Order flomax from india
Similarly prostate cancer outlook order discount flomax line, in 1975 approximately 62% of the people of Sewickley, Pennsylvania, reported gastrointestinal sickness by drinking contaminated water; Centers for Disease Control recognized that cyanotoxins released into open finished-water storage reservoirs are responsible for drinking water contamination (Lippy and Erb, 1976). In January 2007 an acute case of cyanotoxin poisoning of a young man was reported after he accidentally immersed in a lake contaminated with Microcystis (48. After 3 days, dyspnea and respiratory distress with atypical pneumonia were reported; eventually, a week later the patient developed a severe liver infection (hepatotoxicosis) (Giannuzzi et al. Long- and short-term exposure to cyanotoxins induced acute or chronic health issues by affecting the hepatic, nervous, and gastrointestinal systems, which may lead to tumor (Zanchett and Oliveira-Filho, 2013). However, more research is needed to understand how cyanotoxins cause these health issues and promote cancer and tumor growth. Based on these, they are commonly grouped into four to five major classes summarized in Table 20. Low concentration exposure of c these toxins can also cause liver and kidney failure, whereas high doses can lead to acute liver necrosis, intrahepatic hemorrhage, and shock (Svir ev et al. They may also affect other mammalian tissues and can elicit pulmoc nary, reproductive, and neurological toxicity as well as tumor growth (Chen et al. Thus cyanobacterial toxins risk assessment is still not determined (Meissner et al. Anatoxin-a and its analogs are potent agonists of the nicotinic cholinergic receptor present in the opening of the ionic channels, that is, postsynaptic membrane resulting in depolarization of the neuromuscular synapse. Acetylcholin esterase (associated with the acetylcholine receptor) can be hydrolyzed by anatoxin-a leading to an overstimulation of muscle cells (Wonnacott and Gallagher, 2006). The intoxication of anatoxin results as muscle contraction, trembling, abdominal troubles, and balance disturbance, whereas higher doses can be fatal as the respiratory muscles get paralyzed, a situation known as asphyxiation. Anatoxin-a(s) varies structurally from anatoxin-a and is a unique phosphate ester of a cyclic N-hydroxyguanine Dynamics of harmful cyanobacterial blooms and their toxins: environmental Chapter 20 309 with a molecular mass of 252 Da. They also reported that two clusters of ana gene (29 kb) have opposite direction linked with 6 kb spacer region. Structurally saxitoxins are heterocyclic guanidines, comprising about 57 different variants (Table 20. Among them, most are potent natural toxins and mainly produced by freshwater cyanobacteria and marine dinoflagellates (Pearson et al. The putative roles of the core genes comprise the function of electron-carrier methylation or dioxygenase reductase and acyl-carrier protein. They are also involved in cyclization, claisen condensation, amidinotransfer, desaturation, C12 hydroxylation, C1 reduction, and carbamoylation (Neilan, 2014). The position and presence of genes in sxt gene cluster determine the toxic profile of each strain. However, further experimentation is required to understand the actual mechanism behind the synthesis and regulation of cyanotoxins gene. Blockage of neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels has been observed by saxitoxins that stop the transmission of action potentials and leads to rapid paralysis (Wiese et al. Lyngbyatoxins-a, b, and c are three isoforms of lyngbyatoxins having a molecular mass of 437 Da. These toxins are the causal agent of various skin irritations such as redness, itching, blistering, burning, and swelling due to their lipophilic properties. Every approach has advantages and disadvantages that must be a deciding factor for the selection of detection techniques (Sanseverino et al. Costs and time should also be considered as an important factor during the selection of the detection method. In the last few years, advancement has been made in developing specific and sensitive electrochemical biosensors/immunosensors for cyanotoxin detection at low concentration. Diminutions of nutrient load, hydrodynamic variations, and chemical and biological control are the most common strategies to control Cyano-Hbs. Therefore reducing nutrient inputs by strict regulations of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers may solve the problem to some extent and to make it successful, it may take years and sometimes decades (Fastner et al. Recovery of the nutrient may be postponed if the previous eutrophication period has reallocated the lake ecosystem to another stable state that resists to any change (Ibelings et al. Hydrodynamics (artificial mixing) of lakes is a very effective but comparatively costly method to avoid Cyano-Hbs formed by buoyant cyanobacterial species (Visser et al. When the rate of vertical mixing goes above their flotation velocity, cyanobacteria are unable to access benefit from the buoyancy and hence displaced by diatoms and green algae (Visser et al. Cyanobacterial blooms formation requires a longer period, thus reducing the residence time by increasing water flow and aeration may also offer a promising approach for mitigation of stagnant water reservoirs (Mitrovic et al. Aeration throughout the water column may prevent stratification and may limit the accessibility of nutrients to the surface. It restricts the vertical movement of cyanobacteria and decreases the competitive advantage of cyanobacteria by maintaining healthy levels of dissolved oxygen (Visser et al. Diuron, copper sulfate, and some other algicides are not recommended due to their environmental persistence and noxious impacts on other aquatic organisms (Matthijs et al. Furthermore, chemical treatments cause cell lysis and release the cyanotoxins, thus exacerbating water quality problems. As compared to eukaryotic phytoplankton, cyanobacteria are highly sensitive to the low concentration of hydrogen peroxide; hence, it is highly effective against selective elimination of cyanobacterial bloom (Matthijs et al. The main advantage of this method is that after a few days hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water and oxygen, resulting in no trace of hydrogen peroxide detected in the environment (Matthijs et al. The application of decomposing barley straw for the control of Cyano-Hbs has been the topic of substantial interest and exploration since the early 1990s (Ball et al. This decomposing straw, when exposed to the solar radiation with sufficient oxygen, produces a chemical with significant algistatic effects that inhibit the growth of algae. Field studies suggested many reasons for these inhibitory effects; however, the exact mechanism of this process is not clear and need further studies (Prygiel et al. To destroy and control Cyano-Hbs, the use ultrasonic waves at a specific frequency (. These sound waves specifically target the buoyant cyanobacteria and can destroy their cellular morphology by breaking their internal gas vesicles. This technology requires costly instrumentation and the efficiency of this method can vary by the frequency of waves and the algal or cyanobacterial species that need to control (Wu et al. Due to the adaptability of algae during seasons within a lake, the ability to change these ultrasonic frequencies is of importance for long-term algal control. Sedimentation of cyanobacterial cells to the anoxic bottom layer of water column can be aided by using coagulants. Due to this cyanobacteria are unable to access oxygen, light, and other vital resources and therefore unable to proliferate and die ultimately. On the other hand, sedimentation of nutrients to the bottom layer of water column facilitated by flocculants, which limits nutrient availability to the cyanobacterial cells and eventually leads to growth retardation. The previous strategies are applied to control and prevent the incidences of Cyano-Hbs, but if they prevail and start releasing the cyanotoxins and contaminate the water, other measures should be implemented. To treat the contaminated water several conventional water treatment (flocculation, coagulation, sedimentation, and filtration) methods are used to remove the cells and intracellular cyanotoxins, these methods with their effectiveness are summarized in Table 20. The selection of treatment processes is context specific and also depends on the concentration and types of cyanobacteria or cyanotoxins to be removed or inactivated. Finally, expansions of wastewater research and management programs are necessary to check or control the prevalence of Cyano-Hbs to maintain ecological development and sustainability. Public awareness about environmental sustainability and ecosystem health should be increased. Serious steps should be taken up by policy or decision makers to develop and implement strategies and environmental protection laws against anthropogenic environmental pollution. Moreover, numerous environmental protection programs should be launched by environmental protection agencies. Both the government and nongovernment organizations should work on spreading public knowledge about global warming, environmental pollution, and occurrence of Cyano-Hbs. Cyano-Hbs are a raising issue in both the wastewater treatment as well as in drinking water systems. Global climate change and nutrient enrichment in the water system act as crucial factors, which support the formation of Cyano-Hbs. Among these factors, we may point out the reduction in water clearness and levels of oxygen for the production of toxins.
