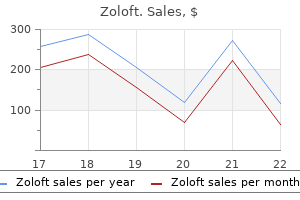
Purchase genuine zoloft line
Remodeling of the proximal phalanx due to growth is usually very good when the epiphyses are still sufficiently open improving depression symptoms quality of life cheap zoloft 100mg with visa. In the case of scaphoid fractures the clinical diagnosis is made from the tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox and the diagnosis is confirmed by special diagnostic imaging. Fractures of the other carpal bones are rare but they are also often overlooked as their clinical features can be less obvious. Dorsal avulsion fracture of the triquetrum must be excluded with certainty after a fall onto the wrist if there is local tenderness over the dorsum of the triquetrum. The first four numbers define the location, followed, after a hyphen, by a letter and number, which describe the fracture type. First number: 7 (identifies the hand as the location of the fracture) the second number identifies the finger: Thumb 1 Index finger 2 Middle finger 3 Ring finger 4 Little finger 5 the third number defines the finger bone: Metacarpal 0 Proximal phalanx 1 Middle phalanx 2 Distal phalanx 3 In the wrist, the second number codes the proximal (6) and distal (7) row and the third number identifies the individual carpal bones from radial to ulnar: Scaphoid 61 Lunate 62 Triquetrum 63 Pisiform 64 Trapezium 71 Trapezoid 72 Capitate 73 Hamate 74 the fourth number, separated by a period, identifies the location within the bone: Proximal 1 Diaphyseal, shaft 2 Distal 3 A letter and a further number, separated from the first three numbers by a hyphen, describes the fracture type: Carpus: A1: avulsion, A2: chip, A3: comminuted With reference to the forearm axis: B1: transverse, B2: spiral, B3: parallel With regard to the number of fragments: C1: with a third fragment, C2: multiple fragments, C3: comminuted Metacarpal, proximal phalanx, middle phalanx, distal phalanx: A = diaphyseal: 1 simple, 2: with a third fragment, 3: multifragmentary B = metaphyseal: 1 simple, 2: with a third fragment, 3: multifragmentary C = intra-articular fracture: 1: unicondylar, 2: bicondylar, 3: multifragmentary, depression Additional Information the author would like to emphasize that the listed operation methods represent a treatment possibility only if surgery is indicated. Each must be considered individually to establish which of the possible treatment options may be appropriate. The results determine management and may decide whether or not surgery is necessary. Operation procedure: Atraumatic approach (see Chapter 9) Atraumatic technique ("Ten Commandments," see Chapter 4. Adapt the implant: Determine plate type (standard or fixed-angle locking plate) or screw type, contour, shorten and/or bend the plate. Before drilling for the first hole, check rotation by flexing the fingers passively. Drilling: sliding hole to match screw diameter, threaded hole to match screw core diameter. Whenever possible, obtain interfragmentary compression: lag screw(s), dynamic fixation, compression by means of reduction forceps. Establish and document whether the internal fixation is rigid, loading-stable or limited, and motion-stable. Final hemostasis by bipolar cautery Atraumatic wound closure without tension, preferably without a drain Intraoperative/postoperative X-ray Sterile dressing, if necessary applying a splint for immobilization Elevation of the arm Postoperative measures: Explain further treatment to the patient in detail Postoperative early functional treatment: physical therapy, ergotherapy Note the patient must always be informed of potential complications of surgical management and this information must be documented. Hand and wrist fractures are stabilized surgically according to the following basic plan. Present the treatment options: conservative or surgical; explain the advantages and disadvantages of the treatments. Address potential complications: impaired motion, infections, sympathetic reflex dystrophy. Record the information provided: General anesthesia / plexus anesthesia, complications Screw/plate loosening Wound infection Absence of bony consolidation, pseudarthrosis, delayed fracture healing Injury of sensory cutaneous nerves Malpositioning, malalignment Restriction of movement of uninvolved fingers Sympathetic reflex dystrophy Re-operation: tenolysis, repeat fixation Postoperative arthrosis Precise preoperative preparation: hand bath, cleaning, drying, removal of nail varnish, sterile packing. Use sterile draping; if an image converter is used, do not forget to place a lead shield. After surgery, edema is caused by accumulation of excessive fluid in the intercellular space. This swelling diminishes perfusion and may lead to congestion, dysregulation, and increased risk of infection. The following postoperative measures are essential: Analgesia and exercise therapy. Adequate analgesia must be ensured as otherwise the patient will likely not tolerate or actively participate in appropriate postoperative treatment. Priority should be given to an effective and more consistent application of preferably active mobilization, muscle pump activity by active isometric muscle exercise, wherever possible, and elevation of the limb above shoulder height. Regular dressing changes, under analgesia/anesthesia (children) if necessary, are essential. The plaster cast should be checked for cleanliness, fit, functional position, and pressure sites, and replaced if necessary. Physical therapy for the shoulder and elbow starts on the first postoperative day to avoid disorders in the chain of movements of the upper extremity. Depending on progress, mobilization is increased with controlled physical therapy, which is supplemented by occupational therapy later on. Additional physical measures include intermittent ice application for pain relief and to improve perfusion. When used appropriately, passive exercises can help to prevent adhesions of tendons and sliding surfaces. Treatment can be supported by manual therapy to maintain rolling and sliding joint movements with traction and translation. Lymph drainage reduces swelling but is only indicated after the wound is well healed. Treatment of scars consisting of pressure dressings, compression hose, and compression gloves is occasionally helpful. After complete wound healing, scar ointments will have a positive effect, not least for psychological reasons. As soon as the internal fixation is stable on motion and loading, physical therapy must be supplemented with occupational therapy. Functional improvements are achieved by having the patient perform active tasks with the injured hand in order to attain pain-free precision, power, and key grips. The occupational therapy repertoire also includes self-help training, provision of aids and, if necessary, use of a dynamic splint. Note the importance of physical therapy and occupational therapy must be emphasized. Preference should be given to therapists with a certified qualification in hand therapy, as provided by specialist courses. They have slender profiles and can be used for different bone shapes and fracture types. With the introduction of titanium, allergenic components have largely disappeared. One method locks the thread of the screw head in the plate hole through a reshaping process due to differences in material hardness and design. Fixed-angle locking fixation allows the components to become ever smaller in size, which is naturally an advantage given the delicacy of the hand and finger structures. Because fixed-angle fixation is rigid, implant placement outside the tension band side is possible. Different options are provided by the industry: Unidirectional fixed-angle locking fixation Multidirectional fixed-angle rigid fixation by means of locking Unidirectional connection. Tightening the screw in the hole produces a firm connection between screw and plate. All of these factors contribute to a more secure fracture healing and, when used correctly, reduce the typical complications of surgically treated fractures. The disadvantage is the higher financial cost compared with conventional standard implants. Precise documentation of the materials used is essential so that the corresponding instruments are available if implant removal becomes necessary. An advantage is that perfusion of the periosteum is not affected because of the gap between plate and bone surface. T-plates L-plates H-plates Y-plates Z-plates Condylar plates Strut plates 3-D plates Grid plates Trapezoid plates Mesh modules Double plates Rotation plates the profile height of standard plates is lower than that of fixed-angle plates, which is between 0. Compression holes and oval compression holes are suitable exclusively for standard cortical screws. With noneccentric drilling, fixation is by friction; with asymmetrical drilling, displacement of the plate relative to the bone can be achieved through the gliding hole principle. By contrast, straight incisions are possible on the extensor aspect of the hand; however, these should pass laterally to the joints. Straight incisions should not be made directly over the extensor tendons, so as to avoid adhesions due to scarring. Scars on the sensitive fingertips and edges of the hand interfere with hand function. Whenever possible, the radial side of the index, middle and ring fingertips and the ulnar side of the little fingertip should be spared. Structures that run longitudinally, nerves, and vessels must be noted particularly. Veins that run longitudinally must be preserved, whereas transversely running veins may be ligated if necessary. If deeper structures have to be divided to obtain adequate vision, they must be divided in a way that they can be repaired by suture. Practical Tip Preserve the vessels and nerves on the radial and ulnar sides and, if possible, the A4 annular pulley.
