Purchase cheap aspirin online
If a patient meets two of the three criteria (respiratory rate > 22/min knee pain treatment home remedy generic aspirin 100pills amex, altered mental status, and systolic blood pressure < 100 mm Hg), further workup and treatment for sepsis is indicated. The term sepsis has also been changed to represent a more serious physiologic process. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). Infection and Antimicrobial Therapy 333 sonal health information and does not need to be disclosed to anyone. With a blood exposure, the first step is to determine the risk (severity) of the exposure and the risk of the patient. The risk of puncture by hollow needle with fresh blood is greater than the risk of puncture with a solid (surgical) needle, which is greater than the risk of splashing of a few blood drops on mucous membranes or nonintact skin, which is greater than the risk of blood drops on intact skin (no risk) (E). Part of the initial evaluation of the exposed health-care worker should involve counseling regarding appropriate precautions including the use of barrier protection, not to donate blood, practicing safe sex, and to avoid breast-feeding if possible. For health-care workers there is no need to stop working or to inform patients of a possible exposure (C). Additionally, they often have significant tenderness that is out of proportion to exam findings. Previously, operative interventions were avoided because of the risk of perianal sepsis. Incision and drainage is recommended for this patient (even if no fluctuance is detected) with a concurrent seton placement in the event a fistula is discovered. Over 80% of all intra-abdominal abscesses are postsurgical and diagnosed in the post-operative period. They typically arise from one of two mechanisms: persistent walled off infection after the resolution of peritonitis or after an anastomotic breakdown or perforation that is effectively controlled by peritoneal defense mechanisms. Presentation can be highly variable depending on their location, ranging from hiccoughing with subphrenic abscesses to a palpable mass in the paracolic gutter or even sepsis. Pelvic abscesses can also present primarily with urinary or fecal symptoms such as urinary retention or tenesmus. Agents such as cephalosporins and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are not effective against Bacillus anthracis (B, D). Inhalational anthrax develops after a 1- to 6-day incubation period, with nonspecific symptoms including malaise, myalgia, and fever. Over a short period, these symptoms worsen with the development of respiratory distress, chest pain, and diaphoresis. Treatment for fulminant anthrax infection includes combination therapy with ciprofloxacin, clindamycin, and rifampin (E). Clindamycin is added to block toxin production and rifampin is added for its ability to penetrate the central nervous system and intracellular locations (C). Other signs include tense edema, violaceous skin color, severe pain, and neurologic deficit. A low serum sodium is theorized to be the result of either sepsis-induced syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone or adrenal insufficiency, but this has not been confirmed. Type I infections are caused by polymicrobial infection with aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Treatment includes rapid administration of broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents, aggressive fluid resuscitation, and aggressive surgical debridement. The mortality rate remains at 20% to 40% and is higher with surgical delays, particularly beyond 24 hours. A second-look operation is often required and should be performed for this patient in order to ensure that no additional tissues have become involved since the initial debridement. Amputation may be necessary, but only a second-look operation will indicate whether this is the case (A). With septic shock, pressors may be necessary, but this would not tatic disease can cause urinary retention after surgery, a more serious etiology needs to be ruled out first (A, B). Almost all intra-abdominal abscesses can be treated with percutaneous drainage and antibiotics. In the absence of diffuse peritonitis, operative intervention is likely unnecessary (E). Aspergillus species are widely dispersed in the environment and, when implicated as a pathogen, primarily affect the lung. Aspergilloma typically presents as an asymptomatic radiographic finding in patients with a preexisting cavitary lung disease such as sarcoidosis. A soft-tissue mass within a cavity that is surrounded by a crescent of air (Monad sign) is diagnostic, and because the aspergilloma is not adherent to the cavity walls, the air will remain in a nondependent position. As long as the patient is asymptomatic, no further workup or treatment is necessary. The most common symptom associated with aspergilloma is hemoptysis, which can occasionally be life threatening. In this setting, an emergency bronchial artery embolization should be performed followed by surgical resection (D). Therapy is aimed at treatment of acute exacerbations either with inhaled bronchodilators/steroids (mild disease) or systemic corticosteroids (severe disease) to prevent longterm sequelae. Serial chest radiographs, pulmonary function tests, and IgE levels should be monitored because permanent pulmonary damage can take place even in asymptomatic patients. Invasive aspergillosis and chronic necrotizing Aspergillus pneumonia are both treated with intravenous antifungals (C). Invasive disease can be rapidly fatal and is typically only found in immunocompromised hosts. High-risk transplant patients, such as bone marrow recipients, receive prophylactic agents to prevent invasive infection. An official American Thoracic Society statement: treatment of fungal infections in adult pulmonary and critical care patients. Hepatitis B surface antigen is found on the surface of the hepatitis B virus and is found in high quantities in the serum of individuals with acute or chronic infection. Presence of these antibodies indicates either active or previous infection with hepatitis B but do not confer a timeline associated with that infection. However, IgM against hepatitis B core antigen is only present for the first 6 months of infection, so its presence indicates a recent exposure to the virus. Additionally, no hemodynamic parameters (blood pressure, central venous pressure) are provided that would indicate that pressors are needed. Similarly, adding antifungal coverage can be considered, but this is not a definitive intervention (C). A simple model to help distinguish necrotizing fasciitis from nonnecrotizing soft tissue infection. Use of admission serum lactate and sodium levels to predict mortality in necrotizing soft-tissue infections. Infection and Antimicrobial Therapy 335 wound infection in diabetic patients after cardiac surgical procedures. Perioperative normothermia to reduce the incidence of surgical-wound infection and shorten hospitalization: study of Wound Infection and Temperature Group. Effects of preoperative warming on the incidence of wound infection after clean surgery: a randomized controlled trial. The National Nosocomial Infection Surveillance risk index is a useful tool to assess the risk of wound infection. In a randomized study of patients undergoing colorectal surgery, surgical wound infections were found in 19% who were permitted to become hypothermic but in only 6% who were actively kept normothermic. In a randomized study of clean surgery (breast, varicose vein, hernia), those who were actively warmed 30 minutes before surgery had only a 5% wound infection rate versus 14% in nonwarmed patients. Active control of glucose via continuous infusion was shown to decrease sternal wound infection in diabetic patients undergoing cardiac surgery. The main concern with aggressive glucose control, however, is that it may incite episodes of hypoglycemia. A recent study also highlighted the risk of blood transfusion in wound infection, likely the result of its immunosuppressive effects.
Syndromes
- You may be asked not to drink or eat anything for 6 - 8 hours before this procedure.
- Prazosin (Minipress)
- Chills
- High white blood cell counts may be a sign of peritonitis.
