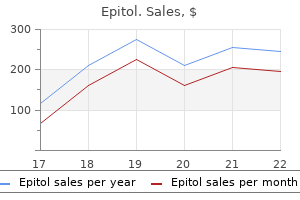
Buy discount epitol 100 mg on line
He is at high risk of cancer spread beyond the prostate and is unlikely to be cured symptoms after conception discount 100mg epitol overnight delivery. For locally advanced prostate cancer (T3 or greater), radiation therapy combined with androgen deprivation results in longer survival than radiation therapy alone. Acknowledgment he author and editors gratefully acknowledge the contributions of the previous authors, Drs. Most patients are older than 50 years, incidence increases with age, and the male-to-female ratio is 2:1 to 5:1. The ageadjusted incidence is higher among black men, and, stage-for-stage, survival among African Americans is lower overall than in whites. Death rates have been decreasing since at least 1975, with rates declining more rapidly in the past decade. The most common sites of head and neck cancer are the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, and hypopharynx in the United States. Nasal cavity, buccal, paranasal sinus cancers, salivary gland malignancies, and various sarcomas, lymphomas, and melanoma are less common. This article will limit its discussion to the more common tumors found in the head and neck region, namely squamous cell carcinomas and related histologies. Lymphomas, sarcomas, cutaneous malignancies including melanoma and thyroid gland cancer will not be discussed. Common risk factors include tobacco (smoking tobacco and other forms) and alcohol intake. Heavy alcohol consumption increases the risk of developing squamous head and neck cancer 2- to 6-fold, whereas smoking increases the risk 5- to 25-fold, depending on gender, race, and the amount of smoking. Use of smokeless tobacco, or chewing betel with or without tobacco, and slaked lime (common in many parts of Asia and some parts of Africa), is associated with premalignant lesions and oral squamous cancers. Chronic dental irritation due to ill-fitting dentures, sharp teeth, or inflammatory lesions like oral lichen planus also predispose to oral cavity cancers. Multifocal mucosal abnormalities have been described in patients with head and neck cancer ("field cancerization"). There is a 2% to 6% risk per year for a second head and neck, lung, or esophageal cancer in patients with a history of a tobacco-related cancer in this area. Second primary cancers represent a major risk factor for death among survivors of an initial squamous carcinoma of the head and neck. The supraglottic larynx comprises the epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds, false vocal cords, and ventricles. The glottis comprises the true vocal cords, anterior commissure, and posterior commissure. The subglottis extends under the glottis to the cricoid cartilage and continues as the trachea. Adult patients with any of these symptoms for more than 2 weeks should be referred to an otolaryngologist. Delay in diagnosis is common due to patient delay, repeated courses of antibiotics for otitis media or sore throat, or lack of follow-up. For nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal cancers, a common presenting symptom is a neck mass, often in a node in the jugulodigastric area and/or the posterior triangle. Symptoms like hoarseness, hemoptysis, and odynophagia or dysphagia may indicate a laryngeal or hypopharyngeal primary. Distant metastases are uncommon at presentation, but may occur with nasopharyngeal, oropharyngeal, and hypopharyngeal cancers. The most common sites of distant metastases are lung and bone; liver and central nervous system involvement is less common. Tobacco exposure (pack-years; amount chewed; and duration of habit, current or former) 3. Other risk factors (chewing betel nut, chronic dental irritation, oral lichen planus, oral submucous fibrosis, leukoplakia, or erythroplakia) 5. Cancer history of patient and family; history of immunosuppression or congenital disorder 6. Thorough review of systems the head and neck physical examination should include the following: 1. Palpation of the neck including the thyroid gland and oral cavity, assessment of tongue mobility, determination of restrictions in the ability to open the mouth (trismus), and bimanual palpation of the base of the tongue and floor of the mouth. When a neck mass with occult primary is the first presentation, the primary site can be located by clinical or flexible endoscopic examination in approximately 80% of cases. For abnormalities identified by history, physical examination, and/or endoscopy, the following evaluations should be performed. Superficial cutaneous or oral mucosal lesions, with irregular shape, erythema, induration, ulceration, and/or friability (easy bleeding) of greater than 2week duration warrant biopsy, as these frequently are early indicators of severe dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, or invasive malignant process. Surgical biopsy of a neck mass before endoscopy is generally not advisable if a squamous cell carcinoma is suspected. Intraoperative endoscopic biopsy is then done with a secure airway under anesthesia. Esophagoscopy and bronchoscopy may be indicated for symptoms such as dysphagia, hoarseness, cough, or to search for occult primary. Laboratory tests typically obtained prior to initiating therapy include complete blood counts, renal and liver function tests, serum calcium and magnesium (if platinum-based chemotherapy is to be given), baseline thyroid function tests, and pregnancy testing in females of child-bearing age. Dental evaluation should be performed and any necessary extractions should be carried out at least 2 weeks prior to any planned radiation. Baseline speech, swallow, and audiometry evaluation may be indicated depending on the primary site involved and the treatment anticipated. Clinical staging is based on physical and endoscopic examinations and imaging tests. The staging of primary tumors is different for each site within the head and neck, although some common themes exist. The objective is to achieve high rates of locoregional control and cure while limiting morbidity of treatment and preserving functional outcomes. The choice of modality is dependent on how best these goals are achieved along with availability of expertise and patient choice. Two or more treatment modalities are often combined to achieve optimal disease control. For example, while primary surgery is considered standard for oral cavity cases, radiation with chemotherapy might be considered for laryngeal cancer cases. Examples include surgery followed by adjuvant chemoradiation for locally advanced oral cavity cancers or surgical salvage after definitive chemoradiation for oropharynx/larynx/hypopharynx cancers. While organ preservation remains an important goal for larynx and hypopharynx cancers, disease control is the primary objective. Multimodality therapy including surgical resection is often required to reduce the risk of locoregional recurrence and/or distant metastases and improve survival when organ preservation is not possible. These categories may have a long natural history and a comparatively long disease course with therapy. The large bulk of recurrent/metastatic cancers are best treated with palliative therapy. Palliative radiation, palliative chemotherapy, or a combination of the two is often used. Occasionally surgery might be used to debulk the cancer and offer quick relief of symptoms. A tracheostomy may be necessary for airway compromise and a feeding tube procedure may be required for alimentation. High-dose radiation with stereotactic techniques may be used to achieve durable palliation with lower toxicity rates. Early intervention with hospice care and palliative medicine may be appropriate during the course of disease. For the primary cancer, surgical goals include resection of the tumor with an adequate margin (usually 0. Exceptions include resection of sinus tumors via an endoscopic approach as opposed to an open surgical approach. The extent of primary oncologic cancer surgery depends on the subsite involved and is variably described as such. For example, oral tongue cancer surgery can span the spectrum of wide local excision to hemiglossectomy to total glossectomy depending on the extent of the disease.
