Order duphaston online from canada
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any signs or symptoms of a urinary tract infection such as a burning feeling when passing urine women's health clinic fremantle cheap duphaston 10 mg visa, a need to urinate often, the need to urinate right away, pain in the lower part of your stomach (pelvis), or blood in the urine. Signs and symptoms of low blood sugar may include: o headache o weakness o confusion o shaking or feeling jittery o drowsiness o dizziness o irritability o sweating o hunger o fast heartbeat A rare but serious bacterial infection that causes damage to the tissue under the skin (necrotizing fasciitis) in the area between and around the anus and genitals (perineum). Necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum may lead to hospitalization, may require multiple surgeries, and may lead to death. Inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, anhydrous lactose, crospovidone, silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate. The film coating contains: polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, and yellow iron oxide. The dose may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg/day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. In addition to the daily dose adjustment, administer a supplemental dose immediately following every 4-hour hemodialysis treatment (see Table 2). Angioedema and hypersensitivity reactions have occurred in patients receiving pregabalin therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5. Specific symptoms included swelling of the face, mouth (tongue, lips, and gums), and neck (throat and larynx). There were reports of life-threatening angioedema with respiratory compromise requiring emergency treatment. Adverse reactions included skin redness, blisters, hives, rash, dyspnea, and wheezing. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5-100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed. Risk by Indication for Antiepileptic Drugs in the Pooled Analysis Indication Placebo Patients Drug Patients Relative Risk: Risk Difference: with Events Per with Events Per Incidence of Events in Additional Drug 1000 Patients 1000 Patients Drug Patients with Patients/Incidence in Events Per Placebo Patients 1000 Patients Epilepsy 1. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated. In short-term trials of patients without clinically significant heart or peripheral vascular disease, there was no apparent association between peripheral edema and cardiovascular complications such as hypertension or congestive heart failure. Peripheral edema was not associated with laboratory changes suggestive of deterioration in renal or hepatic function. The majority of patients using thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agents in the overall safety database were participants in studies of pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Dizziness and somnolence were the adverse reactions most frequently leading to withdrawal (4% each) from controlled studies. Weight gain was not limited to patients with edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5. In clinical studies across various patient populations, comprising 6396 patient-years of exposure in patients greater than 12 years of age, new or worsening-preexisting tumors were reported in 57 patients. Prospectively planned ophthalmologic testing, including visual acuity testing, formal visual field testing and dilated funduscopic examination, was performed in over 3600 patients. Although the clinical significance of the ophthalmologic findings is unknown, inform patients to notify their physician if changes in vision occur. Consider more frequent assessment for patients who are already routinely monitored for ocular conditions [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Instruct patients to promptly report unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, particularly if these muscle symptoms are accompanied by malaise or fever. However, these analyses cannot be considered definitive because of the limited number of patients in these categories. Approximately 5000 patients were treated for 6 months or more, over 3100 patients were treated for 1 year or longer, and over 1400 patients were treated for at least 2 years. In the placebo group, 1% of patients withdrew due to dizziness and less than 1% withdrew due to somnolence. In comparison, less than 1% of placebo patients withdrew due to dizziness and somnolence. A majority of pregabalin-treated patients in clinical studies had adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate". In comparison, less than 1% of patients in the placebo group withdrew due to each of these events. Dose-relatedness was defined as the incidence of the adverse event in the 600 mg/day group was at least 2% greater than the rate in both the placebo and 150 mg/day groups. Thinking abnormal primarily consists of events related to difficulty with concentration/attention but also includes events related to cognition and language problems and slowed thinking. Controlled Study of Adjunctive Therapy for Partial Onset Seizures in Patients 4 to Less Than 17 Years of Age Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation Approximately 2. Dose-relatedness was defined as an incidence of the adverse event in the 10 mg/kg/day group that was at least 2% greater than the rate in both the placebo and 2. A majority of pregabalin-treated patients in the clinical study had adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate". Dose-related Adverse Reaction Incidence in a Controlled Trial in Adjunctive Therapy for Partial Onset Seizures in Patients 4 to Less Than 17 Years of Age Body System Preferred Term Gastrointestinal disorders Salivary hypersecretion Investigations Weight increased Metabolism and nutrition disorders Increased appetite Nervous system disorders Somnolence 2. Controlled Studies with Fibromyalgia Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation In clinical trials of patients with fibromyalgia, 19% of patients treated with pregabalin (150-600 mg/day) and 10% of patients treated with placebo discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the pregabalin treatment group, the most common reasons for discontinuation due to adverse reactions were dizziness (6%) and somnolence (3%). In comparison, less than 1% of placebo-treated patients withdrew due to dizziness and somnolence. Other reasons for discontinuation from the trials, occurring with greater frequency in the pregabalin treatment group than in the placebo treatment group, were fatigue, headache, balance disorder, and weight increased. Each of these adverse reactions led to withdrawal in approximately 1% of patients. A majority of pregabalin-treated patients in clinical studies experienced adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate". In the pregabalin treatment group, the most common reasons for discontinuation due to adverse reactions were somnolence (3%) and edema (2%). In comparison, none of the placebo-treated patients withdrew due to somnolence and edema. Other reasons for discontinuation from the trials, occurring with greater frequency in the pregabalin treatment group than in the placebo treatment group, were fatigue and balance disorder. Most Common Adverse Reactions Table 9 lists all adverse reactions, regardless of causality, occurring in greater than or equal to 2% of patients for which the incidence was greater than in the placebo treatment group with neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury in the controlled trials. The listing does not include those events already listed in the previous tables or elsewhere in labeling, those events for which a drug cause was remote, those events which were so general as to be uninformative, and those events reported only once which did not have a substantial probability of being acutely life-threatening. Events are categorized by body system and listed in order of decreasing frequency according to the following definitions: frequent adverse reactions are those occurring on one or more occasions in at least 1/100 patients; infrequent adverse reactions are those occurring in 1/100 to 1/1000 patients; rare reactions are those occurring in fewer than 1/1000 patients. Events of major clinical importance are described in the Warnings and Precautions section (5). There are insufficient data to support a statement regarding the distribution of adverse experience reports by race. Specifically, there are no pharmacokinetic interactions between pregabalin and the following antiepileptic drugs: carbamazepine, valproic acid, lamotrigine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, and topiramate. In an animal development study, lethality, growth retardation, and nervous and reproductive system functional impairment were observed in the offspring of rats given pregabalin during gestation and lactation. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. The effect on offspring survival was pronounced at doses greater than or equal to 1250 mg/kg, with 100% mortality in high-dose litters. When offspring were tested as adults, neurobehavioral abnormalities (decreased auditory startle responding) were observed at greater than or equal to 250 mg/kg and reproductive impairment (decreased fertility and litter size) was seen at 1250 mg/kg. A pharmacokinetic study in lactating women detected pregabalin in breast milk at average steady state concentrations approximately 76% of those in maternal plasma. Based on animal studies, there is a potential risk of tumorigenicity with pregabalin exposure via breast milk to the breastfed infant [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13. Available clinical study data in patients greater than 12 years of age do not provide a clear conclusion about the potential risk of tumorigenicity with pregabalin [see Warnings and Precautions (5. Data A pharmacokinetic study in ten lactating women, who were at least 12 weeks postpartum, evaluated the concentrations of pregabalin in plasma and breast milk.