- Abnormal eye movements (nystagmus)
- Constipation
- Fluids by mouth or IV
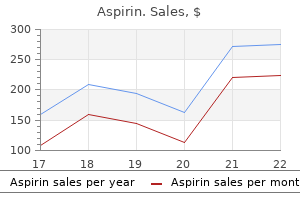
Aspirin 100 pills on line
This idea gives credence to the old concept of bone remodeling as a controlled inflammatory response pain treatment associates west plains mo purchase aspirin 100 pills. Knowledge of these pathways will allow tailoring of drug therapies to target skeletal damage more specifically and thus more effectively. In addition, further insight into the role that bone and bone marrow play in shaping the immune responses, particularly in maintaining plasma cells in the bone marrow niche, will open a new perspective in autoimmune diseases. Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Treg cells suppress osteoclast formation: a new link between the immune system and bone. Th17 functions as an osteoclastogenic helper T cell subset that links T cell activation and bone destruction. Denosumab treatment effects on structural damage, bone mineral density and bone turnover in rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. Tocilizumab inhibits progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis irrespective of its anti-inflammatory effects: disassociation of the link between inflammation and destruction. Inhibition of interleukin-6 receptor directly blocks osteoclast formation in vitro and in vivo. Induction of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss by human autoantibodies against citrullinated vimentin. Identification of a novel chemokine-dependent molecular mechanism underlying rheumatoid arthritis-associated autoantibody-mediated bone loss. Glycosylation of immunoglobulin G determines osteoclast differentiation and bone loss. Age- and, sex-dependent changes of intra-articular cortical and trabecular bone structure and the effects of rheumatoid arthritis. Interaction between synovial inflammatory tissue and bone marrow in rheumatoid arthritis. Differences in bone structure between rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis patients relative to autoantibody positivity. Bone mineral density in patients with recently diagnosed, active rheumatoid arthritis. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and risk of nontraumatic fractures in the Bruneck study. Clinical assessment of the long-term risk of fracture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Microbiota from obese mice regulate hematopoietic stem cell differentiation by altering the bone niche. Osteoclasts promote the formation of hematopoietic stem cell niches in the bone marrow. Cellular niches controlling B lymphocyte behavior within bone marrow during development. Canonical Wnt, signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation. Osteoblast function is comprised at sites of focal bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis. Resolution of inflammation induces osteoblast function and regulates the Wnt signaling pathway. Critical appraisal of assessment of structural damage in ankylosing spondylitis: implications for treatment outcomes. The anatomical basis for disease localization in seronegative spondylarthropathy at entheses and related sites. Wilkinson 17 Key Points Cartilage is made up of collagens, proteoglycans, and minor glycoproteins. Different classes of proteinases play a part in connective tissue turnover, but the proteinase that predominates varies with different tissues and the resorptive situation. Various cytokines and growth factors, alone or in combination, inhibit matrix synthesis and stimulate proteinase production and matrix destruction. Growth factor combinations can be used in conjunction with stem cells and chondrocytes within artificial matrices to promote the repair of small cartilage defects in large joints. Cartilage contains different types of collagen, which are composed of rod-shaped molecules that aggregate in staggered arrays to form cross-linked fibers that give connective tissue strength and rigidity. In the presence of hyaluronic acid, these form highly charged aggregates, attract water into the tissue, and allow cartilage to resist compression. Chondrocytes in normal adult cartilage maintain a steady state in which the extent of matrix synthesis equals that of degradation. During disease progression, a phenotypic shift in the chondrocytes disturbs this steady state, which detrimentally alters the functional integrity of cartilage. During growth and development, synthesis of matrix components exceeds degradation. In pathology, there is an increase in the rate of degradation that is often associated with a reduction in matrix synthesis. The primary cause of cartilage and bone destruction in the arthritides is elevated levels of active proteinases, secreted from a variety of cells, which degrade collagen and aggrecan. In contrast, in a highly inflamed rheumatoid joint, chondrocytes, synovial cells, and inflammatory cells all contribute to the proteolytic loss of tissue matrix. Joint tissues are capable of repair; although aggrecan can be readily resynthesized, replacement of collagen after its destruction is more difficult. Cysteine and aspartic proteinases are predominantly active at acidic pH and act intracellularly; threonine proteinases, the proteasome being the most characterized, also act intracellularly at nearly neutral pH; and the serine proteinases and metalloproteinases, active at neutral pH, mostly act extracellularly. Other enzymes, such as elastase, are stored and released when neutrophils are stimulated. Some enzymes, such as furin, may not participate directly in the proteolysis of matrix proteins but activate proenzymes that subsequently degrade the matrix. The complete repertoire of human proteases (defined as the degradome)5 comprises approximately 588 proteinases, and all classes of proteinases have roles in the turnover of connective tissues. One proteinase pathway may act in concert with or precede another, and the pathway that predominates varies with different resorptive situations. The osteoid layer in bone is removed by osteoblast metalloproteinases before the attachment of osteoclasts, which secrete predominantly cysteine proteinases such as cathepsin K. An intricate series of interactions among T cells, macrophages, synovial fibroblasts, and chondrocytes occur in the rheumatoid joint. In septic arthritis, both serine proteinases and metalloproteinases released from neutrophils exceed the local concentration of inhibitors, which results in rapid removal of the cartilage matrix from the joint cavity. Zinc is present at the catalytic center within the N-terminal catalytic domain, which is joined to the C-terminal hemopexin domain by a flexible linking peptide. The three stromelysins have similar substrate specificities, but their expression patterns are often quite distinct. These enzymes, when activated, cleave fibrillar collagens at a single site to produce fragments three quarters and one quarter the original size. The five main classes of proteinases4 are grouped according to the chemical group that participates in the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. Most contain a C-terminal hemopexin domain (blue), which is involved in protein binding and substrate specificity. It is also likely that multiple cytokines will be present within such an inflammatory milieu, thus making it difficult to predict the outcome of blocking the action of an individual cytokine to prevent tissue destruction. Cytokines and growth factors mediate their effects on cells by binding to specific cell-surface receptors. A "signal" is transduced to the nucleus via specific intracellular signal transduction pathways that culminate in the activation or repression of target genes. Signaling in inflammation is complex, and multiple signaling cascades are often activated by a given cytokine in different cell types. A further level of complexity is that interactions, or "cross-talk," between different signaling pathways can occur to effect the gene expression of degradative molecules. The propeptide is removed proteolytically, which allows the enzyme to hydrolyze peptide bonds, and activation is likely to be achieved in a tightly controlled environment close to the cell surface.
Generic 100 pills aspirin free shipping
The incidence has been rising pain medication for cancer in dogs buy 100 pills aspirin with visa, and women and older patients are more commonly affected. Antibiotic use is the most widely recognized risk factor and patients believed to have antibiotic-associated C. Additionally, oral vancomycin has near 0% bioavailability and so remains fully in the colonic lumen. Which of the following is true regarding daily caloric and/or protein requirements Use of serial measurements of albumin and prealbumin is the "gold standard" for trauma patients. Measurement of nitrogen balance is limited because it underestimates nitrogen input. The Mini Nutritional Assessment is designed specifically for hospitalized patients. Out of all of the serum protein measurements, transferrin seems to correlate the closest to nitrogen balance. A 23-year-old male was admitted 7 days ago for pharmacologic treatment of cancer cachexia Cannabinoids are superior to megestrol acetate in stimulating appetite and weight gain. When initiated early, megestrol acetate has been demonstrated to improve survival. Anabolic steroids have been shown to have lasting improvements in appetite and improved long-term weight gain. Which of the following is true regarding fluid homeostasis during and immediately after a 4-hour laparotomy The majority of postoperative oral fluid replacement will be primarily absorbed in the colon. Administration of 5% albumin pulls thirdspace fluids into the intravascular space. Shift of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the right be synthesized de novo in humans in any physiologic state Slightly overfeeding for 7 days is preferable as a means to maximize replacement of caloric deficits. Calcium absorption will be minimally affected because this primarily occurs in the ileum. It may lead to a mucin gel matrix of cholesterol crystals and calcium bilirubinate in the gallbladder. There is also an increased demand for protein in pediatric patients because of active growth, with the largest being preterm infants who may need 3 to 4 g/kg per day (A). This can then be extrapolated to the nutritional state of the patient by knowing what substrates are being used at various phases of fasting. Hypoglycemia can present with diaphoresis, confusion, agitation, tachycardia, and, if severe, diabetic coma. The effect of abrupt cessation of total parenteral nutrition on serum glucose: a randomized trial. Nutritional assessment in the hospitalized patient is limited by multiple confounding factors. Though nitrogen balance is a fairly accurate measurement of nutritional status, it is limited by the impracticality of 24-hour urine collection and the often inaccurate recording of daily nitrogen input. Of the serum proteins, prealbumin seems to correlate the closest with nitrogen balance (E). While the creatinine height index can give you an estimate of lean body mass, changes in creatinine excretion from systemic processes. Developing suitable methods of nutritional status assessment: a continuous challenge. Cancer-related cachexia/anorexia has been associated with failure of cancer treatment, delay in initiation of treatment, increased treatment toxicity, early discontinuation of treatment, and shorter survival in terminal cancer patients. It has even been implicated as a direct cause of death in 20% to 40% of cancer patients. Before initiation of appetite stimulation, treatable causes of anorexia such as oral candidiasis or depression should be addressed. Megestrol acetate (Megace) is the most widely studied and, so far, most efficacious medication available to help improve appetite and weight gain in this patient population. It has been found to improve appetite, caloric intake, and nutritional status in several clinical trials. A study done in 2010 demonstrated that megestrol acetate used in combination with olanzapine was associated with improvements in weight gain, appetite, nausea, and overall quality of life when compared with megestrol