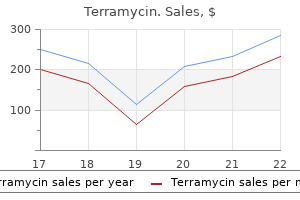
Buy terramycin toronto
It is important to discuss with the proxy his or her own value system infection in finger order terramycin 250 mg with amex, and whether he or she could make a decision for someone else that he or she would not make for him or herself. The purpose of a living will is to give specific instructions about emergency or end-of-life health care. In some states the person who is authorized may be called a proxy, in others the person may be called an agent. Description A health care proxy form is part of a set of legal documents that allows a person to appoint someone to make medical decisions for them if they cannot act on their own behalf, and to make sure that health care professionals follow their wishes regarding specific medical treatments at the end of life. The document naming the person appointed to make the decisions is called a health care proxy. The document that lists acceptable and unacceptable measures of artificial life support is called a living will. In addition to naming the specific person who will make those decisions, one should think about what lifesustaining treatments one would be willing to undergo in the event of a medical emergency or terminal illness. A health care proxy form does not deprive a person of the right to make decisions about medical treatment as long as he or she is able to do so. Proxy-A person authorized or empowered to act on behalf of another; also, the document or written authorization appointing that person. Improving Care for the End of Life: a Sourcebook for Health Care Managers and Clinicians. Even if a living will is not legal in the state in which one resides, writing such a will is an opportunity to think through personal beliefs and health care preferences. The proxy or agent can then can use the living will as a guide in making health care decisions as need arises. What religious or personal beliefs do I hold that affect my health care decisions Do I want my proxy to make health care decisions on his or her own, or are there other people I would want him or her to consult One can change or revoke the proxy at any time, usually by filling out a new form. In some states, one can specify that the health care proxy will expire on a certain date or if certain events occur. If a person has named his or her spouse as an agent, the proxy is no longer in effect in the event of separation or divorce. People who want a former spouse to continue as their agent must complete a new proxy form. In addition to keeping a copy of the proxy form in a person file of important documents, the person should give copies to the proxy, the alternate, and his or her physicians. Caring Connections, (800) 658-8898, (877) 658-8896 (Multilingual), caringinfo@nhpco. Relevant aspects of the history include biographical, demographic, physical, mental, emotional, sociocultural, sexual, and spiritual data. Subjective-Influenced by the perspective of the information provider; potentially biased. Purpose the health history aids both individuals and health care providers by supplying essential information that will assist with diagnosis, treatment decisions, and establishment of trust and rapport between lay persons and medical professionals. Every person should have a thorough health history recorded as a component of a periodic physical examination. These occur frequently (monthly at first) in infants and gradually reach a frequency of once per year for adolescents and adults. When a person or a designated representative can communicate effectively, the clinical interview is a valuable means for obtaining information. When circumstances allow, a history may be holistic and comprehensive, but at times only a cursory review of the most pertinent facts is possible. Often a hospital or clinic will provide a form, template, or computer database that serves as a guide and documentation tool for the history. Identifying or basic demographic data includes facts such as: Once the basic identifying data is collected, the history addresses the reason for the current visit in expanded detail. The reason for the visit is sometimes referred to as the chief complaint or the presenting complaint. Once the reason for the visit is established, additional data are solicited by asking for details that provide a more complete picture of the current clinical situation. For example, in the case of pain, aspects such as location, duration, intensity, precipitating factors, aggravating factors, relieving factors, and associated symptoms should be recorded. The review of systems is a useful method for gathering medical information in an orderly fashion. A thorough record of relevant dates is important in determining relevance of past illnesses or events to the current condition. An example of a series of questions might include the following: the relevant findings. A health professional should discuss any recommendations for treatment or follow-up visits. This is also an opportunity for persons to ask any remaining questions about their own health concerns. Health history Health care team roles A health history is best obtained by a physician who has the training to appreciate nuances and details that may be overlooked by those with less training. Other health care professionals such as physician assistants and nurse practitioners have similar but somewhat limited training. If an individual indicates a history of auditory difficulties, this would prompt further questions about medicines, surgeries, procedures, or associated problems related to the current or past condition. The clinicians also tailor their interviewing style to the age, culture, educational level, and attitudes of the persons being interviewed. Thorough training and practice in techniques of interviewing such as asking open-ended questions, listening effectively, and approaching sensitive topics such as substance abuse, chemical dependency, domestic violence, or sexual practices assists a clinician in obtaining the maximum amount of information without upsetting the person being questioned or disrupting the interview. The interview should be preceded by a review of the chart and an introduction by the clinician. The health care professional should explain the scope and purpose of the interview and provide privacy for the person being interviewed. Department of Health and Human Services Office of the Surgeon General and the National Human Genome Research Institute. Purpose Recent technology can help most people with hearing loss understand speech better and achieve better communication. Precautions It is important that a person being fitted for a hearing aid understand what an aid can and cannot do. An aid can help a person hear better, but it will not return hearing to normal levels. Especially when the source of sound is far away (such as up on a stage), environmental noise can interfere with good speech perception. In addition, while the aid amplifies sound, it does not necessarily improve the clarity of the sound. A hearing aid is a machine and can never duplicate the true sound that people with normal hearing experience, but it will help the person take advantage of the hearing that remains. All of them include a microphone (to pick up sound), amplifier (to boost sound strength), a receiver or speaker (to deliver sound to the ear), and are powered by a battery. Depending on the style, it is possible to add features to filter or block out background noise, minimize feedback, lower sound in noisy settings, or boost power when needed. Hearing aids are either 'monaural' (a hearing aid for one ear), or 'binaural' (for two ears); more than 65% of all users have binaural aids. Hearing aids are divided into several different types: Adjusting the volume may be hard, since a person must stick a finger down into the ear to adjust volume, and this very tiny aid does not have the power of other, larger aids. Behind-the-ear aids include a microphone, amplifier, and receiver inside a small curved case worn behind the ear; the case is connected to the earmold by a short plastic tube. Behind-the-ear aids: Hearing aids digital in-the-ear in-the-canal behind-the-ear on-the-body Digital aids are sophisticated, very expensive aids that borrow computer technology to allow a person to tailor an aid to a specific hearing loss pattern. Using miniature computer chips, the aids can selectively boost certain frequencies while leaving others alone.