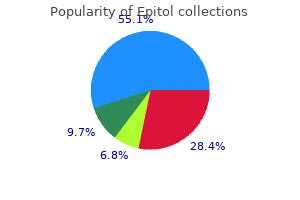
Epitol 100 mg amex
A prospective study to assess in vivo optical coherence tomography imaging for early detection of chemotherapyinduced oral mucositis medications in spanish generic epitol 100mg with amex. Using high throughput sequencing to explore the biodiversity in oral bacterial communities. Patient-reported measurements of oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy: Demonstration of increased frequency, severity, resistance to palliation, and impact on quality of life. Oral mucosal injury caused by mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors: Emerging perspectives on pathobiology and impact on clinical practice. Oral mucosal changes induced by anticancer targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Managing stomatitis in patients treated with mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors. Preliminary characterization of oral lesions associated with inhibitors of mammalian target of rapamycin in cancer patients. Stomatitis associated with mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition: A review of pathogenesis, prevention, treatment, and clinical implications for oral practice in metastatic breast cancer. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: V. Treatment of oral mucosal manifestations of chronic graft-versus-host disease: Dexamethasone vs. Patients with treatmentrequiring chronic graft versus host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation have altered metabolic profiles due to the disease and immunosuppressive therapy: Potential implication for biomarkers. Effect of leaving chronic oral foci untreated on infectious complications during intensive chemotherapy. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: A global perspective. Identification of Candida species in patients with oral lesion undergoing chemotherapy along with minimum inhibitory concentration to fluconazole. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw-2014 update. Disease stage and mode of therapy are important determinants of treatment outcomes for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Weyant, ms, dmd, drph the interdisciplinary field of human genomic science has grown rapidly over the last two decades as key technologic developments have led to landmark projects and a newfound capacity to generate vast quantities of biologic data. In turn, these developments have led to the birth of new fields of study and accelerated the pace of biomedical research. We find ourselves in a world where whole genomes can be quickly and cheaply sequenced. To accommodate the immensity of the data generated, information storage systems have been stretched to the point where the cost of storing these data may in some cases exceed the cost of simply regenerating the data from a stored biologic sample. And despite the numerous computational and bioinformatics tools that have been developed to manage, analyze, and interpret these data, our current capacity to produce genomic data far outstrips our ability to make sense of it. The specific 292 answers to these questions are difficult to predict, in part because of how rapidly the state of the science has evolved. The overwhelming trend in genomic science is one of increasing complexity, with new genomic discoveries often revealing that the gap between basic science and clinical application is wider than previously thought. The reality in dentistry is that genomic science has of yet not contributed in substantial ways to direct improvements in routine patient care, but this will not always be so. We are confident that the benefits that come from the precision medicine initiative will ultimately contribute in important ways to improved dental care as well. As we approach the study of the genetic basis of oral disease and its possible linkage with systemic disease, it should be kept in mind that almost all diseases arise through some interaction of environmental (eg, social, chemical), behavioral (eg, smoking, exercise), and biologic (eg, genetic) mechanisms. It is important not to limit our thinking about common risks among various diseases to only one domain or mechanism. In this article we review genetic risk, but in most cases, genetic risk can be highly variable based on interactions with environmental and behavioral factors. In this article we focus on issues of importance to clinical dentists and patient care. We start with the current state of genomic science State of Genomic Science by describing the technologies, research methodologies, and conceptual approaches used to investigate the genetic basis of disease. Next, we briefly review our understanding of the genomic basis of selected oral diseases and where genetic research may suggest that oral and systemic disease share a common pathophysiology or causal relationship. Finally, we touch on how our growing understanding of the genetic basis of oral diseases will play an expanding role in clinical dentistry in the future. The Human Genome Project Launched in 1990 based on plans formed in the mid-1980s, this international initiative to sequence the human genome was audacious in scope and difficulty given the technology of the time. These far-reaching implications are all based on the creation of a fairly simple information resource: the reference sequence of approximately 3 billion nucleic acid base pairs in the human genome. Most of these diseases are associated with serious morbidity but also tend to be rare in the general population. It took several more decades for the technology to mature and allow for the study of polygenic (ie, contributions of many genetic variants of small individual effects) disease. The diseases that carry the most social consequences due to their high prevalence in the general population are polygenic diseases, often referred to as common complex diseases. To shed light on the current state of genomic science, consider some seminal projects that the International HapMap and 1000 Genomes projects With the human reference genome complete, the International HapMap Project6,7 (2002 to 2009) was conceived to map the haplotype (ie, inheritance of multiple genetic variants together as a group from a single parent) and correlational structure of the human genome, representing important patterns of human genetic variation. Eleven ancestry groups from across the world were