acetate alone, even when corrected for improvements in depression. Unfortunately, megestrol acetate, either alone or in combination with olanzapine, has not been demonstrated consistently in the literature to improve survival (C). It is also important to note that 1 in 23 patients using megestrol acetate will have a thromboembolic event; therefore it should be used with caution in susceptible patients. While it has been demonstrated that steroids have results equivalent to megestrol acetate, they are short-lived and patients quickly return to baseline after cessation of the drug (E). While many patients can undergo oral fluid resuscitation, most of this fluid is absorbed by the small bowel, not the colon (A). Hypocalcemia is a very common sequela of massive transfusion and can worsen coagulopathy and potentially increase mortality if not addressed. This is primarily caused by the chelation of calcium by citrate, which is used to prevent clotting of stored blood. Generally, it is not a problem with small volume transfusions because it is rapidly cleared by the liver. However, in the trauma patient receiving massive transfusion, the higher number of transfused products, the corresponding hypothermia, and multiorgan system dysfunction all contribute to reduced clearance. A study done in 2015 showed that 90% of trauma patients requiring activation of a massive transfusion protocol had some degree of calcium deficiency. The strongest predictor of severe hypocalcemia was transfusion of more than 15 units of total blood products. The severe hypocalcemia group in this study showed a significantly higher mortality (49% vs 24%), potentially highlighting its importance in clinical practice. However, this group also required more blood products so causation is difficult to determine. Patients with massive transfusions also can develop hyperkalemia due to potassium leakage from lysed red blood cells (C). Additionally, the metabolism of citrate in the liver can result in metabolic alkalosis (A). Treatment of cancer-related anorexia with olanzapine and megestrol acetate: a randomized trial. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing peptide, in the treatment of cardiopulmonary-associated cachexia. After a meal, carbohydrates are rapidly used, and any excess is stored as fatty acids or as glycogen (primarily in the liver and skeletal muscle). Though the skeletal muscle has proportionally more glycogen stored, it is not available systemically during fasting because these cells lack glucose6-phosphatase, which is the final step needed for creation of glucose from glycogen (B). Liver stores of glycogen are normally used within 16 to 36 hours, but it can be shorter in certain disease states. After glycogen stores are depleted, the body turns to the breakdown of skeletal muscle and lipids for energy. The largest source of energy is free fatty acids, but they are a relatively poor source of free glucose. While amino acids from protein breakdown can be used for gluconeogenesis in the liver (early in starvation) and kidney (late in starvation), most proteins serve an important role in bodily functions. However, gluconeogenesis never completely stops because several cells are heavily reliant on glucose as a fuel source. Red blood cells are solely reliant on the anaerobic conversion of glucose to lactate because they lack a mitochondria required for the utilization of fatty acids or for aerobic breakdown of glucose (D). In addition, white blood cells, cells in the adrenal medulla, and peripheral nerves are all obligate glucose users. While the brain is heavily reliant on glucose as a fuel source, it can use ketones to some degree (E).
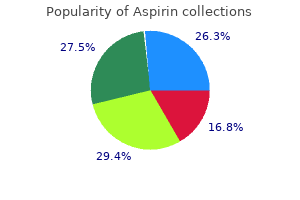
Order 100pills aspirin amex
All protein mass spectrometers measure mass/charge ratios (m/z) of peptides and require three key components pain treatment center hazard ky buy aspirin toronto. The first is an ionization source, where the peptides are transferred to gas phase and charged by bombardment of electrons; the second is the mass analyzer, where ionized molecules travel through a vacuum and can be selected or focused according to their mass by differentially located and differentially strong magnets. The third and last component of every mass spectrometer is the detector that converts the energy of the ions that arrive into a signal that is registered by the electronic devices and conveyed to computer. The signal obtained is compared to a theoretical signal computed by analysis of the genomic information or databases of already registered signals. Through comparison of many peptides to sequences, a protein is identified more or less unambiguously. It is important to know that because peptides are selected and analyzed one at a time, frequently occurring peptides of abundant proteins may "suppress" less frequently occurring peptides even if these would be otherwise detectable. In a great simplification, this means that not only the concentration of a particular protein in a given sample will determine the likelihood to be detected but also the "competition" with all other proteins present. Hence, unabundant proteins and peptides in body fluids will typically need to be partially purified before detection. However, under certain circumstances when two mass analyzers are put in tandem, the machine can be "trained" to select particular peptides and analyze only them. The first 20 years of the 21st century have seen the explosion of genomic technologies and information. Much of the expectations associated with the concepts of personalized medicine are associated with the hope that genetic signatures can serve as so-called biomarkers to instruct treatment and patient stratification. Moreover, biologic processes typically require the interaction of several proteins into protein complexes that collectively form the molecular machinery of a cell. The approaches that allow for this broad biochemical analysis of proteins go under the heading "proteomics. The vast majority of drug targets, either of small chemical molecules or larger biologics, are proteins. An increasing number of therapeutics, from insulin to the latest immunomodulatory agent, are proteins. Several innovative therapeutic approaches aim at restoring proper proteostasis, correcting defects of unstable, misfolded, or mislocalized proteins. This article reviews the technologies that allow for the parallel analysis of proteins, or proteomic technologies. It is worth reminding at the onset of the fundamental properties of the proteome that make its analysis particularly challenging. Although the genome, except for the rearrangements occurring in lymphocytes, remains more or less the same in all cells of our body, the proteome is extremely dynamic, changing from cell to cell, from differentiation state to differentiation state, from tissue to tissue, and dependent on a great number of constantly changing environmental and physiologic factors. The second factor, at least as challenging from an analytical point of view, is that in contrast to genes, which are more or less equimolar, proteins change in their abundance over seven orders of magnitude, from one copy per cell to 10 million copies per cell. We provide example studies and discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the individual methods (Table 21. In discovery proteomics, mass spectra of all ion species that co-elute at a specific point in the gradient elution are recorded. Characteristic (proteotypic) peptides are selectively and recursively isolated and fragmented over their chromatographic elution time, and several fragments are monitored over time. Specific software packages are used for peptide identification and result interpretation. Help understanding cellular pathways and developing effective therapies for the treatment of human diseases 2. Its findings need, however, to be further validated by using orthogonal biochemical and functional assays. It involves immobilization of the "bait" protein to a solid support to capture proteins from a cell lysate. After being affinity purified, captured proteins are digested with proteases to generate peptides. This technology was originally developed in yeast but has also been successfully applied to mammalian cells. Other limitations are possible improper folding or mislocalization of the epitope-tagged proteins as well as altered protein expression levels. A frequent question in biomedicine regards the actual impact of an agent, typically a therapeutic agent, such as a small molecule drug. Several experimental approaches can provide partial answers to these questions, including thermal shift proteomics (see later). The most straightforward approach is to immobilize the chemical entity on a resin support and then go "fishing" in cellular or tissue protein extracts. The approach is just a modern version of the classical affinity purification in which the analytical part is executed through proteomics. This is a powerful method that can lead to the discovery of the mechanism of action of therapeutics and experimental agents. Not all compounds can be coupled easily, and it may not be feasible to retain target engagement with the chemical modifications necessary. Some compounds may be too small or simple to use as affinity reagents or the target too unabundant. However, despite all these caveats, the approach is one of the most medically useful among the proteomics varieties and has been instrumental to understand the target profiles of clinically relevant drugs affecting kinases, proteases, and the epigenetic machinery. Ligands that alter the "melting point" (or, more correctly, unfolding temperature) of a protein are considered binders of the protein under investigation. These combined methods can help drug discovery efforts by confirming drug-target binding and identifying off-targets (see also Table 21. Further modification of the protein extraction protocol, allowing for the identification of membranebound target proteins of small molecules by including mild detergent, makes it possible to additionally identify transmembrane receptors, the majority of current drug targets. Subsequently, proteins are extracted with or without detergent to retain membrane proteins or not. Each sample is then digested with trypsin and labeled with different isotope tags. Using this quantitative proteomics approach, melting curves are fitted, and the melting temperatures are calculated and compared for all proteins in the vehicle- and drug-treated conditions. Furthermore, the method requires that both interacting proteins access the nucleus. Often proteins in this assay are overexpressed, potentially leading to a high false-positive rate. For instance, late-stage failure of compounds in clinical development caused by a lack of target engagement or unexpected side effects can be minimized. Reconstitution of the inactive fragments Nub and Cub upon interaction of proteins to which they are fused is recognized by cellular deubiquitinating enzymes that cleave after the Cub C-terminus. Such modifications can lead to alterations in protein conformation, changes in enzyme activity, alterations in subcellular localization, and changes in protein binding and in protein lifetimes. Furthermore, it allows longitudinal measurements of risk factors as well as effects of pharmacologic interventions eventually contributing to the individual health. They provide comparative information about the uniqueness of potential therapeutic candidates. Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers are very important to monitor disease progression, ensure better care of patients, and better understand disease mechanisms. Traditionally, exploring and defining "molecular signatures" of diseases are mostly based on gene expression analysis. To better understand disease mechanisms and to monitor if differences at the transcriptomics level can also be observed at a more mechanistic level, complementary technologies such as epigenetics, metabolomics, and proteomics are very valuable. However, measuring proteins in these samples poses technical challenges because of the high number of proteins present in a cell and their vast dynamic range of expression.