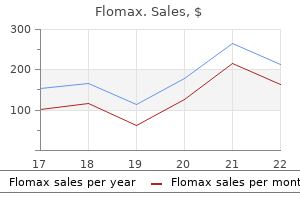
Cheap flomax 0.2 mg line
Enterocutaneous fistula in patients with peritoneal malignancy following cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy: Incidence anti-androgen hormone therapy for prostate cancer discount flomax 0.2mg overnight delivery, management and outcomes. Advanced pseudomyxoma peritonei requiring gastrectomy to achieve complete cytoreduction results in good long-term oncologic outcomes. Effect of a concomitant urologic procedure on outcomes following cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Critical care management and intensive care unit outcomes following cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal 14. Prognostic factors of hemorrhagic complications after oxaliplatin-based hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy: Toward routine preoperative dosage of Von Willebrand factor Thrombin generation and platelet activation in cytoreductive surgery combined with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy - A prospective cohort study. Factors associated with thromboembolic events following cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Incidence, risk factors, and impact of severe neutropenia after hyperthermic intraperitoneal mitomycin C. A comparative study of complete cytoreductive surgery plus intraperitoneal chemotherapy to treat peritoneal dissemination from colon, 126 Postoperative complications 23. A novel tool for predicting major complications after cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Predictors of severe morbidity after cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for patients with colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis. Comparison of 2 perioperative management protocols and their influence on postoperative recovery after cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy: Standard parenteral nutrition, selective bowel decontamination and suprapubic catheters Adverse events postoperatively had no impact on long-term survival of patients treated with cytoreductive surgery with 27. Quality of life after cytoreductive surgery and intraoperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for peritoneal surface malignancies: A systematic review. Detailed discussion of histopathological differential diagnosis is beyond the scope of this chapter and the interested reader is referred to specialist literature in the field. As with neoplasia anywhere in the body, neoplasms of the peritoneum can be primary or metastatic (Table 12. Tumours can metastasise to the peritoneum via transcoelomic dissemination of tumour cells that have breached the serosa of the organ of origin. In keeping with this hypothesis, diapedesis of tumour cells through a layer of mesothelial cells has been observed in vitro [1]. Such cells could subsequently experience the redistribution 129 130 Histopathological aspects of peritoneal malignancy Table 12. In general, it may be assumed that malignancies in which the pattern of spread is consistent with the redistribution phenomenon are probably due to transcoelomic dissemination. At the malignant end of the spectrum are mucinous adenocarcinomas of the appendix; by definition they show infiltrative invasion of the muscularis mucosae and large amounts of extracellular mucin. At the benign end are low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasms that often distend the appendiceal lumen with mucin, forming a mucocoele. Non-mucinous, intestinal-type adenocarcinomas of the appendix also occur, but are less common. They resemble typical colorectal carcinoma histologically and tend to behave in a similar way with nodal and haematogenous metastases more frequent than transcoelomic spread to peritoneal surfaces. Another distinct group is the goblet cell family of neoplasms, as discussed later. As discussed in Chapter 1, the classification of mucinous appendiceal neoplasia has been contentious, and over the years a number of different classifications have been proposed with inconsistent use of terminology. There may also be extravasation of extracellular mucin into the wall of the appendix. True signet ring cells need to be distinguished from degenerative cells within mucus pools. All appendiceal adenocarcinomas, irrespective of the presence of signet ring cells, exhibit a high propensity for peritoneal metastasis [14]. They are unusual neoplasms that occur in adults of any age and are thought to develop at the base of the mucosa, possibly arising from lysozyme-producing goblet cells [15]. The appendix is almost always the primary site, although very rare cases arising elsewhere have been reported. They are often unsuspected until histopathological examination because the appendix commonly appears unremarkable macroscopically or shows only diffuse wall thickening. Immunohistochemical markers for neuroendocrine differentiation such as synaptophysin and chromogranin are usually positive, but expression of the latter is often confined to the cells morphologically showing neuroendocrine features. Transcoelomic spread is common, leading to involvement of peritoneal surfaces and ovaries; haematogenous metastases are unusual [20]. Their prognosis is worse than goblet cell adenocarcinomas because of their highly aggressive behaviour. Lesions are assessed for three features: cytological atypia involving an area of at least 1 mm2; desmoplasia distorting the appendiceal architecture; and solid growth of tightly packed cells involving an area of at least 1 mm2. Tumours with no more than one feature are classified low-grade, whereas lesions with two or three features are high-grade. Other studies have shown an association between the proportion of tumour showing malignant features and survival [19,23]. The relationship of genetic alterations to morphology and biological behaviour remains to be elucidated. On the other hand, they show immunohistochemical evidence of Notch signalling similar to appendiceal adenocarcinoma [26]. Furthermore, diagnostic criteria appropriate for neuroendocrine tumours such as tumour size and Ki-67 proliferation index are not used to classify them [21,22,27,29]. The mucin may be associated with fibrosis, scattered chronic inflammatory cells, mesothelial hyperplasia and calcification. The degree of atypia of the cells in the mucin determines its overall biological behaviour, with higher grades behaving more like intestinaltype adenocarcinoma of the colorectum. This classification, which has been the result of multiple consensus-seeking meetings, overlaps and supersedes earlier classifications, such as the one by Ronnett et al. It is important to adequately sample resection specimens for histology, including any extra-appendiceal mucus encountered in appendicectomies. Genetic analyses of peritoneal and pleural mesothelioma have shown many similarities, but there are also differences between them [36]. Macroscopically, most malignant mesotheliomas show a diffuse pattern of growth on serosal surfaces producing multiple small tumour nodules, plaque-like masses, or a rind encasing abdominal viscera. Distant metastases can occur, but from a clinical point of view it is the locoregional disease that is usually most important. There are three main histological patterns of malignant mesothelioma: epithelioid, sarcomatoid and biphasic [35]. Solitary fibrous tumours are not mesothelial and are believed to originate from submesothelial mesenchymal stem cells. Specific histological features that have been found to be associated with a poor prognosis in these patients include a solid pattern of growth, a high mitotic count and a high Ki-67 proliferation index [34,38]. Epithelioid mesotheliomas with a tubulopapillary pattern of growth and minimal invasion of underlying tissue may be more likely to be associated with prolonged survival [34]. In general, biphasic and sarcomatoid mesotheliomas are aggressive neoplasms with a dismal prognosis. Differentiating between malignant mesothelioma and reactive mesothelial proliferations can be very difficult [33]. Both conditions can 138 Histopathological aspects of peritoneal malignancy be associated with papillary structures, enlargement of cells, nuclear atypia, prominent nucleoli and mitotic activity.
Syndromes
- Abnormal white blood cells
- Nausea
- What drugs you are taking, even drugs or herbs you bought without a prescription
- Blurred or decreased vision
- Arthritis
- Do not need pain medicine through an IV or given by shot
- Sexual function problems
- Short attention span
Generic 0.2mg flomax overnight delivery
Recent advancement in the genomic and transcriptomic level studies of various cyanobacterial strains provides lots of knowledge regarding the complex metabolic pathways of pigment production that permits researchers to explore various emerging techniques to produce potential cyanobacterial strains for the production of pigments prostate nerves order discount flomax. Furthermore, the production cost of the cyanobacterial pigments would be reduced by using system biology approaches. The production coast of pigments can also be minimized by developing strains which may produce other industrial product simultaneously. Further studies of cyanobacterial pigments are needed to improve their stability, compatibility, and other beneficial effects to enhance their commercial value in the international market. Industrial potential of carotenoid pigments from microalgae: current trends & future prospects. Interaction of salinity and temperature on morphology, growth and cell composition of a halotolerant cyanobacterium (Aphanothece sp. Iron-chelating ability and antioxidant properties of phycocyanin isolated from a protein extract of Spirulina platensis. A simple method for efficient extraction and purification of C-phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis Geitler. Haematococcus pluvialis as a source of fatty acids & phytosterols: potential nutritional & biological implications. Dietary chlorophyllin is a potent inhibitor of aflatoxin B1 hepatocarcinogenesis in rainbow trout. Characterization and structural properties of the major biliproteins in Anabaena sp. Chromophore content of a cyanobacterial phycoerythrin carrying phycourobilin chromophore. Protective activity of processed tomato products on postprandial oxidation & inflammation: a clinical trial in healthy weight men & women. Analytical methods for determining bio-availability & bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds from fruits & vegetables: a review. Isolation, purification and regulation of c-phycocyanin from cyanobacterial species (Doctoral dissertation, PhD thesis, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi). Effect of light and temperature on the cyanobacterium Arthronema africanum-a prospective phycobiliprotein producing strain. An unusual cyanophyte, containing phycourobilin and symbiotic with ascidians and sponges. Optimization of the extraction of chlorophylls in green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L. Chemomodulation of carcinogen metabolising enzymes, antioxidant profiles and skin and forestomach papillomagenesis by Spirulina platensis. Microorganisms & microalgae as sources of pigments for food use: a scientific oddity or an industrial reality Pigmentation and spectral absorbance signatures in deep-water corals from the Trondheimsfjord, Norway. Production of phycocyanin