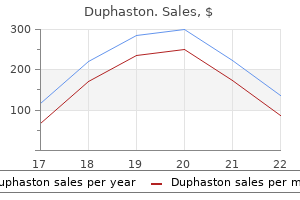
Duphaston 10mg for sale
Salivary stasis and ductal inflammation and injury are important contributing factors menopause gerd discount duphaston 10 mg line. Submandibular secretions are more viscous and have a higher calcium and phosphorus concentration. Parotid stones are mostly located at the hilum or parenchyma, while in the submandibular gland, they tend to develop in the duct. The hyperplastic follicles and germinal centers show abundant mitoses and necrotic nuclear debris. They occur singly or in groups and are found in cortical and paracortical zones and sinuses. Confirmation of a presumptive histological diagnosis is made by acute and convalescent serologic testing. Clinical features: Patients usually presents with gradual, nontender enlargement of one or more of the salivary glands. Surgical management: It consists of: Incision of duct: Submandibular stones, which are no more than 2 cm from the duct orifice, may be either manually milked out through the duct opening or the duct is incised directly over the stone. Recent advances: Use of various combination of baskets, graspers and intracorporeal lithotripsy have been employed to treat sialolithiasis in both the parotid and submandibular glands. Sialoendoscopy: Rigid endoscopes are used to visualize and remove salivary duct stones. The sign and symptoms of malignancy are: rapid growth, restricted mobility, fixity of overlying skin, pain and facial nerve involvement. Management of other types of salivary neoplasms is challenging because of their relative infrequency and variable biologic behavior. Bicellular reserve cell theory: According to this theory, various types of salivary neoplasms originate from the basal cells (pluripotential cell populations) of either the excretory or the intercalated duct, which act as a reserve cell with the potential for differentiation into a variety of epithelial cells. Hence, all the heterogeneity salivary tumors are thought to arise from one of these two cells. Some patients of salivary gland cancer were found to have past history of skin cancer. Genetic factors: Genetic aberrations, which are found associated with the salivary gland neoplasia, include allelic loss and point mutation, structural rearrangement of chromosomal units (most commonly translocations), the monosomy and the presence of polysomy. Viral: Epstein-Barr virus has been found associated with lymphoepithelial carcinoma in the Asian population but there is no evidence of its causal role in other primary benign and malignant neoplasms of salivary glands. Other viruses including human papillomavirus, human herpesvirus 8 and cytomegalovirus do not have any etiologic role. Occupational factors: Exposure to silica dust, nickel alloys this most common benign slow growing tumor of salivary glands, usually arise from the tail of parotid. These "mixed tumors" have both epithelial and mesenchymal elements in variable amount. This encapsulated tumor sends pseudopods into the surrounding glands, therefore it is essential that surgical excision of the tumor should include surrounding normal gland tissue. It is a rounded encapsulated tumor, which may be at times cystic with mucoid or brownish fluid. Characteristically, they are soft and painless and increase in size with crying or straining. Tumor extending into parapharyngeal space posterior to stylomandibular ligament lymphangiomaS these less common tumors feel soft and cystic and involve parotid and submandibular glands. Mucoepidermoid tumors of minor salivary glands are more aggressive while in major salivary glands they behave like pleomorphic adenoma. The mucoepidermoid tumor has both the areas of mucin producing cells as well as squamous cells. The aggressive high grade tumors need total parotidectomy and facial nerve is sacrificed if invaded by tumor. It spreads through perineural spaces and lymphatics and causes pain and facial nerve palsy. SquamouS cell carcinoma this rapidly growing painful tumor infiltrates and ulcerates through the skin, and metastasizes to neck nodes. Rapid growth and appearance of pain in a slow growing benign tumor indicates malignant change. The disease is most commonly seen in patients during their fourth to fifth decade of life. Xerostomia causes difficulty in chewing, swallowing and phonation, adherence of food to the buccal mucosa and multiple dental caries. Sedatives, antipsychotics, antidepressants, antihistamines and diuretics are most often associated with oral dryness. Patients with persistent unilateral or bilateral parotid gland enlargement are at higher risk for the development of lymphoma. Systemic sialogogues: Pilocarpine (muscarinic cholinergic agonist) 5 mg three to four times daily, side effects include sweating, flushing and increased urination. Chronic irritation and destruction of the corneal and conjunctival epithelium causes keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Staining of damaged corneal and conjunctival epithelia by rose Bengal dye is specific for keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Biopsy from lip confirms the diagnosis and shows atrophy of minor salivary glands with an abundance of lymphocytes and histiocytes. This condition is the result of aberrant innervation of sweat glands by parasympathetic secretomotor fibers which were destined for the parotid. Thus, these postganglionic fibers from the otic ganglion carried by auriculotemporal nerve, instead of causing salivary secretion cause secretion from the sweat glands. Sarcoidosis: the clinical features include parotid swelling, facial paralysis, cervical lymphadenopathy, and diabetes insipidus. Because of the section of greater auricular nerve, superficial parotidectomy is followed by anesthesia of the lower part of pinna. Parotid enlargement, which may be chronic or relapsing, develops in one-third of patients. Effects of radiotherapy on parotid salivary sialochemistry in head and neck cancer patients. When do you excise Submandibular Salivary Gland in such cases where obstruction is due to calculus Die you must, but have a great ideal to die for and it is better to die with a great ideal in life. Most common sites are soft and hard palate, uvula, tongue, lips and buccal mucosa. The lesion may be either diffuse (macroglossia) or localized compressible soft swelling. Congenital epulis, which is a granular cell tumor, involves the gums of future incisors in female infants. Treatment: Congenital hemangioma usually does not need any treatment as the spontaneous regression is wellknown. These pedunculated or multilobulated broadly based smooth bony masses are usually asymptomatic. It mostly involves anterior gingivae but can be seen over tongue, buccal mucosa or lips. They contain elements of epidermal appendages such as hair follicles, sweat glands and connective tissue. This preventable disease is caused by tobacco, alcohol, paan, reverse smoking, areca nut and betel quid. Reverse smoking, where burning end of the "churat" (rolled tobacco leaf) is put in the mouth, gives still higher incidence of cancer of the hard palate. Forty percent of patients who continue smoking after definitive treatment develop recurrence or second head and neck malignancy. Avitaminosis and malnutrition: Riboflavin deficiency is proposed to be responsible for cancer in alcoholics. Long-term immunosuppression: There is 30 fold increased risk with renal transplant. Lack of bel-2 expression found consistent with an improved 3-year disease-free survival. Syphilis: the syphilitic interstitial glossitis with an endarteritis causes atrophy of the overlying epithelium that is more vulnerable to carcinogenic irritants. Plummer-Vinson syndrome or Paterson-Kelly syndrome or Sideropenic dysphagia: It consists of achlorhydria, iron deficiency anemia, and mucosal atrophy of mouth, pharynx and esophagus.
Diseases
- Angel shaped phalangoep
- Deafness hyperuricemia neurologic ataxia
- Eosinophilia myalgia syndrome
- Young Simpson syndrome
- Ependymoma
- Paraomphalocele
- Delusional disorder
Order duphaston 10 mg mastercard
Rhythm is usually sinus pregnancy zero station order 10mg duphaston otc, but in the setting of an abnormal situs, one may come across various degrees of conduction blocks including complete heart block. However, with advancing age, it may also show pressure overload pattern due to increasing pulmonary vascular resistance. Chest radiograph A well taken chest radiograph in posteroanterior projection is an invaluable tool in management decisions. Plethoric lung fields suggest clear operability, whereas oligemic lung fields are against it. Both coronal and sagital planes help in delineating the absence of interatrial septum and also in establishing the normal and abnormal patterns of pulmonary and systemic veins. ColorDoppler of the pulmonary veins with scales set to optimal Nyquist limit will help in quantifying the venous return, which is an indirect marker of operability. Every echocardiographic examination should also encompass all the other views to rule out any other coexisting anomaly. It is not uncommon to find cases in which a coexisting large ductus or aortopulmonary window was missed. Hence, even after establishing the diagnosis from subcostal and apical views, it is still important to do a meticulous evaluation via parasternal and suprasternal windows to determine the presence and absence of coexisting anomalies. With some effort, additional information can be obtained regarding the venous drainages. With advanced software, volumetrics can be assessed using 3D echocardiography enabling the shunt calculations. The ratio would reduce in the same proportion as pulmonary to systemic vascular resistance increases. It is pertinent to make use of any modality of investigation which helps surgical decision making. An asymptomatic child with normal pulmonary artery pressures need not be given any medication other than watchful observation. In asplenia or reduced splenic function, use of irradiated blood, special precautions to ensure sepsis free handling, dedicated staffing, judicious isolation and limitation of visitors in the perioperative period would add to the success of the procedure. Common atrium can present technical challenges to the surgeon, even when the anatomical details are well delineated. Issues like absence of coronary sinus take away the landmark of conduction system for the surgeon on the table. Whether development of early pulmonary vascular disease in some common atrium patients is due to a genetic predisposition (related to coexisting abnormal substrate in the lung or congenital abnormalities in the pulmonary arterial vasculature) or an association with idiopathic pulmonary hypertension is unknown. Due to the rarity of condition and the eventual paucity of data on the natural history of common atrium and pulmonary vascular disease, determining which patients with common atrium will develop early