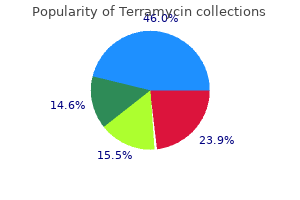
Buy terramycin with a mastercard
Women might not seek treatment because of a lack of such resources as money xnl antibiotic order 250mg terramycin with visa, transportation, or time away from child-care duties. Men, on the other hand, might not seek treatment because it is incongruent with their image of masculinity. Therapists may need to offer men less threatening forms of treatment, such as those that focus on cognitive problem solving rather than on emotions. Therapists should recognize the potential for shame and defensiveness when exploring gender norms. Men may be encouraged to connect to the spiritual aspects of their being and to consider less stringent views of masculinity. Therapists should also consider the associated influences of generation, culture, class, occupation, and educational level when exploring gender-role issues. Men often are entering therapy under duress, as the result of a court order or a spousal ultimatum and may begin the therapeutic process from a perspective of defensiveness. Taking either masculine or feminine qualities to an extreme and to the exclusion of the other appears to be detrimental. A non-traditional gender-role orientation would combine the best of both genders: a social focus (reciprocally supportive relationships and a balance between interests of self and others) and active coping strategies. Active, problem-focused coping strategies help to change the situation that is causing the problem. Avoidant or emotion-focused coping strategies manage or reduce emotional distress. Avoidant and emotion-focused strategies may be helpful for the immediate crisis but should be used in combination with more active strategies for complete problem resolution. Society for the Psychological Study of Men and Masculinity (Division 51), American Psychological Association, 750 First St. Gene therapy seeks to provide genes that correct or supplant the disease-controlling functions of cells that are not, in essence, doing their job. Somatic gene therapy introduces therapeutic genes at the tissue or cellular level to treat a specific individual. Germ-line gene therapy inserts genes into reproductive cells or possibly into embryos to correct genetic defects that could be passed on to future generations. Although gene therapy testing in humans has advanced rapidly, many questions surround its use. For example, some scientists are concerned that the therapeutic genes themselves may cause disease. Others fear that germline gene therapy may be used to control human development in ways not connected with disease, like intelligence or appearance. Gene therapy the biological basis of gene therapy Gene therapy has grown out of the science of genetics or how heredity works. Humans, for instance, are made up of trillions of cells, each performing a specific function. The rungs of these ladders meet (resulting in a spiral staircase-like structure) and are called base pairs. Scientists have long known that alterations in genes present within cells can cause inherited diseases like cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell anemia, and hemophilia. Similarly, errors in the total number of chromosomes can cause conditions such as Down syndrome or Turner syndrome. As the study of genetics advanced, however, scientists learned that an altered genetic sequence can also make people more susceptible to diseases, like atherosclerosis, cancer, and even schizophrenia. These diseases have a genetic component, but are also influenced by environmental factors (such as diet and lifestyle). The objective of gene therapy is to treat diseases by introducing functional genes into the body to alter the cells involved in the disease process by either replacing missing genes or providing copies of functioning genes to replace nonfunctioning ones. The inserted genes can be naturally occurring genes that produce the desired effect or may be genetically engineered (or altered) genes. Germline gene therapy introduces genes into reproductive 2138 cells (sperm and eggs) or someday possibly into embryos in hopes of correcting genetic abnormalities that could be passed on to future generations. Most of the current work in applying gene therapy, however, has been in the realm of somatic gene therapy. In this type of gene therapy, therapeutic genes are inserted into tissue or cells to produce a naturally occurring protein or substance that is lacking or not functioning correctly in an individual patient. One of the first and most popular vectors developed were viruses because they invade cells as part of the natural infection process. Viruses have the potential to be excellent vectors because they have a specific relationship with the host in that they colonize certain cell types and tissues in specific organs. As a result, vectors are chosen according to their attraction to certain cells and areas of the body. Because these viruses are easily cloned (artificially reproduced) in the laboratory, scientists have studied them extensively and learned a great deal about their biological action. They have also learned how to remove the genetic information which governs viral replication, thus reducing the chances of infection. Retroviruses work best in actively dividing cells, but cells in the body are relatively stable and do not divide often. As a result, these cells are used primarily for ex vivo (outside the body) manipulation. Once enough cells are gathered, they are returned to the body, usually by injection into the bloodstream. Theoretically, as long as these cells survive, they will provide the desired therapy. Another class of viruses, called the adenoviruses, may also prove to be good gene vectors. These viruses can effectively infect nondividing cells in the body, where the desired gene product is then expressed naturally. In addition to being a more efficient approach to gene transportation, these viruses, which cause respiratory infections, are more easily purified and made stable than retroviruses, resulting in less chance of an unwanted viral infection. Other viral vectors include influenza viruses, Sindbis virus, and a herpes virus that infects nerve cells. These vectors rely on the natural biological process in which cells uptake (or gather) macromolecules. One approach is to use liposomes, globules of fat produced by the body and taken up by cells. A class of polymers (naturally occurring or artificial substances that have a high molecular weight and formed by smaller molecules of the same or similar substances), is 'constructed' in the laboratory by combining these smaller molecules. They have been used in manufacturing Styrofoam, polyethylene cartons, and Plexiglass. In the laboratory, dendrimers have shown the ability to transport genetic material into human cells. They can also be designed to form an affinity for particular cell membranes by attaching to certain sugars and protein groups. Although the genes may not be the only cause of the disease in all cases, they may make certain individuals more susceptible to developing the disease because of environmental influences, like smoking, pollution, and stress. On September 14, 1990, a four-year-old girl with a genetic disorder that prevented her body from producing a crucial enzyme became the first person to undergo gene therapy in the United States. Nevertheless, a new era of gene therapy began as more and more scientists sought to conduct clinical trial (testing in humans) research in this area. In that same year, gene therapy was tested on patients with melanoma (skin cancer). The goal was to help them produce antibodies (disease fighting substances in the immune system) to battle the cancer. These experiments have spawned an ever-growing number of attempts at gene therapies designed to perform a variety of functions in the body. For example, a gene therapy for cystic fibrosis aims to supply a gene that alters cells, enabling them to produce a specific protein to battle the disease. Another approach was used for brain cancer patients, in which the inserted gene was designed to make the cancer cells more likely to respond to drug treatment.
Diseases
- Ectodermal dysplasia Berlin type
- Holmes Benacerraf syndrome
- Pseudomarfanism
- Oculocerebral syndrome with hypopigmentation
- Caffeine-induced sleep disorder
- Lassueur Graham Little syndrome
- Achromatopsia
- Warfarin necrosis
- Pericardium absent mental retardation short stature
Generic 250mg terramycin amex
Hormones and diuretics that increase the amount of fluid released by the body can also trigger hypercalcemia infection 8 weeks after miscarriage buy cheap terramycin 250 mg on line. During therapy for peptic ulcers, abnormally high amounts of calcium antacids are sometimes taken. As in cancer or paralysis of the arms and legs, any condition in which the patient is immobilized for long periods of time can lead to hypercalcemia due to bone loss. Causes and symptoms Causes of hypercalcemia Many different conditions can cause hypercalcemia; the most common are hyperparathyroidism and cancer. Primary hyper- Common symptoms Many patients with mild hypercalcemia have no symptoms and the condition is discovered during routine laboratory screening. Gastrointestinal symptoms include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and abdominal pain. Women have this condition more frequently than men do, and it is more common 2534 bowel. If the kidneys are involved, the individual will have to urinate frequently during both the day and night and will be very thirsty. The individual may experience mood swings, confusion, psychosis, and eventually, coma and death. Treatment of the underlying cause of the hypercalcemia will also correct the imbalance. Hyperparathyroidism is usually treated by surgical removal of one or more of the parathyroid glands and any tissue, other than the glands themselves, that is producing excessive amounts of the hormone. The hypercalcemia caused by cancer is difficult to treat without controlling the cancer. Hypercholesterolemia Diagnosis High levels of calcium in the blood are a good indication of hypercalcemia, but these levels may fluctuate. Calcium levels are influenced by other compounds in the blood that may combine with calcium. Higher calcium and lower phosphate levels may suggest primary hyperparathyroidism. The medical history and physical condition of the individual must be taken into consideration, especially in the early stages of hypercalcemia when symptoms are mild. Prognosis Surgery to remove the parathyroid glands and any misplaced tissue that is producing excessive amounts of hormone succeeds in about 90% of all cases. Mild hypercalcemia can be controlled through good fluid intake and the use of effective drugs. Hypercalcemia generally develops as a late complication of cancer and the expected outlook is poor without effective anticancer therapy. Prevention People with cancer who are at risk of developing hypercalcemia should be familiar with early symptoms and know when to see a doctor. Good fluid intake (up to four quarts of liquid a day if possible), controlling nausea and vomiting, paying attention to fevers, and keeping physically active as much as possible can help prevent problems. Dietary calcium restriction is not necessary because hypercalcemia reduces absorption of calcium in the intestine. If the patient has normal kidney function, fluids can be given by vein (intravenously) to clear the excess calcium. In this procedure, blood is circulated through tubes made of semi-permeable membranes against a special solution that filters out unwanted substances before returning the blood to the body. Drugs such as furosemide, called loop diuretics, can be given after adequate fluid intake is established. These drugs inhibit calcium reabsorption in the kidneys and promote urine production. Drugs that inhibit bone loss, such as