Cheapest generic zoloft uk
For example depression symptoms seclusion purchase cheap zoloft on line, pregabalin and gabapentin are both absorbed via paracellular pathway. However, in the clinic, these molecules have almost complete oral absorption [30]. It should be noted that paracellular pathway can be identified using Caco-2 by assessing the impact of presence and absence of calcium on the permeability of tested articles. In its absence, the integrity of the tight junction is compromised, and hence, it opens up leading to a significant increase in the permeability of compounds absorbed by paracellular pathway. However, the absence of calcium is not associated with an increase in the permeability for compounds absorbed via transcellular pathway [32]. Similar to other cell lines, there is an inherent significant interlaboratory variability in the data reported with Caco-2, which renders comparison of data obtained from different laboratories challenging. These are epithelial cells that are not comparable to human intestinal enterocytes or Caco-2 cells. However, they are not as expensive, over five times faster to grow, and less borne to contamination [34, 35]. This result is mainly attributed to the inherent low expression of known efflux and influx transporter. The goal is to have a cell line that only assesses the inherent passive permeability of the molecule without the impact of efflux transporters. This prediction was established based on the observation that compounds that have high extent of metabolism tend to have high oral absorption (high fa) provided that solubility/dissolution is a not limiting factor. It should be emphasized that this is valid provided that the absorption is not dissolution/solubility limited [39]. Typically, compounds with an efflux ratio >2 are considered substrate for efflux transporter. In addition, Km and Vmax values can be calculated using statistical software such as GraphPad Prism by setting a relationship between efflux ratio and tested article concentration. The inhibitors listed above at the concentration recommended were reported to show little cytotoxicity (10%) to the cells tested when incubated for 4 h [42]. Thereafter, the cells are harvested, lysed by sonication, and extracted using ice-cold acetonitrile:methanol mixture (1:1, v/v, with 0. All uptake assays in the absence and presence of various inhibitors are conducted in at least three independent experiments on different days. Second, a semicircular incision is made and an 8- to 12-cm-long segment of either ileum or jejunum is isolated and cut at both sides of the intestinal segment. The perfusion buffer that has the tested article is perfused at a constant flow rate of 0. Based on the blood flow from the cannulated mesenteric artery, the infusion rate using the peristaltic pump connected with the jugular vein is adjusted; the rate is typically 0. The perfusion is initiated by infusing the tested article solution from the syringe pump at a rate of 1 mL/min for 5 min. This procedure is then followed throughout the experiment that lasts for 90 min with an infusion rate of 0. Similarly, the intestinal perfusate samples are collected from the distal segment glass cannula every 5 min for 60 min. The blood samples are centrifuged at 6000g for 10 min and the obtained plasma are transferred to tubes and stored at -20 C. In addition to the tested article, antipyrine is typically used as a marker for the integrity of the experiment, and as a reference standard for the permeability class boundary, and phenol red is used as a nonabsorbable marker. The intestinal permeability can be calculated based on compound disappearance from the lumen (Plumen) and the appearance of drug in the blood using the following equations (Pblood) [44]: Plumen = - Pblood = C Q ln lumen 2rl Co (9. In addition, for these agents to work, the tested article should either have low solubility/dissolution or given at a low luminal concentration that is lower than its Km. The low efflux inhibition is most likely attributed to one or more of these factors not being satisfied. It also suggests that assessing the potential role of P-gp to the intestinal transport of tested article may be compromised if the assessment is only limited for measurement of Plumen and Pblood is not determined. While it is expensive and resource intensive, obtaining both values is key for putting P-gp impact in perspective. Interestingly, while accurate, human intestinal perfusion technique is too expensive to use. In this report, the correlation coefficient, also referred to as Spearman rank (indicated by rs), was used to compare the two sets of acquired data [43]. Similar to R2, when rs is close to one, a strong correlation exists between the two observations. Plumen values for 14 compounds were compared with the corresponding literature human fa values. The relationship was not as significant between the same literature human fa values and the apparent permeability (Papp) measured in cell-based assays, where rs was only 0. The following section briefly discusses the more commonly found cell and noncell lines that are frequently considered. This is a cell line that originated from the distal tubules of porcine kidney cells. It is used in drug industry to assess compounds permeability and commonly transfected with known transporters. The authors concluded that the transport mechanism of uracil significantly differed based on the cell line investigated [54]. The group reported a significant correlation in the product ratio of the apparent membrane permeability coefficient and the surface area when the in situ and in vitro experiments were compared [55]. This is a conditionally immortalized cell line that is a temperature-sensitive mutant of the growth-supporting oncogene Simian virus. In 2/4/A1 monolayers, the transport of low permeability drugs was comparable to human jejunum and up to 300 times faster than that in Caco-2 monolayers. Furthermore, a better relationship was reported between 2/4/A1 cell line permeability and human fraction absorbed for 13 assessed radiolabeled drugs in comparison with Caco-2 cell line. This is the key advantage for 2/4/A1 rendering it less resource intensive and would lead to a faster turnaround time. The group reported the presence of tight junctions, desmosomes, and the development of microvilli at the apical surface using both scanning and transmission electron microscopy. The group calculated the permeability of drugs into the stationary phase by providing membrane partition coefficient for a series of analogs. This increase indicates that the mass transfer resistance slows down the penetration of molecules and was used to rank order drug molecules tested. The selection of any of these tools should be based on prior understanding of the compound physiochemical properties and the pros and cons of each tool. For example, talinolol is a known P-gp substrate that saturates P-gp transporter at therapeutically relevant doses. Therefore, coadministration with digoxin, a known P-gp substrate with narrow therapeutic index, leads to an increase in the overall plasma exposure of digoxin and result in potential side effect.
