a radiant heater or warming mattresses. For extreme hypothermia, more invasive measures, such as reheating with warmed plasma expanders or exchange transfusions with warmed blood, have been used. However, it is debatable whether these convey any benefit over the use of a radiant heater and warming mattress. Hypoglycaemia this subject causes much anxiety and continues to generate much controversy. Assuming they are otherwise well, they can utilise alternative fuel sources, such as ketones and lactate, in the short term. This means that for term infants of average birthweight, it is unnecessary to monitor blood glucose and start invasive treatments. Fracture of the clavicle is the most frequently seen, followed by the humerus, femur and skull bones. Fractures usually result from traumatic deliveries, for example in association with shoulder dystocia and difficult instrumental deliveries [D]. Clavicular fractures are best treated conservatively and have an excellent prognosis. Fractures of long bones may require some form of simple splinting to immobilise the limb and thus reduce pain. Skull fractures are more serious, and the possibility of underlying haemorrhage must be considered. The majority of neonatal fractures will heal uneventfully with conservative treatment. Any infant presenting with low blood glucose must be carefully examined for Common neonatal problems presenting on the postnatal ward 487 Cephalohaematomas these result from bleeding between the periosteum and skull bones, and take the shape of the underlying skull bone. As they resolve, they may exacerbate jaundice, and the possibility of associated injury (such as skull fracture or intracranial bleeding) should be ruled out. During resolution, the swelling may increase in size; this is usually due to fluid shift into the haemorrhage by osmosis as the clot breaks down. It entails a clinical examination of the infant, carried out in the first week of life. It is meant as a screening health check, although there has been much controversy concerning its usefulness. Equally, assuming the infant is well, a 24-hour interval provides a chance for the infant to recover from the stresses of birth, and allows bonding to occur. The newborn examination should be performed in a welllit, warm room to prevent the exposed infant getting cold. A full explanation of the examination process would be lengthy, and the reader is referred to any of the standard textbooks of neonatology for this. A few points to remember include the need for proper hand hygiene when examining infants, and that the infant should not be left exposed for prolonged periods of time. As part of the newborn check, parents should be asked about the passage of urine and stool, as well as any feeding concerns. Increasingly, early neonatal pulse oximetry is used as part of the examination to screen babies for both undiagnosed cardiac. The result is usually a flaccid arm held in a pronated and internally rotated position. Between 49 and 94 per cent make a full recovery, with most improving by 12 months of age. Facial palsies are commonly ascribed to obstetric manoeuvres, such as the use of forceps causing pressure damage; however, facial palsies also occur in infants delivered normally. If an upper motor neuron lesion is suspected, the infant should be investigated for possible cerebral injury or congenital disorders. Sternomastoid tumours these are the result of bleeding into the sternomastoid muscle. They are not normally recognised at birth, and do not become obvious until a few weeks of age. Traumatic cyanosis this is a petechial rash present over the face and head, and may extend to the upper body, although the rest of the child is usually spared. It is probably the result of venous congestion, resolves spontaneously and is only of importance because it has been mistaken for true cyanosis. Breastfeeding is clearly the best choice for a number of reasons, including the following: Urine/stools It is not uncommon for neonatologists to be asked to review an infant who has either not passed urine or not opened his/ her bowels. A detailed history, including review of the antenatal progress and birth, is important. If there is any doubt but the infant otherwise appears well, it is worth placing cotton wool ball(s) in the nappy. An infant who has not passed urine within the first couple of days or in whom there is any other concern may need further investigation to exclude either obstruction (such as posterior urethral valves in males) or renal disease. Investigation in such situations may involve gentle rectal examination, radiological tests and possibly rectal biopsy. This can lead to a sense of failure and to the abandonment of breastfeeding if no support is available. In this situation, facilities should be available to help with the expression of breast milk until such time as the child is ready to suckle. There are often concerns about milk volumes; these are usually helped by support and reassurance. Test weighing has previously been used to try to quantify the amount of milk an infant is getting; however, this is not only unhelpful, but indeed can be positively detrimental to breastfeeding as it often instils a further sense of failure in the mother. Other problems include concern about inverted nipples, cracked nipples, engorged breasts, overfeeding and weaning. Probably the most common are chronic ill-health in the mother (such as cystic fibrosis), potential infective risk. Problems specific to this include: Weight loss It is normal for infants to lose weight in the first week of life. There is a long list of causes of excess weight loss, ranging from inadequate intake, through inadequate nutritional content, to feed intolerance and ill-health. Skin lesions Skin lesions are a common cause of concern in the otherwise well newborn. These may be due to anatomical factors, such as cleft palates or large tongues, as well as physiological factors, such as immaturity of the sucking reflexes.