a pigment with applications in biology, biotechnology, foods & medicine. Characterization and biological implications of scytonemin, a cyanobacterial sheath pigment. Evidence for an ultraviolet sunscreen role of the extracellular pigment scytonemin in the terrestrial cyanobacterium Chlorogloeopsis sp. Cyanobacterial pigments and their fluorescence characteristics: applications in research and industry Chapter 5 69 Glazer, A. Systems and synthetic biology for the biotechnological application of cyanobacteria. An in vivo quantitative structure-activity relationship for a congeneric series of pyropheophorbide derivatives as photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Spectroscopic studies on phycoerythrins from cyanophycean and rhodophycean algae with special reference to their phylogenetical relations. Heat and light stability of three natural blue colorants for use in confectionery and beverages. Effects of different light source and media on growth and production of phycobiliprotein from freshwater cyanobacteria. Oxidation of biological systems: oxidative stress phenomena, antioxidants, redox reactions, and methods for their quantification. Invited review: Oxidation of biological systems: oxidative stress phenomena, antioxidants, redox reactions, and methods for their quantification. Morphology of a novel cyanobacterium and characterization of light-harvesting complexes from it: implications for phycobiliprotein evolution. Filamentous cyanophytes containing phycourobilin and in symbiosis with sponges and an ascidian of coral reefs. Marine algal natural products with anti-oxidative, antiinflammatory & anti-cancer properties. High value pigment production from Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis cultured in seawater. Metabolic engineering of the pentose phosphate pathway for enhanced limonene production in the cyanobacterium Synechocysti s sp. Inhibitory effect of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis on the growth of human leukemia K562 cells. Effect of natural supplementation of inositols, fucoxanthin & hydroxytyrosol in pregnancies complicated by metabolic syndrome. Chlorophyll: natural sources, extraction methods and application for textile industry. Pigment composition of a novel oxygenic photosynthetic prokaryote containing chlorophyll d as the major chlorophyll. The potential use of marine microalgae & cyanobacteria in cosmetics & thalassotherapy. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis: a guide to good practice and understanding some new applications. Carotenoid glycoside isolated and identified from cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Chlorophyll derivatives-a new photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy of cancer in mice. Isolation and characterization of phycobiliproteins from symbiotic cyanophytes in ascidians. The structure of scytonemin, an ultraviolet sunscreen pigment from the sheaths of cyanobacteria. Effective inhibition of skin cancer, tyrosinase & antioxidant properties by astaxanthin & astaxanthin esters from the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Co-administration of C-phycocyanin ameliorates thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in Wistar rats. Chlorophyll b expressed in cyanobacteria functions as a light-harvesting antenna in photosystem i through flexibility of the proteins. Cyanobacterial pigments and their fluorescence characteristics: applications in research and industry Chapter 5 71 Scheer, H. X-ray crystallographic structure of the light-harvesting biliprotein C-phycocyanin from the thermophilic cyanobacterium Mastigocladus laminosus and its resemblance to globin structures. Phycobiliproteins as a commodity: trends in applied research, patents and commercialization. The role of lycopene & its derivatives in the regulation of transcription systems: Implications for cancer prevention. C-phycocyanin: cellular targets, mechanisms of action and multi drug resistance in cancer.
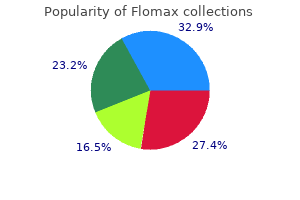
Purchase generic flomax line
The germline mutations are heterozygous man health 4 all discount flomax 0.2mg free shipping, and colon carcinogenesis results from silencing of the nonmutant allele by methylation70,71 or by acquired allelic loss. At a clinical level, protein loss can be demonstrated by immunochemistry and optimally requires four separate stains. The mutational hot spots are found in exon 7, resulting in amino acid substitution Y179C, and in exon 13, resulting in substitution G496D. This form of polyposis carries a lifetime risk of colon carcinoma of 39% and a relative risk of 34. Biomarkers for Colon Cancer Screening Genetic tests Although the number of highly penetrant mutations that predispose to colon carcinoma is large, the proportion of colon carcinomas that can be accounted for by these mutations is approximately 5%43 and has been overestimated in the past. In addition, collection and processing of fecal specimens for a biomarker that is expected to be present at low level and heavily contaminated by nonneoplastic cells is a logistic challenge. Second, some of the genetic abnormalities identified in colon carcinogenesis do not readily lend themselves to screening assays. Finally, wide availability of colonoscopy services that combine polyp detection and excision reduces the cost and improves the attractiveness of direct and systematic colonoscopic population-based surveillance. This test is based on a color change whereby -guaiaconic acid extracted from the wood of tropical Guaiacum tree is rapidly oxidized by hydrogen peroxide to a blue quinone in the presence of heme derived from blood. There is wide variability in results116 as a consequence of the level of compliance with collection methods, type or brand of kit, frequency of testing, user interpretation, and other factors. It has been shown to have a cancer detection rate similar to colonoscopy but has a lower sensitivity for polyps. Despite the availability of these fecal-based tests, the target in early colon cancer intervention appears to be shifting from detection of invasive carcinoma to prevention by detection and thorough clearing of adenomatous polyps from the colon. Defining the biology of colon carcinogenesis and confirming that polyps are the precursor lesions along with improvements in colonoscopic methods have led to reduction in mortality from colon cancer. Colonoscopy enables direct identification of potential precursor lesions and at the same time provides a means for ablating them. This is strikingly evident in the new sigmoidoscopy findings37 indicating that whereas sigmoidoscopy reduces mortality from visible distal colon tumors, mortality from proximal lesions is unaffected. It seems likely that colonoscopy will be the main vehicle for early detection and intervention in colon cancer for the foreseeable future. Lung Carcinogenesis and a Known Carcinogen For several decades lung carcinoma has had the highest mortality of all tumors, accounting for more than twice as many deaths as the next most lethal tumor. Chemoprevention using -carotene and/or -tocopherol dietary supplementation also failed. Central airway premalignancy: squamous dysplasia the predominant premalignant lesion of the central airways is squamous dysplasia134 (also referred to as atypia). Squamous dysplasia was documented over 50 years ago in association with carcinoma135 as well as in smokers without concurrent carcinoma. Prospective studies on the power of dysplasia to prospectively predict future central airway malignancy are few and face the forbidding challenges of inaccessibility of the bronchi and the prolonged follow-up that is required to achieve significant results in a sufficiently powered cohort. Sputum studies indicate that atypia of cells exfoliated from the central airways is associated with elevated risk for incidental carcinoma. Squamous tumors typically form in the central airways, where they are thought to arise from 1, the respiratory mucosa. Adenocarcinomas typically arise peripherally in 5, the alveoli and terminal bronchioles. This category represents a redefinition of the low-grade adenocarcinoma previously known as bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. However, by the time this occurs, tumor is often invasive and must be treated aggressively. The result is a wide range of genomic losses, gains, translocations and point mutations that account for the high degree of molecular heterogeneity in lung tumors with diverse physiologic effects. A recent prospective study of 188 patients who underwent biopsy at mapped bronchial sites found that the persistence of high-grade dysplasia at the same bronchial site was associated with future squamous carcinoma but not adenocarcinoma, suggesting that persistent dysplasia may be a marker of progressive field change. The corollary question of whether ablation of premalignant central airway lesions could reduce lung cancer mortality remains an open one. The findings of a chemoprevention study140 using iloprost, a prostacyclin agonist, have suggested that reversal of premalignant dysplasia morphological features may be possible, but the study was a small one and the end point was purely histological. The long-term effect on mortality of agents that may alter the premalignant morphologic characteristics of central airway epithelium remains unknown. The greatest experience regarding the use of epigenetic changes in the context of early detection of lung cancer has been obtained with regard to methylation. In lung carcinogenesis, methylation preferentially occurs in CpG-rich regions (CpG islands) that are present in normally unmethylated promoter regions of critical genes (hypermethylation) and may silence gene expression. This finding initially led to optimism that methylation could be used to screen selected populations at risk for lung carcinoma. However, the predictive power of single-gene methylation or methylation of a small number of genes is limited by the ubiquity of methylation in smokers and the consequent high rate of false-positive results. This problem led to the strategy of testing promoter regions in large numbers of genes to estimate overall methylation burden. It is also frequently observed in high-grade dysplastic lesions in the central airways. Larger solitary ground-glass lesions of pure lepidic carcinomas as well as some lesions with areas of consolidation and even multifocal ground-glass lesions also are characterized by slow growth and excellent prognosis and may persist for many months to years without changing size or evincing evidence of alveolar wall invasion. Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, adenocarcinoma in situ, and lepidic carcinoma Molecular Changes During Lung Carcinogenesis As in other organs, most notably the colon, molecular changes that accompany the morphologic changes of dysplasia have been investigated in considerable detail. These studies are informed by the well-established role of tobacco smoke as a carcinogen in lung cancer. Over time, molecular alterations accumulate, providing a selective advantage to mutant cells for growth and survival. Components of this pathway have been associated with increased risk for future lung cancer. Case control studies indicate that current smokers with tumors have higher levels of adducts in blood or tissue than non-tumor controls. Clinically applicable adduct levels predictive of lung cancer have not been established. It seems unlikely that single-gene mutation analysis will be sufficiently sensitive for use as a screening tool. High-throughput methodologies have been suggested as possible early detection tools. However, this region of the gene is still being explored for more powerful biomarkers. Gene expression microarrays have identified consistent changes in the transcriptome of epithelium brushed from nonmalignant bronchial surfaces that distinguish smokers from nonsmokers. High-throughput technologies refers to destructive, invasive malignant tumors that form solid masses. The primary tool of the pathologist remains the hematoxylin-and-eosin stained section, but this is now supplemented by an arsenal of immunohistochemical stains and other tissue testing procedures that permit much greater specificity of diagnosis than was previously possible. Diagnostic immunohistochemical tests are relatively simple and inexpensive and can be assessed in conjunction with in situ cellular architecture, which ensures a high level of specificity and permits an assessment of the relevance of results to the overall clinical and anatomic features. Interpretation of immunohistochemical data is now assisted by online databases that provide frequencies of immunohistochemical results in specific tumors and organ sites. Histologic diagnosis was discussed earlier in the context of early detection and is addressed elsewhere in this book in relation to individual tumor types. Although histologic evaluation remains the primary method for diagnosis of solid tumors, molecular methods are increasingly influential not only in identification of treatment targets as discussed here, but also in tumor classification. Both molecular and cellular diagnostics continue to depend not only on consistent and effective fixation and processing of tissue, but also on reliable accessioning and informatics. Other Organ Sites Premalignant cellular and molecular changes are described in several other tumors including breast, prostate, bladder, and esophagus. Detailed review of these changes may be found in appropriate chapters of this text. However, to date, identification of these changes has not led to mortality reductions. Accessioning and Informatics Registering patients and biopsy specimens is a demanding exercise that is often overlooked and underfunded. Although numerous and variable protocols are available for tracking specimens, virtually all tracking systems include a secure electronic database with passwordlimited access and reliable backup. Appropriate specimen identifiers, which today are increasingly bar-coded, access to signed consent forms when associated research studies are underway, and timely data entry are all essential for any well-run laboratory. A detailed discussion of laboratory information systems for molecular testing is beyond the scope of this chapter but must be a major consideration in the management and quality assurance programs of all clinical molecular testing laboratories.
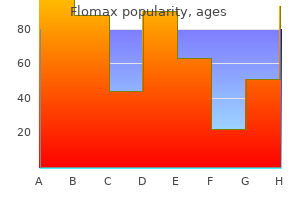
Buy cheap flomax
Impact of pesticides applications on the growth and function of cyanobacteria Chapter 10 161 Ma anti-androgen hormone therapy discount flomax 0.2mg without a prescription, J. Differential responses of eight cyanobacterial and green algal species, to carbamate insecticides. Differential toxicity of agricultural fungicides toward three cyanobacterial and five green algal species. Organic chemicals jeopardize the health of freshwater ecosystems on the continental scale. Isoproturon degradation as affected by the growth of two algal species at different concentrations and pH values. Chronic toxicity of a triazole fungicide tebuconazole on the growth and metabolic activities of heterocystous, nitrogen-fixing paddy field cyanobacterium, Westiellopsis prolifica Janet. Nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in paddy soils (Part 1) characteristics of the nitrogen fixation in paddy soils. Probit Analysis of Carbamate-Pesticide-Toxicity at Soil-Water Interface to N2-Fixing Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermum sp. Antagonism at combined effects of chemical fertilizer and carbamate insecticides on the rice field N-fixing cyanobacterium Cylindrospermum sp. Toxicity of methyl parathion to cells, heterocysts and akinetes of cyanobacterium Cylindrospermum sp. Toxicity of Carbamate Pesticides to Cells, Heterocysts and a Kinetes of the Cyanobacterium Cylindrospennum sp. Growth, photosynthesis, active oxygen species and antioxidants responses of paddy field cyanobacterium Plectonema boryanum to endosulfan stress. Influence of diverse rice soil ecologies on cyanobacterial diversity and abundance. Microbial mat compositional and functional sensitivity to environmental disturbance. Effects of a fungicide, an insecticide, and a biopesticide on Tolypothrix scytonemoides. Effect of salinity on nitrogenase activity and composition of the active diazotrophic community in intertidal microbial mats. Effects of monosulfuron on growth, photosynthesis, and nitrogenase activity of three nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. Effects of monosulfuron-ester on metabolic processes of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria Anabaena flos-aquae and Anabaena azotica. Cyanobacteria: a vital bio-agent in eco-restoration of degraded lands and sustainable agriculture. Outdoor evaluation of herbicide resistant strains of Anabaena variabilis as biofertilizer for rice plants. Diversity and distribution pattern analysis of cyanobacteria isolated from paddy fields of Chhattisgarh. A synthesis of the effects of pesticides on microbial persistence in aquatic ecosystems. N2-Fixing Cyanobacterial Systems as Biofertilizer in Agro-Environmental Sustainability. Effect of the systemic fungicide, Bavistin on the nitrogen status of cyanobacteria under immobilized state in polyurethane foam. International Symposium on Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Farming Systems of Humid Tropics. Effects of cyanobacterial toxicity and morphology on the population growth of freshwater zooplankton: meta-analyses of laboratory experiments. Physiological effects of the herbicide glyphosate on the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Enantioselective physiological effects of the herbicide diclofop on cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Enantioselective changes in oxidative stress and toxin release in Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to chiral herbicide diclofop acid. Effect of benthiocarb and butachlor on growth and nitrogen fixation by cyanobacteria. The influence of abiotic factors on biological nitrogen fixation in different types of vegetation in the High Arctic, Svalbard. Chapter 11 Cyanoomics: an advancement in the fields cyanobacterial omics biology with special reference to proteomics and transcriptomics Savita Singh Department of Botany, Babu Shivnath Agrawal College, Mathura, India 11. They made the anoxygenic environment oxygenic by performing photosynthesis and thus provided a platform for the emergence of other complex life forms. Diverse habitats of cyanobacteria inhabitants range from moderate climatic conditions to extremes of environmental cues, that is, extremes of temperature, salt, or pressure and life forms (Tamura et al. They may be freshwater or marine forms; some forms are terrestrially occurring on rocks or logs of wood or buildings. The complexity in life forms ranges from unicellular to filamentous forms (Tamura et al. Some of the cyanobacteria are bestowed with unique differentiation in terms of ability to form specialized cells besides vegetative cells, called heterocysts, having the ability to fix nitrogen (Kumar et al. Although cyanobacteria lack motile reproductive units, and initially, it was reported that reproduction is dominantly by asexual means such as fragmentation, fission, and hormogone formation (Whitton, 1992). They exhibit three means of genetic exchange like bacteria, that is, through a conjugation pilus (Finnegan and Sherratt, 1982), transformation (Yoshihara et al. Besides these, mutations are also common in cyanobacteria cells for genetic recombination (Kumar, 1962). All these prerequisites help cyanobacteria to overcome its genetic recombination limitations due to asexual reproduction. It is suggested that horizontal gene transfer along with intragenomic rearrangements and duplication has aided cyanobacteria in adapting to different environmental niches and variance in closely related species (Eisen, 2000). If we look into cyanobacteria in terms of economic gains, the benefits are alluring such as cyanobacteria commonly produce diverse secondary metabolites and bioactive compounds having great potential for drug development and other biotechnological uses (Ducat et al. Ability to perform photosynthesis and ease of growth makes them promising third-generation biofuels (Dechatiwongse et al. Furthermore, these life forms are continuously subjected to stresses that negatively affect their metabolism and physiology (Higo et al. Despite having these constraints, these life forms live happily with these stressors and survive in paddy fields by changing their normal physiology (Bhargava et al. A large number of transcriptomics and proteomics studies have been conducted to unlock the survival mechanism of these tiny organisms. However, all these studies signify a large chunk of proteins and transcripts belong to a hypothetical category. Our knowledge and understanding of structure and evolution of genomes are on a high note owing to the recent advent of high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics tools. Moreover, molecular studies have provided a good understanding of the phylogeny of life, providing the framework for examining the evolution of genomes across all life forms (Walsh, 2001). Till now, 85 fully sequenced genomes are available on the cyan base database comprising 32 genera, and almost all the species possess. Thus, there is a need to unlock the cyanobacterial genome and understand the functional aspect of these genes and their functional role in the life of cyanobacteria. In this direction concerted action of genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics along with interactomics will surely build a milestone in the understanding of cyanobacteria and its myriad applications to biotechnology and turn to serve humankind. The present chapter helps one to pinpoint the past present and future of functional genomics with the amalgamation of studies in the field of transcriptomics, proteomics, and interactomics of cyanobacteria to decode the role of hypothetical proteins. This nomenclature takes into account phenotypic characters such as morphology of the filament, vegetative cells, heterocyst and akinetes, structure of the colony, shape of the terminal cells, presence or absence of sheath, gas vesicles, and other characters that often lead to misidentification of phylogenetically related taxa (Desikachary, 1959; Komarek and Anagnostidis, 1989). Due to its highly conservative domain along with nine hypervariable regions and its universal distribution (Nubel et al. Cyanobacterial phylogeny and taxonomy have been assessed by employing different molecular markers for a quite considerable time and still are popular.