50 mg zoloft amex
One caveat of this approach is that not all automated counters are able detect very small platelets mood disorder help zoloft 100 mg on line. The utility of this technology has not yet been clearly defined; however, the parameter may be useful in predicting platelet recovery following chemotherapy, and also in the initial diagnostic evaluation of the thrombocytopenic patient [15]. There is a modest female predominance in adults, while young boys and girls are affected equally. In children the condition is typically acute and spontaneous resolution is common, while in adults it is frequently a chronic disorder with an insidious onset, often diagnosed incidentally when a blood count is 146 Practical Hemostasis and Thrombosis performed for other reasons [20]. Underlying systemic diseases, drug-induced thrombocytopenias, as well as congenital thrombocytopenias (positive family history, abnormal blood film) should be ruled out. In the absence of atypical clinical features (weight loss, persistent fever, bone pain, night sweats, lymphadenopathy, recurrent infections, and dysmorphic features), and when additional abnormalities are not noted on the peripheral smear, bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are no longer recommended, irrespective of the age of the patients [10,22]. Platelet autoantibody measurements are neither sensitive nor specific enough to be clinically useful, and should not be relied upon for diagnosis. Testing for antinuclear antibodies, lupus anticoagulant, and anticardiolipin antibodies, or for abnormal serum immunoglobulin levels is not recommended in the acute setting, though testing may be indicated for patients with persistent or chronic thrombocytopenia. Several studies have evaluated both clinical and 10 Quantitative Platelet Disorders 147 laboratory markers that might predict a chronic course. Principles of Management the therapeutic goal is to attain a safe platelet count that prevents major bleeding and allows a patient to lead a relatively normal life, rather than correcting the platelet counts to normal levels [17]. Those with higher counts can be observed, as the bleeding risk is low and early treatment does not modify the course of the disease. The current guidelines, however, indicate that observation is sufficient for children with no symptoms, or skin manifestations (petechiae, purpura, or ecchymosis) alone, regardless of the platelet count [10]. However, treatment may be considered when the family is geographically isolated and compliance to close follow up is difficult. Chronic and Refractory Immune Thrombocytopenia Around 70% of patients will respond to first-line therapy with corticosteroids or immunoglobulin; however, in adults, the effect is often transient or requires repeated doses to maintain response. In contrast, only 20% of children will relapse, and late spontaneous remission is wellrecognized in this subgroup. In children, splenectomy is generally deferred for at least 12 months following diagnosis, due to the higher lifelong risk of postsplenectomy sepsis, and the greater chance of remission compared with adults [26]. Examples include high-dose dexamethasone, danazol, dapsone, azathioprine, cyclosporine, mycophenolate, vincristine, and cyclophosphamide. Viral reactivation and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy are rare sideeffects of rituximab. Romiplostim is administered as a weekly subcutaneous injection and was shown to be superior to both placebo and standard of care in two randomized trials [31,32]. Recurrent thrombocytopenia on discontinuation, arterial and venous thrombosis, bone marrow reticulin deposition, and hepatotoxicity (with eltrombopag) are known side-effects. Response to standard therapy is poorly sustained, and multiple relapses with significant long-term morbidity is typical. Drug-induced Thrombocytopenia the incidence of drug-induced thrombocytopenia is estimated to be 1 case per 100 000 annually [36]. This is thought to be an underestimation, either because a platelet count is not measured or thrombocytopenia is attributed to other factors. Chemotherapeutic agents used for malignancy or potent immunosuppression often cause dose-dependent thrombocytopenia as a result of generalized bone marrow suppression, although some of these agents can also induce immune-mediated platelet destruction. Some drugs known to specifically inhibit 10 Quantitative Platelet Disorders 149 megakaryopoiesis are listed in Table 10. Anagrelide, used in the treatment of thrombocythemia in patients with myeloproliferative diseases, can cause severe thrombocytopenia. Valproic acid, commonly used in seizure disorders, has been associated with dose-dependent thrombocytopenia resulting from direct megakaryocyte suppression. The pathogenesis is poorly understood, although direct or immune-mediated endothelial injury may be an important trigger. Drug-induced, antibody mediated platelet destruction is the most common mechanism of iatrogenic thrombocytopenia [38]. There are several mechanisms of drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia, although the "quinine-type" accounts for the majority: Diagnosis of drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia requires a high index of suspicion, as systemic illness or other coexistent factors may confuse the clinical picture. Inadvertent rechallenge with the causative drug may induce rapid and severe thrombocytopenia and should be avoided. Pregnancy-associated Thrombocytopenia Drugs that bind to platelet glycoproteins forming a "compound epitope" include penicillin, quinidine, quinine, and sulfonamide. The antibody binding to such platelets is dependent on the presence of the offending drug. Gold salts and procainamide, on the other hand, can induce true autoantibodies which subsequently can bind to platelets in the absence of the original offending drug. Post-Transfusion Purpura Gestational thrombocytopenia is a diagnosis of exclusion, but in 95% of cases it manifests as mild thrombocytopenia in an asymptomatic pregnant patient with a previously normal platelet count. Thrombocytopenia develops in approximately 20% of patients with pre-eclampsia, and there is an inverse relationship between platelet count and severity of disease. It is caused by the formation of high-titer alloantibodies against platelet glycoproteins, and represents an anamnestic immune response in a patient previously sensitized through antigen exposure during pregnancy and/or transfusion. The alloantibodies paradoxically cause destruction of autologous as well as transfused platelets through poorly understood mechanisms. The observation of a decline in platelet count below baseline following a platelet transfusion can be an important clue to differentiate this condition from platelet refractoriness which is multifactorial and far more common. These disorders share the common pathophysiological endpoint of platelet trapping and thrombus formation in the microvasculature, with subsequent fragmentation of red cells due to mechanical damage. Multiple factors contribute to the development of thrombocytopenia in this setting including splenic sequestration secondary to portal hypertension, bone marrow suppression either from the hepatitis C virus or interferon therapy, and thrombopoietin deficiency secondary to hepatic dysfunction [45]. Concurrent consumption of platelets and clotting factors from the ongoing coagulation may result in hemorrhage [47]. It is important to highlight that the hemangioma may not be clinically obvious, and investigation of any newborn with microangiopathic hemolysis should include appropriate imaging studies, such as cranial and abdominal ultrasound to exclude the presence of concealed vascular lesions. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome however, in the presence of massive splenomegaly thrombocytopenia can be severe and increases following platelet transfusion are poor. Intervention is rarely indicated for management of thrombocytopenia alone; however, improvement in counts usually follows splenectomy or splenic embolization. In the setting of portal hypertension, surgical procedures that redirect or bypass the portal circulation can reduce the risk of bleeding associated with thrombocytopenia and esophageal varices.