pulmonary vascular obstructive disease remains challenging. The mixing of pulmonary and systemic venous returns is near complete due to lack of any interface between them. Hence, in the presence of low 642 valve posteriorly to be carried on to right atrial wall beyond the tricuspid annulus. However, it should be noted that all children with altered splenic function should receive life-long prophylaxis and vaccination against encapsulated bacteria and preferably, annual influenza vaccine. This should be emphasized to parents at the time of discharge and reemphasized during follow up visits. It is useful to get all this practical information on patient care printed on a handy card and issued to the parents for their reference. Common atrium is a part of complex coexisting anomalies, whereas single atrium is isolated. Surgical results are good and age should not be a deterrent as long as the patient is operable. Single atrium, atrioventricular canal/postaxial hexadactyly indicating Ellis van Creveld syndrome. Use of non-invasive phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging for estimation of atrial septal defect size and morphology: a comparison with transesophageal echo. An elder case of common atrium: surgical repair in a 56-year-old man [in Japanese]. Unique in its complexity and scope, the univentricular heart has sparked intense debates about embryology and nomenclature, challenged our understanding of cardiovascular physiology and hemodynamics and inspired some of the most creative surgical and interventional approaches in human history. The terms single and common ventricle were used interchangeably by Abbott, Taussig and Edwards. The hearts considered in this topic are those, where the atrial chambers functionally connect to only one ventricle, which is well-developed and dominant. As pointed out by Van Praagh,8 the so called univentricular heart also has an additional incomplete or rudimentary ventricle that lacks a proper atrioventricular connection. In late 1970s and early 1980s, Anderson et al9 attempted to clarify the confusion surrounding these hearts by dividing them into the following: 1. They also proposed that a chamber must receive greater than or equal to 50 percent of an inlet to be classified as a ventricle whereas the chamber need not have an outlet to qualify as same. The apical trabeculations are extremely coarse and the ventricular morphology is indeterminate. The inset shows the bizarre conduction system with a sling of conduction axis connecting dual atrioventricular nodes, and giving rise to a solitary strand, which activates the ventricular mass. The solid red line indicates the atrioventricular junction, while the dotted red line indicates the ventriculoarterial junction. Thus, according to Van Praagh, a single or common ventricle is one ventricular chamber that receives both the tricuspid and mitral valves or a common atrioventricular valve. A second ventricular chamber, if present, will lack any atrioventricular connection and hence be rudimentary. This system makes the distinction between hearts with a double inlet ventricle versus hearts with absence of an atrioventricular connection, but acknowledges that because a heart with absence of one atrioventricular connection is also a univentricular heart, then tricuspid atresia is among those anomalies associated with a univentricular heart. Courtesy: Reprinted with permission from reference 16 true univentricular heart Very occasionally, the instance of a single chamber5,13 within the ventricular mass without any anatomic evidence of a second chamber has been reported. This heart with a solitary ventricle has both a double inlet as well as a double outlet. The ventricular morphology is best described as indeterminate and shows extremely coarse trabeculations. The developmental basis is as yet not understood, however it is reasonable to propose that it represents failure of ballooning of separate apical components for the morphologically right and left ventricles as proposed by Christoffels14 et al. The yellow arrow shows the atrioventricular valve which is anterosuperior to the ventricular septum (star). The first morphologic principle states that left ventricles have relatively smooth internal walls and lack chordal attachments of the atrioventricular valves to the rudimentary septal surface. Right ventricles are more heavily trabeculated and generally have chordal attachments of the atrioventricular valve to the septal surface. The second principle states that the ventricular chamber that includes an infundibulum giving rise to a great artery represents the morphologic right ventricle. As a corollary, the ventricular chamber having a direct arterial Question I: Does the Rudimentary Chamber Really Matter Identification of ventricular morphology is the first-step in determining the type of atrioventricular connections and eventually the ventricular function. This also helps in determining the location of ventricular septum and orientation of conduction tissues. Additionally, each class of univentricular heart may have associated abnormalities of atriovisceral situs, of one or both atrioventricular valves, of one or both semilunar valves and of the relations (transposition or malposition) of the great arteries. The risk to siblings and offspring of affected individuals is generally in the order of 2 to 5 percent. The natural history is even bleaker for patients with univentricular hearts of right ventricular morphology, with 50 percent survival 4 years after diagnosis. Ammash and Warnes reviewed their experience with 13 unoperated adults with univentricular hearts to determine, which characteristics permitted long-term survival. The left ventricular ejection fraction was normal (n = 11) or mildly depressed (n = 2) and no patient had more than mild atrioventricular valve regurgitation. In patients with mild to moderate pulmonary stenosis, they present like tetralogy of Fallot. They may be relatively asymptomatic,with mild to moderate cyanosis, clubbing and attain adulthood with retarded growth. There can be a visible, palpable impulse in the third left intercostal space (due to inverted outlet chamber).
Order 10 mg duphaston with mastercard
Histopathological classification: In addition to the location and extent of tumor menopause 2014 speaker slides order generic duphaston, histological nature of malignancy is also important in deciding the line of treatment. Late features: Later on other features appear when tumor spreads and destroys the bony confines and involves surrounding structures. Inferior spread towards alveolus: Expansion of alveolus, dental pain, loosening of teeth, poor fitting of dentures, ulceration of gingiva and swelling in the hard palate. Superior spread towards orbit: Facial paresthesia/anesthesia, proptosis, diplopia, ocular pain and epiphora. Posterior spread into pterygomaxillary and infratemporal fossa: Trismus due to involvement of pterygoid plates and the muscles. Distant metastases: Though rare they mostly occur in lungs and occasionally in bones. Near the medial canthus of eye it turns laterally in a rounded fashion to go 5 mm below the lower lid margin b. Eye ball: Some surgeons prefer to spare the eye whereas others intentionally include the eye during surgery and irradiation. Orbital exenteration in patients with ethmoid tumor has been reported to increase survival. It is adequate when tumor is confined to maxilla, or extends to facial soft tissues, palate, or anterior orbit but without invasion of the ethmoidal roof, posterior orbit, or pterygoid region. The multimodal treatment, which is combination of chemotherapy, radiation and surgery, improve the results. Early features include nasal obstruction, blood stained nasal discharge and retro-orbital pain. Late features: Broadening of the nasal root, lateral displacement of eyeball and diplopia. Most of the patients are of 50 years of age and both the sexes are equally affected. Metastases: Regional (cervical lymph node) metastases and distant (blood stream) metastases are common. Treatment: Preoperative radiation followed by surgery, which includes removal of frontal and ethmoid sinuses and orbital exenteration. SarcomaS Osteogenic sarcomas and chondrosarcoma, which have relentless local progression, are more common in mandible than maxilla. Treatment: It usually includes surgical resection with irradiation (preferably neutron beam). Three modality therapy: Some recommend combination of chemotherapy (regional infusion with 5-fluorouracil), surgery (maxillary resection) and irradiation. Immunohistochemistry advised to confirm the origin 360 Treatment includes en bloc resection and/or irradiation (preferably neutron beam). Benign: A slow-growing, painless, nonspecific swelling is the usual clinical picture. Bruit: A bruit over the mass or in the common carotid is often present in a vascular malformation and tumor. Pain: Pain or paresthesias usually indicate neural invasion or compression and raise the suspicion of a malignancy. Treatment: It is usually multimodality and includes clear surgical margins supplemented by irradiation and chemotherapy. Masses related to teeth are called odontogenic, while masses not related to the teeth are called nonodontogenic. In addition, the masses of the jaw can be further categorized into neoplastic (benign and malignant), infectious/inflammatory, and congenital groups (Table 4). Salient features of some of the common jaw swellings will be mentioned in this chapter. Well demarcated lesions surrounded by sclerotic bone are often benign and slow growing masses. Ill-defined lytic lesions with resorption of bone and neighboring teeth are locally aggressive masses and can be malignant. Median palatal cysts: Formerly number of nonodontogenic developmental cysts (such as nasopalatine duct cysts, globulomaxillary cysts, and nasoalveolar cysts) was thought to be fissural. But now median palatal cyst is said to be the only true fissural cyst of the jaw, which is formed by the growth of epithelium, trapped between embryonic palatal shelves. Clinical features: They develop secondary to inflammation at the apex of a non-vital tooth. The condition is often asymptomatic but may present with pain either on biting or percussion. The odontogenic keratocyst cannot be adequately treated with enucleation and curettage. But whether patient would be able to chew food depends on the size and location of the defect and the type of reconstruction. Clinical feature: A past history often of a Caldwell-Luc procedure may be elicited from the patient. Radiology: It can be radiopaque or radiolucent and the normal radiologic landmarks are distorted. Large masses can show the evidence of both bone destructions as well as bone formation. About 20% of ameloblastomas are associated with impacted teeth or dentigerous cysts. Imaging: A multiloculated, radiolucent area resembling "soap bubbles" or "honeycomb" is