Discount ponstel 500 mg free shipping
Those who are young muscle relaxant safe in pregnancy cheap ponstel online amex, with a good nutritional status (normal albumin levels) Germ-cell tumours of the ovary Adequate surgical staging, removal of primary tumour and adjuvant chemotherapy is current standard therapy for germcell tumours of the ovary. As these malignancies usually occur in young women, conservation of the contralateral ovary and 904 Benign and malignant ovarian masses uterus is appropriate. All other patients should be treated with three or more cycles of combination chemotherapy (bleomycin, etoposide and cisplatin). Most patients with these tumours are cured of disease and most survivors can anticipate normal menstrual and reproductive function. This is likely to improve outcomes and facilitate research in this poorly studied field. The centralisation of gynaecological cancer services has improved compliance with management guidelines, provided specialist training and treatment, facilitated research and consequently improved patient care and outcomes which are particularly pertinent to the care of women with ovarian cancer. Sex-cord stromal tumours Although they are reported to be most common among postmenopausal women, these tumours often affect children and young adults. They are the most hormonally active of all ovarian tumours and there is an association with endometrial hyperplasia and well-differentiated adenocarcinoma of the endometrium. Surgery is the cornerstone of management, but early-stage disease may be managed by unilateral oophorectomy and endometrial biopsy when fertility sparing is important. Pseudomyxoma peritoneii this condition involves the accumulation of gelatinous material in the peritoneal cavity. A histopathological diagnosis of pseudomyxoma ovarii would warrant such a referral. Specialized care and survival of ovarian cancer patients in the Netherlands: nationwide cohort study. The outcomes of ovarian cancer treatment are better when provided by gynecologic oncologists and in specialized hospitals: a systematic review. Cure is the ultimate goal of patient and oncologist, but is not achieved for the majority. Therefore a careful balance must be struck between the pursuit of that goal and optimisation of the quality of the period of life remaining. Specific treatments and their potential impact on disease must be weighed against the morbidity of each therapy. The optimum balance between these opposing aims will be different for each patient. A candidate precursor to serous carcinoma that originates in the distal fallopian tube. Factors influencing uptake and timing of risk-reducing salpingooophorectomy in women at risk of familial ovarian cancer: a competing risk time to event analysis. Improved progression-free and overall survival in advanced ovarian cancer as a result of a change in surgical paradigm. The effect of maximal surgical cytoreduction on sensitivity to platinumtaxane chemotherapy and subsequent survival in patients with advanced ovarian cancer. Ultra-radical (extensive) surgery versus standard surgery for the primary cytoreduction of advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. The effect of debulking surgery after induction chemotherapy on the prognosis in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecological Cancer Cooperative Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer. Systematic review of adjuvant therapy for early stage (epithelial) ovarian cancer. Aetiology Pathology Certain pre-existing vulval dermatoses are known to be associated with the development of vulval carcinoma. The risk of this condition progressing to invasive cancer is highly variable, according to the literature. It is important to recognise the symptoms and signs associated with these cancers to make an early diagnosis. As in all cancers, appropriate treatment at an early stage in the disease will lead to a better outcome for the patient, as reported by a population-based study of a series of 411 women in the West Midlands [D]. Vulval cancer 907 Variations in the cell-cycle regulatory protein p53 are reported in approximately 30 per cent