Order zoloft pills in toronto
Patients should be warned that as debridement occurs the wound might appear to become bigger before it starts to heal depression medication list order generic zoloft pills. Occasionally pain associated with the wound can i as the wound heals, due to the healing of damaged nerve endings. Frequency of reviews (and dressing changes) depends on the severity and nature of the wound. It is important to avoid renewing a dressing unnecessarily because this can expose the wound to cooling, dehydration, or mechanical damage. Including photographs of the wound enables progress (or deterioration) to be monitored. Selection of wound dressing there is no universal wound dressing and different types of dressing suit different wounds. Dressings are divided into the following two categories: Primary dressings-applied directly to the wound surface Secondary dressings-placed over the primary dressings to hold them in place and/or provide additional padding or protection. Each time a dressing is changed, it exposes the wound to contamination, dehydration, and cooling. Secondary dressings can be changed more frequently, without disturbing the primary dressing. Selection of the correct dressing is important both to ensure that the wound is healed as efficiently as possible and to ensure cost-effective use because interactive dressings are usually more expensive than non-interactive dressings (table 25. Use of topical antimicrobials these agents are not usually recommended because of the risk of development of resistance and high incidence of local sensitivity reactions (which could ultimately lead to systemic allergic reactions). Liberal application of metronidazole suppresses bacterial growth and thus d odour. Excessive use could (theoretically) lead to the emergence of metronidazole resistance. With more modern desloughing dressings available, the disadvantages of these agents outweigh the benefits. Bacterial growth is inhibited because of the i osmotic pressure in the wound, and honey (especially manuka honey) has some inherent antimicrobial effect. Pharmaceutical quality honey should be used as it is prepared according to set standards and gamma irradiated to reduce the risk of bacterial contamination. VaC helps to remove excess exudates and mechanically draws the edges of the wound inwards, promoting healing. It is suitable for any chronic open wound or acute and traumatic surgical wounds, and is used in plastic surgery to promote healing of grafts and flaps. VaC therapy should not be used on infected wounds (including those involving osteomyelitis) unless these are being treated with systemic antimicrobials. VaC is unsuitable for fistulae, which connect with body cavities or organs, and malignant or necrotic wounds, and should be used with caution on bleeding wounds. Larval (maggot) therapy Larvae of the common greenbottle are used in the management of necrotic or sloughy wounds. Larvae are supplied either in a gauze bag-various sizes contain different numbers of larvae-or loose. During this time, they i in size, and as long as they are still active and i in size, they are still effective. Most interactive dressings are unsuitable (and unnecessary) for use on a wound being treated with larvae, they may also be lethal to larvae by i osmotic pressure or d O2 supply. During treatment, the amount of exudate can i and appear greenish in colour, but this is normal. It might be necessary to protect surrounding healthy skin from maceration caused by i exudates by applying a barrier film. It nearly always causes itching but its appearance can vary, depending on the site, cause, and severity, and whether it is acute or chronic. Signs can include dryness, scaling, erythema, oedema, weeping, crusting, papules, and vesicles. Nickel and latex are common causes, but it should be noted that some medicines and excipients can act as allergens. Once the causative irritant or allergen has been identified, steps should be taken to try and avoid it, or if that is not possible to minimize the risk of exposure. Emollient bath oils can be added to bath water to enhance rehydration and ensure that the whole skin is treated. Corticosteroids topical corticosteroids are an effective treatment for eczema and are the firstline treatment for atopic eczema exacerbations. The fingertip unit Some patients or their carers may be inclined to undertreat eczema because of fear of medication side effects. It is defined as the amount of cream or ointment that can be applied to the terminal phalanx of an adult index finger and is 7500mg. Other topical treatments Wet wraps are wet bandages applied to the areas affected by eczema. Wet wraps cool the eczema, enhance the absorption of the corticosteroid, and act as a barrier to scratching. It is important to prevent over-drying of the skin, therefore stop treatment when the exudation stops and only use on weeping areas not on normal skin. Primary Care Dermatology Society and British association of Dermatologists (2009). Parental knowledge of topical therapies in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis. Section 3: Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies. Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis (790% of cases) It is not known why psoriasis develops but there is a strong genetic component. Other treatments, although well tolerated, have risks of severe toxicity to the liver, bone marrow, kidney, or unborn fetus, and may even i the risk of malignancy. Patients with psoriasis may have low self-esteem, not necessarily related to the extent of the skin involvement. Optimization of therapy and emotional support will be required, in differing degrees, for all patients. Lifestyle recommendations the following may affect symptoms of psoriasis and support or counselling may be provided in the appropriate area: Smoking cessation alcohol moderation Weight management (including reducing high lipid levels). Patients with psoriasis have an i risk of cardiovascular co-morbidities, therefore the listed recommendations will further d the patient risks. Coal tar this has been an effective treatment for inducing remissions in psoriasis for many years. Topical corticosteroids Effective treatment for some forms of psoriasis. Limited by adverse effects which include causing rebound exacerbation of psoriasis on discontinuation and precipitating unstable forms of psoriasis. Potent topical corticosteroids can be used initially on the scalp, palms, and soles, with the strength adjusted according to clinical improvement. If the patient uses over the recommended dose, systemic absorption may occur leading to hypercalcaemia. Ultraviolet B radiation an effective treatment of guttate psoriasis or plaque psoriasis that is unresponsive to topical treatment. Ultraviolet A radiation and psoralen topical or systemic administration of a psoralen followed by exposure to ultraviolet a radiation (PuVa) is an effective treatment for most forms of psoriasis and is used in some centres. Acitretin an oral retinoid which normalizes the epidermal cell proliferation in psoriasis Least effective of the systemic therapies when used alone, but it also lacks many of their toxicities. Methotrexate an effective treatment for severe psoriasis which cannot be controlled with topical therapies alone. Ciclosporin Licensed in the uK for severe psoriasis when conventional therapy is ineffective or inappropriate. Consideration should be made for: age of patient nature of disease, severity, and impact conception plans co-morbidities patient views presence of psoriatic arthritis cost.
Discount 25mg zoloft visa
The desperate need for goodquality clinical trials to evaluate the optimal source and dose of fibrinogen in managing bleeding depression symptome test kostenlos buy cheap zoloft. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: current concepts in pathophysiology and management. Efficacy and safety of tifacogin (recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor) in severe sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. Direct oral anticoagulants compared with vitamin K antagonists for acute venous thromboembolism: evidence from phase 3 trials. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians EvidenceBased Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Risk factors and impact of major bleeding in criticall ill patients receiving hpearin thrombprophylaxis. Is regional citrate superior to systemic heparin anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy Identifying patients at risk of renal allograft thrombosis and evaluating strategies for prevention. However, because they are live human tissue, they carry risks related to immunization and infection. Blood and blood products are also in finite supply from donors and need to be used appropriately. This chapter updates recent advice on transfusion therapy, especially in management of trauma. However, the transfused cells contain surface proteins that are foreign to the host and give rise to an immune reaction. Introduction the most common request to hematologists for help in the emergency management of patients in the hospital setting relates to the control of hemorrhage and the use of blood products. Whereas most treatment involves the use of purified drugs, blood and blood products are derived from human blood donors. They are rarely pure; they are subject to biological variation and carry the risk of infection. This chapter discusses some of these issues and describes their use in specialized clinical settings. If individuals lack an A or B antigen, they make anti-A or anti-B, respectively, after exposure to these glycopeptides in food. Blood group O is due to the lack of A or B antigen and so these people develop anti-A and anti-B antibodies. Blood Transfusion as a Form of Transplantation Transfusion with red cells and other blood products is a form of tissue transplantation, which is made easier because the cells lack Individuals have naturally occurring circulating immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies to the A and B groups they lack. In allogeneic blood and marrow stem cell transplantation, the picture is more complex because patients take on the blood group of the donor, and hemolysis may occur during the period of changeover. The use of Rh D-negative blood for Rh D-negative patients is partly to prevent immunization but also to prevent hemolytic disease of the newborn due to the transplacental passage of anti-D to Rh D-positive children of Rh D-negative mothers. Red Cell Cross-Matching Confidence in the blood group results and the detection of clinically relevant alloantibodies has led to increasing acceptance of electronic cross-matching, where the donor cells and patient serum are not actually tested against each other but a negative result is predicted. These advances have dramatically reduced the time needed to supply suitable blood, enabling many operations to go ahead on a "blood grouped and screen basis. However, the speed of the process may lead clinicians to forget that, when antibodies are present or develop, more steps are necessary to provide compatible blood and this takes longer. Use of O-Negative Blood Just over 100 years ago, Landsteiner discovered blood groups. In many emergencies where the blood group is not known, group O, Rh D-negative blood products may be required. If there is a shortage of group O blood, the Rh D-negative blood is reserved for children and women of childbearing age. Men can be given group O Rh D-positive blood and only a proportion will make anti-D. Infective Risks syphilis, hepatitis C virus, human T cell leukemia virus, and some donors for cytomegalovirus. Reducing Risk Despite these tests, there exist a small number of donors who are infected but lack antibody; this will be reduced further by nucleic acid testing using polymerase chain reaction technology to look for viral genome. Steps taken to reduce these risks include: Donor screening is designed to select out potential donors who are at higher risk of infection because of lifestyle or travel. For plasma products, it is also possible to: heat treat, nanofilter, or disrupt lipid membranes with solvents, methylene blue, or psoralens with ultraviolet light. No test suitable for donor screening is currently available to detect the