pathognomonic radiological sign. Malignant ameloblastoma: In a malignant ameloblastoma though the cells retain their benign histologic pattern, they metastasize to lung and lymph nodes. Juvenile aggressive type of fibrous dysplasia: It is a rapidly destructive lesion and obliterates tooth buds. There is no need to be radical in removing the diseased bone because distinct border is not found. Clinical features: the child usually present with premature tooth displacement and loss. Radiological examination: It shows bilateral, multiple, multilocular, well-defined radiolucencies with a thin or absent cortex. Prognosis: It is usually good as the features generally regress spontaneously by puberty. Site: Two-third of cases involve mandible, and most are anterior to the permanent molars. Even if some portions of the tumor, difficult to access are left in maxilla, there is no need for revision because recurrence is rare. Inward growth of squamous or transitional cell epithelium towards fibrovascular stroma lends the name of inverted papilloma to it. Other sites in decreasing order are nasal cavity, ethmoid sinuses, frontal and sphenoid sinus. Patients with adenocarcinoma of ethmoid usually give history of wood-dust exposure. Superior orbital foramen (fissure): In cases of tumor compressing the structures traversing the superior orbital foramen, patient experiences pain and altered sensation on the skin of the anterior scalp and dorsum of the nose. Treatment of T3N0m0 squamous cell carcinoma of maxilla: maxillectomy and radiotherapy. The clinical radiological and histological correlation of orbital assessment in malignant lesions of the maxillo-ethmoid complex. An attempt to define the type of biopsy in a sinonasal lesion showing bony erosion. Anterior craniofacial resection-for paranasal sinus tumors involving anterior skull base. Oral Cavity Symptoms Patients may come to doctor after observing some findings in their mouth, such as an abnormal growth, coating of tongue, cleft lip, cleft palate or oroantral fistula. Excessive salivation: the common causes of excessive salivation are: ulcers of mouth and pharynx, poor orodental hygiene, ill fitting denture and iodide therapy. Dysgeusia:2 Taste buds on the anterior two third of tongue appreciate sweet, sour and salt tastes. Tender red swelling extending over ramus of mandible and obliterating subangular depression Lips: Lips have an outer (cutaneous), an inner (mucosal) surface and a vermilion border. Buccal mucosa: Is examined by asking the patient to open the mouth and then retracting the cheek with a tongue depressor.
10 mg duphaston sale
Bony Part: the two nasal bones meet in the midline and rest on the nasal process of the frontal bone zanaflex menstrual cramps purchase duphaston 10mg online. The various cartilages are connected with one another and with the adjoining bones by perichondrium and periosteum. Upper lateral cartilages: They are attached to the under surface of the nasal bones above and extend up to the lower lateral cartilages below. The lateral crus, which overlaps lower margin of upper lateral cartilage, forms the ala while medial crus lies in columella. The anterior and inferior skin-lined portion of internal nose is called vestibule and posterior mucosa-lined portion makes nasal cavity proper. Superior turbinate: this is the smallest turbinate and a part of ethmoidal bone and may get pneumatized by one or more ethmoidal air cells. Supreme turbinate: It may be seen lying above the superior turbinate in some cases. The sphenoid sinus opens into this recess Atrium: this shallow depression lies in front of the middle meatus and above the vestibule. Medial Wall: It is formed by the nasal septum, which has been described in other section of this chapter. It is made up of two bones: palatine process of the maxilla (anterior three-fourth) and horizontal plate of the palatine bone (posterior one-fourth). Lateral wall of nose after removal of turbinates this anteroinferior portion of nasal cavity is lined by skin, which contains sebaceous glands, hair follicles and the hair (vibrissae). Limen Nasi (nasal valve): this area is the greatest constriction of respiratory tract. Injudicious resection of lateral nasal cartilage during rhinoplasty can produce collapse (obstruction) of nose during inspiration. Probe lies in the ethmoidal infundibulum and is coming out through the lower attachment of uncinate process. Note the maxillary ostium medial to the superior turbinate about 1 cm above the upper margin of posterior choana close to the posterior border of septum. The columella contains medial crura of lower lateral cartilages, which are joined together with fibrous tissue. Septum Proper: It is covered with mucous membrane and consists of osteocartilaginous framework. The principal constituents of septum proper are the perpendicular plate of ethmoid, the vomer and a large quadrilateral septal cartilage, which is wedged between vomer and ethmoid plate. Other bones, which make very small contributions, include crest of nasal bones, nasal spine of frontal bone, rostrum of sphenoid, crests of palatine and maxilla and the anterior nasal spine of maxilla. Septal Cartilage: this large quadrilateral septal cartilage is wedged between vomer and ethmoid plate. Inferior margin: It lies in a groove of vomer and rests anteriorly on anterior nasal spine. It may get dislocated from anterior nasal spine (caudal septal deviation) or vomerine groove (septal spur). Therefore septal deviation may be associated with deviation of cartilaginous part of external nose. Coronal section of nose and paranasal sinuses at the level of osteomeatal complex. The uncinate process is in sagittal plane bounding the infundibulum in which opens the ostium of maxillary sinus Section 1 Middle Turbinate: this lower ethmoidal turbinate is attached to the lateral wall through the ground basal lamella. Its middle one-third lies in frontal plane and is attached to lamina papyracea, which forms medial wall of orbit. Septal cartilage destruction, which can be caused due to septal abscess, injuries, tuberculosis or excessive removal during septal surgery, results in depression of lower part of dorsum of nose and drooping of the nasal tip. It requires endoscopic sinus surgery (removal of medial wall of concha or entire concha bullosa). It is important as ostium of frontal, maxillary and anterior ethmoidal sinuses are present in this area. As the bulla ethmoidalis lies anterior to the ground lamella of middle turbinate, these air cells are considered part of anterior group of ethmoidal cells. It is bounded superiorly by the base of skull, laterally by lamina papyracea, inferiorly by the bulla, and medially opens (through hiatus semilunaris superior) in to the middle meatus bounded by the middle turbinate. Hiatus Semilunaris: this two-dimensional gap lies between the posterosuperior free border of uncinate process and front of bulla. It opens laterally into a three-dimensional funnel-shaped space called ethmoidal infundibulum. Uncinate Process: this small thin lamina of ethmoid bone forms floor and medial wall of the ethmoidal infundibulum. Two ends: Posteroinferior end is attached to inferior turbinate and divides the lower membranous part of middle meatus into anterior and posterior fontanelle, which are devoid of bone. Ethmoidal Infundibulum: Frontal sinus opens into the anterosuperior part of infundibulum just posterior to posterior wall (opening) of agger nasi cells (curved ridge running downwards and forwards above the atrium). Agger Nasi: It is an elevation that lies just anterior to the attachment of middle turbinate and if pneumatized contains agger nasi cells, which communicate with frontal recess. This is the most common site for epistaxis and bleeding polyp (fibroangioma) of septum. This deeper specialized vascular plexus is present in the erectile tissue of inferior turbinate and adjacent septum and posterior part of middle turbinate. Stimulation of sympathetic vasomotor nerves causes vasoconstriction (noradrenaline secretion), while parasympathetic stimulation causes vasodilation (acetylcholine secretion) and watery nasal discharge (secretomotor). Stronger mechanical or chemical stimulation of internal nose may cause apnea and bradycardia. Olfactory Epithelium: the olfactory epithelium that is paler in color lines the olfactory region, which includes roof of nasal cavity and area above superior concha. This respiratory mucous membrane is pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium and contain plenty of goblet cells. The submucosal layer contains both racemose and tubular glands that secrete serous and mucous secretions for the surface mucous blanket. The deeper specialized vascular plexus (erectile tissue) consists of arterioles, capillaries, vascular sinusoids, venous plexuses and venules. Anterosuperior part of the nasal cavity (lateral wall and septum) is supplied by anterior ethmoidal nerve, which can be blocked by placing the cotton pledget impregnated in 4% xylocaine high up inside of nasal bones. Autonomic Nervous System Parasympathetic: Parasympathetic nerve fibers are secretomotor and supply the nasal glands. Sympathetic: the preganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers come from upper two thoracic segments of spinal cord (origin from hypothalamus) and relay in superior cervical ganglion. The postganglionic fibers form a plexus around internal carotid artery, from which deep petrosal nerve arises that joins the preganglionic parasympathetic fibers of greater petrosal nerve to form the nerve to pterygoid canal (vidian nerve). Lymphatic Drainage Submandibular Lymph Nodes: the external nose and anterior part of nasal cavity drain into submandibular lymph nodes. Perineural Intracranial Spread: the perineural intracranial spread of cancer is possible through the lymphatics of the upper nasal cavity, which communicate with subarachnoid space along the olfactory nerves. Posterior Group: the sinuses, which open posterior and superior to basal lamella of middle turbinate, form posterior group of paranasal sinuses. Accessory Ostium: In 30% of population, an accessory ostium, which may be quite large, is seen behind and in front of the natural main ostium. The maxillary sinus does not drain through accessory ostium and is bypassed by the mucus blanket. Frontal Sinus the frontal sinus is situated above and deep to the supraorbital margin. The intervening bony septum, which is thin and often obliquely placed, may be deficient in some cases. Ostium of frontal sinus is situated in its floor and opens into the frontal recess, which depending upon the attachment of uncinate process opens either in the infundibulum or medial to the uncinate process into the middle meatus. Posterior wall: It is in relation with the infratemporal and pterygopalatine fossa. Medial wall: It is thin and membranous at places and faces middle and inferior meatuses.