represented, including 293 14 Oral-Systemic Health: the Genomic Connection European Americans, African Americans, Chinese Americans, Mexican Americans, and Gujarati Indians from the United States, as well as people from China, Japan, Nigeria, Kenya, and Italy. Whereas the Human Genome Project provided an initial reference point for the genomic sequence, the International HapMap Project provided detailed information about the differences in this sequence between individuals and between populations, and it greatly expanded (by many millions) the list of known polymorphic sites in the human genome. A key advancement provided by the International HapMap Project was its utility as the first "imputation base"-that is, a reference of the correlation across polymorphic sites, which allowed researchers to impute alleles of unobserved genetic loci based on the loci genotyped in an experimental sample. In other words, genotyping projects could leverage the HapMap reference data to collect much higher-resolution genetic data based on lower-resolution genotyping. As a successor to the International HapMap Project, with a similar goal of cataloging human genetic variation, the 1000 Genomes Project8,9 was launched in 2008 and employed newly developed high-throughput sequencing technologies to sequence the genomes of over a thousand people across multiple ethnicities. The major contribution of the 1000 Genomes Project was to provide a more comprehensive catalog of human genetic variation than previously known, which has proved to be a valuable resource for disciplines such as genomics, bioinformatics, human evolution, genetic epidemiology, and pharmacogenomics. Advances in the field these seminal projects and others have rapidly reshaped our current understanding of the human genome and its roles in health and disease. The organizational structure of the genome is depicted from chromosome to double helix. The blue boxes represent the methods and tools, mostly based on high-throughput sequencing technologies, used to collect multiomics data on functional elements. Black arrows represent the correspondence between method, target of the assay, and functional element. Further work has shown that even this estimate was high, as there is currently believed to be approximately 20,000 protein-coding genes comprising only 1. Transcription is possible for active (open) chromatin (top), characterized by unmethylated cytosines (white circles) and acetylated histones. Transcription is impeded for inactive (silent) chromatin (bottom), characterized by methylated cytosines (red circles) and deacetylated histones. Histone methylation (not depicted) also differs between active and inactive chromatin. In fact, 80% of the noncoding sequence of the genome is functional in the sense that it is involved in biochemical activities relevant to biomedical sciences. Other sequences affect the packaging of the genome within the nucleus of the cell, which is itself a major modality of gene regulation. These insights into the composition and structure of the human genome have also reshaped our understanding of the genetic basis of human disease. Whereas genetic disease had traditionally been viewed as the result of a disruption of a protein-coding gene that was passed on through families under relatively simple inheritance models (eg, dominant, recessive, sex-linked), we now know that the contributions of genetics to human disease also operates through regulatory variants and epigenetic modifications. In fact, an important theme that has emerged from genomic studies is that the majority (about 90%) of disease-associated variants are regulatory in nature rather than protein-coding. These studies have been made possible through the use of high-throughput genotyping and sequencing technologies, many of which were developed or honed via the seminal genomics projects described earlier. Among the most important genomic technologies of the last decade was the development of high-throughput sequencing methods, also known as massively parallel sequencing or next-generation sequencing. Billions of these snippets, known as reads, must then be assembled into one continuous sequence guided by their partial overlap, which is a computationally intensive task made possible by concurrent advancements in computing power.
Order epitol once a day
Through inflammatory pathways symptoms jaundice buy generic epitol 100 mg on-line, these cytokines interfere with insulin-signaling homeostasis. Therefore, carbohydrate metab- olism, hormonal control, and inflammatory mediators together influence health during pregnancy and the outcome of labor. As the understanding of inflammation pathways has matured, a better understanding of the molecular basis of resolution of inflammation has emerged. Resolution of inflammation involves an active, agonist-mediated, well-orchestrated return of tissue homeostasis. The distinction between anti-inflammation and resolution has biologic and clinical relevance. Anti-inflammation involves pharmacologic blocking of specific inflammatory pathways; resolution is mediated by physiologic pathways that restore homeostasis. Animal models of periodontitis have revealed the potential of this therapeutic approach for prevention and treatment and forced reconsideration of the understanding of the pathogenesis of human periodontal diseases72 (see Table 4-1; for review, see Freire and Van Dyke73). The importance of agonists of resolution in eliminating inflammation has been confirmed in demonstrations of control of systemic inflammatory disease by exogenous addition of excess lipoxins or resolvins. The report provided support and a rationale for the mechanism of the observed connections as well as a basis for the clinical concern that periodontitis increases the risk for many important systemic inflammatory diseases. A more precise picture is also emerging of the central role of inflammation in association with metabolism and microbiome in the local and systemic compartments. The target of periodontal therapy, whether control of the biofilm or control of local inflammation, is control of systemic inflammation associated with chronic systemic diseases. Resolving inflammation: Dual anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution lipid mediators. Review of osteoimmunology and the host response in endodontic and periodontal lesions. Impaired phagocytosis in