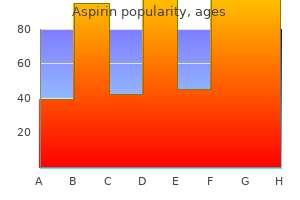
Buy generic aspirin on-line
Although the quality of evidence is insufficient to determine whether this translates into an increased fracture risk [32] unifour pain treatment center nc generic aspirin 100pills line, this may be a consideration for renal patients taking high-dose or long-term steroid therapy. There are also conflicting and inconsistent data linking synthetic progestogen use to an adverse lipid profile. However, to date, this finding remains a surrogate end point and there is an absence of evidence that this translates into a significant clinical effect. Recent prospective data demonstrates an increase in the relative risk of breast cancer with both oestrogen and progesterone-only contraceptive formulations [34]. In contrast to the Mirena, which reduces menstrual bleeding, the main side effect of the copper coil is that it can increase menstrual flow by 30 percent and cause dysmenorrhea [4]. There are no reports of intrauterine contraceptive failure in renal transplant recipients in contemporary literature. The theoretical concern presented at that time was that intrauterine contraception was less effective in a patient maintained on immunosuppressive therapy due to an attenuation of the uterine inflammatory response that forms part of the contraceptive mechanism. It is recognized that macrophages play the most important role in the uterine milieu and that calcineurin inhibitors, antimetabolites and biological agents, including basiliximab and daclizumab, which act primarily via T-cell inhibition, are unlikely to affect this process. In addition, steroid therapy is recognized to increase macrophage activity via activation of macrophage migration inhibiting factor. A second theoretical concern regarding the use of intrauterine methods in the transplant population is one of infection. Such anecdotal data should be appropriately balanced with an understanding of both the relative contraindications and typical use failure rates of alternative contraceptive methods, and the known risks of an unintended pregnancy. Barrier Methods Barrier methods of contraception include condoms, cervical caps, diaphragms and sponges. Their effectiveness depends upon consistent and correct use by the patient or her partner. Therefore, failure rates are variable and it is important to consider their "typical-use" effectiveness (see Table 3. Both male and female condoms are available with "typical-use" failure rates of 18 percent and 21 percent, respectively [5]. For this reason, for women for whom an unintended pregnancy would be unacceptable either on health or personal grounds, sole use of a barrier method is not an appropriate contraceptive choice. Male and female condom use should not be combined due to an increased chance of slippage of both devices [38]. Diaphragms are thin, dome-shaped devices that lie between the posterior fornix and pubic bone. Both caps and diaphragms need to be sized appropriately for the individual patient. Use of caps and diaphragms should be combined with a spermicide in order to achieve acceptable levels of efficacy [38]. The contraceptive 04 sponge covers the cervix in a similar manner to the cap, but can be used without prior pelvic examination and individual fitting. It is impregnated with a spermicide that is activated when water is applied before use. In addition, spermicides in the United Kingdom contain nonoxinol-9 (N-9), which is associated with epithelial disruption in the vagina and rectum with repeated and high-dose use and may increase transmission of blood-borne viruses. Sterilization Voluntary sterilization can be offered to all women who understand the nature of the procedure, including its low failure rate and effective irreversibility, in combination with a certainty that they do not want any more children. The probability of regret following sterilization has been found to be higher for women sterilized before the age of 30 compared to those older than 30 [43]. However, life events can also become sources of regret in family-planning decisions [4]. Such life events can be prevalent in the complex disease journey of the renal patient who transitions from disease stability to disease decline, renal replacement and, potentially, in and out of transplantation. The requirement for an operative procedure means that hypertension, diabetic control, bleeding time, fluid balance and vascular risk are important considerations in being able to provide an appropriate level of perioperative and anesthetic care. A hysteroscope is used to place micro inserts into the fallopian tubes, which induce ingrowth, fibrosis and eventual blockage. Patients must continue to use alternative, effective contraception for three months following the procedure and wait until correct placement of the micro inserts is confirmed by pelvic x-ray, transvaginal ultrasound or hysterosalpingogram imaging. It is estimated that 10 percent of women will be unable to undergo the procedure due to tubal spasm, occlusion or anatomical variation. Based on the number of kits distributed worldwide, pregnancy rates following hysteroscopic sterilization are estimated to be 0. When compliance and misinterpretation of follow-up imaging are factored out, pregnancy rates fall to two pregnancies for every one million kits [44]. If confirmation of tubal occlusion requires hysterosalpingography, then contrast volume will be small with almost immediate drainage from the uterus upon conclusion of the radiographic procedure [45]. Although concurrent immune suppression is not an absolute contraindication to hysteroscopic sterilization, manufacturers of the different available micro inserts generally caution against its use due to a theoretical concern that the tissue response that leads to tubal occlusion will be inhibited by immunosuppressive therapy. However, isolated case reports of successful hysteroscopic sterilization exist in women with renal transplants [46]. Lactational Amenorrhea Lactational amenorrhea utilizes a physiological birth spacing tool. In order to ensure a sufficient contraceptive effect, the baby must be exclusively breastfed and the mother should be amenorrheic, both within six months of childbirth. When applied correctly, this is estimated to be 98 percent effective as a contraceptive method [4]. However, this contraceptive approach is largely promoted only when other forms of contraception are unavailable. A Cochrane review of lactational amenorrhea for family planning concluded that a wiser approach to the postpartum period would be to encourage breastfeeding and, in addition, to motivate the mother to use an alternative form of contraception if contraception is required [48]. Emergency Contraception the most widely used emergency contraceptive contains levonorgestrel at either a single high dose of 1,500g, or two doses of 750g taken 12 hours apart, within a 72hour window of unprotected sexual intercourse. As a progesterone-only preparation there are no contraindications to use in renal disease, hypertension, coagulopathy and lupus. In addition, there is no evidence of an associated increase in cardiovascular risk [18]. This is then combined with either abstinence or barrier methods within the fertile window. Studies of these methods are not methodologically robust and are poorly reported [47], but fertility awareness is estimated to result in 24 percent of women experiencing an unintended pregnancy within a year [5]. Drugs that affect cycle regularity, cycle hormones and fertility signs and symptoms will further reduce the contraceptive efficacy of these methods. For the renal patient, relevant 04 Drug Interactions Patients with renal disease can be prescribed a variety of different long-term and short-term medications. Class of Drug Antihypertensives Diuretics Effect/Interaction May be antagonized by combined contraceptives 1. Plasma levels of tacrolimus possibly increased by ethinylestradiol, gestodene and norethisterone 2. None Antidiabetic drugs Monitor blood glucose Immunosuppressants Monitor tacrolimus and ciclosporin levels. Proton-pump inhibitors and H2 receptor blockers Increased gastric pH theoretically reduces absorption of ulipristal acetate Reduced efficacy of ulipristal acetate Use alternative emergency contraception contraceptive efficacy. Drug interactions of particular relevance to the nephrologist are outlined in Table 3. For other methods, potential side effects, "typical-use" failure rates, anticipated length of use and acceptability should be considered on an individual basis. Prospective measurement of blood pressure and heart rate over 24 h in women using combined oral contraceptives with estradiol. Oral and transdermal hormonal contraception in women after kidney transplantation. Renal hemodynamic and tubular responses to salt in women using oral contraceptives.
Toxicodendron radicans (Poison Ivy). Aspirin.
- Pain.
- How does Poison Ivy work?
- What is Poison Ivy?