Syndromes
- Giant cell arteritis
- Tell your doctor if you are taking sildenafil (Viagra), vardenafil (Levitra), or tadalafil (Cialis).
- High-dose test: normal suppression (however, some do not suppress, and another test is needed)
- Developmental milestones record - 6 months
- Aortic rupture
- Skin cancer
Buy duphaston in united states online
Gait changes in patients with knee osteoarthritis are replicated by experimental knee pain the women's health big book of exercises pdf download generic duphaston 10mg online. The endocrine system: basic science and clinical conditions Edinburgh Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. Experimental muscle pain challenges the postural stability during quiet stance and unexpected posture perturbation. Studies comparing numerical rating scales, verbal rating scales, and visual analogue scales for assessment of pain intensity in adults: A systematic literature review. Interaction between pain, movement and physical activity: Shortterm benefits, long-term consequences, and targets for treatment. Relationship between quantitative sensory testing and pain or disability in people with spinal pain-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Activation of the prostaglandin system in response to sleep loss in healthy humans: Potential mediator of increased spontaneous pain. Elevated inflammatory markers in response to prolonged sleep restriction are associated with increased pain experience in healthy volunteers. Long-term fluctuations of pressure pain thresholds in healthy men, normally menstruating women and oral contraceptive users. Serotonergic vulnerability and depression: Assumptions, experimental evidence and implications. Relationship between pressure pain thresholds and pain ratings in patients with whiplash-associated disorders. The sacroiliac joint: A potential cause of pain after lumbar fusion to the sacrum. Radiosteriometric analysis of movement in the sacroiliac joint during a single-leg stance in patients with long-lasting pelvic girdle pain. Depression and changed pain perception: Hints for a central disinhibition mechanism. Development of an assessment schedule for patients with low back-associated leg pain in primary care: A Delphi consensus study. Increased pressure pain sensibility in fibromyalgia patients is located deep to the skin but not restricted to muscle tissue. Prevalence and factors associated with low back pain and pelvic girdle pain during pregnancy: A multicenter study conducted in the Spanish national health service. Symptom-giving pelvic girdle relaxation in pregnancy, I: Prevalence and risk factors. Diagnosis of sacroiliac joint pain: Validity of individual provocation tests and composites of tests. Diagnosing painful sacroiliac joints: A validity study of a McKenzie evaluation and sacroiliac provocation tests. Central sensitization: A generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. Neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions of estrogens and their therapeutic implications. Observations relating to referred pain, visceromotor reflexes and other associated phenomena. Do psychological factors increase the risk for back pain in the general population in both a cross-sectional and prospective analysis Periarticular corticosteroid treatment of the sacroiliac joint in patients with seronegative spondylarthropathy. Efficacy of periarticular corticosteroid treatment of the sacroiliac joint in non-spondylarthropathic patients with chronic low back pain in the region of the sacroiliac joint. Roles of capsaicin-insensitive nociceptors in cutaneous pain and secondary hyperalgesia. Results of sacroiliac joint double block and value of sacroiliac pain provocation tests in 54 patients with low back pain. Sex-dependent differences in the activity and modulation of N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptors in rat dorsal root ganglia neurons. Early predictive biomarkers for postpartum depression point to a role for estrogen receptor signaling. The mechanical effect of a pelvic belt in patients with pregnancy-related pelvic pain. Reliability and validity of the active straight leg raise test in posterior pelvic pain since pregnancy. Classification of chronic pain: Descriptions of chronic pain syndromes and definitions of pain terms. Perceived health, sick leave, psychosocial situation, and sexual life in women with lowback pain and pelvic pain during pregnancy. Reduced variability of postural strategy prevents normalization of motor changes induced by back pain: A risk factor for chronic trouble Effect of periarticular and intraarticular lidocaine injections for sacroiliac joint pain: Prospective comparative study. Clinical findings, pain descriptions and physical complaints reported by women with post-natal pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain. Ultrasound guided, painful electrical stimulation of lumbar facet joint structures: An experimental model of acute low back pain. Low pressure pain thresholds are associated with, but does not predispose for, low back pain. Association between a composite score of pain sensitivity and clinical parameters in low-back pain. The effect of different standing and sitting postures on trunk muscle activity in a pain-free population. Chronic low back pain measurement with visual analogue scales in different settings. Prevalence of sleep deficiency in early gestation and its associations with stress and depressive symptoms. Behavioral and psychosocial factors associated with insomnia in adolescents with chronic pain. A comparison of manual diagnosis with a diagnosis established by a uni-level lumbar spinal block procedure. Effects of a single session of posterior-to-anterior spinal mobilization and press-up exercise on pain response and lumbar spine extension in people with nonspecific low back pain. Pelvic girdle pain - associations between risk factors in early pregnancy and disability or pain intensity in late pregnancy: A prospective cohort study. The Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia: further examination of psychometric properties in patients with chronic low back pain and fibromyalgia. Physical characteristics of women with severe pelvic girdle pain after pregnancy: A descriptive cohort study. Computerized tomographic localization of clinically-guided sacroiliac joint injections. Prognosis of women with pelvic pain during pregnancy: A long-term follow-up study. The role of central hypersensitivity in the determination of intradiscal mechanical hyperalgesia in discogenic pain. One night of total sleep deprivation promotes a state of generalized ~ 60 ~ hyperalgesia: A surrogate pain model to study the relationship of insomnia and pain. Widespread sensory hypersensitivity is a feature of chronic whiplash-associated disorder but not chronic idiopathic neck pain. Back and pelvic pain in an underserved United States pregnant population: A preliminary descriptive survey. Widespread sensitization in patients with chronic pain after revision total knee arthroplasty. Experimental deep tissue pain in wrist extensors-a model of lateral epicondylalgia. Sensory and motor effects of experimental muscle pain in patients with lateral epicondylalgia and controls with delayed onset muscle soreness. Sensory responses to mechanically and chemically induced tendon pain in healthy subjects. The predictive value of provocative sacroiliac joint stress maneuvers in the diagnosis of sacroiliac joint syndrome. Classification of sagittal thoraco-lumbo-pelvic alignment of the adolescent spine in standing and its relationship to low back pain. The influence of slouching and lumbar support on iliolumbar ligaments, intervertebral discs and sacroiliac joints.