localized aggressive periodontitis: Rescue by Resolvin E1. Conclusion the link between oral and systemic inflammatory processes and its consequences are directly related to the tissue response to challenge, usually microbial, and inflammation. This biologic process is controlled by the balance between mediators and sensors that amplify the inflammatory process and those that regulate the return to homeostasis. Diseases associated with uncontrolled acute inflammation are characterized by insufficient actions of resolution programs and inappropriate release and maintenance of high levels of toxic substances and proinflammatory mediators that may result in damage to host tissues and prolong the inflammatory response. In experimental animal models, compelling evidence demonstrates the actions of proresolution mediators in the regulation of local and systemic inflammatory responses, elucidating the role of endogenous mediators in systemic inflammatory processes and disease regulation. A clearer picture of 99 4 the Role of Inflammation in Oral-Systemic Interactions 14. Bringing light to the heat: "Inflammation and periodontal diseases: A reappraisal. A review of the evidence for pathogenic mechanisms that may link periodontitis and diabetes. Periodontal treatment with topical antibiotics improves glycemic control in association with elevated serum adiponectin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. No evidence for mouse pancreatic beta-cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Effect of periodontal disease on diabetes: Systematic review of epidemiologic observational evidence. Toothbrushing, inflammation, and risk of cardiovascular disease: Results from Scottish Health Survey. Levels of periodontal pathogens in neonatal gastric aspirates and possible maternal sites of origin. Fusobacterium nucleatum induces premature and term stillbirths in pregnant mice: Implication of oral bacteria in preterm birth. Periodontal status and neutrophilic enzyme levels in gingival crevicular fluid during pregnancy and postpartum. Resolution of inflammation: A new paradigm for the pathogenesis of periodontal diseases. Reduced inflammation and tissue damage in transgenic rabbits overexpressing 15-lipoxygenase and endogenous anti-inflammatory lipid mediators. RvE1 protects from local inflammation and osteoclast-mediated bone destruction in periodontitis. Resolvin E1 regulates inflammation at the cellular and tissue level and restores tissue homeostasis in vivo. Molecular circuits of resolution: Formation and actions of resolvins and protectins. Resolvin E1, an endogenous lipid mediator derived from omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid, protects against 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis. Resolvin D1 controls inflammation initiated by glutathione-lipid conjugates formed during oxidative stress. Resolvin D1 limits polymorphonuclear leukocyte recruitment to inflammatory loci: Receptor-dependent actions. Maresins: Novel macrophage mediators with potent antiinflammatory and proresolving actions. Lipoxin A4 analogs attenuate induction of intestinal epithelial proinflammatory gene expression and reduce the severity of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Resolvin E1, an endogenous lipid mediator derived from eicosapentaenoic acid, prevents dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Omega-3 fatty acid-derived mediators 17(R)hydroxy docosahexaenoic acid, aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 and resolvin D2 prevent experimental colitis in mice. Increased dietary intake of omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids reduces pathological retinal angiogenesis. Lamster, dds, mmsc Nadia Laniado, dds, mph Ilene Fennoy, md, mph Obesity has been identified as a major health problem across the globe. In the United States, it has been estimated that state-specific medical expenditures would be 6. Given the negative effects of obesity on health and an expanding literature on the relationship between obesity and oral disease, all oral health care professionals must consider the impact of obesity on the provision of oral health care services. By ethnicity, black (22%) and Hispanic (25%) children had the highest prevalence of obesity, with non-Hispanic whites having a 14. Children demonstrate these same trends in overweight and obesity, with increases from 16. Prevalence was higher at all ages in developed countries compared to developing countries. However, there are distinct geographic patterns for the prevalence of overweight and obesity, with the Middle East, North Africa, and Oceania and Micronesia demonstrating some of the highest numbers for children and adults. Globally, 62% of all persons with obesity live in developing Etiology of Obesity countries, though the United States accounts for 13% of all persons with obesity. However, the etiology of that imbalance has been shown to be at least 50% genetic,26,27 while the remainder involves environmental, psychologic, socioeconomic, and physiologic factors. Additionally, the prenatal problem of intrauterine growth restriction is associated with childhood obesity and insulin resistance. High-fat diets have been hypothesized as responsible for the increasing obesity of populations based on their contribution to increased energy density. Certain dietary components, however, have been identified as more commonly associated with weight gain. Non-Hispanic black persons consume the greatest amount as a percent of total calories ingested, both children (8. The independent contributions of physical activity and sedentary behaviors to obesity have been demonstrated by Stamatakis et al66 in adults and Loprinzi et al63,64 in children. Efforts to modify lifestyle behaviors for prevention or treatment of obesity must address both sedentary behavior and physical activity. Emphasis on the importance of a healthy lifestyle, which is a potential new practice activity for oral health care providers and is discussed later in this chapter, includes increased physical activity. Pathophysiology of Obesity Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance Adipose tissue is a vibrant, active tissue involved in physiologic and immune regulation. Adipose tissue demonstrating both adipocytes, preadipocytes, endothelial cells, and M1 macrophages with their secretory products, which support inflammation.