abnormal prion. The most common cause is a patient receiving the wrong blood, in 70% because of the labeling or checking errors at the bedside or in the laboratory. These errors are preventable by the adherence to clear transfusion 436 Practical Hemostasis and Thrombosis protocols [1]. Delayed Hemolytic Reactions these are usually caused by extravascular hemolysis and the boosting of alloantibody levels. The patient becomes acutely short of breath and often requires artificial ventilation and circulatory support. Leukodepleted Red Cells in Additive Solution: Alloimmunization can affect the efficacy of transfusion, especially platelets. Immunomodulation can follow transfusion with an increase in infections and increase in relapse of carcinoma following surgery to patients who were transfused. Washed Red Cells: For patients who have severe reactions to leukodepleted blood, or who have IgA deficiency, red cells washed in saline can remove plasma proteins that cause the reactions. Platelets Platelet concentrates are prepared from either: plateletpheresis of donors using a cell separator machine; or combining platelet-rich plasma from buffy coats and packed in four-donor pools. The latter two conditions are associated with thrombosis, and platelet transfusions can exacerbate the disease [4]. Of the platelet concentrates made from blood donation or plateletpheresis, a significant quantity is given to patients with bone marrow failure. Counting platelets accurately at this level is difficult, even using modern automated blood counters. Giving larger doses of platelets less frequently or only treating if the patient has bleeding results in less platelet transfusions but more days of bleeding [5]. Vitamin K and prothrombin complex concentrate should be used when reversing coumarin anticoagulants in patients who are bleeding or at high risk of bleeding. It is an important colloid for maintaining the oncotic pressure in the intravascular compartment, and its main indication relates to replacing albumin in severe edematous states. Its use as plasma expander has largely been superseded by crystalloids and gelatin solutions. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Mixing thrombin and fibrinogen forms "fibrin glue," which is applied to the site of bleeding and is a popular treatment in neurosurgery. However, there are still risks with using autologous blood, mainly related to bacterial infection and the blood being transfused to the wrong patient. Because supply cannot meet demand, most countries have adopted national clinical guidelines together with a demand management plan. Coagulation Factor Concentrates Concentrates are prepared from large pools of donor plasma. They all have steps to reduce viral contamination and most have steps to remove impure proteins. Increasing use of Blood is venesected prior to elective surgery and retained for up to 4 weeks.
Salvia bowleyana (Danshen). Zoloft.
- Dosing considerations for Danshen.
- How does Danshen work?
- Blood circulation problems, stroke, chest pain and other heart diseases, menstrual problems, abdominal masses, sleeplessness (insomnia) due to chest complaints, acne, skin conditions, bruising, chronic liver inflammation (hepatitis), and wound healing.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96894
Purchase 25mg zoloft with visa
Therefore a buffer was added to the fluids in the form of either lactate or acetate depression test during pregnancy buy zoloft cheap, both of which are converted to bicarbonate by the patient. The resulting coagulation clogs the filter circuit, reducing its efficiency and ultimately destroying its patency. Heparin heparin has long been used to maintain filter patency through its inhibitory effects on the enzyme cascade. Epoprostenol prostaglandins produced by the endothelial lining of the vasculature inhibit the effect of thromboxane on platelet activation. Citrate Citrate has been used to bind up ionized calcium in the circuit, thus inhibiting several calcium-dependent steps in the clotting cascade and inhibiting calcium influx into platelets, preventing platelet activation. Large quantities of citrate are needed, and this results in a large solute load and metabolic alkalosis. Many alcohol-dependent people require no medication when withdrawing from alcohol. Supportive care, including information on the withdrawal syndrome, monitoring, reassurance, and a low-stimulus environment, are effective in d withdrawal severity. If medication is required, a benzodiazepine loading dose technique is usually employed. By modulating the inhibitory GaBa neurotransmitter pathway, benzodiazepines replace the inhibitory effect of the ethanol that has been withdrawn the patient is given repeated doses until symptoms have diminished to an acceptable level. Chlordiazepoxide or diazepam is effective in the prevention and treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal seizures. Because of the relatively large doses usually given, and the long half-lives, it might not be necessary to give any further medication for withdrawal relief. Suggested withdrawal regimen Therapy should be started as soon as the patient can tolerate oral medication. Review dose daily and titrate on individual patient basis There is a clinical opinion that patients given the recommended maximum dose and still suffering symptoms of withdrawal should be given further doses every 2h until symptoms are controlled or they are obviously too drowsy to swallow any more! Cautions patients might experience seizures as the dose of benzodiazepine is tailed off. This, and the need to avoid benzodiazepine dependence, are reasons for keeping the length of treatment to a maximum of 5 days. Thiamine and vitamin supplements poor nutrition is common in patients who drink for the following reasons: Inadequate intake of food associated chronic liver disease Chronic pancreatitis Malabsorption (water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins should be replaced and severely malnourished patients should be considered for enteral feeding). Thiamine Thiamine deficiency leads to polyneuritis with motor and sensory defects. Oral thiamine replacement If symptoms of withdrawal are not severe the following regimen is recommended: Oral thiamine 100mg should be given four times daily until withdrawal is complete. At discharge Oral supplements should be continued at discharge in patients who are malnourished or have inadequate diets. Thiamine should be continued long term if there is cognitive impairment or peripheral neuropathy (100mg twice daily). Careful monitoring of withdrawal severity is essential in all cases, and more severe withdrawal requires in-patient care. Specialist alcohol treatment services and most hospitals can provide charts to be used in the monitoring of symptom severity. Recommendations on the prevention of relapse in alcohol dependence acamprosate and supervised oral disulfiram are treatment options recommended as adjuncts to psychosocial interventions. The opioid system modulator nalmefene is the first pharmacological therapy to be approved in the eU to reduce alcohol consumption in adults with alcohol dependence and a high drinking risk level. Thus, as-needed nalmefene provides an important new option for use in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Questioning can quickly establish if there is little possibility of harm, but if there is any doubt the patient should be referred to the nearest a&e department and/or a poisons information centre should be contacted for advice. Some misconceptions Members of the public might not be aware of the following: alcohol poisoning can be potentially fatal, especially in children and adolescents. In children, if there are any signs of intoxication the patient should be referred to an a&e department. Referral to an a&e department should be made if sufficient tablets have been taken, even in the absence of symptoms. Be aware that some over-the-counter preparations might have similar brand names. Details of potential hazardous doses, toxicity, features of poisoning, and appropriate management are provided, which is continually updated daily. If there is any cause for concern in an acute poisoning incident, a poisons information centre should be contacted immediately. It is inappropriate to cause unnecessary delay in what might be a life-threatening situation by looking elsewhere for information. The doctor dealing with an acute incident should contact the poisons information centre direct so that first-hand information is given and received. For a non-acute or general enquiry, it is appropriate for a pharmacist to contact the centre. Information required to deal with a poisoning enquiry eliciting as much information as possible about a poisoning incident can facilitate speedy management. It is especially important to have the relevant information available when contacting a poisons information centre: Identity-brand name and active ingredients, including whether it was a mixed overdose or taken with alcohol. Checking the quantity left in a container versus its full contents at least gives an estimate of the maximum quantity ingested. If attendance at an a&e department is recommended, the enquirer should be advised to take any containers or plant material with them that could help with identification (taking suitable precautions to avoid contamination of skin or clothing with the poison). Drug desensitization is potentially hazardous and should never be attempted in patients who have had a severe allergic reaction, such as bronchospasm, facial swelling, or anaphylaxis. Desensitization schedules using both oral and parenteral administration have been developed for a variety of drugs, but mostly for antibacterials (notably penicillins) and some chemotherapy drugs. Drug desensitization is potentially hazardous because there is always a risk of anaphylaxis. Thus, when attempting the procedure, the following precautions should be observed: the patient is informed of the potential risks (it is advisable that they give written consent to the procedure). If very small volumes are involved, rinse the syringe with water after the dose has been given and ask the patient to also take this. Because of the requirement for direct medical observation throughout the procedure, most schedules involve rapid desensitization. It is important that patients performing drug desensitization at home are carefully selected and that the patient agrees to the following: Undertakes never to be on their own throughout the procedure. If it is probable that further courses of the drug will be needed, low doses should be administered until the next course is required. It is important that patients understand that drug desensitization is only temporary. Further reading Examples of drug desensitization schedules Confino-Cohen R, Fishman a, altaras M, et al. Successful carboplatin desensitisation in patients with proven carboplatin allergy. Successful oral desensitisation to trimethoprimsulpha-methoxazole in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Desensitisation of patients allergic to penicillin using orally administered beta-lactam antibiotics. The result is inaccurate because of a problem with an in vitro laboratory test procedure, or occurs when a substance or process falsely alters an assay result. This may lead to inappropriate further tests, incorrect diagnoses, and treatments with potentially unfavourable outcomes for the patient. Drug interference may be (1) chemical where the parent drug, metabolites, or additives cross-react; (2) where drugs or additives act as accelerators or inhibitors of the assay; or (3) photometric where the parent drug, metabolites, or additives may have similar absorption peaks to that of the measured chromogen. Measured plasma/blood levels will enable a more accurate idea of the pharmacokinetic values in specific patients. This will result in a reduction in the risk of toxicity and/or optimization of the effectiveness of the drug regimen. The timing of the sample (relative to the previous dose and method of administration) influences the interpretation of a drug concentration measurement. For most drugs there is a relationship between response and concentration which is based on steady-state samples taken at specific times after the dose.