calcitonin, biphosphates, and plicamycin, are helpful in achieving long-term control. Phosphate pills help lower high calcium levels caused by a deficiency in phosphate. Anti-inflammatory agents such as steroids are helpful with some cancers and toxic levels of vitamin D. Cholesterol is 2535 Hypercholesterolemia a molecule from which hormones and steroids are made. A normal or desirable cholesterol level is defined as less than 200 mg of cholesterol per deciliter of blood (mg/dL). Diet, exercise, smoking, alcohol, and certain illnesses can affect the levels of both types of cholesterol. The most common cause of elevated serum cholesterol is eating foods that are rich in saturated fats or contain high levels of cholesterol. Elevated cholesterol also can be caused by an underlying disease that raises blood cholesterol levels such as diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, liver disease, or hypothyroidism. It also can be caused by an inherited disorder in which cholesterol is not metabolized properly by the body. Obesity, which generally results from eating a diet high in fat, also can lead to elevated cholesterol levels in the blood. This is because obesity itself leads the body to produce excessive amounts of cholesterol. Elevated levels of circulating cholesterol cause deposits to form inside blood vessels. These deposits, called plaque, are composed of fats deposited from the bloodstream. When the deposits become sufficiently large, they block blood vessels and decrease the flow of blood. These deposits result in a disease process called atherosclerosis, which can cause blood clots to form that will ultimately stop blood flow. If it happens in the brain, the result is a stroke where a portion of brain tissue dies. Atherosclerosis causes more deaths from heart disease than any other single condition. Heart disease has been the leading cause of death in the United States for the past half century. Approximately 85% of men with this disorder have experienced a heart attack by the time they reach 60 years of age. A blood specimen is obtained after the patient does not eat or drink anything (except water) for 12 hours. Initial treatment for hypercholesterolemia usually requires dietary changes to reduce the intake of total fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol. In addition to diet, guidelines recommend exercise to help bring weight and cholesterol to acceptable levels. Further, experts counsel persons with elevated blood cholesterol levels to increase their intake of soluble fiber. Sources of soluble fiber include bran, foods containing whole grains and other sources of indigestible fiber such as lignin. Physicians also recommend that patients with high cholesterol stop smoking as part of first-line therapy for hypercholesterolemia. For every 1% reduction in cholesterol level, the risk of heart disease is reduced by 2%. It also is possible to partially reverse atherosclerosis that has already occurred by aggressively lowering cholesterol levels with diet and medications. These may be used as first-line therapy in high-risk patients or after about three months of dietary and lifestyle therapy. Cholestyramine, cholestipol, lovastatin, simvastatin, pravastatin, fluvaststin, rosuvastatin, and gemfibrazol are some of the drugs approved for use in the United States. The most often prescribed group of drugs are the statins, which also have been shown in some studies to reduce risk of depression and dementia. Alternatives There are advocates of treatment using vitamins, minerals and antioxidant substances in relatively high amounts. Some people have advocated the use of garlic, soy and isoflavones to lower serum cholesterol levels. After 30 years, more than 85% of persons with cholesterol levels of 180 mg/dL or less were still alive; almost a third of those with cholesterol levels greater than 260 mg/dL had died. Changing dietary habits by reducing the amount of fat and cholesterol consumed is advised. Doctors recommend avoiding smoking by not starting or quitting if currently a smoker.
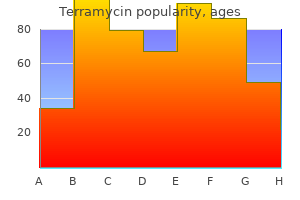
Purchase discount terramycin on line
The route of its transmission is under study as clinicians believe there are numerous routes for the bacterium antibiotics zinc generic 250 mg terramycin visa. Ulcer symptoms include dull, gnawing pain, often two to three hours after meals and pain in the middle of the night when the stomach is empty. Although even low doses of aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may cause some gastric upset, low doses generally will not lead to gastritis. When symptoms do occur, they may include anorexia nervosa, gastric pain, nausea and vomiting. Other forms of gastritis Less common forms of gastritis may result from a number of generalized diseases or from complications of chronic gastritis. Any number of mechanisms may 2109 Acute stress gastritis-the most serious form of gastritis which usually occurs in critically ill patients, such as those in intensive care. Stress erosions may develop suddenly as a result of severe trauma or stress to the stomach lining. Atrophic gastritis is the result of chronic gastritis which is leading to atrophy, or decrease in size and wasting away, of the gastric lining. Gastric atrophy is the final stage of chronic gastritis and may be a precursor to gastric cancer. Proton pump inhibitors help reduce stomach acid by halting the mechanism that pumps acid into the stomach. Dual therapy has not been proven to be as effective as triple therapy, but may be ordered for some patients who can more comfortably handle the use of less drugs and will therefore more likely follow the two-week course of therapy. An antibiotic such as amoxicillin or tetracycline, and another antibiotic such as clarithomycin or metronidazole are used in combination with bismuth subsalicylate, a substance found in the over-the-counter medication, Pepto-Bismol, which helps protect the lining of the stomach from acid. Physicians were experimenting with various combinations of drugs and time of treatment to balance side effects with effectiveness. Side effects of triple therapy are not serious, but may cause enough discomfort that patients are not inclined to follow the treatment. Scientists have experimented with quadruple therapy, which adds an antisecretory drug, or one which suppresses gastric secretion, to the standard triple therapy. Short course therapy was attempted with triple therapy involving antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor and seemed effective in eliminating H. The goal is to develop the most effective therapy combination that can work in one week of treatment or less. Endoscopy, or the examination of the stomach area using a hollow tube inserted through the mouth, may be ordered to confirm diagnosis. Other forms of gastritis Gastritis that has developed to the stage of duodenal or gastric ulcers usually requires endoscopy for diagnosis. Some diseases such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, an ulcer disease of the upper gastrointestinal tract, may show large mucosal folds in the stomach and duodenum on radiographs or in endoscopy. In particular, relapse rates for duodenal and gastric ulcers has been reduced with successful treatment of H. Since the infection can be treated with antibiotics, the bacterium can be completely eliminated up to 90% of the time. When symptoms do occur, patients may be treated with therapy similar to that for H. Other forms of gastritis Specific treatment will depend on the cause and type of gastritis. Critically ill patients at high risk for bleeding may be treated with preventive drugs to reduce risk of acute stress gastritis. If stress gastritis does occur, the patient is treated with constant infusion of a drug to stop bleeding. Sometimes surgery is recommended, but is weighed with the possibility of surgical complications or death. Once torrential bleeding occurs in acute stress gastritis, mortality is as high as greater than 60%. Alternatives Alternative forms of treatment for gastritis and ulcers should be used cautiously and in conjunction with conventional medical care, particularly now that scientists have confirmed the role of H. Alternative treatments can help address gastritis symptoms with diet and nutritional supplements, herbal medicine and ayurvedic medicine. Herbs thought to stimulate the immune system and reduce inflammation include echinacea (Echinacea spp. There are also certain herbs and nutritional supplements aimed at helping to treat ulcers. Mucosa-The mucous membrane, or the thin layer which lines body cavities and passages. The prognosis for patients with acute stress gastritis is much poorer, with a 60 percent or higher mortality rate among those bleeding heavily. Since treatment exists to eradicate the infection, recurrence is much less common. Regular treatment of patients with gastric and duodenal ulcers has been recommended, since H. Teresa Odle Gastroduodenostomy (Billroth I) see Ulcer surgery 2111 Gastroenteritis Definition Gastroenteritis is a catchall term for infection or irritation of the digestive tract, particularly the stomach and intestine. It is frequently referred to as the stomach or intestinal flu, although the influenza virus is not associated with this illness. Adults usually recover without problem, but children, the elderly, and anyone with an underlying disease are more vulnerable to complications such as dehydration. Natural or man-made disasters can make underlying problems in sanitation and food safety worse. In developed nations, the modern food production system potentially exposes millions of people to disease-causing bacteria through its intensive production and distribution methods. Common types of bacterial gastroenteritis can be linked to Salmonella and Campylobacter bacteria; however, Escherichia coli 0157 and Listeria monocytogenes are creating increased concern in developed nations. Cholera and Shigella remain two diseases of great concern in developing countries, and research to develop longterm vaccines against them is underway. Gastroenteritis Causes and symptoms Gastroenteritis arises from ingestion of viruses, certain bacteria, or parasites. Certain medications and excessive alcohol can irritate the digestive tract to the point of inducing gastroenteritis. Regardless of the cause, the symptoms of gastroenteritis include diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and abdominal pain and cramps. Typically, the symptoms last only two to three days, but some viruses may last up to a week. However, medical treatment is essential if symptoms worsen or if there are complications. Infants, young children, the elderly, and persons with underlying disease require special attention in this regard. Dehydration should be suspected if a dry mouth, increased or excessive thirst, or scanty urination is experienced. If symptoms do not resolve within a week, an infection or disorder more serious than gastroenteritis may be involved. Demographics Gastroenteritis is an uncomfortable and inconvenient ailment, but it is rarely life-threatening in the United States and other developed nations. However, an estimated 220,000 children younger than age five are hospitalized with gastroenteritis symptoms in the United States annually. Worldwide, inadequate treatment of gastroenteritis kills 5 to 8 million people per year, and is a leading cause of death among infants and children under the age of 5. Annually, worldwide, rotaviruses are estimated to cause 800,000 deaths in children below age five. Description Typically, children are more vulnerable to rotaviruses, the most significant cause of acute watery diarrhea. For this reason, much research has gone into developing a vaccine to protect children from this virus. Adults can be infected with rotaviruses, but these infections typically have minimal or no symptoms.