Purchase 0.4mg flomax overnight delivery
A subsequent 2010 systematic review of 50 studies containing 340 estimates by the same group documented that tax/price policies could significantly reduce alcohol-related morbidity and mortality prostate oncology times order flomax 0.2mg otc, with a 35% reduction in alcohol-related mortality expected from a doubling of alcohol taxes. There is limited evidence that these types of brief behavioral interventions are ineffective in the setting of alcohol abuse or dependence. In such cases the benefits of specialty treatment are well established, and this type of treatment is recommended. This section reviews the role of obesity in cancer and proposed mechanisms linking obesity with cancer. Role of Obesity in Cancer In obesity, adipose tissue typically accumulates in two different regions: the android region or abdominal area, and the gynoid region, which consists of the hips and thighs. Android obesity differs from gynoid obesity such that it contains two different types of adipose tissue deposits, subcutaneous and visceral. In an observational study conducted by Britton and colleagues,77 adiposity measurements in four different areas (subcutaneous, visceral, periaortic, and pericardial) were compared with incident cancer, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality over a median 5-year follow-up period. Proposed Mechanisms Linking Obesity With Cancer Although the relationship between obesity and cancer is evident from observational data, the physiologic mechanisms explaining this relationship have recently emerged in the literature. Along with macrophage activity, adipokine profiles, notably adiponectin and leptin, are altered in the obese state. Normal physiologic levels of adiponectin are linked with enhancement of insulin sensitivity and reduction in angiogenesis. The increase in leptin is associated with increases in cellular proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis in breast, ovarian, and cervical cancers. Considering that adiponectin is associated with insulin sensitivity, in the obese state a reduction in adiponectin also contributes to a reduction in insulin sensitivity and subsequent insulin resistance. In addition to insulin serving as a contributing factor for increased estrogen and protumorigenic effects, it is important to note that adipose tissue is a major site for estrogen synthesis in postmenopausal women and men; thus, increased adipose tissue leads to increased estrogen production, and consequently a greater ratio of circulating estrogens to androgens may lead to cancer. Physical Inactivity Physical activity consists of two subtypes of activity: exercise or structured physical activity, which is defined as activity pursued for the purpose of improving fitness, and lifestyle physical activity. Therefore physical inactivity is identified when one not only does not engage in exercise but also has minimal lifestyle activity. Role of Physical Inactivity in Cancer Current public health guidelines recommend 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity, and at least 2 days per week of strength training exercise. Overall, both subjective and objective evidence is available linking regular, structured physical activity with reduced risk of chronic disease and certain cancers such as colon and breast cancer. In addition to structured physical activity, when lifestyle activity decreases, it is typically replaced by increased sedentary behavior. A meta-analysis by Schmid and Leitzmann90 noted that colon cancer risk increased by 8% and endometrial cancer risk by 10% for every 2-hour increase in total sitting time per day. In addition, in a prospective cohort study conducted by Nomura and colleagues,91 a significant association with sitting time and breast cancer incidence was observed when individuals spent more than 10 hours sitting per day. Taken together, sedentary behavior is linked with increased risk of colon, breast, and endometrial cancer. As mentioned previously, obesity-induced insulin resistance promotes tumorigenesis. Along with obesity-related mechanisms, there are also mechanisms unique to skeletal muscle activity-notably, release of cytokines from contracting skeletal muscle, commonly referred to as myokines. Diet the link between diet and cancer risk is complex, such that not all dietary components. This section presents the dietary components containing the most evidence in relation to increased or decreased cancer risk. For colorectal and pancreatic cancer, these effects seem to be more relevant to men. High-salt foods and salt intake Unique to processed meats is the high salt content. The following diets were compared: vegetarian, defined as consumption of meat less than once per month; semivegetarian, defined as consumption of meat more than once per month but less than once per week; pescovegetarian, defined as consumption of fish as the only type of meat, more than once per month; and nonvegetarian, defined as consumption of meat more than once per week. Taken together, these findings suggest an association between lower intake of meat and cancer risk reduction. In assessing individual micronutrient supplementation in relation to cancer risk, the majority of evidence has demonstrated null or adverse health effects. Yet adequate intake of vitamin C can easily be achieved through consumption of fruits and vegetables. Thus, current recommendations for nutrition and cancer prevention state that unless an individual has micronutrient deficiencies, which would require supplementation beyond dietary intake, micronutrient consumption from a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains will suffice in terms of health benefits related to cancer prevention. Despite being highly preventable, skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States, with 5 billion cases treated annually at a cost of $8. In general, lighter-skinned individuals have a higher risk of all skin cancers than do darker-skinned individuals. Important to note, there is no evidence to suggest that indoor tanning is safer than tanning outdoors or that it protects from the effects of future sun exposure. An increase in dietary water and fiber content may increase satiety, prevent excessive energy intake, and replace or limit poor food choices such as refined grains, added sugars, salty snacks, and processed meats. Obesity, Physical Inactivity, and Dietary Recommendations and Resources for Cancer Prevention Recommendations for cancer prevention63 are shown in Table 22. As evidenced by results from the systematic review conducted by Birks and colleagues,70 weight loss in overweight or obese individuals is linked with reduction in cancer incidence. The underlying theme in weight loss is energy balance-moving more (increasing energy expenditure) and eating less (reducing energy intake). There are countless resources available to assist individuals with energy balance to promote weight loss and maintenance of a healthy weight. This guide includes strategies, such as goal setting and self-monitoring, to establish healthier dietary habits in efforts to incorporate the behavior change component into weight loss. Furthermore, it is well known that organ-transplant recipients who have the immune system suppressed to prevent organ rejection are susceptible to skin cancer. These factors led the Surgeon General to release a report in 2014 that serves as a call to action to prevent skin cancer. The report also sets five goals to support skin cancer prevention across the country and discusses several strategies to achieve each goal (Table 22. Numerous cohort and case-control studies have examined the relationship between sunscreen use and skin cancer, but results are conflicting and most have serious methodological limitations relating to measures of sun exposure, sunscreen use, and adjustment for important confounders. Important to note, family history often determines when an individual begins cancer screenings, how frequently 348 PartI:ScienceandClinicalOncology Table 22. Genetic testing may be warranted in patients with a strong positive family history of cancer. These tools are not cancer specific, but are applicable to all noncommunicable chronic diseases. For more information related to family history in cancer, the reader is referred to Chapter 13. Advances in our understanding of the mechanistic basis for carcinogenesis, with the identification of molecules and signaling pathway alterations critical for tumorigenesis, has enabled the development of molecularly targeted therapies to block tumor development. The novel drugs, signaling inhibitors, and vaccines that have been developed and tested as cancer preventive agents are discussed in this section. Major challenges are (1) to elucidate the critical molecular drivers of early tumorigenesis that can be targeted to prevent cancer development; (2) to develop effective, safe, and tolerable preventive therapies; and (3) to promote the use of these safe preventive therapies in at-risk individuals. The ultimate goal of these efforts is to deliver effective, safe, and acceptable interventions to prevent multiple forms of cancer. However, although these strategies have proven effective for preventing specific tumor subtypes, they are often ineffective or poorly effective in prevention of other tumor subtypes.
Kalidruma (Terminalia). Flomax.
- Treating congestive heart failure (CHF), when used with conventional medications.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Terminalia work?
- Treating chest pain (angina) after a heart attack, when used with conventional medications.
- Dosing considerations for Terminalia.
- Earaches, HIV infection, lung conditions, severe diarrhea, urinary problems, water retention, and other conditions.