of cancers and for the remainder there currently appears to be no aetiological or molecular biological event. Treatment There is increasing emphasis placed on the individualisation of treatment for women with vulval cancer. In deciding the optimum treatment, it is best to consider early and advanced vulval cancers separately and to manage the primary lesion and the regional lymph glands on individual merit. Because of the rarity of vulval cancer, and the need for careful assessment to optimise both vulval preservation and care, these women should be managed by specialised gynaecological oncologists in cancer centres. In addition to imaging, the pathological assessment of these tumours is extremely important in forming decisions about adjuvant treatment. Vulval cancer is uncommon and most evidence arises from observational studies and case series. Population-based observational studies confirm better outcomes with early detection. This probably reflects the variations in the observational studies rather than a widely varying biological effect. Early stage vulval cancer Primary lesion Treatment of the primary lesion is in part determined by the risk of local vulval recurrence and the risk of groin node involvement at the time of diagnosis. In most early cancers this can be achieved by a wide radical local excision and will allow for the preservation of non-involved structures. Re-excision of the vulval lesion to achieve at least 1 cm of disease-free margin has been the standard of care but recent data have shown a low rate of residual disease but high rate of surgical complications. Careful observation and re-excision of any new disease may be a suitable alternative approach. Lateral vulval tumours the management of regional lymph nodes can be modified for patients presenting with lateral vulval tumours. Although there is extensive lymphatic crossover in the midline of the Diagnosis Women with vulval cancer usually present with symptoms, although an asymptomatic mass may be an unusual presentation. The associated symptoms are usually vulval soreness and itching and there may be a mass that is painful and bleeds. Investigation of post-menopausal bleeding should always include examination of the vulva. The most common site of involvement is the labium majus (about 50 per cent of cases). Investigations When women present with vulval symptoms, a full clinical examination should be performed, paying particular attention to palpation of the groins for lymphadenopathy. A full-thickness biopsy should be taken from the tumour and should include the interface between the apparent normal surrounding tissue and the cancer. This allows for the most accurate histological interpretation and for the depth of invasion to be assessed, which is important in determining the future management. The cervix should be visualised to exclude a cervical cancer, which may occasionally coexist. If the ipsilateral nodes are negative, the contralateral nodes are rarely involved [D]. In a prospective trial, the outcome for 26 women who underwent ipsilateral lateral groin node dissection alone was similar when compared with historical controls [C]. A randomised trial comparing inguinal node dissection with radiotherapy to the groin in women with clinically normal inguinal nodes found a survival advantage in favour of the surgical arm; however, this trial has been criticised because an inadequate dose of radiotherapy was given to the inguinal nodes. Unfortunately, superficial inguinal node dissection, which removes only the lymph nodes above the cribriform fascia, is associated with a higher rate of inguinal recurrence compared with inguino-femoral node dissection, which removes tissue below the cribriform fascia (this is the layer deep to the fascia lata) and medial to the femoral vein. In a prospective clinical trial, 155 women underwent a superficial inguinal node dissection and although the overall survival rate was the same compared with a series of historical controls, the rate of inguinal node recurrence was significantly higher. The routine removal of pelvic lymph nodes in early stage vulval cancer is not recommended.