Order 250mg terramycin with visa
However tween 80 bacteria cheap 250mg terramycin amex, this test cannot distinguish between strains of influenza A and, therefore, was not useful in determining if the patient had H1N1 (2009). Tests the most accurate test for influenza is done by taking a mucus sample from the throat of an infected person. During an influenza pandemic, physicians often forgo laboratory confirmation of influenza, relying on signs and symptoms for diagnosis. In the United Kingdom, persons with flu symptoms are given access to antiviral drugs after answering questions that indicate an influenza diagnosis on a government-sponsored public health website. This saves physician resources for handling severe or emergent cases, provides quick access to treatment, and helps the person with symptoms to stay home, thereby reducing the pool of infected persons in public available to infect others. No scientific testing exists to validate any claim of effectiveness of any alternative medical treatments specific to H1N1 flu. Although claims of effectiveness (and/or potential harm) for any alternative medical treatment should be carefully scrutinized for supporting scientific evidence, there are a number of alternative treatments commonly used to support relief of symptoms. Because there is no scientifically validated antiviral treatment, if flu is suspected, persons should consult a physician to determine if they are in need of antiviral medicines. Alternative practitioners recommend herbal teas to soothe the throat and allegedly boost the immune system. Other herbal treatments recommended by alternative practitioners for seasonal flu routinely include the following: Treatment Supportive treatment for H1N1 (2009) appears to be the same as for all influenza viruses and included 2246 Ginger (Zingiber officinalis) to reduce fever and pain, settle the stomach, and suppress cough. Echinacea (Echinacea purpurea or angustifolia) to reduce flu symptoms, including sore throat, chills, sweating, fatigue, weakness, body aches, and headaches. Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus globulus) or peppermint (Mentha piperita) essential oils added to a steam vaporizer to help clear chest and nasal congestion. Prognosis Because 2009 H1N1 was a new strain of influenza, it was difficult to predict the course of the disease. Generally cases were mild, but as with all flu, cases could be life-threatening if complications develop. Underlying health conditions might be worsened by the disease, and pneumonia, a common and sometimes fatal complication of seasonal flu, might develop. Public health officials acknowledged that even under the best scenarios, production of the H1N1 vaccine was expected to fall far short of global demand. As of 2009 production rates, 900 million doses of the new H1N1 vaccine could be produced each year (as two doses are required per person, enough to vaccinate 450 million people). The vaccine is produced in only a handful of countries and there were concerns these countries, along with wealthier nations, would obtain the vast majority of vaccine produced. Also, antiviral medications do not prevent influenza; they simply help shorten the intensity and duration of the illness. World Health Organization, Avenue Appia 20, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland, +2241 791 21 11, Fax: +2241 791 31 11, info@who. Vaccination the first H1N1-specific vaccine was anticipated by late September or early October 2009. World public health officials recommended prioritizing vaccine recipients according to individual risk, as well as to ensure the greatest benefit for overall public health. Pregnant women and people caring for infants, children, young people under 25 years of age, and persons with underlying health conditions such as asthma or diabetes were recommended to receive priority vaccination against pandemic 2009 H1N1 influenza. Histamine is produced in the body and released by mast cells in response to some types of injury or to the presence of an antigen. When histamine reaches the H-1 receptors, the reaction results in dilation of capillaries, leading to redness 2247 H-2 blockers and swelling, along with itching. Histamine that reaches the H-2 receptors causes increased secretion of stomach acid. Purpose H2 receptor blockers are used to treat conditions associated with excess amounts of stomach acid, although in some cases they have been replaced by the proton pump inhibitors, which have a greater effect on reducing acid secretions. All are approved for treatment of duodenal ulcer both acute treatment and maintenance therapy, gastro-esophageal reflux disease, including erosive esophagitis and gastric ulcer short term treatment, although in this group ranitidine alone is approved for maintenance treatment. In their over-the-counter (non-prescription) forms, cimetidine and famotidine are approved for treatment of heartburn, acid indigestion, and sour stomach. Although study results vary, cimetidine will usually show its effects within one hour and last for about five hours after a single dose; famotidine and nizatidine also show effects within one hour but may act for up to 12 hours at maximum dosing. Ranitidine has a comparable onset of action and duration in adults but may be slower in the elderly. Onset and duration of action will vary with the individual, the dose of medication, and the presence or absence of food or antacids in the stomach. When Facts and Comparisons, a widely used online drug information resource, compared the published reports on cure rates for duodenal ulcers, it found that after eight weeks of treatment, all drugs showed healing rates in the range of 82% to 95%. These results were based on comparing separate studies and did not represent comparative trials of the drugs against each other. None of the drugs in this class have been approved for use by children under the age of 12 years. Although they all work in the same manner and have similar effects, they are not all approved for the same uses. Cimetidine (Tagamet) is available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. The oldest of the group and the most studied, this drug is the least potent of the H2 receptor blockers, which means that higher dosages are required to provide comparable effects. Cimetidine is the only drug in its class approved for prevention of upper gastro-intestinal bleeding. Cimetidine, like ranitidine, has shown some benefit in treatment of colorectal cancer. Although some claims have been made that cimetidine is useful in treatment of acetaminophen overdose, the evidence for this use is lacking, and cimetidine should not be used. Treatment of hypersecretory conditions: 300 mg four times a day, with meals and at bedtime. To treat heartburn, acid indigestion, and sour stomach using the over-the-counter product: 10 mg with water when symptoms start. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: 20 mg two times a day, usually for up to six weeks. Therefore, patients with kidney or liver problems may require reduced doses in order to maintain safe blood levels of the drugs. Although the safety and effectiveness of H2 receptor blockers in patients over the age of 65 appears to be similar to that seen in younger patients, age-associated reductions in kidney function may lead to elevated blood levels. There are no adequate and wellcontrolled studies with these agents in pregnant women. Women should use them only when clearly needed and when the potential benefits outweigh the potential hazards to the fetus. All drugs in this class are excreted into breast milk and should not be taken by nursing women. Decide whether to discontinue nursing, or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. H-2 blockers Nizatidine doses for patients over the age of 12 years, for oral administration. Side effects Although side effects due to the H2 receptor blockers are relatively rare and usually mild, a large number of adverse effects have been reported, in part because of the high use of these drugs. For example, the most common single adverse effect of cimetidine has been a 4% incidence of breast enlargement among males taking the drug in high doses for hypersecretory conditions. The reported side effects from the H2 receptor blocks are: Ranitidine doses for patients over the age of 12 years, for oral administration. Heartburn, acid indigestion, and sour stomach, treatment: 75 mg with water when symptoms start.