- Dosing considerations for Poison Ivy.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96477
Buy aspirin amex
This specific pattern of transcribed genes is the basis for the different phenotypes of the cells in the body and is maintained by the epigenome pain solutions treatment center marietta ga generic 100pills aspirin. Epigenetic modifications of chromatin render it more or less accessible to transcription factors and thereby define which genes in a cell are transcribed. To ensure that each daughter cell has the same gene expression pattern as its predecessor and can thus fulfill the same function, the epigenetic code, just as the genetic code, must be heritable. In contrast to the genetic code, however, the epigenetic code must also be modifiable so that the changes in gene expression needed during development and differentiation can occur. Heritable epigenetic modifications are restored after mitosis and after meiosis and thus are passed not only to daughter cells but also to following generations. Transient epigenetic changes, however, are placed and removed, depending on the current requirements of the cell. Accordingly, changes in the epigenetic code can be introduced by environmental conditions. By these means, the cell can adapt to changes in its environment by stable alterations in its gene expression pattern. An impressive example of the interaction of the environment with the epigenome is maturation of the queen bee in a beehive. The contents of the royal jelly are able to influence epigenetic modifications such that only the larva that is fed royal jelly can express the genes necessary to grow into the queen bee. Key experiments by Waterman and colleagues showed that feeding pregnant agouti mice a special diet of folic acid and vitamin B12 changes the fur color of their offspring. Environmental influences can also introduce epigenetic changes in humans that are still visible in the offspring. The more the field advances, the more diseases are found in which the epigenome is affected and possibly contributes to the development and persistence of disease. In parallel, drugs that modify the epigenome are developed in the hope that pathologically changed gene expression can thus be permanently corrected. Acetylation neutralizes the positive charge of the histone tails and thus decondenses the chromatin. The effect on gene transcription depends on the location and quantity of methyl residues placed at the amino acids. For example, whereas trimethylation at lysine 4 of the tail of histone 3 (H3K4me3) is found at sites of active gene transcription, trimethylation of lysine 27 (H3K27me3) suppresses gene transcription. The effect of these combinatorial histone modifications on gene transcription is mediated by the binding of different effector complexes. On the one hand, citrullination of histones was shown to facilitate transcription by loosening the chromatin structure similar to histone acetylation. On the other hand, histone citrullination was also found to be associated with transcriptional repression. This process is crucial for host defense but is also suspected to be a source of antigens for autoantibody formation because intracellular material such as chromatin is exposed. Because these areas comprise the major part of the genome, 60% to 80% of the CpGs are heavily methylated genome wide. In contrast, only 10% of CpG islands in promoter regions, which regulate tissue-specific gene expression, are methylated. There are diseases in which alterations in the epigenetic machinery were found to be causative. In most diseases, however, it is not yet clear whether these changes are a cause or a consequence of the disease. In some cases, correct silencing of maternal or paternal parts of the genome is needed for a balanced expression of gene products. This is true not only for the X chromosome in female organisms but also for a variety of specific genes called imprinted genes. Currently, approximately 80 of these genes have been described in which physiologically only the maternal or the paternal allele is transcribed but not both. On chromosome 15q11-13, for instance, certain genes are known to always be transcribed from the maternal chromosome and others only from the paternal. Disturbances in imprinting at this location, which leads to incorrect silencing or expression of the imprinted genes, are known to be one cause of Angelman syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome. Physiologic changes in the methylation pattern also still occur in the fully developed organism, for instance, at the promoter of estrogen-responsive genes. Usually, these enzymes catalyze the addition of methyl marks to the cytosine ring at genomic locations with a high content of cytosine-phosphatidylguanine (CpG) dinucleotides, so-called CpG islands. In addition, regions that border CpG islands, which are called CpG shores, are methylated. Upon hypomethylation, T cells change their gene expression pattern and become autoreactive. Expression of the early detection of epigenetic changes in some tumors suggests that epigenetic alterations can be causative in cancer. As described earlier for BeckwithWiedemann syndrome, silencing of tumor suppressor genes or activation of oncogenes can confer a critical growth advantage to tumor cells. Accordingly, changes in histone acetylation and methylation are induced in many cancers. Studies of monozygotic twins indeed show that the epigenome of these genetically identical individuals differs more and more over time. Risk factors also relevant for rheumatic diseases such as smoking, ultraviolet light, infection, air pollution, vitamin D, and sex hormones have been shown to induce changes in the epigenome. The production of polyamines, for example, is increased in response to cellular stress, and, accordingly, polyamine synthesis and, more important, recycling are activated in chronic inflammatory diseases. An important point regarding the role of epigenetics in disease development is its fundamental role in embryogenesis and cell differentiation. Limitations of the epigenetic machinery early in life could lead to pathologic conditions at a later time. Studies examining patients who were exposed to prenatal malnutrition suggest that such disturbances in development of the central nervous system lead to mental illness. They might be the basis for dysfunctions of the immune system, as well as for the chronicity of rheumatic diseases. In parallel, either key pathogenic genes lose their epigenetic repressive marks or counterregulatory genes are silenced by aberrant cytosine methylation. Persistent epigenetic differences associated with prenatal exposure to famine in humans. How chromatin-binding modules interpret histone modifications: lessons from professional pocket pickers. Combinatorial patterns of histone acetylations and methylations in the human genome. Chromatin decondensation and nuclear reorganization of the HoxB locus upon induction of transcription. A therapeutic strategy uses histone deacetylase inhibitors to modulate the expression of genes involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. A, chromosomal memory triggered by Xist regulates histone methylation in X inactivation. Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. The human colon cancer methylome shows similar hypo- and hypermethylation at conserved tissue-specific CpG island shores. A differentially methylated imprinting control region within the Kcnq1 locus harbors a methylation-sensitive chromatin insulator. Developmental study of fragile X syndrome using human embryonic stem cells derived from preimplantation genetically diagnosed embryos. Loss of, acetylation at Lys16 and trimethylation at Lys20 of histone H4 is a common hallmark of human cancer. Does polyamine oxidase activity influence the oxidative metabolism of children who suffer of diabetes mellitus Early-life disruption of epigenetic marks may contribute to the origins of mental illness. Clonal populations of T cells in normal elderly humans: the T cell equivalent to "benign monoclonal gammapathy. Treg cell function in rheumatoid arthritis is compromised by ctla-4 promoter methylation resulting in a failure to activate the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase pathway. Enhancement of lymphocyte migration and cytokine production by ephrinB1 system in rheumatoid arthritis.