Generic ponstel 500mg amex
Although the vasa may have been occluded bilaterally spasms and cramps purchase cheap ponstel, if there are any more vasa, spermatozoa can still be released. Early recanalisation is recognised by post-vasectomy sperm counts which may at first be azoospermic or reduced but then rapidly increase again. Late recanalisation presents with a pregnancy several months or years after two consecutive azoospermic samples. Chronic testicular pain this is probably due to distension and granuloma formation in the epididymis and vas deferens following the operation [B]. Men should be informed of this and reassured that there is no sinister association. Cancer There is no increase in testicular or prostatic cancers following the vasectomy operation [B]. Heart disease There is no increased incidence of heart disease associated with vasectomy. These generate fibrosis around the devices and the tubes are occluded by 3 months after the procedure. Additional contraception needs to be used until a hysterosalpingogram is performed at 3 months to confirm full occlusion of the tubes. It is an irreversible procedure and the failure rates quoted are the same as for the other methods of tubal occlusion. Women should be informed that with tubal occlusion pregnancy can occur several years after the procedure. Safety There is no evidence to suggest that there is an increased incidence of bleeding problems and consequently an increased hysterectomy rate after tubal occlusion. Adverse events for placement of intrafallopian implants include uterine or tubal perforation, infection, device migration or expulsion, pelvic pain and vasovagal reaction. Section 4 of the Abortion Act 1967 states that no person is under any obligation to participate in any treatment authorised by the act. The Abortion Act 1967 states that: Male sterilisation: vasectomy Methods the technique of vasectomy involves division of the vas with fascial interposition or diathermy. The procedure can be carried out under a local anaesthetic and is safer than female sterilisation. Following the procedure, men should be advised to use effective contraception until two consecutive semen samples 4 weeks apart confirm azoospermia. They are: 566 Contraception and termination of pregnancy A the continuance of the pregnancy would involve risk to the life of the pregnant woman. B the termination is necessary to prevent grave permanent injury to the physical or mental health of the pregnant woman. C the pregnancy has not exceeded its 24th week and the continuance of the pregnancy would involve risk, greater than if the pregnancy were terminated, or injury to the physical or mental health of the pregnant woman. D the pregnancy has not exceeded its 24th week and the continuance of the pregnancy would involve risk, greater than if the pregnancy were terminated, or injury to the physical or mental health of any existing child(ren) of the family of the pregnant woman. E There is substantial risk that if the child were born it would suffer from such physical or mental abnormalities as to be seriously handicapped. Metronidazole 1 g rectally or 800 mg orally prior to or at the time of abortion plus Azithromycin 1 g orally on the day of abortion. For first-trimester suction termination, either electric or manual aspiration devices may be used, as both are effective and acceptable to women and clinicians. For gestations above 14 weeks, surgical abortion by D&E, preceded by cervical preparation, is safe and effective and should be undertaken by specialist practitioners who have a reasonable caseload to maintain their skills. The various regimens are: Pre-abortion management Pre-abortion management should include non-directive counselling to address alternatives to abortion, i. The majority of women will come to a decision quickly but there will be others who will require additional support. Care pathways for additional support, including access to social services, should be available. An ultrasound scan is usually carried out prior to the procedure to confirm an intrauterine pregnancy and its gestation. Details of the abortion methods, the procedures and their risks should be discussed with the woman. In order to prevent repeat terminations, discussion of future contraception is vital at this stage. Antibiotic prophylaxis at the time of surgical abortion reduces infective complications, whereas there is limited evidence of decreasing infections in case of medical abortions. Medical abortion Medical abortion using mifepristone plus prostaglandin is the most effective method of abortion at gestations of less than 9 weeks [A]. A second dose of 400 mg of misoprostol may have to be given for * this regimen is unlicensed. The risk is lower for abortions performed early in pregnancy and those performed by experienced clinicians [B]. Uterine rupture this has been reported in association with mid-trimester medical abortion. Cervical trauma the risk of damage to the external cervical os at the time of surgical abortion is moderate (no greater than 1 in 100) [B]. The risk is lower when abortion is performed early in pregnancy and when it is performed by an experienced clinician. Cervical preparation prior to the procedure decreases the risk of cervical trauma. An ultrasound scan is helpful in diagnosing retained products but the decision to intervene and perform a surgical evacuation should be made on clinical grounds. Failed abortion and continuing pregnancy All methods of first-trimester abortion carry a small risk of failure to terminate the pregnancy (less than 1 in 100) necessitating another procedure. The risk is lower for early abortions (occurring in less than 1 in 1000 and rising to 4 in 1000 at more than 20 weeks) [B]. The risk is reduced when prophylactic 568 Contraception and termination of pregnancy antibiotics are given or when lower genital tract infection has been excluded by bacteriological screening [B]. However, it may be associated with a small increase in the risk of subsequent miscarriage or preterm delivery [B]. Psychological sequelae There is no evidence to suggest that these are increased following an induced abortion. The chosen method of contraception can be initiated immediately following the abortion. Injectables can be administered on the same day, whilst the subdermal implant and intrauterine contraception can be inserted immediately following a first- or second-trimester termination of pregnancy. However, this is associated with higher rates of failure and regret on the part of the woman [B]. Follow-up Women should be given written information about the symptoms they may experience following the abortion. They should be given a 24-hour telephone helpline number to contact in case of any problems. Hormonal contraception and risk of venous thromboembolism: national follow-up study.