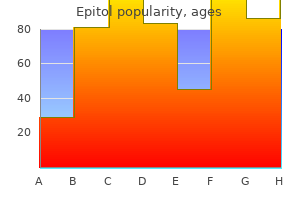
Purchase epitol 100 mg on-line
Miscellaneous: thrombophlebitis medications cause erectile dysfunction generic 100 mg epitol otc, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, membranous nephropathy. It is useful in follow-up and monitoring response to therapy, but not for screening. Gastric tumors involving muscolaris propria (T2), subserosa (T3), and serosa (T4a) are considered resectable whereas tumors with invasion of adjacent structures (T4b) are not. Nodal stage relates to number of involved regional nodes: N1, 1 to 2 involved nodes; N2, 3 to 6 involved nodes; N3a, 7 to 15 involved nodes; and N3b, 16 or more involved nodes. The presence of positive peritoneal cytology is considered M1 as are distant metastases. Prognostic implications of the seventh edition of the international union against cancer classification for patients with gastric cancer: the Western experience of patients treated in a single-center European institution. Initial upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and double-contrast barium swallow identify suggestive lesions and have diagnostic accuracy of 95% and 75%, respectively, but add little to preoperative staging otherwise. Endoscopic ultrasonography assesses the depth of tumor invasion (T staging) and nodal involvement (N staging) with accuracies up to 90% and 75%, respectively. Computerized tomographic scanning is useful for assessing local extension, lymph node involvement, and presence of metastasis, although understaging occurs in most cases. Other prognostic variables that have been proposed to be associated with an unfavorable outcome include the following: Older age Male gender Weight loss greater than 10% Location of tumor Tumor histology: Diffuse versus intestinal (5-year survival after resection, 16% vs. The high rate of recurrence and poor survival of patients following surgery provide a rationale for the use of adjuvant or perioperative treatment. In advanced gastric cancer, chemotherapy enhances quality of life and prolongs survival when compared with the best supportive care. However, there is a pressing need for assessing new agents, both cytotoxic and molecularly targeted, in the advanced and adjuvant settings and enrollment in clinical trial is highly encouraged. Resectable Disease Surgery Complete surgical resection of the tumor and adjacent lymph nodes remains the only chance for cure. An exploration to exclude carcinomatosis just prior to the definitive resection is justified in this disease. Current surgical issues include subtotal versus total gastrectomy, extent of lymph node dissection, and palliative surgery. Extent of Lymph Node Dissection Regional lymph node dissection is important for accurate staging and may have therapeutic benefit as well. The extent of lymphadenectomy is categorized by the regional nodal groups removed (Table 5. D2 lymphadenectomy is reported to improve survival in patients with T1, T2, T3, and some serosa-involved (currently T4a) lesions as compared to D1. However, factors such as operative time, hospitalization length, transfusion requirements, and morbidity are all increased. The routine inclusion of splenectomy in D2 resections is no longer advocated given higher postoperative complications. The greatest benefit of more extensive lymph node dissection may occur in early gastric cancer lesions with small tumors and superficial mucosal involvement as up to 20% of such lesions have occult lymph node involvement. Radiation Therapy For patients with locally advanced or metastatic disease, moderate doses of external-beam radiation can be used to palliate symptoms of pain, obstruction, and bleeding but do not routinely improve survival. Local or regional recurrence in the gastric or tumor bed, the anastomosis, or regional lymph nodes occurs in 40% to 65% of patients after gastric resection with curative intent. The high frequency of such relapses has generated interest in perioperative therapy. A prospective randomized trial from the British Stomach Cancer Group failed to demonstrate a survival benefit for postoperative adjuvant radiation alone, although locoregional failures had decreased from 27% to 10. Although neoadjuvant therapy may reduce the tumor mass in many patients, several randomized controlled trials have shown that compared with primary resection, a multimodal approach does not result in a survival benefit in patients with potentially resectable tumors. However, predicting those likely to benefit from this approach remains an ongoing research question. Although treatmentrelated mortality was 1% in this study, only 65% of patients completed all therapy as planned and many had inadequate lymph node resections (54% D0). In a randomized controlled trial, patients were randomized to 1 year of monotherapy or surveillance alone. S-1 is approved for adjuvant therapy for gastric cancer in Japan and for advanced gastric cancer in Europe, but it is not commercially available in the United States. There appeared to be significant downstaging by chemotherapy treatment, with more patients deemed by the operating surgeon to have had a "curative" resection (79% vs. Toxicity was feasible with postoperative complications comparable; however, nearly one-third of patients who began with preoperative chemotherapy did not receive postoperative chemotherapy owing to progressive disease, complications, or patient request. A French multicenter trial also showed a survival benefit for perioperative chemotherapy. Curative resection rate was significantly improved with perioperative polychemotherapy (84% vs. Postoperative Chemoradiotherapy versus Perioperative Chemotherapy There are no randomized controlled trials directly comparing these two standards of care. After >4 years follow-up, no significant difference in locoregional recurrences (8. Unresectable or Metastatic Disease Primary goals of therapy should focus on improvement in symptoms, delay of disease progression, pain control, nutritional support, and quality of life. Although a role for palliative surgery and radiotherapy exists (see previous sections), chemotherapy remains the primary means of palliative treatment in this setting. The most commonly administered chemotherapeutic agents with objective response rates in advanced gastric cancer include mitomycin, antifolates, anthracyclines, fluoropyrimidines, platinums, taxanes, and topoisomerase inhibitors. Monotherapy with a single agent results in a 10% to 30% response rate with mild toxicities (Table 5. Complete responses with single agents are rare and disease control is relatively brief. Combination chemotherapy provides a better response rate with survival advantage over best supportive care in randomized studies. Gastrojejunostomy bypass surgery alone may provide a 2-fold increase in mean survival. The selection of patients most likely to benefit from this or other palliative surgical interventions require further evaluation with prospective studies and multidisciplinary conference discussion. Palliative Chemotherapy Various combinations of active agents have been reported to improve the response rate (20% to 50%) among patients with advanced gastric carcinoma (Table 5. The addition of cisplatin into combination regimens was supported by subsequent studies in both Europe and the United States. The combination of a fluoropyrimidine and platinum is most commonly used in the United States. Cytotoxic Chemotherapy Agents Chemotherapeutic agents, including irinotecan, docetaxel, paclitaxel, and alternative platinums and fluoropyrimidines, have shown promising activity as single agents and have been actively incorporated into combination therapy (see Tables 5. In a Japanese study, 20% of patients who showed no response to previous chemotherapy had a partial response to monotherapy with docetaxel. The lack of survival benefit but improved toxicity profile could have been due to the lower dose of cisplatin used in the cisplatin/S-1 arm. It was formally evaluated with encouraging results in combination with a platinum alternative. Oxaliplatin is a third-generation platinum with less nephrotoxicity, nausea, and bone marrow suppression than cisplatin. Biologic/Targeted Agents/Immunotherapy New biologic therapies designed to inhibit or modulate targets of aberrant signal transduction in gastric cancer have been actively investigated. In contrast, a breast tumor must demonstrate complete circumferential membrane staining to be designated as 2+ or 3+. It is noteworthy that few patients had received prior trastuzumab (only 7% in lapatinib arm and 15% in combination). This agent has minimal activity as a single agent while in combination with doublet or triplet chemotherapy regimens it showed variable overall response rates (Table 5. The addition of cetuximab provided no benefit in progressionfree survival but added toxicity. The addition of panitumumab to chemotherapy significantly reduced survival from 11. Ramucirumab was associated with significantly improved median progression free (2.