Buy cheap aspirin 100pills
The authors concluded that renal biopsy was safe in pregnancy pain treatment center albany ky order 100 pills aspirin otc, advocated a relaxed approach to renal biopsy in pregnancy and proposed increasing its use. However this suggestion was challenged in an accompanying editorial where a more moderate interventional approach was advanced [14]. The complication rate was relatively high with seven identifiable hematomas (38 percent) and two patients (11 percent) requiring blood transfusion as a consequence. Again, precisely how often biopsy diagnosis altered management is not clear, although the absence of glomerular endotheliosis in some women may have resulted in prolongation of their pregnancy. As a result of these interventions, 11 patients were treated with glucocorticoids [16]. Strevens and colleagues [18] biopsied 36 women with hypertension in pregnancy to compare glomerular endothelial changes with those observed 18:20:03 217 Section 6: Acute Kidney Injury in contemporaneous biopsies from 12 women with normal control pregnancies. The mean blood pressure of the proteinuric hypertensives in this study was 150/101 mmHg. One woman with early-onset severe preeclampsia developed a hemodynamically significant hematoma and required blood transfusion. Glomerular endotheliosis was found in most healthy controls in addition to all the hypertensive women, and the authors concluded that this lesion is not specific for preeclampsia. This series was also reported by Wide-Swensson, Strevens and Willner [19], who provided more details of biopsy-related complications. Three women complained of pain after their biopsy and one had a small peri-renal hematoma. One woman with severe pregnancyinduced hypertension, proteinuria, oliguria and pulmonary edema at 25 weeks of a twin pregnancy suffered a large retroperitoneal bleed requiring renal embolization following renal biopsy. Several questions exist about the ethics of the studies reported by these authors [18, 19]. Few medical practitioners consider renal biopsy an appropriate diagnostic investigation in preeclampsia because management is insufficiently altered to justify the risks involved, regardless of any perceived uncertainties about underlying pathology. Women with poorly controlled blood pressure in the setting of preeclampsia, such as those deliberately enrolled in this study, fall into a group at high risk of complications. In fact, generally accepted clinical criteria (see earlier in this chapter) contraindicate the renal biopsy procedure in individuals with this degree of hypertension. Generally speaking, given the unavoidable risks of renal biopsy, this author believes that subjecting normal controls to the procedure in any study is ethically unacceptable. Despite these concerns, the study was reported twice by the same group in 2003 and 2007. The data in the two papers are very similar, although the latter publication [19] fails to reference the former [18]. Han and colleagues [20] reported a series of renal biopsies performed to assess preeclampsia/eclampsia in the antepartum or immediate postpartum periods. Whether patient 20 management was significantly altered by this information is unclear [20]. A recent systematic review [21], focusing on risks and timing of kidney biopsy in pregnancy, has examined data available in 39 published references reporting 243 biopsies in pregnancy and 1,236 after delivery. Evidence was heterogeneous but suggested that, compared to postpartum biopsy, biopsy in pregnancy is likely more risky with a peak risk around 25 weeks. Overall the available published evidence from studies of contemporary practice suggests that the complication rate of renal biopsy in pregnancy is broadly similar to that encountered with this intervention in general nephrological practice. It is possible that the pro-thrombotic environment engendered by pregnancy may mitigate bleeding. Nonetheless, because the reported experience of renal biopsy in pregnancy in the modern era amounts to only a few hundred cases, compared to thousands in the nonpregnant setting, it is not possible to conclude with complete confidence that rates of unusual but serious complications are equivalent. Clearly, if enough biopsies of pregnant women are performed, a serious complication will eventually follow. Therefore, in pregnancy, consideration should be given to the same absolute and relative contraindications to the biopsy procedure that apply to the nonpregnant situation (see earlier in this chapter). Potential operators should not be tempted to perform a renal biopsy in an unfamiliar manner, for example, with the patient seated rather than prone. Also, as in the nonpregnant setting, renal biopsy should not be performed in the presence of hypertension (> 160/95) [2]. It can be difficult to distinguish between preeclampsia and primary renal disease in pregnancy, and often the two may coexist. However, it is usually possible to distinguish between the two conditions by observing other clinical parameters. Considering this, and in the knowledge that those bleeding complications that have been observed with renal biopsy in pregnancy particularly afflict hypertensive preeclamptics, renal biopsy cannot be recommended routinely as an investigation for preeclampsia. Before 28 weeks of gestation, renal biopsy should be performed to make a histological diagnosis and to guide therapy since some lesions may be amenable to steroid therapy. The major question is whether the mother has a condition, predominantly minimal change disease, that may respond promptly to steroids. In adults of childbearing age, minimal change disease comprises only ~25 percent of all nephrotic syndrome and may respond more slowly to therapy than the same condition diagnosed in children. It may be difficult to justify antepartum biopsy simply in order to prolong pregnancy for a couple of weeks to improve fetal outcome, when any maternal intervention is unlikely to have had a therapeutic effect. A trial of steroids is a possibility, but many clinicians are uncomfortable with blind glucocorticoid treatment given the potential maternal complications such as hypertension, infection and diabetes [22]. Some literature also suggests that the prenatal use of glucocorticoids may initiate, in the fetus, a program of physiological changes resulting in cardiovascular and metabolic disease in adulthood [23]. In some systemic disorders such as lupus, serological investigations may be helpful diagnostically, and elucidation of renal histopathology may be a key determinant of therapy. Indeed, prompt therapeutic intervention may be required to preserve renal function. Therefore, before 28 weeks, biopsy should be performed, but at later gestations, the pregnancy should be brought to an end to facilitate subsequent renal biopsy. A similar approach should be applied to non-nephrotic proteinuria, with or without renal functional impairment. Aspiration biopsy of the kidney, including a report of a case of amyloidosis diagnosed through aspiration biopsy of the kidney in 1944 and investigated at an autopsy in 1950. Safety of ultrasound-guided percutaneous renal biopsy-retrospective analysis of 1090 consecutive cases. Predictors of bleeding complications in percutaneous ultrasound-guided renal biopsy. Intrarenal arteriovenous fistula and aneurysm: A complication of percutaneous renal biopsy. Kidney disease is an independent risk factor for adverse fetal and maternal outcomes in pregnancy. Day C, Hewins P, Hildebrand S, Sheikh L, Taylor G, Kilby M and Lipkin G the role of renal biopsy in women with kidney disease identified in pregnancy. Strevens H, Wide-Swensson D, Hansen A, Horn T, Ingemarsson I, Larsen S, Willner J and Olsen S. Han L, Yang Z, Li K, Zon J, Han J, Zhou L, Liu X, Zhang X, Zheng Y, Yu L and Li L. Antepartum or immediate postpartum renal biopsies in preeclampsia/ eclampsia of pregnancy: New morphologic and clinical findings. Mechanisms of disease: Glucocorticoids, their placental metabolism and fetal programming of adult pathophysiology. Prepregnancy counseling should allow discussion of and, where possible, modification of remediable risk factors, including disease activity, blood pressure control, weight management, stability of renal function, medication and familial conditions. Written information should be shared with the woman (and her referring clinician) to accompany the information shared at the clinic appointment. Women with greater than or equal to +1 dipstick positive proteinuria should have formal quantification of proteinuria. Prednisolone, azathioprine, ciclosporin, tacrolimus and hydroxychloroquine are considered safe in pregnancy. Mycophenolate mofetil, mycophenolic acid, methotrexate and cyclophosphamide are teratogenic and should be avoided in pregnancy. Mycophenolate mofetil and mycophenolic acid are associated with an increased risk of spontaneous miscarriage and fetal abnormality and should be stopped before pregnancy. A threemonth interval is advised before conception to allow conversion to a pregnancy-safe alternative and ensure stable disease/kidney function. Iron supplementation should be given if evidence exists of absolute or functional iron deficiency.