Purchase 250 mg ponstel with mastercard
This works by inhibiting viral replication once the virus has crossed the mucosal barrier muscle relaxant 5859 order ponstel american express. Informed consent must be taken following full discussion including the possible side effects (mainly gastrointestinal) and the need for blood tests at the time, and at three and six months after the event. Hepatitis B screening, immunoglobulin and accelerated vaccination should also be considered. They are also at risk of transmitting the infection both sexually and vertically (to a fetus). Lengthy pre-test counselling is not necessary, simply discussion of the benefits of early diagnosis and how the results will be given. Sexually transmitted infections 805 Do you have any tattoos which were done in unlicensed premises without adequate precautions for sterility In those who wish to have unprotected sex, detailed counselling by experts should be offered. The risk of transmission is related to maternal health, obstetric factors and infant prematurity. There appears to be a linear correlation between maternal viral load and risk of transmission. Viral load is important in terms of transmission and should be measured every three months, at 36 weeks or two weeks after changing therapy, and at delivery. Any opportunistic infections suspected should be investigated and managed as in non-pregnant women. Obstetric factors in untested women that consistently show an association with risk of transmission are mode of delivery and duration of membrane rupture. Delivery before 34 weeks has been shown to be associated with an increased risk of transmission. Safer sex is to be encouraged, with the concomitant use of condoms, as well as a reliable hormonal method to prevent pregnancy. Antiretroviral drugs have the potential to either decrease or increase the bioavailability of steroid hormones in hormonal contraceptives. If progesterone-only emergency contraception is requested, then a 3 mg (double stat dose) is recommended. Any cytological abnormality, however minor, should be taken as an indication for colposcopy. Elsewhere in the world, where formula feeding poses extra risks to the infant because of unsafe water, breastfeeding is recommended. There is no evidence for teratogenicity of any retroviral drugs, but there is an increased risk of preterm delivery. Positive couples these couples are recommended to practise safer sex (condoms) in order to reduce the risk of transmission of viral variants. It is advisable that the couple are in the best possible health before embarking on a pregnancy and are under specialist care. The woman should have normal up-to-date cervical cytology before becoming pregnant. This is more common in those with chronic other liver disease, including hepatitis B and C. There is no evidence that hepatitis A is teratogenic, but there is an increased risk of miscarriage and premature labour. Breastfeeding can be continued and most children will have mild or asymptomatic infection. The diagnosis can be confirmed by positive serum hepatitis A-specific IgM and can remain positive for six months or more. General advice for women should include avoiding food handling and refraining from unprotected sex. Rest and fluids are advised together with advice to seek medical help if there is a deterioration in health. Positive man, negative woman the risk of transmission to the woman is approximately 1:500 per sexual encounter and until recently this was the only way couples could conceive. Limiting exposure to the most fertile period only has been shown to reduce the risk of transmission. Positive woman, negative man Couples are advised to use condoms and then to practise selfinsemination around ovulation to minimise the risk of transmission to the man. It is endemic worldwide with high carriage rates of up to 20 per cent in high-risk areas, such as South and East Asia, Central and South America, Africa and Eastern Europe. In pregnancy, there is an increased risk of miscarriage and premature labour in acute infection and there is a risk of vertical transmission in >90 per cent. Infants born to infected mothers are vaccinated at birth, usually in conjunction with hep B-specific antigen, which decreases transmission by 90 per cent. Partner notification should take place and all children not vaccinated at birth should be screened. This needs to be done before 48 hours, but works for up to 7 days and should be followed up by an accelerated course of hep B vaccine (0, 7 and 21 days). All those with active infection should be referred to a hepatologist (HbsAg-positive). All hepatitis B patients should be considered for hepatitis D testing which can coincide and make patients worse. Transmission is parenteral via shared needles, transfusion pre-1990s and in renal dialysis. There are low rates of sexual transmission (<1 per cent per Pelvic inflammatory disease is most commonly caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae; the long-term sequelae include infertility, ectopic pregnancy and chronic pelvic