Buy duphaston with paypal
The estimated number of illnesses from ciprofloxacin resistant or partially resistant Salmonella Typhi was divided by the U menopause 34 effective duphaston 10mg. Worldwide case estimates3 and pre-antibiotic era mortality4 are from published sources. High prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among Shigella isolates in the United States tested by the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System from 1999 to 2002. Reports include both healthcare-associated infections and community-associated infections, but are limited to invasive infections (approximately 85% are bloodstream infections). Estimates were made using National Center for Health Statistics bridged-race vintage 2011 post-censal file and U. Mortality includes all-cause mortality during hospitalization, and estimates were adjusted in similar fashion as infection estimates. Approximately 18% of cases were reported without a race value, multiple imputation was used to estimate the missing race based on the data that are available and the results were summarized. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-second Informational Supplement. First, numbers of cases were estimated by applying the rate for full resistance to clinically relevant drugs. Attributable Healthcare Utilization and Cost of Pneumonia due to Drug-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. Adverse drug event: When therapeutic drugs (example, antibiotics) have harmful effects; when someone has been harmed by a medication. Aminoglycoside: A type of antibiotic that destroys the functioning of gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotic: Type of medicine made from mold or bacteria that kills or slows the growth of other bacteria. Antibiotic class: A grouping of antibiotics that are similar in how they work and how they are made. Antibiotic growth promotion: Giving farm animals antibiotics to increase their size in order to produce and sell more meat. Antibiotic resistance: the result of bacteria changing in ways that reduce or eliminate the effectiveness of antibiotics. Antibiotic stewardship: Coordinated efforts and programs to improve the use of antimicrobials. For example, facilities with antibiotic stewardship programs have made a commitment to always use antibiotics appropriately and safely-only when they are needed to prevent or treat disease, and to choose the right antibiotics and to administer them in the right way in every case. Antimicrobial: A general term for the drugs, chemicals, or other substances that either kill or slow the growth of microorganisms. Among the antimicrobial agents in use today are antibacterial drugs (which kill bacteria), antiviral agents (which kill viruses), antifungal agents (which kill fungi), and antiparisitic drugs (which kill parasites). Antimicrobial resistance: the result of microorganisms changing in ways that reduce or eliminate the effectiveness of drugs, chemicals, or other agents used to cure or prevent infections. In this report, the focus is on antibiotic resistance, which is one type of antimicrobial resistance. Azithromycin: A macrolide antibiotic used to treat infections caused by gram-positive bacteria and infections such as respiratory tract and soft-tissue infections. Bacteria can be helpful, but in certain conditions can cause illnesses such as strep throat, ear infections, and bacterial pneumonia. Beta ()-lactamase enzyme: A chemical produced by certain bacteria that can destroy some kinds of antibiotics. Broad-spectrum antibiotic: An antibiotic that is effective against a wide range of bacteria. Carbapenem: A type of antibiotic that is resistant to the destructive beta-lactamase enzyme of many bacteria. Carbapenems are used as a last line of defense for many bacteria, but increased resistance to carbapenems has made them less useful. Cefixime: A cephalosporin antibiotic that is resistant to the destructive beta-lactamase enzyme of many bacteria. Ceftriaxone: A cephalosporin antibiotic that is resistant to the destructive beta-lactamase enzyme of many bacteria. Cephalosporin: Cephalosporins are a class of antibiotics containing a large number of drugs. Some more recently developed cephalosporins are resistant to the destructive betalactamase enzyme produced by many bacteria. Ciprofloxacin: A broad-spectum fluoroquinolone antibiotic that is important in treating serious bacterial infections, especially when resistance to older antibiotic classes is suspected. Clindamycin: An antibiotic used to treat certain types of bacterial infections, including infections of the lungs, skin, blood, female reproductive organs, and internal organs. Conjugate vaccine: A vaccine in which an antigen is attached to a carrier protein from the same microorganism. This approach enhances the immunological response to the vaccine and thereby enhances the overall effectiveness of the vaccine. Epidemiology: the study of diseases to find out who is affected, how disease is spread, trends in illnesses and deaths, what behaviors or other risk factors might put a person at risk, and other information that can be used to develop prevention strategies. Epidemiologists use surveys and surveillance systems to track illnesses, and they often investigate disease outbreaks. Extended-spectrum antibiotic: An antibiotic that has been chemically modified to attack additional types of bacteria, usually those that are gram-negative. Fluoroquinolones: Broad-spectrum antibiotics that play an important role in treatment of serious bacterial infections, especially hospital-acquired infections and others in which resistance to older antibacterial classes is suspected. Fungi can also be or pathogens (such as the endemic mycoses, histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis, and superficial mycoses) that cause infections in healthy people. Fungi are used to develop antibiotics, antitoxins, and other drugs used to treat various diseases. Hypervirulent: Increased ability to cause severe disease, relapse rates, and death. Isolate/bacterial isolate: A pure culture or sample of bacteria used to study their properties. Macrolide: A type of antibiotic used to treat infections caused by gram-positive bacteria and infections such as respiratory tract and soft-tissue infections. Macrolides are often used 109 in people allergic to penicillin, but resistance to macrolides is increasing and has made them less useful. Morbidity: the number of people who are infected with a specified illness in a given time period. The exact number of drugs that a microorganism is resistant to varies depending on the infection or pathogen. Narrow-spectrum antibiotic: An antibiotic that is active against a limited range of bacteria. Outbreak: When a group of people develop the same illness around the same time, and the number of people affected is higher than normal. Outbreak investigations are conducted to identify what exposure the affected people had in common. Penicillins: A class of antibiotics including amoxicillin, methicillin, piperacillin and other drugs based on the first true antibiotic discovered in 1928 by Dr. Pneumonia: An inflammatory condition of the lungs affecting primarily the microscopic air 110 sacs known as alveoli. It is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and typical symptoms include a cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. Reservoir: A person, animal, insect, plant, or other host that is carrying a pathogen (for example, bacteria or fungi) that causes infectious diseases. Resistant bacteria: Microorganisms that have changed in ways that reduce or eliminate the effectiveness of drugs, chemicals, or other agents to cure or prevent infections. Strain/bacterial strain: A strain is a genetic variant or subtype of a microorganism (for example, a flu strain is a subtype of the flu virus). When bacteria become resistant to antibiotics, they can share their resistance with other bacteria to create new resistant bacterial strains.
Purchase duphaston discount
Over the years women's health clinic joondalup discount duphaston 10 mg free shipping, the American Heart Association and others have published recreational and sport recommendations for young persons with heart disease. Although oral contraceptives are effective when used by teenagers, it is estimated that 13 percent of teen users between ages of 15 to 17 years will miss an average of three pills per month. Injectables which are also safe still require regular return visits thus placing a certain level of responsibility on the teen to return to clinic. It should be presented in a sensitive and culturally appropriate manner that is in alignment with their individual level of emotional maturity and the value system of their society. It is important for health care providers to proactively address questions and concerns regarding their sexuality, the ability to conceive/bear children, the safety and availability of contraceptives based upon their underlying defects. Its goal is to outline routine health care recommendations and specific information on diagnoses, procedures, operations, medications, allergies, endocarditis prophylaxis, exercise, contraception and the recommended frequency of medical and dental follow-up. They should also carry a list of their cardiologist/health providers and personal emergency contacts. Therefore, such a summary is referred to as a health passport in that it is similar to a travel passport, because it carries vital information to ensure safe health care when one is away from his/her own providers. Patients are also encouraged to carry scanned copies of their medical reports on a password encrypted flash drive so that more detailed medical records are readily available during unforeseen circumstances. Even though this list is not complete, through these contacts more information can be sought at the local and regional levels by the health care providers and then passed on to the patients. Contraceptives the prevention of unplanned pregnancy in adolescent/young adult requires a collaboration between providers, patients and sometimes, their parents. Additionally, the adolescent health care provider should be familiar with the relation between oral contraception, particularly the estrogenic type and venous thromboembolism that makes this form of contraception hazardous for females who are cyanotic and/or in those with conditions such as right-to-left shunts, pulmonary vascular disease, prosthetic valves/conduits. These measures are to ensure a smooth transition into the adult heath care system and avoid the complications resulting from lack of proper long-term care. Transition to adult health care for adolescents and young adults with chronic conditions: Position paper of the Society for Adolescent Medicine. Transition and transfer from pediatric to adult care of the young adult with complex congenital heart disease. Prevalence and correlates of successful transfer from pediatric to adult health care among a cohort of young adults with complex congenital heart defects. Outcomes of noncardiac surgical procedures in children and adults with congenital heart disease. Current insights regarding neurological and developmental abnormalities in children and young adults with complex congenital cardiac disease. Best Practices in Managing Transition to Adulthood for Adolescents With Congenital Heart Disease: the Transition Process and Medical and Psychosocial Issues. Transitional care issues influencing access to health care: employability and insurability. Employability and career counseling for adolescent and adults with congenital heart disease. Sexual behavior and reproductive concerns among adolescents and young adults with congenital heart disease. Adults with congenital heart disease: Patient knowledge of endocarditis prophylaxis. Piercing and tattooing in patients with congenital heart disease: Patient and physician perspectives. Self-efficacy and physical activity in adolescents with trivial, mild, or moderate congenital cardiac malformations. A prospective comparison of bone density in adolescent girls receiving depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depo-Provera), levonorgestrel (Norplant), or oral