Purchase generic epitol line
Should we insert a breathing tube and attach him to a ventilator if he cannot breathe well enough by himself Talking to his other physicians and reading the chart lead me to recommend that we should not continue this aggressive treatment medications versed order epitol with visa. Palliative management of fatigue at the close of life: "it feels like my body is just worn out". An oicial American thoracic society statement: update on the mechanisms, assessment, and management of dyspnea. Barriers to nausea management, end of life conversations, early palliative care interventions, and patient education. Which of the following discussion points about lung cancer screening in asymptomatic current or former heavy smokers is true Laboratory results are notable for total testosterone 180 mg/dL, repeat 160 mg/dL. Despite aggressive diuresis, she remains volume overloaded with declining renal function. She wants to go home, but her son disagrees and wants her care to be pursued more aggressively. Which of the following is true regarding palliative care in patients with advanced heart failure Palliative care focuses on the psychosocial needs of patients and families in addition to their physical needs. A 65-year-old professor presents after a colleague found him wandering, unable to ind his oice. His wife reports two episodes when he thought that one of his former graduate students was at the dinner table and that during sleep he often thrashes around violently. On examination, the patient is orthostatic, with slowed speech, some limb rigidity, and a shuling gait. You diagnose a cervical radiculopathy, refer him for physical therapy, and prescribe tramadol for pain. On examination, he has dilated pupils, rigidity, hyperrelexia, and spontaneous clonus. Her examination is notable for cervical friability and bilateral adnexal tenderness. He takes lisinopril 40 mg, hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, amlodipine 10 mg, and naproxen 500 mg bid. An ambulatory monitor conirms hypertension, which does not improve with discontinuation of naproxen. If you have a test for X that is 90% sensitive and 90% speciic, what fraction of patients with a positive test truly have disease X She is healthy, with no medical history except for vaginal hysterectomy for menorrhagia 5 years ago. Compounded bioidentical hormones provide a better safety proile than synthetic estrogen preparations. Low-dose conjugated equine estrogens plus medroxyprogesterone acetate would be a good choice for her. Transdermal estrogen alone is contraindicated because of increased risk of breast cancer. Hepatitis serologies are negative, transferrin saturation is normal, and testing for autoimmune 18. In addition to weight loss, what is the most appropriate pharmacologic intervention Metformin A 35-year-old female presents with complaints of "spider bites" on her legs. Her examination is notable for clear lungs, ankle swelling, and dusky, tender nodules on her lower extremities. Mediastinoscopy A 65-year-old female presents with 2 weeks of progressive knee pain that began after an evening of dancing at a wedding. On examination there is swelling and tenderness about 2 inches below the joint, medially. Patellar tendinitis A 47-year-old male presents after a spell of left arm weakness that lasted 10 minutes then resolved spontaneously. He has recently been diagnosed with diabetes and is being evaluated for abnormal liver function tests. On examination he has notable bony enlargement of second and third metacarpals but no active synovitis. A 24-year-old woman presents with dysuria and frequency without fever, back pain, or vaginal discharge. A 21-year-old college student presents to your oice complaining of fever, cough, sneezing, and watery eyes. Postexposure prophylaxis with ciproloxacin should be provided for susceptible contacts. Advanced heart failure is the leading cause of hospitalizationforpeopleage>65yearsintheUnitedStates. It is a terminal illness characterized by decompensations and recoveries, often with failure to achieve prior level of functioning. Decision making in advanced heart failure: a scientiic statement from the American Heart Association. Preferences for quality of life or survival expressed by patients with heart failure. No symptoms or examination indings to suggest pheochromocytoma or hypercortisolism. Bladder storage phase symptoms of urgency, frequency, and nocturia are consistent with overactive bladder, in contrast to voiding phase symptoms of incomplete emptying, weak stream, hesitancy/intermittency, which are more consistent with bladder outlet obstruction. Although this patient has an enlarged prostate, he has no symptoms of bladder outlet obstruction, and his postvoid residual is not increased. Test positive Test negative Diseased 9 1 10 Not Diseased 9 81 90 18 82 100 Sensitivity: proportion of patients with disease who test positive 9/10 = 90% Speciicity: proportion of patients without disease who test negative 81/90 = 90% Positive predictive value: proportion of patients with positive test who have the disease 9/18 = 50% 14. Risk factors for breast cancer for women aged 40 to 49 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. As advances in medical technology continue to push the ability to detect, treat, and impact disease states, there is increasing attention to the utility of screening and its role in periodic health assessments. As laid out in a landmark article from 1968, efective screening is predicated on several major tenets: 1. Whereas many screening tests meet the aforementioned criteria, clear evidence that screening improves mortality for a given disease can be more elusive. Studies to assess the eicacy of screening interventions are susceptible to several types of biases. In general, randomized controlled trials rather 1166 than observational studies help avoid these pitfalls and most accurately assess mortality beneits. In the United States, there are several sources for physicians to obtain up-to-date practice guidelines on evidencesupported health screening information. Evidence supports a small but clinically signiicant mortality reduction from screening for breast cancer, particularly among women age 50 years. For women between the ages of 40 and 50, whereas the relative risk reduction from mammography is similar, the absolute beneit from screening is much smaller with high risks of false-positive screens.

Pomegranate. Epitol.
- Dosing considerations for Pomegranate.
- Chronic lung disease (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD).
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Pomegranate work?
- What is Pomegranate?