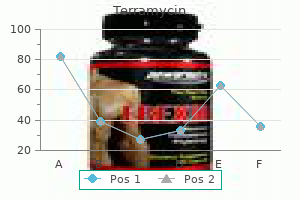
Terramycin 250 mg with mastercard
Part of the state funding for gambling disorder is to certify nearly 300 mental health therapists in the treatment of gambling problems antibiotics for breeding dogs buy terramycin 250 mg online. However, during each of those years, people with a gambling disorder are estimated to have accrued tens to hundreds of thousands of dollars in debt. Besides financial problems, people with gambling disorders suffer from a multitude of mental problems, such as an increased risk of causing domestic violence and child abuse. Children of gamblers with problems are at increased risk from suffering behavioral problems, depression, and substance abuse. Treatment for any underlying psychological disorders or substance abuse can be very helpful. Gamblers Anonymous can help in many cases, although the program has a high dropout and recurrence rate, and there are few studies that fully analyze the benefits or efficacy of the program. For many people, a combination of more than one of these approaches may be most effective. Even when a person has successfully stopped compulsive gambling, it is unlikely that he or she will ever be able to gamble socially again, or even spend time in places where he or she once gambled. The Institute for Research on Gambling Disorders announced that five research projects were awarded in 2010 for the study of gambling disorders. The grants, which totaled $380,466, were awarded by the National Center for Responsible Gaming to researchers at Duke University (North Carolina), Southern Illinois University, the University of Florida, the University of Minnesota, and the University of Missouri. The research studies were in the grant areas called Exploration Grants, Seed Grants, and Large Grants. The Exploration Grants involve evaluating the risk difference of online gambling versus non-Internet based gambling. Duke University researchers were granted a Seed Grant to test the hypothesis that whether 'someone makes a risky or safe choice depends not simply on preferences, but on the strategies they use to acquire and integrate new information. It is estimated that one-third of all people with gambling disorder can recover from the disease without treatment. In fact, as many as two out of three people who begin treatment (medication, therapy, or both) for gambling disorder drop out before its completion. Consequently, the negative effects of gambling disorder often leave their lives, and their family, in ruin. Researchers at the University of Missouri were awarded a Large Grant of $172,500 to test whether college students report more or less gambling when they are provided information about their own behaviors while gambling (in what is called 'personalized feedback-only intervention'). In addition, University of Minnesota scientists will study the various factors, such as race and gender, which distinguish recreational gamblers and pathological gamblers. They will also study factors that may be responsible for turning recreational gamblers into problem gamblers. This study will use data from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. In addition, a research study performed in Australia has shown that nearly one in five problem gamblers (17%) has attempted suicide. Their statistics are based on patients entering the emergency department at the Alfred hospital in Prahran, Victoria, Australia. The report concluded that this rate of suicide among problem gamblers is about 20 times the rate in a normal population without gambling problems. Commenting on the results of the Australian report, state gaming minister Tony Robinson stated that 'one of the underlying drivers of problem gambling is a pre-existing mental health condition. If, however, a person begins to feel that he or she may have a problem, immediate treatment can prevent the development of a disorder that affects all areas of life and may have legal as well as economic consequences. Given the role of proximity to available gambling in the development of the disorder, this factor may be a target in prevention. There are several different types of hepatitis, including the most common forms: hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Inflammation-Pain, redness, swelling, and heat that usually develop in response to injury or illness. When injected into a vein, it produces results more quickly than when injected into a muscle. When Gamma globulins are extracted from the blood of many people and combined, they can be used to prevent or treat infections. When disease-causing agents enter the body, they normally trigger the production of antibodies, proteins that circulate in the blood and help fight the disease. When Gamma globulins are taken from the blood of people who have recovered from diseases such as chickenpox or hepatitis, they can be given to other people to make them temporarily immune to those diseases. With hepatitis, for example, this is done when someone who has not been vaccinated against hepatitis is exposed to the disease. Precautions Anyone who has had unusual reactions to Gamma globulin in the past should let his or her physician know before taking the drugs again. The physician should also be told about any allergies to foods, dyes, preservatives, or other substances. People who have certain medical conditions may have problems if they take Gamma globulins. For example: Gamma globulins may worsen heart problems or deficiencies of immunoglobin A (IgA, a type of antibody. Patients receiving Gamma globulin who have a history of liver and/or kidney problems should be monitored closely while receiving this product. Side effects Minor side effects such as headache, backache, joint or muscle pain, and a general feeling of illness usually go away as the body adjusts to this medicine. Anyone who shows the following signs of overdose should check with a physician immediately: unusual tiredness or weakness dizziness nausea vomiting fever chills tightness in the chest red face sweating Purpose Gamma Knife radiosurgery is used to treat benign and malignant brain tumors which are considered to be inoperable because of their location in the brain which makes them inaccessible to conventional surgical approaches. This type of radiosurgery is also effective in treating cancer which has spread or metastasized to the brain. Gamma Knife surgery can also be used to treat many conditions including the following: Interactions Anyone who takes Gamma globulin should let the physician know all other medicines he or she is taking and should ask whether interactions with Gamma globulin could interfere with treatment. Demographics According to the manufacturer, the number of patients treated with Gamma Knife surgery has increased by more than 300% over the past five years and more than 500,000 people have received treatment utilizing this technology to date. Lars Leksell, a Swedish professor of neurosurgery, and radiation biologist, Borje Larsson, who pioneered the use of radiation beams in combination with stereotactic or precise guiding devices that could focus the beams with surgical precision. In 1967, the first Gamma Knife device, which used cobalt-60 as the radiation source, was constructed. Current Gamma Knife technology utilizes cobalt60 photon radiation to deliver the radiation dose to targeted areas within the brain with pinpoint accuracy while sparing adjacent normal tissue from the deleterious effects of radiation. The radiation dose is calculated specifically for each patient taking into account tumor type, tumor shape, and tumor location including tumor depth. The results of these imaging tests are then placed into dose planning software which can model the affected area in 3 dimensions. The specific dose, individualized for each patient, is based on the results obtained from the treatment planning software, and is calculated by a radiation oncologist and a medical physicist. Despite being called surgery, no actual surgery and no blade or knife is involved in the treatment process. There is no incision made in Gamma Knife surgery and no brain tissue is removed from the body. Radiation, delivered by a machine, is targeted into the affected brain tissue while sparing adjacent normal tissue. Each individual beam does not contain enough energy to harm normal tissue as it passes through brain tissue to reach the target. However, when all of the beams intersect and converge on the target, the combined effect of the energy in all of the radiation beams is powerful enough to treat the tissue in the area. According to the manufacturer, by keeping the patient immobilized during the actual treatment in combination with using three-dimensional treatment planning that is computer-aided, the radiation dose can be targeted with such precision that the level of accuracy is about one-tenth of one millimeter, which is about the thickness of an individual strand of human hair. The end result is that the calculated radiation dose reaches the targeted tissue, adjacent normal tissue is spared and the entire process is accomplished in a single treatment session. Gamma Knife surgery Preparation Unlike other radiation therapy procedures which may require multiple daily treatment visits, treatment using Gamma Knife technology is typically completed in one visit to the treatment center and is done on an outpatient basis. The patient will be asked not to consume food or water past midnight the night before the procedure is scheduled. Patients should ask their physicians if they may consume a small amount of water with their medications, however. Patients should inform the physician if they are taking oral medications or insulin to control diabetes.
Bachnag (Aconite). Terramycin.
- Nerve pain, feeling of coldness, facial paralysis, joint pain, gout, inflammation, wounds, heart problems, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Aconite.