pain. Many patients will have concurrent sexually transmitted infections; therefore genito-urinary screening is recommended. The only way to assess the risk of infection is to take a sexual history, as outlined above. All hepatitis C patients should be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B to decrease the chances of fulminant hepatitis co-infection. There is no firm evidence that breastfeeding increases the risk of transmission, except if the woman is very ill. National Guideline for the Management of Chlamydia trachomatis Genital Tract Infection. Talking to patients about the exact site, nature and other features of the pain is important. It is also important to be comfortable talking about aspects of the sexual act, especially as some dyspareunia may be position related. Remember that patients are usually more embarrassed mentioning these aspects to us and may expect us to bring up the subject. It is important to confirm diagnoses as far as possible with diagnostic tests, such as pelvic ultrasonography, microbiological swabs, laparoscopy or vulval biopsy where appropriate. Some diagnoses or problems are best dealt with by general practitioners or other specialists, such as gastroenterologists. The aetiology of dyspareunia should be viewed on a continuum from primarily physical to primarily psychological, with many women exhibiting components of both. It leads to vasodilatation in the genitals causing swelling of the labia and the tissues surrounding the vagina resulting in heightened labial colouring and increased vaginal lubrication. Excitement can be enhanced or inhibited by signals from the brain, which are in turn influenced by previous experience. Oestrogen affects vaginal lubrication by enhancing the vascular bed beneath the epithelium.

Order ponstel discount
This results in absent or rudimentary development of the upper body structures as the acardiac twin is supplied with deoxygenated blood muscle relaxant euphoria purchase ponstel toronto. The perinatal mortality of the pump twin is considerable, with death usually occurring through complications of high-output cardiac failure leading to hydrops fetalis or polyhydramnios-induced preterm delivery. Single fetal death this may occur either early in gestation or later as the pregnancy progresses. The risk of cerebral palsy is increased in the surviving twin after a co-twin death, and same-sex twins are at greater risk than unlike-sex twins. Congenital anomalies There is an excess of malformations in twins compared with singleton pregnancies. Other malformations occur through disruption in a previously normally formed fetus. A further mechanism leading to maldevelopment is the constraint of sharing the uterine cavity. The diagnosis requires the ultrasound demonstration of polyhydramnios around one twin (the recipient) and oligohydramnios around the other twin (the donor), with the separating membrane completely covering this fetus (stuck twin). The recipient twin is usually appropriately grown for gestational age, has a large distended bladder and may, if severely compromised, be hydropic. Other fetal risks There are complications that usually arise in the third trimester and in particular in the intrapartum period. Maternal risks relate mainly to increased uterine distension and the development of pre-eclampsia [B]. An excess of congenital malformations means that examination of multiple pregnancies by detailed ultrasound scanning is mandatory [B]. The chorionicity of monozygotic twins depends on the timing of embryo splitting after fertilisation. In the first trimester, chorionicity may be determined with nearly 100 per cent accuracy. Visualisation of the twin-peak or lambda sign is also useful in the diagnosis of dichorionicity; however, the absence of this sign is not as reliable in the confirmation of monochorionicity. In addition triplets and quadruplets have higher rates of other adverse outcomes including increased perinatal death, major anomalies, need for neonatal intensive care, respiratory distress syndrome, intrauterine growth restriction and serious neurological morbidity. With increasing experience, post-procedure miscarriage rates are now <10 per cent, such that reductions from triplets to twins and from quadruplets to twins carry outcomes as good as those of unreduced twin gestations, and the chance of taking home a live baby increases from 80 per cent to 90 per cent. Screening for aneuploidy and prenatal diagnosis Serum screening in multiple pregnancies is not as reliable as in singletons. This allows screening in the first trimester with calculation of a risk for each fetus. The pregnancy loss rates for genetic amniocentesis in twins are considered similar to those seen in singletons. Cervical assessment has been suggested as one method to evaluate the risk of preterm labour. In singleton pregnancy a cervical length of 15 mm is predictive of preterm labour. There is currently not enough evidence to support a policy of routine hospitalisation for bed rest in multiple pregnancies. No reduction in