Buy generic aspirin online
Further support can be given by other health care professionals or be obtained from written material advanced diagnostic pain treatment center new haven order generic aspirin from india, the Internet, and patient support groups. Measurement of biomarkers can also be useful for monitoring of treatment efficacy and safety as well as for stratification of patients to predict prognosis and treatment response. Sensitivity and specificity of virtually all biomarkers are limited, and therefore the laboratory diagnostics should be guided by the clinical picture. Laboratory markers provide different positive or negative predictive values; thus, they can be used to exclude a disease in cases of a normal result or to support the clinical diagnosis in cases of an abnormal result. Markers of the acute-phase response are mainly useful for evaluation of disease activity and differentiation of infectious complications. Because laboratory test results are commonly part of classification and diagnostic criteria, it is important to understand some key conceptual issues before using these tests in making diagnostic and treatment decisions. Specificity, on the other hand, is the percentage of true negatives correctly identified. The pretest odds is the likelihood that the patient has a specific disease before testing and is usually related to the prevalence of the disease. The likelihood ratio can be combined with information about the prevalence of the disease, characteristics of the patient pool, and information about the particular patient to determine the posttest odds of disease. The more frequent a given condition or a positive laboratory test result occurs in the healthy population, the more likely that the condition will be diagnosed. Clinicians only seldom appreciate the importance of disease frequency (the pretest probability in Bayesian terms) in making a diagnosis. The concepts of false-negative and false-positive results are the converse of sensitivity and specificity, respectively, but are useful in clinical decision making. For example, patients with vasculitis and other lifethreatening rheumatic diseases may develop irreversible end-organ damage because the diagnosis has been erroneously ruled out just on the basis of negative laboratory results. Finally, there is always the risk of measurement error in any test, and this applies to all laboratory tests in rheumatic diseases. Whenever clinical signs and symptoms do not match the laboratory test results, the tests should be considered possibly in error and should be repeated. White blood cells Increased concentrations of neutrophils typically are seen in bacterial infections. In patients undergoing immunosuppressive treatment, the presence of neutropenia should always raise suspicion of drug-related bone marrow suppression. In contrast, neutropenia in association with splenomegaly is a characteristic feature of Felty syndrome. Eosinophilia, commonly seen in patients with allergies and parasitic infections, also is a typical feature of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Churg-Strauss syndrome) and eosinophilic fasciitis. Of note, eosinophil blood counts are very sensitive to glucocorticoid treatment and show a rapid normalization. Furthermore, decreased thrombocyte counts raise suspicion of drug-induced toxicity. To differentiate these conditions, examination of a peripheral blood smear and ultimately bone marrow aspiration are useful. Examination of bone marrow aspirates reveals the number and appearance of megakaryocytes and is the definitive test for many disorders causing marrow failure. However, normal number and appearance of megakaryocytes does not always indicate normal platelet production. For example, in patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura, platelet production frequently is decreased or not appropriately increased despite the presence of normal-appearing megakaryocytes. Some patients may have platelet dysfunction; a drug cause is suspected if symptoms began only after patients started taking a potentially causative drug. Red blood cells Anemia in rheumatic diseases most commonly reflects decreased production of red blood cells in the bone marrow caused by continued inflammation, with increased hepcidin production leading to disturbed iron metabolism. Anemia of chronic disease is commonly normocytic and normochromic; however, microcytic hypochromic anemia also can be associated with chronic disease. Microcytic hypochromic anemia is commonly seen with iron deficiency and other conditions such as thalassemia and lead poisoning. Macrocytic anemia, commonly caused by vitamin B12 deficiency, folate deficiency, liver disease, and hypothyroidism, is not common in rheumatologic conditions except with methotrexate treatment. Of note, disturbed kidney function is associated with a high risk of methotrexate accumulation, causing toxic effects. Connective tissue diseases and systemic vasculitides are frequently associated with kidney involvement, causing glomerular and interstitial nephritis. In cases of suspected nephritic or nephrotic syndrome, urine tests and kidney biopsy are standard procedures. Urinalysis is also useful for monitoring of kidney involvement and should include detection and quantification of proteins as well as of hematuria and leukocyturia. Measurement of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase is included in guidelines or recommendations for monitoring treatment with all immunosuppressive medications. Albumin levels can also be measured when chronic liver disease or damage to the liver from medications is suspected. Conditions that cause rapid bone growth (puberty), bone disease (osteomalacia or Paget disease), hyperparathyroidism, or liver cell damage can lead to increases in alkaline phosphatase levels. Calcium and vitamin D Determination of calcium and vitamin D levels is part of the evaluation for osteoporosis and high or low bone turnover states and may be considered in patients at risk of these conditions and for monitoring of treatment. Calcium absorption, use, and excretion are regulated and stabilized by a feedback loop involving parathyroid hormone and vitamin D. Conditions and diseases that disrupt calcium regulation can cause inappropriate acute or chronic elevations or decreases in serum calcium and lead to symptoms of hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia. To date, only a few of these have been quantified in blood, but this has widened our understanding of the pathologic role that altered vitamin D metabolism plays in the development of diseases of calcium homeostasis. Currently, awareness is growing of the prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in the general population in association with an increased risk of several diseases. Two metabolites-25-hydroxyvitamin D and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-have received the most attention. The need for measuring serum levels of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D is limited, and this metabolite therefore should not be considered as part of the standard vitamin D testing regimen. On the other hand, serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D provide the single best assessment of vitamin D status, and thus measurement of this metabolite should be the only vitamin D assay typically performed. The acute-phase proteins are mainly produced by hepatocytes upon stimulation by cytokines. Clinicians should be aware of this problem, which seems to be more marked with treatment involving biologics such as the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab, and should rely on clinical examination and imaging tools. Citrullination is the result of deimination of arginine residues in these proteins by activation of Ca2+-dependent peptidylarginine deiminase enzymes during inflammation-induced apoptosis (programmed cell death). Leakage of these active enzymes into cells or onto synovial structures causes citrullination of proteins in many types of synovial inflammation. Some of these autoantibodies are more specific for one disease, and others can be found in several diseases. The use of citrullinated peptides and proteins for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. A high titer increases the likelihood that the presence of antibodies is related to an autoimmune disease. In patients in whom a diagnosis cannot be made based on clinical symptoms, watchful waiting is recommended. Therefore, during pregnancy, the fetus should be screened for congenital heart block by ultrasonography, and newborns of anti-Ro antibody-positive mothers should avoid sunlight exposure during the first weeks of life. Interestingly, these two antibody types rarely occur in the same patient and are associated with distinct clinical pictures. Anticentromere antibodies are more frequently observed in the context of localized scleroderma and pulmonary hypertension. Antiphospholipid antibodies Antiphospholipid antibodies bind to certain serum proteins complexed to phospholipid molecules.

Cheap 100 pills aspirin fast delivery
The beauty of well-conducted disease and exposure registers lies in the variety of questions that can be addressed using these data myofascial pain treatment center san francisco cheap aspirin 100 pills amex. They may pertain to effectiveness, safety, and costs of treatment under real-world conditions. Registers are able to overcome the drawbacks of either spontaneous reporting systems or open-label extensions of clinical trials. Therefore, registers add important knowledge on the effectiveness of treatments under real-life conditions. They may involve all patients in routine rheumatologic care such as the Scandinavian registers or a specific group of 236 Drug survival Another way of judging the effectiveness of treatments is determining the percentage of patients who remain on these drugs over time. The British, German, Swedish, and Danish registers found higher survival rates for etanercept and adalimumab than for infliximab with a slightly higher survival for etanercept than for adalimumab. Earlier reports from the British register have indicated that the likely survival of a second agent was broadly comparable to the first. All registers compared their incidence rates of malignant melanoma with their population rates. The Swedish signal was not confirmed in the other countries; only Denmark had slightly increased rates. Because of their modes of action, specific concern existed regarding whether the agents would trigger the development of lymphoproliferative disorders, solid tumors, or autoimmune diseases or lead to an increase in infections. Today we can provide some intermediate answers to the majority of these questions. This risk score was evaluated in a second cohort, showing high agreement between observed and expected infection rates. Recent data from the German register show that patients who were treated with biologic agents when they had a serious bacterial infection had a significantly lower risk of developing a sepsis and of dying from the sepsis. The registers have provided important data regarding what to expect when new treatments are used in patients who would never be included in clinical trials because of comorbidity, severe functional disability, or currently low disease activity. The registers have confirmed an increased risk of serious infection on biologic agents, and they also showed how to balance benefits and risks. There may be a small risk increase concerning skin cancer and recurrence of melanoma. Some initial concerns about an increase in the development of other autoimmune or demyelinating diseases have not materialized so far. However, we still do not know which adverse effects may result from 20 or more years of continuous immunosuppression by cytokine blockade or depletion of cells. We have learned a lot from the registers about the interaction of risks resulting from high disease activity, comorbidity, comedication, and the index treatment. Therefore, the registers underline the need for tight disease control and enable informed clinical decisions involving the patient. Differences in results between registers have driven analyses leading to more complex explanations of time-dependent risks. Therefore, it is extremely useful that we have different registers in Europe that produce their results independent of each other but collaborate closely. As new registers are set up in many countries with various indications, it is vital to ensure that the best scientific benefit is gained from them. Rheumatologists prescribing the new biologic agents have better information now on the balance of their benefits and risks, including aspects of costs to society. When new treatments arise, either entirely new substances or biosimilars, it is necessary to both evaluate them in the same manner as those currently on the market and compare the effectiveness and safety of the different agents. With longer exposure to multiple biologic treatments and more frequent switches, however, it will be increasingly difficult or even impossible to establish the influence of individual substances. Sophisticated methodology will be required to deal with the challenges of these data. To summarize the evidence, the data available so far are reassuring concerning the overall risk of cancer. Further observation should also consider potentially increased risks in subgroups of patients such as older patients or those undergoing specific additional treatments. Further risk factors were oral steroid use greater than 10 mg or intravenous boluses during the past year. Patients treated with adalimumab had a significantly increased risk compared with those treated with etanercept or infliximab. It is of clinical relevance that one third of the patients taking tocilizumab presented without any of the typical symptoms of lower intestinal perforation. Consistency and utility of data items across European rheumatoid arthritis clinical cohorts and registers. Effectiveness of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis in an observational cohort study: comparison of patients according to their eligibility for major randomized clinical trials. Do changes in prescription practice in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologics affect treatment response and adherence to therapy Effectiveness and drug adherence of biologic monotherapy in routine care of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cohort study of patients registered in the Danish biologics registry. Comparison of the response to infliximab or etanercept monotherapy with the response to cotherapy with methotrexate or another disease-modifying antirheumatic drug in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Comparative, effectiveness of tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in combination with either methotrexate or leflunomide. Direct comparison of treatment responses, remission rates, and drug adherence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab, etanercept, or infliximab: results from eight years of surveillance of clinical practice 11. Sustainability of rituximab therapy in different treatment strategies: results of a 3-year followup of a German biologics register. Effectiveness of tocilizumab with and without synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis: results from a European collaborative study. Comparison of drug retention rates and causes of drug discontinuation between anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in rheumatoid arthritis. B cell depletion may be more effective than switching to an alternative anti-tumor necrosis factor agent in rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate response to anti-tumor necrosis factor agents. Serious infection, following anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: lessons from interpreting data from observational studies. Reduction in the incidence of myocardial infarction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who respond to anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. All-cause and cause-specific mortality in rheumatoid arthritis are not greater than expected when treated with tumour necrosis factor antagonists. Cancer, risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapies: does the risk change with the time since start of treatment Risk of cancer, recurrence or new tumors in ra patients with prior malignancies treated with various biologic agents. The influence of anti-tnf or rituximab on cancer incidence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have had a prior malignancy. Does cancer that, occurs during or after anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy have a worse prognosis A national assessment of overall and site-specific cancer survival in rheumatoid arthritis 239 17. Rheumatoid, arthritis, anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy, and risk of malignant melanoma: nationwide population based prospective cohort study from Sweden. Risk of invasive melanoma in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologics: results from a collaborative project of 11 European biologic registers. Rheumatoid, arthritis, anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment, and risk of squamous cell and basal cell skin cancer: cohort study based on nationwide prospectively recorded data from Sweden. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors may predispose to significant increase in tuberculosis risk: a multicenter active-surveillance report. Risk of tuberculosis, is higher with anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody therapy than with soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor therapy: the three-year prospective French Research Axed on Tolerance of Biotherapies registry. Risk of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with inhibitors of tumour necrosis factor alpha: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rates of new-onset psoriasis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Woolf 32 Key Points the management of any musculoskeletal problem requires assessing its cause and effect and understanding the needs and expectations of the person. The physical examination is pivotal in confirming the cause of musculoskeletal problems. Assessment of the musculoskeletal system should form part of any general medical examination.