contraceptives. Little did he know then that two of his female disciples would generate a new wave in the field of medicine. Maude Abbott, initially barred from studying medicine because she was a woman, with her undying persistence and perseverance acquired medical knowledge from universities around the world. She returned to Montreal, Canada where she soon became the curator of the McGill Pathological Museum in 1901. Categorizing in detail the various congenital heart defects over the course of decades, she published her work in the "Atlas of Congenital Cardiac Disease" in 1936. Her contributions have served as a foundation for understanding the pathology of congenital heart disease. She led the pioneering "blue baby operation" along with Vivien Thomas and Alfred Blalock in 1944. This set the stage for the advent of cardiac surgeries assisted by artificial circulation (bypass machine). Born in India and raised in Australia, Dr Wood became well-known for describing the Eisenmenger syndrome and for writing the first single author cardiology textbook, "Diseases of the Heart and Circulation". Deeply influenced by the chapters from this book on "Physical examination" and "Congenital affections of the heart" another disciple, Dr Joseph Perloff went on to write individual textbooks on these two topics. Advances in all aspects of medicine and surgery have allowed the majority of the infants born with congenital heart defects, 10 Congenital Heart Disease in aDults who have access to healthcare, to survive into adulthood. While most individuals born with congenital heart defects are diagnosed in infancy and childhood, some go undiagnosed until adulthood. There has been organized global effort to integrate multidisciplinary services devoted to this special population. An adequate Valsalva maneuver is essential, while assessing the presence of a right-to-left shunt by an agitated saline contrast study with transthoracic or transesophageal echocardiogram. In most studies, the clinical diagnosis of paradoxical embolism was presumptive and was based on the presence of a rightto left shunt in the absence of a left-sided thromboembolic source. A recent randomized trial (Closure I) did not detect any benefit of closure over medical treatment alone. Palpitations due to atrial arrhythmias and dyspnea are the most common presenting symptoms. Characteristic physical findings are a prominent right ventricular parasternal lift, persistent or wide fixed splitting of the second heart sound and a pulmonary systolic ejection murmur, at the left upper sternal edge due to increased pulmonary flow. Pulmonary hypertension leads to an accentuation of the pulmonary component of the second heart sound. A sinus venosus defect with associated anomalous pulmonary venous return is suspected, when there is right heart enlargement in the absence of a clearly defined interatrial shunt. The consensus is to close defects in symptomatic patients and in those with right heart enlargement. In the presence of pulmonary hypertension, the defect may be safely closed if pulmonary artery systolic pressure is less than 50 percent of the systemic arterial pressure. Right heart catheterization to assess the pulmonary vascular resistance may be required for those with higher pulmonary artery pressures. In general, all defects should be considered for early closure unless there are specific contraindications. Endocarditis/endarteritis prophylaxis is recommended for 6 months after device closure. It was later defined by Dr Paul Wood in 1958 as Eisenmenger syndrome with its distinctive clinical and physiologic characteristics. Although aware of a murmur all through their lives, many asymptomatic individuals are only diagnosed in adulthood. Physical examination is characteristic of a pansystolic murmur (and sometimes precordial). The pulmonic component of the second heart sound may be accentuated in the presence of pulmonary hypertension. The direction and the volume of an interventricular shunt are dictated by the size of the defect and the ratio of pulmonary vascular resistance to the systemic vascular resistance. The left heart experiences volume load and depending on the size of the defect, the right heart may experience a pressure load. In a large unrestrictive ventricular septal defect there is equalization of right and left ventricular pressures due to free communication between the two chambers. This leads to near systemic pressures in the pulmonary arteries that causes irreversible pulmonary vascular disease and pulmonary hypertension. Patent ductus arteriosus is a residual fetal communication between the proximal left pulmonary artery and the descending aorta distal to the left subclavian artery. During fetal life, it allows the diversion of blood from the right ventricle to the descending aorta, thus bypassing the pulmonary circulation.
Cheap duphaston 10 mg visa
Auditory brainstem responses is affected in disorders of external women's safety and health issues at work discount duphaston 10mg on-line, middle and internal ears and auditory nerve and brainstem. Hearing tests Evoked otoacoustic Emission Evoked otoacoustic emissions are acoustic signals generated by cochlear outer hair cells in response to auditory stimulation. Transient evoked otoacoustic emission are observed in neonatal ears in the absence of external and middle ear disorders. Visual reinforcement audiometry: Visual reinforcement audiometry is a form of conditioning technique. If this response is rewarded by activation of a lighted, animated toy, the infant usually continue to respond and an audiogram is obtained. Older infants, who yield fewer false positive responses than 6 months infant, tend to reject earphones. Speech audiometry: the spondee words are presented to the child along with the pictures. Cessation reflex: In response to a sound of 90 dB, an infant stops activity or starts crying. The acts may be placing a marble in a box, a wooden or plastic block in the bucket, or a ring on a post. Ear Section 2 clinical Features Congenital toxoplasmosis: Usually associated with chorioretinitis, intracerebral calcification and microcephaly. Congenital rubella: Fifty percent of the patients present with hearing loss alone. Magnetic Resonance Imaging: It is done prior to cochlear implantation to assess patency of the cochlea, position of facial nerve and presence of auditory nerve. It is essential to know not only the degree and type of hearing loss but also other associated handicaps, such as blindness or mental retardation. Aims of rehabilitation include development of speech and language, adjustment in society and useful vocational employment. Parents should know regarding the following requirements: Care and periodic replacement of hearing aid Change of ear moulds as the child grows Follow up visits for reevaluation Education at home Selection of vocation trEatmEnt Otitis media: In infants of acute otitis media, antibiotic therapy is given with close follow-up for the effusion resolution. Auditory rehabilitation: After identifying the type and extent of hearing loss, appropriate rehabilitative measures should be initiated at the earliest, which include amplification and cochlear implantation. The abstract ideas are difficult to express because general public does not understand it. Regular follow-up appointments with audiologists is important (Chapter "Hearing Aid and Cochlear Implant"). Vibrotactile aids: these are useful in children who are both deaf, as well as blind. The vibrations of speech are perceived by the child through tactile sensation (Have you seen film "Black" of Amitabh and Rani Mukherji Post meningitis deafness needs early implantation to avoid later difficulties of implantation due to cochlear ossification. Comparative evaluation of transient evoked otoacoustic emissions and brainstem evoked response audiometry: a screening modality for hearing impairment in neonates. The auditory rehabilitation includes not only instrumental devices but also training. The heightened volume increases audibility and reduces the strain of understanding sound in daily listening situations. The skill is useful for hearing impaired individuals who have high frequency loss and difficulty in hearing in noisy surroundings. Bone conduction hearing aid: the amplified sound is transmitted to the mastoid bone through a bone vibrator which snugly fits on the mastoid. Acoustic gain: It is the difference between the output and input of a hearing aid. The patient is exposed to various listening situations with different degrees of difficulty. Speech conservation: Patients with profound hearing loss loses the ability to monitor their own speech production. Acoustic feedback: It occurs when amplified sound leaks from the receiver back into the microphone. Through a 176 soft polyethylene tube and an earmold, it is coupled to the ear canal. It has been used for mild-to-moderate hearing loss particularly high frequency ones. A relatively large vent is required if less output at low frequency is desirable as in cases of high frequency hearing loss. Monaural/Binaural Amplification In cases of bilateral hearing loss, binaural hearing aid amplification eliminates head shadow effect and is advantageous. The other benefits of binaural amplification include better speech discrimination and localization. Head shadow effect: When sound has to cross the head to reach other side of the ear, 6 dB loss in sound intensity occurs. Hearing aids in children An infant should be fitted with a hearing aid based on available audiometric information. In infants with congenital atresia or microtia, hearing aid can be fitted at the age of 2 months. Section 2 w ear analog, Hybrid and digital Hearing aids Analog hearing aids: Traditional hearing aids are analog machines. Hybrid hearing aids: They use digital components that control and modify the operation of the analog components in the signal-processing stage. These have not only the higher fidelity signal but can also modify output in many ways. The microphone in the deaf ear picks up sounds, which are passed to the receiver placed in the better ear. This type of arrangement, which is useful in patients with unilateral profound hearing loss, helps in localizing the sound coming from the side of the deaf ear. A nonoccluding or open earmold is used in better ear to allow detection of sounds without amplification. Hearing dog: It is trained to bark loudly at the sound of a doorbell and cry of a baby. Sound processor: After the completion of osseointegration, it is attached to the abutment. The piezoelectric transducer is coupled to ossicles and drives the ossicular chain by vibration. Section 2 Chronic otitis media and externa: Chronic otorrhea not amenable to treatment. Otosclerosis and tympanosclerosis: When surgery is contraindicated or patient is not willing for surgery. Surgical Technique: Surgery is performed in single stage in adults but children need two stages. In second stage, which is performed after the 6 months (period of osseointegration) titanium abutment is connected through the skin to the fixture. Surgical procedure: the receiver of the internal device is positioned under the skin over the mastoid bone. After performing mastoidectomy, the ossicular chain is visualized through a posterior tympanotomy approach. The residual hearing is not affected as the middle ear ossicular chain is not disturbed. Depending on whether the child was deafened before or after the acquisition of speech and language, hearing loss is called prelingual or postlingual. The children with congenital and early childhood hearing loss need early intervention with hearing aids or cochlear implants. The speech processor selects specific characteristics of sound, which are important for understanding the speech. Children and adults with postlingual short duration deafness achieve very good results. It uses specific speech coding strategy to translate acoustic information into electric stimulation. Internal component: It is surgically implanted and comprises following: Receiver/Stimulator, magnet and antenna: Receiver/ stimulator has a magnet and antenna. Electrode: Electrode is placed into the scala tympani through round window cochleostomy.