- How does Aconite work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Aconite?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96604
Order terramycin without a prescription
This can be detected in a blood test treatment for uti burning cheap terramycin 250 mg without a prescription, but it can also manifest clinically as jaundice. Elevated bilirubin levels and clinical jaundice can also occur with other conditions, such as gallstones. About 1% of all patients who have their gallbladder removed for symptomatic gallstones are found to have gallbladder cancer. The cancer is found either by the surgeon or by the pathologist who inspects the gallbladder with a microscope. Treatment About 90% of gallbladder cancers are adenocarcinomas, which means that they are a type of cancer that begins in the gland-like cells that line the interiors of such organs as the gallbladder. Most gallbladder cancers begin in the innermost wall of the organ and grow through the various layers of tissue toward the outside of the gallbladder. Stage 0 gallbladder cancer is very small and confined to the inner wall of the gallbladder. Approximately 20% of cancers are at this stage at the time of diagnosis; the 5-year survival rate is 80%. Stage I cancer has grown into the intermediate walls of the organ; its 5-year survival rate is 50%. Early Stage I cancers involving only the innermost layer of the gallbladder wall can be cured by simple removal of the gallbladder; this procedure is called a cholecystectomy. Cancers at this stage are sometimes found incidentally when the gallbladder is removed in the treatment of gallstones or cholecystitis. The surgeon also removes nearby lymph nodes as well as a portion of the adjacent liver; this is called an extended or radical cholecystectomy. The imaging tests that are utilized to evaluate these other conditions, however, can also detect gallbladder cancer. For example, ultrasound is a quick, noninvasive imaging test that reliably diagnoses gallstones and cholecystitis. It can also detect the presence of gallbladder cancer as well as show how far the cancer has spread. If cancer is suspected, a computed tomography scan is useful in confirming the presence of an abnormal mass and further demonstrating the size and extent of the tumor. Cholangiography, usually performed to evaluate a patient with jaundice, can also detect gallbladder cancer. Blood tests are sometimes useful because tumors in the gallbladder can obstruct the normal flow of bile from the liver to the small intestine. Cholangiography-Radiographic examination of the bile ducts after injection with a special dye. It is used to determine whether the bile ducts are enlarged, narrowed, or blocked. Cholecystitis-Inflammation of the gallbladder, usually due to infection Computed tomography-A radiology test by which images of cross-sectional planes of the body are obtained Congenital-Present at birth. Jaundice-Yellowish staining of the skin and eyes due to excess bilirubin in the bloodstream Metastasis (plural, metastases)-The spread of tumor cells from one part of the body to another through blood vessels or lymphatic vessels Pancreatitis-Inflammation of the pancreas Porcelain gallbladder-A condition in which calcium is deposited in the walls of the gallbladder, causing the organ to become whitish or bluishwhite in appearance and brittle. Stent-Slender hollow catheter or rod placed within a vessel or duct to provide support or maintain patency Tumor marker-A protein found in blood, urine, or body tissues that can be measured and used to detect the presence of cancer. Ultrasound-A radiology test utilizing high-frequency sound waves and blockage of the stomach are two problems faced by patients with advanced cancer of the gallbladder. These can be treated with surgery, or alternatively, by special interventional techniques employed by the gastroenterologist or radiologist. A stent can be placed across the bile ducts in order to re-establish the flow of bile and relieve jaundice. A small feeding tube can be placed in the small intestine to allow feeding when the stomach is blocked. Pain may be treated with conventional pain medicines or a celiac ganglion nerve block. Another palliative treatment that is sometimes used to relieve pain in gallbladder cancer is alcohol injections to deaden the nerves that carry pain sensations from the gallbladder and digestive tract to the brain. Current chemotherapy or radiation therapy cannot cure gallbladder cancer, but these modalities may offer some benefit in certain patients. For cancer that is too advanced for surgical cure, treatment with such chemotherapeutic agents as 5-fluorouracil, gemcitabine, cisplatin, or capecitabine may lengthen survival for a few months. The limited benefit of chemotherapy must be weighed carefully against its side effects. Radiation therapy is sometimes used after attempted surgical resection of the cancer to extend survival for a few months or relieve jaundice. The most common form of radiation therapy used to treat gallbladder cancer is external beam radiation therapy. Radiation therapy may be used as a palliative treatment to relieve pain in patients with advanced gallbladder cancer. Acupuncture is reported to relieve nausea associated with chemotherapy, and essential oils used in aromatherapy (particularly lavender and Roman chamomile) are calming and relaxing for some patients. Prayer, meditation, journaling or expressive writing, and guided imagery are helpful for others. Other therapies When long-term survival is not likely, the focus of therapy shifts to improving quality of life. The procedure uses a small amount of radioactive dye which is injected into the body. A special camera called a scintillation or gamma camera produces images based on how the dye travels through the system and how the radiation is absorbed by the tissues. It can also be used to diagnose blockages of the bile duct that leads from the gallbladder to the small intestine. Unlike ultrasound, a gallbladder nuclear medicine scan can assess gallbladder function. Some medications or even eating a high fat meal before the procedure can interfere with the results of the scan. The liver produces bile, a yellowishgreen mixture of salts, acids, and other chemicals, that are stored in the gallbladder. Bile is secreted into the small intestine to help the body digest fats from foods. Gallbladder disease, gallstones, cancer, or other abnormalities can cause pain and other symptoms. A gallbladder condition might be suspected if a patient has chronic or occasional pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. The pain may be stabbing and intense with sudden onset or it may be more of a dull, occasional ache. Jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, may also indicate that the gallbladder is involved. Scintillation or gamma camera-A camera, somewhat like an x-ray machine, used to photograph internal organs after the patient has been injected with a radioactive material. An abnormal scan may show abnormal gallbladder emptying (suggesting gallbladder dysfunction or inflammation), or gallstones in the gallbladder or in the bile duct. The presence of tumors, growths or other types of blockages of the duct or the gallbladder itself could also appear on an abnormal scan. Risks Nuclear medicine scans use a very small amount of radioactive material, and the risk of radiation is minimal. The patient lies on an examination table while a small amount of radioactive dye is injected into a vein in the arm. As the dye moves through the gallbladder, a series of pictures is taken using a special camera called a scintillation or gamma camera. The test usually takes one to two hours to complete, but can last up to four hours. The results of the scan are read by a radiologist, a doctor specializing in x rays and other types of scanning techniques. A report is sent, usually within 24 hours, to the doctor who will discuss the results with the patient. The study involves taking tablets containing dye (contrast) which outline any abnormalities when x rays are taken the following day. This is due to advances in diagnostic ultrasound, which is quick, accurate, and does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation. When functional parameters of the gallbladder need to be demonstrated, scintigraphy is now the study of choice.