Syndromes
- Injury to the penis
- Fatigue
- Eye patching
- Wrist x-rays should be done to rule out other problems (such as wrist arthritis)
- Cough
- Confusion
- Alcoholic neuropathy
- Coma
- Tube through the mouth into the stomach to wash out the stomach (gastric lavage)
- Long term, heavy alcohol use
Order zoloft 50 mg online
Unlike tubular reabsorption anxiety 9 year old son buy 100mg zoloft amex, apparent low passive permeability across basolateral membrane compared to apical membrane [10], and a high counter concentration-gradient created by water reabsorption makes contribution of passive tubular secretion negligible, if any. Indeed, physicochemical properties of drug molecules that determine passive permeability are key determinants of drug renal clearance [6]. For example, increasing lipophilicity would increase passive permeability and is associated with a decrease in renal clearance. However, polar descriptors such as polar surface area or hydrogen bond donors or acceptors are positively correlated to renal clearance [128, 129]. However, most of the high-affinity substrates to these transporters are relatively hydrophilic (c log P < 0) [7, 131]. Furthermore, hydrogen bonding ability seems to be an advantageous mechanism to stabilize the substrate-transporter complex [130]. Collectively, hydrophilic and ionized compounds with hydrogen bonding ability are most likely to be secreted in the clinic, mainly because they (i) can interact with the renal transporter systems at the proximal tubule and (ii) do not possess appropriate physicochemical descriptors to undergo reabsorption process along the length of the nephron [6, 124]. For example, two hydrophilic bases (c log D < 0) with predominately renal elimination are more likely to result in clinical interaction as discussed subsequently. In the last decade, a better understanding of hepatic clearance emerged that is not consistent with the proposed additive nature. This observation was not similar to the trend observed with compounds that were taken up by the liver hepatocyte via passive diffusion and metabolized by the same enzymes. The following section is a discussion of these transporters, their expression, and known substrates. It is pivotal to emphasize that for transporters to influence drug disposition the substrate should not always have poor permeability, a perception that some drug discovery scientists may have. It is composed of 12 putative transmembrane domains that are expressed in various body organs that include liver, kidney, and brain [37, 164]. They play a key role in the absorption, distribution, and elimination of endogenous substances and xenobiotics. Typically, compounds that are substrates for these transporters are amphiphilic organic anions. It has a significant impact on exposure, pharmacological, and toxicological effects of drugs [279, 280]. The following section is a discussion on the efflux transporters that were not discussed earlier under renal elimination section. It plays a key role in the biliary secretion of many endogenous substances and xenobiotics [164]. It mediates the biliary secretion of numerous conjugated bile salts into the bile canaliculus. In addition, these substrates have large molecular weight, that is >400 Da with polar surface area. Collectively, our group noted that hepatic active uptake could be the predominant clearance mechanism for acids and zwitterions with a molecular weight >400 Da, irrespective of their membrane permeability [325]. However, it should be emphasized that unlike active hepatic uptake, biliary eliminated compounds have low permeability [325, 328]. Compounds that have high passive permeability are prone to have high renal clearance relative to their total clearance. The rate-determining step is renal elimination/active hepatic uptake that is followed by metabolism. Identification of a liver-specific human organic anion transporting polypeptide and identification of rat and human hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor transporters. A qualitative understanding of permeability, solubility, and their impact on drug absorption is essential to achieve acceptable oral bioavailability. Other factors such as dose and drug stability in the intestinal medium, which can significantly impact oral absorption, must also be considered. Second, the physicochemical and biopharmaceutical drug properties that would influence drug permeability, solubility, and dissolution are reviewed. Passive diffusion comprises two pathways: the paracellular pathway, in which drug diffuses through the aqueous pores at the tight junctions between the intestinal enterocytes, and the transcellular (lipophilic) pathway, which requires drug diffusion across the lipid cell membrane of the enterocyte. The active transport pathway is mediated by transporters and is divided into active drug influx and efflux. Since the junctional complex has a net negative charge, positively charged molecules pass through more readily, whereas negatively charged molecules are repelled [7]. Furthermore, the paracellular pathway offers a limited window for absorption and accounts for <0. In addition, the tight junctions between cells become tighter traveling from the jejunum toward the colon. Therefore, compounds that are absorbed via this pathway are not amenable for traditional controlled release formulation targeting the colon such as metformin and gabapentin. In general, the rate of passive transcellular permeability is mainly determined by the rate of transport across the apical cell membrane, which is controlled by the physicochemical properties of the absorbed compound. Unlike the paracellular pathway, compounds that are absorbed through the transcellular pathway are unionized, with lipophilicity of log P > 0 and Mwt > 300 g/mole. For example, compounds that have small molecular weight and hydrophilic tend to be absorbed via the paracellular route. In this case, rat will be a better model to use to investigate their fa relative to the use of dogs, which tend to overestimate the fa of these molecules and potentially misguide the discovery team. Interestingly, different labels were used to describe molecular weight such as molecular bulkiness, surface area, volume, geometry, conformation, radius, radius of gyration, cross-sectional diameter, hydrodynamic size, and hydrodynamic radius. Herein, for the focus of this chapter, the discussion is limited to molecular radius or diameter, molecular weight, and radius of gyration. Molecular size plays a key role to determine compound diffusion across intestinal membrane. Molecules with a molecular weight smaller than 200 Da passed the intestinal mucosa via paracellular and transcellular transport. Molecules with molecular weight from 200 to 500 Da had rather nonrestricted membrane diffusion. However, molecules with a molecular weight larger than 500 Da resulted in a decrease in membrane diffusion. Interestingly, molecules with large molecular weight can permeate brush border membrane via endocytosis/transcytosis. It should be emphasized that the radius of gyration for compounds investigated considered three pivotal factors, which are mass, molecular radius, and total nuclear mass. Compounds with larger radius of gyration are more difficult to cross Caco-2 monolayers than those with smaller radius of gyration. Interestingly, rigid and larger molecules are associated with lower Caco-2 monolayers permeability. In general, it is difficult to have a reliable estimation of hydrogen-bonding estimation because of these inherent differences in the computational methods. For example, simple counting can be rather problematic and arbitrary since bulky groups or conformational flexibility may shield the hydrogen-bond strength. Some workers also included sulfur and phosphorus and attached hydrogen as polar atoms [1]. A homologous series of -adrenoreceptor antagonists were used as model drug molecules. Most molecules are believed to be absorbed as a result of diffusion through intestinal membranes in a mucosal layer that is rich in lipids and lipoproteins. Generally, hydrophobicity refers to the degree to which a solute is disruptive to the array of water molecules established by hydrogen bonding. Hydrophobicity is often used synonymously with lipophilicity, although the latter includes the idea of attractive forces between the solute and lipid [22, 23].