- What other names is Terminalia known by?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96788
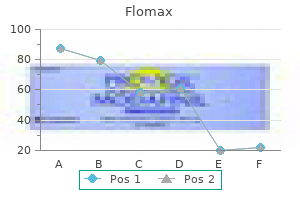
Cheap flomax online american express
Analysis of nanoparticles is a major challenge due to its multidisciplinary nature androgen hormone kalin buy flomax overnight delivery, lacking reference materials for the calibration of tools, sample preparation for the examination, measurement of their concentration, and interpretation of the data. Nanoparticles require different analytical tools for characterization than a conventional technique used to characterize organic and inorganic compounds and chemicals. Nanoparticles were characterized based on dimension, shape, surface properties, crystallinity, and dispersion state of nanoparticles. Different characterization tools and techniques were applied for the characterization of nanomaterials mentioned in Table 21. Nanoparticles were mainly assessed using nanoparticle dimension, shape, and distribution. This characteristic feature is handy for imaging of biological and polymeric nanostructures. The crystal phase, crystal structure, lattice parameters, and particle sizes of nanoparticles have been determined by the powder X-ray diffraction technique. Raman spectroscopy is based on monochromatic light scattering, usually from a laser source. It provides information related to vibration, rotation, and other low-frequency transitions in molecules. The application of nanoparticles synthesized by biological systems is an emerging field of science. The interest of biologically synthesized nanoparticles for biomedical application use has increased, because they are more biocompatible than their nonbiological counterparts (Thakkar et al. Here in this section, we discussed some of the prospective applications of the nanoparticles. Conventionally diagnostic methods depend on the appearance of symptoms after illness for most disorders, which delay the treatment period. Therefore it is the primary objective of early detection of disease for better treatment. Nanotechnology currently plays an important role in the development of disease diagnosis available, resulting in much higher sensitivity and better efficiency and economy. Several nanomaterials such as quantum dots (semiconductor nanoparticles), gold nanoparticles, and iron oxide are being investigated to construct nanosensors designed for diagnosis of diseases (El-Ansary and Faddah, 2010). Nanoparticle-based technology provides new routes for drug delivery and medicine formulations, which have significant efficacy and low side effects. The polymer nanoparticles such as chitosan nanoparticles are used as a carrier for drugs, synthetic peptides, proteins, oligonucleotides, and plasmids. The nanoparticles protected these drugs and peptides from enzymatic degradation and delivered them into the target cells in an active form and showed maximum therapeutic effects on targeted cell (Janes et al. When therapeutics are chemically attached with nanoparticles, they can easily reach the target sites where conventional drugs cannot reach. Sustain release of drugs can be achieved by encapsulating these drugs in nanosized polymers such as dendrimers and nanoshells. The metal and metal oxide nanoparticles are used as cosmetics, abrasives, and in biomedical implants. They are also used as scaffolds to enhance constructive communication between orthopedic implants and native bone, reduced infection rates, and improved bone and tendon healing. However, further research has been needed to thoroughly understand its safety and potential application of this exciting technology (Smith et al. The use of nanoparticles in dental care 326 Advances in Cyanobacterial Biology will ensure better oral health. The nanoparticles are used for preventing oral diseases, prostheses, and for teeth implantation. Nanocomposites such as hydroxyapatite and ceramics were used for filling of dental defects, enamel surface polishing, and to prevent erosion and as implant materials (Priyadarsini et al. The wide and haphazard use of antibiotics, pesticides, and other related compounds in agriculture also increases the number of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms. The control of these antibiotic-resistant microorganisms is the major challenge for scientists and researchers worldwide (Rai et al. In recent years, nanoparticles are being used as broadspectrum antimicrobial agents to inhibit or kill pathogenic microorganisms. Nanoparticles such as silver, copper, gold, zinc, titanium and iron have been used as antimicrobial agent in clinical and healthcare products (Thakkar et al. The nanoparticles exerted against a wide range of microorganisms in a very low concentration. The growth of microorganisms, such as Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes, protozoa, and other pathogenic groups, was inhibited by the presence of nanoparticles. Silver has a long history to use as antimicrobial agents, because it possesses antifungal, antibacterial, antiinflammatory, and anticancerous properties (Rai et al. Silver nanoparticles have been used commercially in surgically implanted catheters and in personal care products for preventing the chances of infection. The research study indicates that the silver nanoparticles can interact with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and inhibit the virus from binding to the host cells (Elechiguerra et al. The broad-spectrum antimicrobial efficacy of nanosized silver is relatively superior to the prominent antibiotics used around the world (Bankura et al. The gold nanoparticles also inhibit the growth of several Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and fungi. Like silver, copper oxide (CuO), zinc oxide (ZnO), and titanium oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles may have great potential of antimicrobial applications (Ren et al. TiO2 can be potentially used in various fields such as water purification, foods, cosmetics, and sunscreens. The gold and magnetic nanoparticles are commonly used for preparing biosensors as they have unique electronic and optical properties (Holzinger et al. The drug delivery system maintains the concentration and stability of drugs over time, which is helpful for sustain release of drugs at the target site (Kubik et al. Use of nanoparticles in drug delivery system has come forwarded as an advance move toward drug delivery. The research illustrated that antibody-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles functionalized or encapsulated with poly-(D,L-lactide-coglycolide) and doxorubicin can be used for sustained release of anticancerous drugs and imaging system (Zhao et al. Cellulose-based nanopolymers were used as tablets for oral drug delivery due to its compaction property. Nanocellulose-based drug carriers are developed in the form of microspheres, hydrogels, and membranes. These microspheres have high encapsulation capacity, good swelling behavior, and continuous and sustained release of the drug (Lin et al. The drug release behavior showed that the hydrogels containing cyclodextrin display sustained release of the drug (Seabra et al. Cyanobacteria as a source of nanoparticle: application and future projections Chapter 21 327 21. Several environmental protection agencies were worked on contaminated sites to test the efficiency of nanoparticles, especially nanozerovalent iron for removal or degradation of environmental contaminants. Iron and other nanoparticles from iron rust can be used to remove contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals, and radionuclides from the soil. New innovative techniques such as precise farming; enhancing the ability of plants to absorb nutrients; disease detection; and control, effective processing, storage, and packaging enhance the quality of agriculture, which is essential in the current scenario to fulfill the food demand of world (Singh et al. Nanoparticles are being developed as biofertilizer in agriculture to overcome the limitations of conventional farming. Nanoparticles have the potential to enhance the fertility of the soil by providing nutrients to plants at an optimum level. Nanostructured materials having nutrients essential for plant growth and development in aqueous solution and hydrogels are being studied for use in growing plants or crops. Nanoparticle used in various fields of the food industry, including the processing of food, packaging of food, enhance the nutritional value of food and promotes food safety, detection of foodborne pathogens, and shelf life extension of food and food products (Singh et al. The common pathogens linked with foodborne illnesses are norovirus, Campylobacter spp. Several conventional methods such as freezing, heat and refrigeration storage, filtration, drying, chemical preservatives, as well as radiation and other thermal procedures are used to minimize the risks associated with foodborne illnesses. These approaches have several drawbacks that are not in compliance with the current trend of new organic and chemical-free food demands. These techniques are also associated with high-energy costs, an increased possibility of degradation, as well as serious occupational and health implications. The common applications of nanotechnology in food industry are nanosized encapsulated agrochemicals, food additives and supplements, and antimicrobial active food packaging agents (Eleftheriadou et al.