Order cheap terramycin line
Urate crystals may be present in the joint for a long time without causing symptoms treatment for dogs gum disease discount terramycin 250 mg with amex. Infection, injury to the joint, surgery, drinking too much, or eating the wrong kinds of foods may suddenly bring on the symptoms, which include pain, tenderness, redness, warmth, and swelling of the joint. The pain is often so excruciating that the sufferer cannot bear weight on the joint or tolerate the pressure of bedcovers. The inflamed skin over the joint may be red, shiny, and dry, and the inflammation may be accompanied by a mild fever. These symptoms may go away in about a week and disappear for months or years at a time. However, over the course of time, attacks of gout recur more and more frequently, last longer, and affect more joints. Eventually, stone-like deposits known as tophi may build up in the joints, ligaments, and tendons, leading to permanent joint deformity and decreased motion. It 2215 Uric acid crystals Gout, a form of acute arthritis, most commonly occurs in the big toe. It is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, in which urate crystals settle in the tissues of the joints and produce severe pain and swelling. Uric-acid levels tend to increase in men at puberty, and, because it takes 20 years of hyperuricemia to cause gout symptoms, men commonly develop gout in their late 30s or early 40s. According to some medical experts, estrogen protects against hyperuricemia, and when estrogen levels fall during menopause, urate crystals can begin to build up in the joints. According to a study published in November 2002, there was a twofold increase in the incidence of gout over the 20 years between 1977 and 1997. It is not yet known whether this increase is the result of improved diagnosis or whether it is associated with risk factors that have not yet been identified. Corticosteroids-Medications related to a natural body hormone called hydrocortisone, which are used to treat inflammation. Probenecid-A drug that corrects hyperuricemia by increasing the urinary excretion of urate. Purine-A substance found in foods that is broken down into urate and may contribute to hyperuricemia and gout. Sulfinpyrazone-A drug that corrects hyperuricemia by increasing the urinary excretion of urate. Synovial fluid-Fluid surrounding the joints which acts as a lubricant, reducing the friction between the joints. Doctors can also administer a test that measures the level of uric acid in the blood. The most definitive way to diagnose gout is to take a sample of fluid from the joint and test it for urate crystals. Treatment the goals of treatment for gout consist of alleviating pain, avoiding severe attacks in the future, and preventing long-term joint damage. In addition to taking pain medications as prescribed by their doctors, people having gout attacks are encouraged to rest and to increase the amount of fluids that they drink. In some cases, these drugs can aggravate a peptic ulcer or existing kidney disease and cannot be used. Doctors may also use colchicine (Colbenemid), especially in cases where nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs cannot be used. Colchicine may cause diarrhea, which tends to go away once the 2216 patient stops taking it. Corticosteroids such as prednisone (Deltasone) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (Acthar) may be given orally or may be injected directly into the joint for a more concentrated effect. While all of these drugs have the potential to cause side effects, they are used for only about 48 hours and are not likely to cause major problems. However, aspirin and closely related drugs (salicylates) should be avoided because they can ultimately worsen gout. Once an acute attack has been successfully treated, doctors try to prevent future attacks of gout and longterm joint damage by lowering uric acid levels in the blood. Such uricosuric drugs as probenecid (Benemid) and sulfinpyrazone (Anturane) lower the levels of urate in the blood by increasing its removal from the body (excretion) through the urine. These drugs may promote the formation of kidney stones, however, and they may not work for all patients, especially those with kidney disease. The potential side effects of allopurinol include rash, a skin condition known as dermatitis, and liver dysfunction. Alternatives Alternative approaches to gout focus on correcting hyperuricemia by encouraging weight loss and limiting the intake of alcohol and purine-rich foods. In addition, consuming garlic (Allium sativum) has been recommended to help prevent gout. Since obesity and excessive alcohol intake are associated with hyperuricemia and gout, losing weight and limiting alcohol intake can help ward off gout. Dehydration may also promote the formation of urate crystals, so people taking diuretics or 'water pills' may be better off switching to another type of blood pressure medication. Since purine is broken down in the body into urate, it may also be helpful to avoid foods high in purine, such as organ meats, sardines, anchovies, red meat, gravies, beans, beer, and wine. A 2004 study revealed that eating more low-fat dairy products could reduce risk of developing gout. Purpose Gout is a disease in which uric acid, a waste product that normally passes out of the body in urine, collects and forms crystals in the joints and the kidneys. When uric acid crystals build up in the joints, the tissue around the joint becomes inflamed, and nerve endings in the area become irritated, causing extreme pain. Uric acid crystals in the kidneys can lead to kidney stones and eventually to kidney failure. The symptoms of gout-severe pain, usually in the hand or foot (often at the base of the big toe), but sometimes in the elbow or knee-should be 2217 reported to a healthcare professional. If not treated, gout can lead to high blood presssure, deformed joints, and even death from kidney failure. For patients who have just had their first attack, physicians may prescribe only medicine to reduce the pain and inflammatin, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, or colchicine. Patients may also be advised to change their eating and drinking habits, avoiding organ meats and other protein-rich foods, cutting out alcoholic beverages, and drinking more water. For those who do, physicians may prescribe additional drugs that either help the body get rid of uric acid or reduce the amount of uric acid the body produces. These drugs will not relieve gout attacks that already have started, but will help prevent attacks when taken regularly. Gout drugs serious side effects is greater when this medicine is taken in high doses for short periods. Blood tests may be ordered to help the physician monitor how well the drug is working. Drinking alcohol, including beer and wine, may increase the amount of uric acid in the body and may interfere with the effects of gout medicine. People with gout (or other conditions that result from excess uric acid) may need to limit the amount of alcohol they drink or stop drinking alcohol altogether. Anyone who takes this type of medicine should not drive, use machines or do anything else that might be dangerous until they have found out how the drugs affect them. Before having medical tests, anyone taking this medicine should alert the healthcare professional in charge. Both the increased sensitivity to the drug and the longer time for the drug to leave the body may increase the chance of side effects. Special conditions People who have certain medical conditions or who are taking certain other medicines can have problems if they take gout drugs. Anyone who has ever had unusual reactions to gout drugs or to medicines used to relieve pain or inflammation should let his or her physician know before taking gout drugs. Some gout drugs may cause false results on certain urine sugar tests, but not on others. Diabetic patients who take gout drugs should check with their physicians to find out if their medicine will affect the results of their urine sugar tests.
Discount 250 mg terramycin free shipping
Feces-Undigested food and other waste that is eliminated through the anus; also called stools virus x reader order terramycin 250 mg on line. After food has passed through the stomach and intestines and been digested, the leftover material, in the form of feces, enters the rectum, where it stays until defecation. Suppository-A medicinal substance that slowly dissolves after being inserted into the rectum (or other body cavity). Herbal teas, ointments, and suppositories, and other kinds of herbal preparations, are suggested for reducing discomfort and eliminating hemorrhoids. In particular, pilewort (Ranunculusficaria), applied in an ointment or taken as a tea, can reduce the pain of external hemorrhoids. Acupuncture, acupressure, aromatherapy, and homeopathy are also used to treat hemorrhoids. Howard Baker Karl Finley Prognosis Hemorrhoids do not cause cancer and are rarely dangerous or life threatening. However, because colorectal cancer and other digestive system diseases can cause anal bleeding and other hemorrhoid-like symptoms, people should always consult a doctor when those symptoms occur. The disease is usually transmitted by food or water contaminated by human wastes containing the virus or by close human contact. As far as is known, only humans can get hepatitis A; it is not carried by other animals. Hepatitis A was previously known as infectious hepatitis because it spread relatively easily from those infected to close household contacts. It differs from hepatitis B and hepatitis C in that it does not cause long-term liver damage. Even though people can take several weeks or months to recover completely from hepatitis A, they have lifelong immunity afterward. Complications from hepatitis A are rare and usually limited to people with chronic liver disease or those who have received a liver transplant. Children and younger adults may have no symptoms at all, although they can still spread the disease. In general, adults are more likely to have noticeable symptoms than children or teenagers. Some people develop a mild flu-like illness with diarrhea, low-grade fever, nausea, vomiting, and muscle cramps. People with more severe symptoms may have pain in the abdomen in the area of the liver (below the rib cage on the right side of the body); they may notice that their urine has turned dark brown or that they have jaundice-yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. Alternately, epidemics may develop when food or drinking water is contaminated by the feces of an infected person. It is true that food-handlers, who may themselves have no symptoms, can start an alarming, widespread epidemic. Risk factors Some people are at increased risk of hepatitis A, including: Hepatitis A Hepatitis A virus magnified 225,000 times. The rates of hepatitis A in North America have been steadily dropping since the 1980s due to improvements in public health policies and sanitation; on the other hand, the rates of hepatitis A among frequent travelers have been rising during the same time period. In developing countries, children below age 2 account for most new cases of hepatitis A; in the United States, the age group most often affected is children between the ages of 5 and 14. The states with the highest incidence of hepatitis A account for 50% of the reported cases. The states are Arizona, Alaska, California, Idaho, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Oregon, South Dakota, Utah, and Washington. Males and females are equally likely to get hepatitis A, as are people from all races and ethnic groups in the United States. Bile-A yellow-green fluid secreted by the liver that aids in the digestion of fats. Epidemic-A situation where a large number of infections by a particular agent, such as a virus, develops in a short time. Immune globulin-A preparation of antibodies that can be given before exposure for short-term protection against hepatitis A and for persons who have already been exposed to hepatitis A virus. Immune globulin must be given within two weeks after exposure to hepatitis A virus for maximum protection. Incubation period-The interval from initial exposure to an infectious agent, such as a virus, and the first symptoms of illness. Vaccine-A substance prepared from a weakened or killed microorganism that, when injected, helps the body to form antibodies that will prevent infection by the natural microorganism. That means that people can spread the virus through their feces before they know that they are sick. The liver often enlarges, causing pain or tenderness in the right upper part of the abdomen. In addition to fatigue, the most common symptoms of hepatitis A include: Causes and symptoms Causes Hepatitis A is caused by a virus that is transmitted by close personal contact with an infected person, by needle sharing, and by eating food or drinking water contaminated by fecal matter. Drugs Patients with hepatitis A may take acetaminophen to reduce fever and relieve pain. Patients with mild vomiting may be prescribed antiemetics (drugs to control nausea); the drug most commonly prescribed for hepatitis patients is metoclopramide (Reglan). Those with severe vomiting may need to be hospitalized in order to receive intravenous fluids. This test always registers positive when a patient has symptoms and should continue to register positive for four to six months. Hepatitis A IgM antibody will persist lifelong in the blood and is protective against reinfection. In some cases the doctor may also have the sample of blood checked for abnormally high levels of liver enzymes. Prognosis Most people recover fully from hepatitis A within a few weeks or months. Between 3% and 20% have relapses (temporary recurrences of symptoms) for as long as six to nine months after infection. In the United States, serious complications are infrequent and deaths are very rare. As many as 75% of adults over 50 years of age in North America will have blood test evidence of previous hepatitis A. There are about 100 deaths from hepatitis A reported each year in the United States. The vaccine is given in two shots, the second given between 6 and 18 months after the first. Those who should receive the vaccine include people in the military and those who travel abroad frequently; men who have sex with other men; people who use intravenous drugs; people with hemophilia who must receive human blood products; and people who have chronic hepatitis B or C infection. A vaccine against hepatitis A introduced in 2007 is called Epaxal; there is a version for children called Epaxal Junior that appears to be a good choice for 2391 Treatment Traditional There is no specific drug treatment for hepatitis A, as antibiotics cannot be used to treat virus infections. Most people can care for themselves at home by making sure they get plenty of fluids and adequate nutrition. People whose appetite has been affected may benefit from eating small snacks throughout the day rather than three main meals and by eating soft and easily digested foods. Patients with hepatitis A should avoid drinking alcohol, which makes it harder for the liver to recover from inflammation. When traveling, drink only bottled water; avoid raw or undercooked meat or shellfish; and avoid eating fresh fruits or vegetables unless you have washed and peeled them yourself. If someone in the family has hepatitis A, wash their glasses and utensils separately in hot, soapy water. Frey, PhD Hepatitis, alcoholic Definition Alcoholic hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by alcohol. Description Irritation, whether from toxins or infections, causes a similar response in body organs. Fatty liver-An abnormal amount of fat tissue in the liver caused by alcohol abuse. Lingering activity-chronic disease-has a milder presentation with similar ingredients. Healing often takes the form of scarring, wherein normal functioning tissue is replaced by tough, fibrous, and non-productive scar tissue.