- High cholesterol (hyperlipidemia), heart disease, intestinal worm infestations, high blood pressure (hypertension), hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), obesity and weight loss, gum disease, fungal mouth infections, diarrhea, dysentery, sore throat, hemorrhoids, prostate cancer, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96406
Cheap epitol american express
No therapy is warranted for preinvasive lesions; colposcopy treatment thesaurus discount epitol 100 mg without prescription, but not endocervical curettage, is recommended to rule out invasive cancer. Conization is reserved for suspicion of invasion or for persistent cytologic evidence of invasive cancer in the absence of colposcopic confirmation. If cancer is diagnosed before fetal maturity, immediate appropriate cancer therapy for the relevant stage is recommended. For more advanced disease, delaying therapy is not recommended unless diagnosis is made in the final trimester. When the fetus reaches acceptable maturity, a cesarean section precedes definitive treatment. Each examination should include a thorough visual inspection of the anus, vulva, vagina, as well as the uterine cervix. Follow-up visits, including thorough physical examination, should occur every 3 to 6 months in the first 2 years posttherapy, every 6 to 12 months for the following 3 years then annually to detect any potentially curable recurrences. Additionally, patients should have annual cervical or vaginal cytology, though an exception can be made for those that have undergone pelvic radiation. Patients should be counseled about signs and symptoms of recurrence to include persistent abdominal and pelvic pain, leg symptoms such as pain or lymphedema, vaginal bleeding or discharge, urinary symptoms, cough, weight loss, and anorexia. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that females aged 9 to 12 years of age be vaccinated by the three (3) dose regimen. Comparison of risk factors for invasive squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the cervix: collaborative reanalysis of individual data on 8,097 women with squamous cell carcinoma and 1,374 women with adenocarcinoma from 12 epidemiological studies. Natural history of cervical neoplasia and risk of invasive cancer in women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 3: a retrospective cohort study. Pelvic radiation with concurrent chemotherapy compared with pelvic and para-aortic radiation for high-risk cervical cancer. Concurrent chemotherapy and pelvic radiation therapy compared with pelvic radiation therapy alone as adjuvant therapy after radical surgery in high-risk early-stage cancer of the cervix. Concurrent cisplatin-based radiotherapy and chemotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer. Posttreatment surveillance and diagnosis of recurrence in women with gynecologic malignancies: Society of Gynecologic Oncologists recommendations. A total of 5,950 new cases and 1,110 deaths from vulvar cancer were projected for 2016. It is most frequently diagnosed in postmenopausal women, with a median age of diagnosis of 68 years. The rate of vulvar cancer has remained stable over the past 20 years, however the incidence of its precursor (vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia 3) has doubled. Signs and symptoms in order of decreasing frequency are pruritus, mass, pain, bleeding, ulceration, dysuria, and discharge. Diagnostic Workup Biopsy must include adequate tissue to determine histology and grade, depth of invasion, and stromal reaction present. Use of colposcopy following application of 5% acetic acid solution is helpful in delineating multifocal lesions, which occur in 5% of cases. Cystoscopy, proctoscopy, chest x-ray, and intravenous urography should be performed as needed based on the extent of disease. Studies suggest a high overall incidence of local recurrence following primary surgical treatment. Disease presence at the excised tumor margin has been postulated as a significant prognostic factor for recurrence. Management Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia 2/3 Therapeutic options are based on individual patient need and can include any of the following: Surgical excision. Patients with inoperable disease can achieve long-term survival with radical chemoradiation therapy. Radiation fraction size of 180 cGy has been proven to minimize the radiation complication rate. Radical vulvectomy and pelvic exenteration are not commonly used due to extensive morbidity and uncertain survival benefit. Chemotherapy choices for advanced, recurrent/metastatic disease commonly include cisplatin, cisplatin/vinorelbine, or cisplatin/paclitaxel. Verrucous carcinoma is very rare and can be confused with condyloma acuminatum because of an exophytic growth pattern. Radiation therapy is contraindicated because it is ineffective and can potentially lead to more aggressive disease. Although Paget disease is histologically a preinvasive disease locally, it should be treated with radical wide local excision, as with other vulvar malignancies. Patients require radical excision, often with intraoperative frozen section confirmation of clear margins, because microscopic disease often extends beyond the gross visual margin observed by the operating surgeon. Suggested therapy is radical vulvectomy with inguinal and pelvic lymphadenectomy, although there is a current trend toward a more conservative approach. For most well-demarcated lesions, 2 cm margins are suggested for thin (up to 7 mm) lesions and 3 to 4 cm margins for thicker lesions. Enlargement of the Bartholin gland area in postmenopausal women requires evaluation for malignancy with biopsy. Therapy includes radical vulvectomy with wide excision to achieve adequate margins and inguinal lymphadenectomy. Basal Cell Carcinoma the natural history and therapeutic approach for basal cell carcinoma are similar to those for primary tumors seen in other sites. Shepard Epidemiology Sarcomas are tumors of mesenchymal tissues and represent about 1% of adult cancers and about 10% of pediatric cancers. Soft Tissue Sarcoma Clinical Presentation Patients with soft tissue sarcomas rarely have constitutional symptoms, such as weight loss or increased fatigue. They may experience pain, paresthesia, or edema from compression by an enlarging tumor. While soft tissue sarcomas can occur throughout the body, the majority of them are in the extremities. In one series of 4500 sarcomas, 46% were in the groin, thigh, or buttock; 13% in the upper extremity; 18% in the torso, and 13% in the retroperitoneum. Red flags that suggest presence of a soft tissue sarcoma include Mass greater than 5 cm in size Rapid growth of the mass Mass that is deep to the fascia New pain in a previously painless mass Recurrence of a mass Pathology the World Health Organization classifies soft tissue sarcomas into over 100 subtypes based on histology with designation based on the presumed tissue of origin, such as