Purchase discount flomax on-line
Nanoparticles are composed of three layers-the outer man health 1 purchase flomax now, surface layer; the middle as shell and the innermost layer is called the core layer. The outermost layer of nanoparticles is usually fabricated with various compounds such as macromolecules, metal ions, surfactants or polymers which impart each nanoparticle with unique properties (Li et al. Through the ability to Cyanobacteria: potential source of biofertilizer and synthesizer of metallic nanoparticles Chapter 23 359 synthesize phycobiliproteins, which is about 70% of total protein by dry weight (MubarakAli et al. Phycobiliproteins show fluorescent properties due to the presence of aromatic amino acids-tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine forms through the shikimate pathway. The phycobiliproteins are probably involved in the synthesis of metal nanoparticles (Khan et al. With involving some other higher plants containing a high amount of aromatic compounds, zerovalent iron nanoparticles have also been synthesized (Kumar et al. The reason for such type of metal nanoparticles synthesis is due to cyanobacteria secrets extracellular chemical compounds to capture such heavy metals or mediate electrostatic interactions. Microalgae use both intracellular and extracellular pathways for the synthesis of metal nanoparticles (Brayner et al. The ZnO nanoparticles have also been synthesized and characterized by the use of cyanobacteria (Anabaena strain 1. During the past few years the pathogenic microbes are developing resistance against various relatively higher doses of antibiotics, so there is a considerable threat to the health of our society. Various microbes have developed antibiotic-resistant strains against narrow as well as broad-spectrum antibiotics such as penicillin, sulfonamide, vancomycin, and methicillin (Fair and Tor, 2014). So to overcome the risk of antibiotics resistance in microbes, there is an urgent need to find alternative ways to kill such drug-resistant bacteria. The nanoparticles can be seen as a hope for the killing of such pathogenic bacteria. Due to their novel and advanced features, metal nanoparticles appear to be a multifaceted material as compared to their larger particles from which they are derived (Rajeshkumar et al. The nanoparticles synthesized from green technology using plants and microorganisms have diverse applications in biomedical fields. Due to the larger surface area to volume ratio, metal nanoparticles come in contact with large number microbes and get attached to the cell membrane and also penetrate inside the cell (Rai et al. Silver nanoparticles have bactericidal property that interacts with sulfur and phosphorus-containing biomolecules inside bacterial cells and inhibits their related functions (Matsumura et al. These sources have been used to reduce different sources of energy as butanol, ethanol, propanol, cooking oils, etc. Despite that, energy crops, which have been utilized from one generation to other for energy production, compete as the energy sources for nutrients, water, and fertile land, for which use of microalgae as biofuels are emerging as a new alternative source of avoiding competition with conventional sources of energy. For the third generation the most promising source for the production of biofuels is cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria consist of smaller genome sizes; therefore it gives an exceptional opportunity to conduct metabolic and genetic engineering for the improvement of biomass production, which is not possible with the eukaryotic algae (Heimann, 2016). Carbon dioxide taken up cyanobacteria through photosynthesis converted it to carbon-containing lipids that can be used in the productions of biofuels. The biomass of cyanobacteria contains lignocellulosic compounds that can also process for syngas production. The significance of using molecular H2 as clean biofuels is that it can be stored in liquid form or gas metal hydride. It has greater efficiency of energy conversion; if it used as a source of fuel, it will not cause any environmental issues, because of its only byproduct is water. Several known genera such as Nostoc, Calothrix, Oscillatoria, Microcystis, Anabaena, Cyanthece are present that can produce syngas H2 under various conditions (Rajneesh et al. Usually, photoautotrophic cyanobacteria can produce 100 mg of biochemicals per liter cell culture, which is very less in quantity, will not be viable for the application (Lowe et al. The cyanobacteria have pigments that can trap radiant energy into chemical energy, so great potential for production of biofuel by the use of cyanobacteria is well established (Heimann, 2016). The functions of cyanobacteria such as photosynthesis (carbon sequestration) and biological nitrogen fixation (used as fertilizer) and their application for production of biofuels, secondary metabolites and many other purposes make it significant microorganisms for the sustainablility of environment and agriculture. Also, the ability of cyanobacteria to synthesize zerovalent nanoparticles size of metals indicates its importance in the future in the medicinal field, bioremediation of toxic chemical and metals, and also as nutrients for crops. The cyanobacterial groups may play a potential role as test organisms in the field of genetic engineering for the recent valuable aspects in the demands of modern human society. The more studies are required following recent technologies, phylogenetic studies and interactions with other living organisms, for the beneficial uses of cyanobacterial groups in the field of medicines, biofertilizers, synthesis of metal nanoparticles, plant pathology, production of secondary metabolites, and sustainability of environment under rapidly changing climatic conditions. Acknowledgments Authors are grateful to the Botany Department, Lucknow University, for providing library facility for the collection of literature. Sharma (Plant Cyanobacteria: potential source of biofertilizer and synthesizer of metallic nanoparticles Chapter 23 363 Nutrition, Rtd. The direct role of aerobic heterotrophic bacteria associated with cyanobacteria in the degradation of oil compounds. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from methanol leaf extract of Cassia didymobotyra and assessment of their antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Environment friendly fluid loss additives to protect the marine environment from the detrimental effect of mud additives. Intracellular biosynthesis of superparamagnetic 2-lines ferrihydrite nanoparticles using Euglena gracilis microalgae. Identification on factors influencing the restoration of cyanobacteria-dominated biological soil crusts. Biorecovery of gold using cyanobacteria and an eukaryotic alga with special reference to nanogold formation -a novel phenomenon. Recycling and adaptation of Klebsormidium flaccidum microalgae for the sustained production of gold nanoparticles. A global approach of the mechanism involved in the biosynthesis of gold colloids using microalgae. Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Silver nanoparticles: Synthetic routes, in vitro toxicity and theranostic applications for cancer disease. Potential Use of silver nanoparticles on pathogenic bacteria, their toxicity, and possible mechanisms of action. Characterisation of native microalgal strain for their chromium bioaccumulation potential: Phytoplankton response in polluted habitats. The role of algal growth in the calonization of new ground and in the determination of scenery. Silver, gold and bimetallic nanoparticles production using single-cell protein (Spirulina platensis) Geitler. Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by a marine alga, Sargassum wightii Grevilli and their antibacterial effects. Ag nanoparticle-catalyzed chemiluminescent reaction between luminol and hydrogen peroxide. Enhancing the toxicity of cancer chemotherapeutics with gold nanorod hyperthermia. Noval approaches to microalgal and cyanobacterial cultivation for bioenergy and biofuel production. Plasma enhanced deposition of silver nanoparticles onto polymer and metal surfaces for the generation of antimicrobial characteristics. In: Proceeding of the International Conference Nanomaterials: Application and Properties, vol. A novel green chemical route for synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Camellia sinensis. Field evaluations of agrochemical toxicity to cyanobacteria in rice field ecosystem: a review. The potential for using cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and algae in biological control of plant pathogenic bacteria and fungi.
Purchase flomax 0.2 mg on-line
Twister ribozymes as highly versatile expression platforms for artificial riboswitches man health and fitness best 0.4 mg flomax. Photosynthetic production of ethanol from carbon dioxide in genetically engineered cyanobacteria. Cyanobacterial chassis engineering for enhancing the production of biofuels and chemicals. Co-overexpression of response regulator genes slr1037 and sll0039 improves tolerance of Synechocystis sp. Identification of the direct regulon of NtcA during early acclimation to nitrogen starvation in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid detection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6. Applications of genome-scale metabolic models of microalgae and cyanobacteria in biotechnology. Ethylene synthesis and regulated expression of recombinant protein in Synechocystis sp. Single-cell screening of photosynthetic growth and lactate production by cyanobacteria. Simulating cyanobacterial phenotypes by integrating flux balance analysis, kinetics, and a light distribution function. Cyanobacteria and eukaryotic algae use different chemical variants of vitamin B (12). Design and characterization of molecular tools for a synthetic biology approach towards developing cyanobacterial biotechnology. Physical, chemical, and metabolic state sensors expand the synthetic biology toolbox for Synechocystis sp. Isotopically nonstationary (13)C flux analysis of cyanobacterial iso-butyraldehyde production. Heterologous production of cyanobacterial mycosporine-like amino acids mycosporine-ornithine and mycosporine-lysine in Escherichia coli. A rhamnose inducible system for precise and temporal control of gene expression in cyanobacteria. The effect of transcription and translation initiation frequencies on the stochastic fluctuations in prokaryotic gene expression. The LexA transcription factor regulates fatty acid biosynthetic genes in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. A computational analysis of stoichiometric constraints and trade-offs in cyanobacterial biofuel production. Engineered xylose utilization enhances bio-products productivity in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. Exploring native genetic elements as plug-in tools for synthetic biology in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. The nitrogen-regulated response regulator NrrA controls cyanophycin synthesis and glycogen catabolism in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. Environmental control of phosphorylation pathways in a branched two-component system. Regulation of gene expression in diverse cyanobacterial species by using theophylline-responsive riboswitches. A data integration and visualization resource for the metabolic network of Synechocystis sp. Synthetic biology toolbox for controlling gene expression in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. A simplified method for