Buy online duphaston
Treatment of restrictive cardiomyopathy is difficult because the underlying processes usually do not respond to interventions zoladex menstrual cycle purchase cheap duphaston online. Their dose needs to be monitored carefully as they may cause a decline in the preload and lead to hypotension. Arteriolar and balanced vasodilators are not useful because excessive afterload is not a problem. Venous vasodilators may decrease congestive symptoms, but can provoke significant Diagnostic Studies Hypereosinophilia may be present. Hemodynamics A dip and plateau curve with high diastolic pressure is seen in the corresponding ventricle. Endomyocardial biopsy showed fibrous thickening of the endocardium made up of collagen without classic fibers. Treatment: Endarterectomy with atrioventricular valve replacement of the diseased ventricle has been done with mixed outcome. Amyloidosis is a systemic disorder characterized by interstitial deposition of linear, rigid, nonbranching, amyloid protein fibrils in multiple organs. However, absence of extracardiac amyloid does not exclude the presence of amyloid heart disease Currently, 5 subtypes of amyloidosis have been recognized. Cardiac involvement is common in all types of amyloidosis and is the most frequent cause of morbidity and mortality. Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome is characterized by prolonged overproduction of eosinophils of unknown cause in addition to specific organ damage due to eosinophil derived protein toxicity. Usually a disease affecting men of temperate climate and the diagnostic criteria for this disease are: 1. Signs or symptoms of cardiac, hematological, pulmonary, neurologic and cutaneous involvement. Because this is an eosinophil mediated damage, aim is to reduce peripheral blood eosinophila and reduce cardiac infiltration. Corticosteroids and hydroxyurea are widely used to reduce eosinophil count and have improved survival in hypereosinophilic syndrome. In some patients where a favorable response is not seen with these drugs, interferon alpha has been used to reduce the eosinophil count, but reduction of organ damage still remains controversial. Case reports of high doses of interferonalpha causing a definite improvement in the disease are present. Diagnostic studies: the cardiac silhouette can be normal or enlarged on the chest X-ray. In one study patients with biopsy proven amyloidosis and wall thickness of greater than 15 mm had a median survival of 0. In a recent study, qualitative global and subendocardial enhancement of the myocardium associated with faster gadolinium clearance from the blood pool was higher in patients with cardiac amyloidosis than hypertensive controls. Autologous stem cell infusion reduces the monoclonal gammopathy, but has little effect on existing infiltrative amyloid deposits. Orthotopic cardiac transplantation is generally not recommended because of systemic nature of the disease and possibility of recurrence in the transplant. It may result from a genetic defect (hereditary hemochromatosis) or from secondary causes. Echocardiography may show granular sparkling, atrial enlargement, but these are not specific. Ultrasonic analysis of integrated backscatter has been used experimentally to detect changes in echocardiographic reflectivity of the myocardium with iron deposits. Endomyocardial biopsy can be confirmatory and reveals stainable iron in the heart. Repeated phlebotomy is recommended for primary hemochromatosis and chelating agent desferrioxamine is beneficial in secondary hemochromatosis. Combinations with oral active chelator deferiprone have been successful in Europe. An extensive clinical trial has shown its efficacy in adults and children and it has a safety profile, which is manageable with regular clinical monitoring. Familial phenotypes may include an associated skeletal myopathy with or without conduction abnormalities. Children may present with reactive airway disease, recurrent respiratory infections, breathlessness on exertion, or more ominously with palpitations, syncope or sudden death. Most of these are manifestations are of increased left-sided filling pressures and decreased myocardial reserve. Those with elevated but reversible pulmonary hypertension are at an urgent need for cardiac transplant, while those with mildly elevated, pulmonary artery pressures may remain stable for years and may not require urgent listing for transplant. The use of beta blocker, implantable cardioverter defibrillator and urgent listing of cardiac transplant is indicated for these patients. Disorders of energy metabolism that produce suspected cardiotoxic intermediary metabolites. It affects young adults between 10 to 40 years of age and presents with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, reticular pulmonary opacities, joints, eyes and skin involvement (erythema nodosum). Cardiac involvement occurs in 5 percent and heart failure can be due to restrictive or dilated cardiomyopathy and has a progressive course. The indications to screen for a biochemical abnormality are onset of acute/chronic encephalopathy, hypotonia, growth retardation, failure to thrive, etc. Patients with storage diseases who cannot degrade certain structural components of cells typically develop coarse or dysmorphic facial features, organomegaly, short stature or chronic encephalopathy with a degenerative course. Skeletal muscle weakness without encephalopathy is usually due to a primary neuromuscular and rarely due to inborn error of metabolism. While in infants evaluation for congenital metabolic syndromes like Gaucher or Hurler is required, many pediatric cases remain idiopathic with upto a third being 719 9 congenital cardiomyopathies Metabolic Cardiomyopathies Glycogen Storage Diseases Pompe disease: An autosomal recessive disorder caused by deficiency of lysosomal enzyme acid-alpha-glucosidase. Classic infantile onset disease, characterized by cardiomegaly and profound weakness, leads to death in the year of life from cardiorespiratory failure. It is divided into 3 types depending on the severity and onset of neurological symptoms. Fabry disease: X-linked recessive lysosomal storage disease, hence a male predominant disease, usually manifesting at 11 + 7 years. Cerebrovascular manifestations include early stroke, hemiparesis, diplopia, dysarthria, nystagmus, etc. Disease is diagnosed by alpha-galactosidase A activity in plasma and peripheral leukocytes. Double component of septal dip in atrial systole-atrial systolic notch, additional dip occurs in early to mid diastole -early diastolic notch. Slight or moderate at the most Usually marked S/D ratio = 1 Prominent inspiratory decrease of S and D waves. Diastolic gradients rise equally or even decrease with these stresses End-diastolic pressure more than one-third of the systolic pressure in most cases Usually not present Pericardial thickness > 4mm is abnormal (may occur in the absence of constriction). At present, medical therapy remains supportive and appears to be ineffective and the development of pulmonary hypertension is common. Extracardiac medical and neuromuscular implications in restrictive cardiomyopathy. A case of chloroquine-induced cardiomyopathy that presented as sick sinus syndrome. Idiopathic restrictive cardiomyopathy in childhood: Diagnostic features and clinical course. Comparison of usefulness of tissue Doppler imaging versus Brain natriuretic peptide for differentiation of constrictive pericardial disease from restrictive cardiomyopathy. Echocardiographic aspects of restrictive cardiomyopathy: their relationship with pathophysiology. Pitfalls in diagnosis and clinical echocardiographic and hemodynamic findings in endomyocardial fibrosis. Favorable response to high-dose interferon Alpha in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome with restrictive cardiomyopathy. Congestive cardiomyopathy and endobronchial granulomas as manifestations of Churg-Strauss Syndrome.