Buy 25mg zoloft with mastercard
Hereditary h aem orrh agic telan giectasia: Pathophysiology anxiety 27 weeks pregnant buy zoloft visa, diagn osis an d treatm en t. Sagittal bone algorithm com puted tom ographic im age shows m ultifocal areas of expansile osseous lesions with a "ground-glass" internal m atrix and without aggressive periosteal reaction. Areas involved include the frontal bone (red arrow), parietal bone (red arrowhead), occipital squam a (green arrow), basiocciput (green arrowhead), and basisphenoid (white arrow). When an isolated finding, fibrous dysplasia of the skull is most com m only seen within the basisphenoid bone. Adult prim ary brain tum ors are m ost com m on ly in th e supraten torial brain; h ow ever, t um ors in ch ildren can arise an d spread th rough out th e brain as w ell as th e spin. Alth ough som e tum ors, such as pilocytic astrocytom a, are n ot t ypically m etastatic to th e leptom en in ges, th e exact h istologic ch aracterization of th ese t um ors depen ds on th eir surgical biopsy/resect ion, an d th e auth or th erefore believes th at all t um ors sh ould h ave an appropriate preoperative w orkup. Th e presen ce of en h an cem en t sh ould n ot be a dissuasion from recognizing th is lesion as a low -grade tum or. Th ey rarely calcify, an d apart from th ose th at occur in th e spin al cord, th ey rarely exhibit in tern al h em orrh age. Epen dym om as of th e posterior fossa are m ost often extra-axial, an d can fill th e fourth ven tricle an d exten d th rough on e (or both) foram in a of Lusch ka. There is an enhancing m ural nodule, as well as thin enhancem ent along an internal septation. Th e ten den cy of epen dym om as to spread th rough crevices h as been described as "tooth paste-like" spread, an d can result in m ass e ect on, or th e en casem en t of, cran ial n er ves. Because epen dym om as som etim es dem on st rate on ly m in im al en h an cem en t, th e evaluation of all im aging sequen ces of th ese tum ors, as with all tum ors, an d as opposed sim ply to postcon t rast T1 W im ages, is im portan t. The fiber bundle of the left corticospinal tract is seen (arrowhead) surrounded by tum or, confirm ing the tumor as an infiltrating lesion. W h en large, cran ioph ar yn giom as can exten d superiorly in to th e th ird ven t ricle. A leadin g di eren tial con sideration with suprasellar lesion s is a gliom a of th e optic path w ay. Histologically, such gliom as are often pilocytic astrocytom as, an d th ey rarely calcify with out prior radiation t reatm en t. Germ in om as are suprasellar lesion s th at ten d to presen t as irregularly sh aped, en h an cin g lesion s alon g th e pituitar y stalk. Sarcoidosis can h ave an appearan ce overlapping th at of germ in om as, but it is rare in ch ildren. Di use in t rin sic pon t in e gliom a is n ot a surgically curable disease, an d th e treatm en t for it is radiation th erapy. It is m ost often a low -grade t um or, but can h ave areas of m align an t degen eration. Subepen dym al gian t-cell ast rocytom a sh ould be stron gly suspected if a lesion exceeds 10 m m in m axim um dim en sion or is en largin g. Sagit tal T1 plus contrast im age shows a predominantly solid, slightly heterogeneous suprasellar enhancing mass that fills the anterior recesses and body of the third ventricle. This represents a chiasm atic gliom a, which histologically is a pilocytic astrocytom a. A n on -n eoplast ic en tit y th at w arran ts aw aren ess an d th at can m im ic a suprasellar m ass is an ectopic n eurohypophysis. An ectopic n eurohypophysis can appear as a globular m ass in th e region of th e in fun dibular recess of th e th ird ven t ricle. Men in giom as can occur in ch ildren, but are m uch less com m on th an in adults. Both tum ors m ay h ave calcification s, but th is m ore com m on with gangliogliom a. Features that sh ould raise concern in clude large size of a cyst (greater than 10 m m), periph erally splayed calcifications, and thick, en hancing cyst walls with n odular enh an cem ent. Pin eal parenchym al tum ors can be low grade (pineocytom a) or h igh grade (pin eoblastom a). The mass results in partial effacement of the body of the ventricles and right-to-left midline shift. Oligoden drogliom a is an addit ion al consideration for a cort ical/ju xtacortical tum or in th e sett in g of seizures an d th at h as h eterogen eous en h an cem en t an d som e calcification. A large pin eal cyst can be di cult to di eren t iate from an arach n oid cyst in a cavum vellum in terposit um; a feature th at can aid in its ch aracterization is th e location of th e in tern al cerebral vein s. A lesion arisin g from th e vellum in terposit um or th e splen ium of th e corpus callosum w ill in feriorly displace th e in tern al cerebral vein s, w h ereas a pin eal-region lesion w ill superiorly displace th e vein s. Desm oplastic in fan tile gangliogliom as are larger th an regular gan gliogliom as an d are m ore likely to present due to m ass e ect rath er th an seizures. Because of th eir vascularit y, preresection em bolization of th ese lesion s is som etim es attem pted. Apparen t di usion coe cien ts for di eren tiation of cerebellar tum ors in ch ildren. From th e radiologic path ology arch ives: In t raven t ricular n eoplasm s: Radiologic-path ologic correlation. Axial T2 W im age of the head of a 15-m onth-old girl shows a large supratentorial m ass that expands the atrium of the left lateral ventricle (red arrow). There is ipsilateral prom inence of the thalam ostriate vein (green arrowhead), and enlargement of what may be a feeding choroidal artery (red arrowhead). Alth ough un com plicated febrile seizures do n ot require im aging of th e brain, n early all oth er in stan ces of seizures in ch ildren w ill even tually result in im aging. Seizures that are (on a conceptual basis) believed to originate and rem ain within a single cerebral hem isphere. Tem poral lobectomy procedures are often characterized by surgeons as the distance from the tem poral pole that was resected. This usually involves resection of the temporal pole, uncus, and am ygdala, and may or m ay not involve resection of the head of the hippocampus. Transection of the corpus callosum, often to prevent seizure propagation in patients with atonic seizures, so as to prevent drop attacks. The callosotomy m ay involve the entire corpus callosum, spare the splenium (som etim es called a 90% callosotom y), or spare the splenium and isthm us (som etim es called a 70% callosotom y). This involves a temporal lobectomy, resection of the insula and portions of the frontal and parietal lobes, and a corpus callosotom y to disconnect the rem aining parenchym a. A focal surgical resection of an epileptogenic focus, possibly involving a structural lesion, such as cortical dysplasia or a cavernom a. An im planted device with an electrode that wraps around the vagal nerve and interm it tently stim ulates it. There was no abnorm al enhancem ent, and this finding was stable on subsequent follow-up examination, confirm ing that this was an incidental choroidal-fissure cyst. Patien ts with h em im egalen ceph aly h ave h am artom atous/dysplastic overgrow th of on e cerebral h em isph ere with relat ive sparin g of th e oth er. Hem im egalen ceph aly is t ypically sporadic, but it can be a part of a rare n eurocutan eous disorder kn ow n as hypom elan osis of Ito. A fun ction al h em isph erectom y involves a tem poral lobectom y, resection of th e in sula, an d partial parietooccipital resection. Sagit tal T1 W im age in a 4-year-old boy with gelastic seizures demonstrates a nodular area of thickening (red arrowhead) associated with the floor of the third ventricle. This did not dem onstrate postcontrast enhancem ent, and represents a hypothalamic ham artom a (ham artom a of the tuber cinereum).