conjugal gene transfer into the filamentous cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. A systems biology approach to reconcile metabolic network models with application to Synechocystis sp. Fine-tuning of photoautotrophic protein production by combining promoters and neutral sites in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. Flux balance analysis of photoautotrophic metabolism: Uncovering new biological details of subsystems involved in cyanobacterial photosynthesis. Integrated proteomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals novel genes and regulatory mechanisms involved in salt stress responses in Synechocystis sp. Natural and synthetic tetracycline-inducible promoters for use in the antibiotic-producing bacteria Streptomyces. Automated design of synthetic ribosome binding sites to control protein expression. Engineered promoters enable constant gene expression at any copy number in bacteria. Ribozymes, riboswitches, and beyond: regulation of gene expression without proteins. Computational metabolic engineering strategies for growth-coupled biofuel production by Synechocystis. Designing intracellular metabolism for production of target compounds by introducing a heterologous metabolic reaction based on a Synechosystis sp. Adjudged by hasty up-accumulation of transporter and signaling and severe down-accumulation of nitrogen metabolism proteins. Cadmium-mediated morphological, biochemical and physiological tuning in three different Anabaena species. The SphS-SphR two-component system is the exclusive sensor for the induction of gene expression in response to phosphate limitation in Synechocystis. Broad-host-range vector system for synthetic biology and biotechnology in cyanobacteria. Transcription factors in microalgae: genome-wide prediction and comparative analysis. High-throughput screen for poly-3-hydroxybutyrate in Escherichia coli and Synechocystis sp. Applying a riboregulator as a new chromosomal gene regulation tool for higher glycogen production in Synechocystis sp. De novo design of a synthetic riboswitch that regulates transcription termination. A genetic toolbox for modulating the expression of heterologous genes in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. Construction of shuttle vectors capable of conjugative transfer from Escherichia coli to nitrogenfixing filamentous cyanobacteria. Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of the global response of Synechococcus to high light stress. Spanning high-dimensional expression space using ribosome-binding site combinatorics. Construction of new synthetic biology tools for the control of gene expression in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. Discovery of a super-strong promoter enables efficient production of heterologous proteins in cyanobacteria. Enhancing photosynthetic production of ethylene in genetically engineered Synechocystis sp. Chapter 10 Impact of pesticides applications on the growth and function of cyanobacteria Vipin Kumar Singh1, Sandeep Kumar Singh1, Prashant Kumar Singh2, Hariom Verma1, K. Singh1 and Ajay Kumar3 1 Center of Advanced Study in Botany, Institute of Science, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India, 2Department of Vegetables and Field Crops, Institute of Plant Sciences, Agricultural Research Organization, the Volcani Centre, Rishon LeZion, Israel, 3Department of Post-harvest Science, Agricultural Research Organization, the Volcani Centre, Rishon LeZion, Israel 10. Cyanobacteria is one of the oldest organisms having a long course of evolutionary lineage and play an essential role in photosynthetic oxygenic evolution and in maintaining global carbon or nitrogen cycle. Cyanobacterial species harboring varied morphological features may survive freely as well as symbiotically with different life forms in a given environment (Adams, 2000; Whitton, 2000; Singh et al. They have been described to contribute significantly in the mobility of essential minerals, redox status, water retention in soil, the texture of the soil, amelioration of soil profoundly affected by high salt content and may modulate the physiology and biochemistry of host plants. The annual crop plant paddy (Oryza sativa) belonging to Poaceae is described to have 20 different wild and two domesticated species (Bernis and Pamies, 2008; Pareja et al. Prevailing environmental conditions considerably determine the yield of paddy crop.
Flomax 0.2 mg lowest price
Quantitation prostate cancer usually occurs because of exposure to buy flomax 0.4mg lowest price, and physiological characterization of angiogenic vessels in mice-effect of basic fibroblast growth factor vascular endothelial growth factor vascular permeability factor, and host microenvironment. Rolling in P-selectin-deficient mice is reduced but not eliminated in the dorsal skin. Imaging of activated natural killer cells in mice by positron emission tomography: preferential uptake in tumors. Reduction of rigidity in human activated natural killer cells by thioglycollate treatment. Kinetics of interleukin-2 induced changes in rigidity of human natural killer cells. Low deformability of lymphokine-activated killer cells as a possible determinant of in vivo distribution. Interaction of activated natural killer cells with normal and tumor vessels in cranial windows in mice. Analysis of cell flux in the parallel plate flow chamber: implications for cell capture studies. Kinetics of adhesion molecule expression and spatial organization using targeted sampling fluorometry. Preferential localization of human adherent lymphokine-activated killer cells in tumor microcirculation. Adhesion of activated natural killer cells to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-treated endothelium under physiological flow conditions. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits E-selectin expression on human endothelial cells. Endothelial adhesiveness for blood neutrophils is inhibited by transforming growth factor-beta. Endothelial cell adhesiveness for human T lymphocytes is inhibited by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Interactions between lymphocytes and myeloid cells regulate proversus anti-tumor immunity. Heterotypic signaling between epithelial tumor cells and fibroblasts in carcinoma formation. Fluorescence photobleaching with spatial Fourier analysis: measurement of diffusion in light-scattering media. Direct measurement of interstitial convection and diffusion of albumin in normal and neoplastic tissues by fluorescence photobleaching. Multiscale measurements distinguish cellular and interstitial hindrances to diffusion in vivo. Comparison of IgG diffusion and extracellular matrix composition in rhabdomyosarcomas grown in mice versus in vitro as spheroids reveals the role of host stromal cells. Diffusion of macromolecules in agarose gels: comparison of linear and globular configurations. Intratumoral infusion of fluid: estimation of hydraulic conductivity and implications for the delivery of therapeutic agents. Irradiation reduces interstitial fluid transport and increases the collagen content in tumors. Diffusion and convection in collagen gels: implications for transport in the tumor interstitium. Diffusion of particles in the extracellular matrix: the effect of repulsive electrostatic interactions. Micropharmacology of monoclonal antibodies in solid tumors: direct experimental evidence for a binding site barrier. Quantification of transport and binding parameters using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching. Measurement of mass transport and reaction parameters in bulk solution using photobleaching: Reaction limited binding regime. Effect of bivalent interaction upon apparent antibody affinity: experimental confirmation of theory using fluorescence photobleaching and implications for antibody binding assays. In vitro measurement and screening of monoclonal antibody affinity using fluorescence photobleaching. Absence of functional lymphatics within a murine sarcoma: a molecular and functional evaluation. Imaging steps of lymphatic metastasis reveals that vascular endothelial growth factor-C increases metastasis by increasing delivery of cancer cells to lymph nodes: therapeutic implications. The rediscovery of the lymphatic system: old and new insights into the development and biological function of the lymphatic vasculature. Angiopoietin-2 is required for postnatal angiogenesis and lymphatic patterning, and only the latter role is rescued by angiopoietin-1. Conventional and high-speed intravital multiphoton laser scanning microscopy of microvasculature, lymphatics, and leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Peritumor lymphatics induced by vascular endothelial growth factor-C exhibit abnormal function. Tumor microvasculature and microenvironment: novel insights through intravital imaging in pre-clinical models. Interstitial pressure gradients in tissue-isolated and subcutaneous tumors: implications for therapy. Interstitial hypertension in carcinoma of uterine cervix in patients: possible correlation with tumor oxygenation and radiation response. Interstitial hypertension in head and neck tumors in patients: correlation with tumor size. Interstitial pressure of subcutaneous nodules in melanoma and lymphoma patients: changes during treatment. Interstitial hypertension in human brain tumors: possible role in peritumoral edema formulation. Interstitial fluid pressure in breast-cancer, benign breast conditions, and breast parenchyma. Lack of general correlation between interstitial fluid pressure and oxygen partial pressure in solid tumors. Interstitial fluid pressure predicts survival in patients with cervix cancer independent of clinical prognostic factors and tumor: oxygen measurements. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment augments tumor radiation response under normoxic or hypoxic conditions. Artificial lymphatic system": a new approach to reduce interstitial hypertension and increase blood flow, pH and pO(2) in solid tumors. Timedependent behavior of interstitial fluid pressure in solid tumors: implications for drug delivery. Enhancement of fluid filtration across tumor vessels: implication for delivery of macromolecules. Effect of vascular normalization by antiangiogenic therapy on interstitial hypertension, peritumor edema, and lymphatic metastasis: insights from a mathematical model. Interstitial pH and pO2 gradients in solid tumors in vivo: high-resolution measurements reveal a lack of correlation. The unique physiology of solid tumors: opportunities (and problems) for cancer therapy. Acid production in glycolysis-impaired tumors provides new insights into tumor metabolism. Prognostic value of tumor oxygenation in 397 head and neck tumors after primary radiation therapy. Expression of hypoxia-inducible carbonic anhydrase-9 relates to angiogenic pathways and independently to poor outcome in non-small cell lung cancer. Hypoxia in tumors: pathogenesis, related classification, characterization of hypoxia subtypes, and associated biological and clinical implications. Hypoxia triggers hedgehog-mediated tumor-stromal interactions in pancreatic cancer. Tumor oxygenation predicts for the likelihood of distant metastases in human soft tissue sarcoma. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2-blocking antibody potentiates radiation-induced long-term control of human tumor xenografts. Oxygen sensing by T cells establishes an immunologically tolerant metastatic niche. Normalizing tumor microenvironment to treat cancer: bench to bedside to biomarkers.