the risk of preterm birth or perinatal death is evident, although there is a suggestion that fetal growth is improved. Indeed, in uncomplicated twin pregnancies, there Monitoring of fetal growth Serial growth scans should be performed to evaluate fetal growth velocity and to detect any abnormalities in umbilical/fetal artery Doppler waveform analysis and amniotic fluid volume. A recent Cochrane Review (2014)10 concluded that although, compared with amnioreduction, laser does not appear to improve survival significantly, it remains the treatment of choice due to the significant reduction in long-term neurological morbidity. There may be no discordance in liquor volume but there is a large difference in Hb level. At later gestations, delivery may be more appropriate if there are significant concerns regarding the wellbeing of the survivor. But caution must be exercised as any damage is likely to have occurred and delivery may only add risks of prematurity and not improve outcome. If these changes are apparent, offering termination of the pregnancy is an option. Women with triplet pregnancies should be informed that continuing uncomplicated triplet pregnancies beyond 36 weeks 0 days increases the risk of fetal death. If elective birth is declined, appointments with a specialist obstetrician should be made with weekly ultrasound assessment of wellbeing and fortnightly fetal growth scans. The optimal mode of birth for the second twin presenting as non-vertex is unknown, with retrospective reviews in the literature providing support for both caesarean birth and vaginal birth for the second non-vertex twin. For the very-low-birthweight infant (1500 g), opinion is divided as to the optimal mode of delivery. Whereas some advocate caesarean delivery in all cases, there is little evidence that caesarean section improves perinatal outcome. Cervical length measurement may be useful in predicting preterm birth in multiple pregnancy [B]. These pregnancies are at increased risk of maternal and fetal complications that require specialised management. There is an increasing vogue to manage these patients in specialised multiple pregnancy clinics, with access to a fetal medicine specialist with a special interest in multiple pregnancy. For those with an infected fetus careful and empathetic counselling is then necessary covering any intrauterine treatment, fetal surveillance and in some situations the possibility of termination of pregnancy. This chapter will concentrate on the prenatal diagnosis and management of some of the more common or serious fetal infections. There is often a lymphadenopathy, most commonly suboccipital, post-auricular and cervical, prior to and lasting after the disappearance of the rash. These signs are often accompanied by a prodromal phase with malaise and low-grade fever and also headache, sore throat and cough. In adults the most common complications are arthralgia and arthritis; rarely post-infection encephalopathy (1:6000) and thrombocytopenia (1:3000) are seen. The effect on the fetus is dependent on not only the type of infection but also the gestation acquired. Prenatal diagnosis is usually initiated as a result of routine screening at booking, a history of exposure of the mother to infectious contacts or differences seen on ultrasound scan. Independent of the infection type, management always requires a multidisciplinary team approach including microbiologists, obstetricians, fetal medicine experts and paediatricians. The presence of rubella-specific IgG indicates previous infection or immunisation and immunity is normally lifelong. Treatment and prevention In the absence of an antiviral drug to treat rubella or prevent transmission, the cornerstone of prevention is childhood vaccination. Primary rubella vaccination failure is rare, with many studies showing a 100 per cent seroconversion rate. Vaccination programmes have been shown to be cost-effective in both developing and developed countries if coverage rates of more than 80 per cent are achieved. Pre-pregnancy counselling should include evidence of immunity, with vaccination offered to susceptible women [C]. There is insufficient evidence to support rescreening of previously seropositive women and no data to support or refute the principle of offering rubella vaccination to women who have low titres. The vaccine is contraindicated in pregnancy and pregnancy should be avoided for 1 month afterwards. Fetal infection There are few prospective studies using sensitive laboratory techniques to accurately determine the rate of fetal infection. The most vulnerable gestation for transplacental infection is in the first trimester, occurring in approximately 80 per cent of cases. Of these, congenital defects occur in about 85 per cent, with multiple defects common if the infection was in the first 8 weeks of gestation, and in 20 per cent of cases in this gestation range the infection results in miscarriage. Fetal rubella infection can result in a number of abnormalities referred to collectively as congenital rubella syndrome.