100mg zoloft with mastercard
This is an autosomal recessive disorder of impaired fatty acid transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane depression definition anatomy purchase generic zoloft canada. It clinically manifests after sustained exercise, fasting, or a febrile illness (there is also a lethal neonatal form). Although this patient has no history of recent exercise, he does have a gastrointestinal illness with very poor oral intake. Patients with disorders of glycolysis often describe that after brief rest their cramps and weakness will resolve; activity can then be resumed at the previous level ("second wind phenomenon"). An electromyogram/ nerve conduction study is not required for diagnosis of a metabolic myopathy but is often done to evaluate for other atypical neuromuscular presentations. Obtain a total serum carnitine, which will usually be low while the acylcarnitine fraction is increased. This pattern is also consistent with secondary causes of carnitine deficiency, such as valproic acid or zidovudine use, chronic dialysis, and disorders of beta oxidation. This patient is not taking any of these medications, and disorders of beta oxidation are not relevant here, as most patients present in infancy or childhood with Reys-like episodes. Of note, if both the acylcarnitine and carnitine levels are low, this is consistent with a primary carnitine myopathy, which is usually a disorder of fatty acid metabolism. It typically presents with progressive proximal weakness, while myoglobinuria is rare. There is also a systemic variant of primary carnitine myopathy that manifests by age 10, but weakness is overshadowed by multisystem involvement. If genetic testing is negative, muscle (or skin) biopsy will be required for diagnostic confirmation (results showing reduced enzyme activity). For patients where there is concern for a glycolytic problem, muscle biopsy is usually diagnostic. In the case of myophosphorylase deficiency, there will be low or absent myophosphorylase activity; however, if this is highly suspected, the biopsy should be delayed for at least 1 month when there is a history of overt myoglobinuria. The reason is that there may be a false-positive presence of myophosphorylase as fetal isozyme can be present in the first month after myoglobinuria. However, there are asymptomatic patients with this deficiency; thus, a positive result must be interpreted with caution. The forearm ischemic exercise test may also be helpful in the diagnosis of glycolytic disorders. When it comes to any unexplained myopathy, especially if there is concern for a metabolic myopathy, there should be consideration of a mitochondrial disease. Many mitochondrial disorders present with multiple neurological problems, such as deafness, seizures, encephalopathy, ptosis, or ophthalmoplegia. In these cases blood tests for mitochondrial mutations are needed, which can pick up many of the most common mitochondrial myopathies. Brain magnetic resonance imaging as well as lumbar puncture and serum looking for elevated lactate and/or pyruvate also become important (but are beyond the scope of this discussion). There are, however, a few mitochondrial disorders that present with an isolated or mainly a myopathic picture. Muscle biopsy is needed for diagnosis and, if done in an affected muscle, is very sensitive and specific. It is important not to miss primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency, as replacement leads to full resolution of weakness. He had no renal damage supported by laboratory testing, but he should be hydrated aggressively with normal saline to prevent renal damage (also serum alkalization may be considered in severe cases). Details of myoglobinuria management can be found in the sources listed under "Further Reading. Examination reveals moderate diffuse weakness, mildly reduced tone, but normal bulk. Thyroid-stimulating hormone, complete blood count, liver function tests, creatine kinase, urine electrolytes, and urine toxicology screen are otherwise negative. The emergency department physician asks whether this is a neuromuscular problem and whether it requires a medicine consult. Possible causes include renal, adrenal, or thyroid dysfunction; renal tubular acidosis; diuretic or laxative abuse; and finally, a channelopathy. In this case there are no signs such as upgoing toes, increased tone, or hyperactive reflexes that would suggest a central etiology. The weakness is not confined to a single limb, peripheral nerve pattern, or root level; and the temporal profile is acute. While the acute onset of weakness often suggests a vascular etiology, the anatomic distribution does not fit a vascular event. Indeed, it appears the patient may have had prior episodes, although they were not as severe. This presentation, associated with critically low potassium, improvement after replacement, and an otherwise normal laboratory workup, should make you consider hypokalemic periodic paralyses. Family history is helpful if positive but not if negative; sporadic mutations, reduced penetrance, unrecognized diagnosis, and recall bias make a negative family history unreliable. Distal renal tubular acidosis is clinically characterized by episodic weakness with reduced reflexes, hypokalemia, hypercalciuria, hypocitraturia, and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis in unlikely in our case due to normal thyroid studies but is important for the clinician to remember (the reader is referred to a particularly illustrative case published in the British Medical Journal; also discussion by Lin [2005]. It is more common in patients of Asian descent, where myalgias and signs of thyrotoxicosis are distinct and precede paralysis. The incidence is about 2% of thyrotoxicosis from any cause, with onset between 20 and 50 years of age. Andersen-Tawil syndrome is a rare hereditary disorder clinically characterized by the triad of dyskalemic periodic paralysis (potassium can be high, low, or normal), cardiac arrhythmias, and multiple dysmorphic features. It is clinically characterized by acute, episodic, flaccid weakness associated with a drop in potassium lasting several hours to days. It commonly occurs in the morning after waking, as in our case, but can be triggered by exercise, cold, emotional stress, a carbohydrate-rich meal, alcohol, or infection. Clinical criteria for the diagnosis of hyper- and hypokalemic periodic paralysis were proposed by an expert committee at the 87th European Neuromuscular Center International Workshop in 2000. One attack of muscle weakness in the proband and one attack of weakness in one relative with documented serum K <3. Positive family history or genetically confirmed skeletal calcium or sodium channel mutation f. Exclusion of other causes of hypokalemia (renal, adrenal, thyroid dysfunction; renal tubular acidosis; diuretic and laxative abuse) Diagnostic Criteria for Primary Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis 1. One attack of muscle weakness in the proband and one attack of weakness in one relative with documented serum K >4. Positive family history or genetically confirmed skeletal sodium channel mutation f. Amplitudes of compound muscle action potentials are decreased during attacks but normal between attacks. Most patients demonstrate a significant postexercise decrement (>40%) initially and subsequent slow recovery. Muscle biopsy is typically not required, but in difficult cases with negative genetic testing it may reveal central vacuoles, increased fiber-size variation, fiber splitting, angulated muscle fibers, and internalization of nuclei or tubular aggregates. They carry the risk of provoking a severe attack and require the presence of an experienced physician and possibly an anesthesiologist. Now these tests are restricted to cases in which genetic testing fails to make a diagnosis.