Buy cheap terramycin online
As is the case with the basal gastric secretion test bacteria during pregnancy order terramycin 250 mg fast delivery, the patient can have no liquids during this test, and must eject saliva to avoid diluting the stomach contents. Pernicious anemia-One of the main types of anemia, caused by inadequate absorption of vitamin B12. Symptoms include tingling in the hands, legs, and feet, spastic movements, weight loss, confusion, depression, and decreased intellectual function. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome-A rare condition characterized by severe and recurrent peptic ulcers in the stomach, duodenum, and upper small intestine, caused by a tumor, or tumors, usually found in the pancreas. The tumor secretes the hormone gastrin, which stimulates the stomach and duodenum to produce large quantities of acid, leading to ulceration. Antacids, anticholinergics, cholinergics, alcohol, H2receptor antagonists (Tagamet, Pepcid, Axid, Zantac), reserpine, adrenergic blockers, and adrenocorticosteroids should be withheld for one to three days before the test, as the physician requests. If pentagastrin is to be administered for the gastric acid secretion test, medical supervision should be maintained, as possible side effects may occur. If this happens, the patient may have a difficult time breathing or may experience a coughing spell until the tube is removed and reinserted properly. Also, because the tube can be difficult to swallow, if a patient has an overactive gag reflex, there may be a transient rise in blood pressure due to anxiety. Abnormal Abnormal findings in the basal gastric secretion test are considered nonspecific and must be evaluated in conjunction with the results of a gastric acid stimulation test. Elevated secretion may suggest different types of ulcers; when markedly elevated, Zollinger-Ellison 2099 Aftercare Complications such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal distention or pain are possible following removal of the gastric tube. The patient may also resume the usual diet and any medications that were withheld for the test(s). Depressed secretion can indicate gastric cancer, while complete absence of secretion (achlorhydria) may suggest pernicious anemia. Elevated gastric secretion levels in the gastric acid stimulation test may be indicative of duodenal ulcer; high levels of secretion again suggest Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Purpose Gastric bypass surgery is intended to treat severe (morbid) obesity in people who have tried unsuccessfully to lose weight and whose excess weight threatens their health and well-being. Adults age 20 and older are evaluated as follows: Pagana, Kathleen Deska, and Timothy J. Gastric bypass surgery reduces the amount of nutrients that are absorbed from food. It is Stomach Esophagus Staples Bypassed portion of stomach New smaller stomach Food passes through jejunum Large intestine Small intestine Jejunum Greater omentum Ileum Digestive fluids from the stomach A. To large intestine In this Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, a large incision is made down the middle of the abdomen (A). A section of jejunum (small intestine) is then brought up to empty food from the new smaller stomach (B). Finally, the surgeon connects the duodenum to the jejunum, allowing digestive secretions to mix with food further down the jejunum. People who have had restriction surgery can eat only small amounts at a time before feeling full. Reduced food intake along with reduced nutrient absorption can lead to dramatic weight loss. According to the National Institutes of Health, in 2012, 34% of Americans were overweight and 34% were obese. In the United States, about 200,000 people have some type of weight-loss surgery each year. The total number of surgical weight-loss procedures performed each year has increased rapidly. By 2006, 170,000 of these surgeries were done, and by 2012, the number had increased to over 200,000. With Medicare coverage, it is likely that more older people will have weight-loss surgery. In 2006, the average patient having bariatric surgery was a woman in her late 30s who weighed about 300 lb. All bariatric procedures create an alternate route for food through the digestive system so that the food bypasses part of the intestine. These procedures are accompanied by a reduction in the size of the stomach so that less food can be consumed comfortably. In the operating room, the patient is put under general anesthesia by the anesthesiologist. Once the patient is asleep, an endotracheal tube is placed through the mouth into the trachea (windpipe) to connect the patient to a respirator during surgery. A urinary catheter is placed in the bladder to drain urine during surgery and for the first two days after surgery. It is created along the more muscular side of the stomach, which makes it less likely to stretch over time. Next, a Y-shaped piece of intestine is attached to the pouch on one end, and to the jejunum, or middle part of the small intestine, on the other. This allows food to bypass the duodenum, or first part of the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed. The food then continues normally through the rest of the small intestine and the large intestine. A registered dietitian usually provides dietary counseling before and after the procedure. There are several variations on gastric bypass, but all are malabsorptive surgeries designed to lower caloric intake by reducing the amount of nutrients absorbed by the digestive system. As a result, most obesity-related health problems are substantially reduced or cured when weight is lost and that weight loss is maintained. However, Roux-en-Y surgery also has some serious disadvantages, including: the surgery is more difficult for the surgeon than restrictive surgeries, and involves permanently altering the digestive system. Many vitamins and minerals are absorbed in the part of the small intestine bypassed by this surgery. The individual must commit to a lifetime of taking nutritional supplements to prevent serious vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Tearing, bleeding, and infection at the incision and reconnection sites can be potentially fatal complications. Dumping occurs when food moves too fast through the intestine and causes symptoms of nausea, bloating, weakness, sweating, fainting, and diarrhea. To be candidates for gastric bypass surgery, individuals need to have failed at serious attempts to lose weight in the past, be in good mental health, demonstrate an understanding of the risks associated with this surgery, and be willing to make a lifetime commitment to changing eating habits. Gastric bypass Preparation Before the surgery, the patient will undergo a physical and psychological examination and receive nutritional counseling. A large dressing covers the surgical incision on the abdomen of the patient and is usually removed by the second day in the hospital. Patients are also fitted with special socks to improve blood flow in their legs and prevent blood clot formation. It is kept in place in the unlikely event that the patient may need direct feeding into the stomach. By the evening after surgery or the next day at the latest, patients are usually able to sit up or walk around. Gradually, physical activity may be increased, with normal activity resuming three to four weeks after surgery. Patients are also taught breathing exercises and are asked to cough frequently to clear their lungs of mucus. Postoperative pain medication is prescribed to ease discomfort and is initially administered by an epidural. At the time patients are discharged from the hospital, they will be given oral medications for pain.