Buy genuine aspirin on line
Skeletal abnormalities may occur secondary to interference of collagen cross-linking pain treatment for bursitis discount aspirin 100pills fast delivery. Patients are at increased risk of thrombosis due to the disruption of vascular endothelium by homocysteine leading to platelet activation and aggregation. Transfusionrelated mortality: the ongoing risks of allogeneic blood transfusion and the available strategies for their prevention. Patients undergoing a transurethral prostate resection are at increased risk of bleeding from primary fibrinolysis. Transurethral prostate resection leads to the release of urokinase and tissue plasminogen activator from the prostate. However, several studies have demonstrated efficacy of antifibrinolytic agents such as Amicar (aminocaproic acid) and Cyklokapron (tranexamic acid) in the treatment of bleeding during transurethral prostate resection. Postoperative blood loss after transurethral prostatectomy is dependent on in situ fibrinolysis. Tranexamic acid in control of primary hemorrhage during transurethral prostatectomy. Bacterial contamination now accounts for 1 in every 38,500 cases of blood transfusion. Gram-negative sepsis is the most lethal (A), and Yersinia is one of the most common organisms. Gram-negative sepsis can become clinically apparent within 9-24 hours after blood transfusion. Cytomegalovirus is the most common infectious agent transmitted, but because it is so ubiquitous, it is generally not a threat to most patients. Transfusion-transmitted bacterial infection in the United States, 1998 through 2000. Hemophilia A is a sex-linked recessive genetic condition and considered the most common coagulation disorder, accounting for 80% of all inherited coagulation disorders. Other options that have been used but are only a temporary fix in patients with significant bleeding are plasmapheresis and immune absorption. Bleeding time tests platelet adhesion and aggregation and will be normal in derangement of the coagulation pathways. Drugs that inhibit platelet function, such as aspirin (which works by inhibiting cyclooxygenase), will increase bleeding time (A). Severe thrombocytopenia (quantitative) and platelet dysfunction (qualitative) both prolong bleeding time (D, E). Fibrinogen deficiency also prolongs bleeding time because fibrinogen is required for platelet aggregation. The most important element in detecting an increased risk of abnormal bleeding before surgery is a detailed history and physical examination. Other studies have likewise shown that routine use of laboratory testing is neither sensitive nor specific for determining increased risk of bleeding. One needs to inquire about a history of prolonged bleeding after minor trauma, tooth extraction, menstruation, and in association with major and minor surgery. In addition, one must make inquiries into medications and over-the-counter supplements that might affect hemostasis. If a careful history is negative and the planned surgical procedure is minor, then further testing is not necessary. A potential pitfall in relying solely on the history is that the history obtained might not be sufficiently thorough or the patients might not recall or recognize that they had previous abnormal 14. Levels should be increased to 50% of normal if major joint or intramuscular bleeding is already present and to 100% in cases of lifethreatening bleeding or before a major operation (C, D). If there is high suspicion for a history of abnormal bleeding, a hematology consult should also be obtained. Guidelines on the assessment of bleeding risk prior to surgery or invasive procedures. Preoperative clinical assessment of hemostatic function in patients scheduled for a cardiac operation. How well does the activated partial thromboplastin time predict postoperative hemorrhage Dialysis is also effective in the treatment of uremic bleeding by removing toxins that cause platelet dysfunction. Recombinant human erythropoietin (Epogen [epoetin alfa]) has been shown to help uremic bleeding in several studies as well (D). In addition to stimulating erythropoiesis, Epogen (epoetin alfa) enhances platelet aggregation. The increased red cell mass also seems to displace platelets from the center of the blood vessel and places them closer to the endothelium. The exact mechanism is unknown, but it is theorized that they decrease arginine levels, which decreases nitric oxide. In uremic patients, the bleeding time is the most useful clinical laboratory test to assess both bleeding risk and response to therapy. The etiology of abnormal bleeding in uremic patients is multifactorial, but the most important is impairment of platelet function due to a functional defect in von Willebrand factor, which leads to impaired platelet aggregation. Uremic patients may also have a decreased platelet count, but the absolute count does not accurately reflect their risk of bleeding (B). The most common bleeding manifestation in uremic patients is excessive bleeding from puncture sites, followed by nasal, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary bleeding. A key concept is that platelet defects cause superficial bleeding and defective initial hemostasis while defects to the coagulation cascade cause deep space bleeding and platelet plug instability. Thrombin time will be prolonged with a low fibrinogen level, which can be congenital or acquired (E). Primary fibrinolysis can be triggered by several conditions, including malignancy, shock, sepsis, cirrhosis, and the use of cardiopulmonary bypass. It seems to be induced by the release into the circulation of excess plasminogen activator. However, with primary fibrinolysis, inhibitors of fibrinolysis can be helpful, such as aminocaproic acid or tranexamic acid, which acts by inhibiting plasminogen activation. Amicar (aminocaproic acid) and antifibrinolytic agents (tranexamic acid) have been used in orthopedic surgery to reduce bleeding. Another antifibrinolytic, aprotinin, was frequently used in cardiac surgery for bleeding but was withdrawn because recent studies showed an increased long-term mortality rate. There is no evidence of an increased mortality rate with the use of Amicar (aminocaproic acid) and tranexamic acid. Vitamin K should be given at least 6 to 12 hours before a procedure in patients with adequate liver function. Vitamin K deficiency and D-dimer levels in the intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Is routine vitamin K supplementation required in hospitalized patients receiving parenteral nutrition Aprotinin and epsilon aminocaproic acid are effective in reducing blood loss after primary total hip arthroplasty- a prospective randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Transfusion purpura is an uncommon cause of thrombocytopenia and bleeding after transfusion. This usually presents 5 to 12 days after a transfusion and leads to profound thrombocytopenia and bleeding that can last for weeks. Although sensitization can occur after prior blood transfusions, it has become less common with leukocytereduced red cells and therefore this issue is most common in women who have been pregnant (A). The presentation can easily be confused with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia without appropriate testing.