liposarcoma, synovial sarcoma, fibrosarcoma, peripheral nerve sheath tumors, or angiosarcoma. Pathology should be reviewed by a center that specializes in sarcoma to ensure the proper diagnosis based on morphology, immunohistochemistry, and molecular genetic studies. Tumors should be sampled with image-guided core needle biopsies or an incisional biopsy with a preference for a needle biopsy. A sentinel lymph node biopsy should be obtained in patients with enlarged nodes by palpation or imaging and sarcomas likely to have lymphatic spread (rhabdomyosarcoma, angiosarcoma, clear cell sarcoma, epithelioid sarcoma, or synovial sarcoma). There are no serum or plasma biomarkers that should be used for diagnosis, assessing treatment response, or monitoring for recurrence of disease. Treatment Surgery is the treatment of choice for patients with a primary sarcoma of the extremity or the trunk. Negative surgical margins are associated with improved overall survival and surgery is usually done with at least a 1 cm margin with consideration for presence of bone or fascia as a margin. Involvement of the bone or vasculature or the inability to achieve proper margins requires discussion of amputation. Radiation therapy with imageguided external beam radiation should be considered either preoperatively or postoperatively for patients with intermediate or high-grade soft tissue sarcomas. Brachytherapy is an alternative for radiotherapy delivery at the time of surgery either alone or in combination with external beam radiation. Neoadjuvant radiation therapy should also be considered for patients with low-grade tumors if this may improve the likelihood for appropriate surgical margins. There are conflicting data for the use of neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with soft tissue sarcoma of an extremity. A metaanalysis of 1953 patients enrolled in 18 trials failed to show a survival benefit for treatment with adjuvant doxorubicin, but there was a significant hazard ratio for the combination of doxorubicin and ifosfamide. However, a separate pooled analysis of 2 large trials of patients treated with adjuvant doxorubicin and ifosfamide was negative. Trials have not identified the patients most likely to benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy with inconsistent data on the importance of completeness of resection, tumor size, and tumor grade. Similarly, there is no consensus in the literature on the role of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Even trials enriched for large- or high-grade tumors or utilizing chemotherapy thought to be more specific, for the tumor histology failed to show a benefit.
Syndromes
- People with nervous system (neurological) disorders
- Follows a fast moving object
- Increased night-time urination (nocturia)
- Nausea, vomiting
- Splenic infarction (tissue death)
- Do not drink alcohol, especially if you have liver damage
- Cryptosporidium enterocolitis (or other protozoal infections)
Purchase epitol overnight
Otherwise symptoms 9dpo bfp generic epitol 100 mg free shipping, for low risk or intermediate-1 risk patients, or non-transplant candidate higher risk patients, management is directed toward relieving symptoms caused by splenomegaly or cytopenias, and decreasing risk of further progression. Erythropoietin replacement is a consideration in patients with inappropriately low erythropoietin levels (<500 mU/mL in the setting of anemia can be considered as inappropriately low). The main cautions are that ruxolitinib has a high chance of lowering platelet and hemoglobin levels, which is why it may be appropriate to sometimes start at lower than approved doses in the package insert, and for rebound disease growth and inflammatory symptoms if the drugs are discontinued abruptly (dosage should be tapered off rather than abruptly discontinued). Difficulties arise when confronted with symptomatic splenomegaly and clinically significant anemia or thrombocytopenia. Splenectomy is an option to alleviate pain and early satiety, depending on local surgical experience and thus surgical risk. Secondary progressive hepatomegaly is a potential long-term complication of splenectomy. Also a possible consideration depending on local expertize is splenic artery embolization via interventional radiology. Analgesia may be required for splenic infarct pain, whether or not a patient has splenic artery embolization. Curative therapy: Allogeneic transplantation should be considered for intermediate-2 or high risk patients who are transplant candidates. A recommendation for transplantation is not clear-cut in lower risk patients because the median survival in this group is >14 years with non-transplant therapy. Pretransplantation splenectomy, although not necessary in every patient, is associated with faster engraftment and can be considered in those with massive splenomegaly. This can result in hypercalcemia, renal dysfunction, anemia, or extensive skeletal destruction with osteolytic lesions that are the major presenting signs of the disease. Unlike most other malignancies, diagnosis requires the presence of these clinical features and its attribution to clonal plasma cell proliferation. Recently, the diagnostic criteria have been updated to include biomarkers predictive of high risk of developing the above clinical features. Incidence in the African American population is two- to threefold higher than that in Caucasians, whereas it is lower in Asians. Evidence of end organ damage attributable to the underlying plasma cell proliferative disorder, specifically: a. Hypercalcemia: serum calcium >1 mg/dL higher than the upper limit of normal or >11 mg/dL b. Renal insufficiency: creatinine clearance <40 mL per minute or serum creatinine >2 mg/dL c. Anemia: hemoglobin >2 g/dL below the lower limit of normal, or a hemoglobin <10 g/dL d. The clonal plasma cells in myeloma are characterized by recurrent genetic abnormalities, with the majority having one or more well-characterized abnormalities. Five recurrent translocations involving the heavy chain locus on chromosome 14 have been identified and are present in approximately 40% of all patients. Trisomies of odd-numbered chromosomes are detected in nearly half of the patients, with monosomies or deletions of other chromosomes overlapping with these two sets of abnormalities. Patients may present with pathologic fractures and can also have loss of height because of vertebral collapse. Other common clinical features include fatigue (32%), weight loss (24%), normocytic normochromic anemia (73%), and hypercalcemia (28%). Other etiologies may include renal amyloidosis, light chain deposition disease, cryoglobulinemia, or drug-induced kidney injury. In some patients, concurrent light chain amyloidosis can cause nephrotic syndrome (<5%). Patients can also present with radiculopathy or spinal cord compression that can result from compression of nerve roots by paravertebral plasmacytoma or by a fractured vertebral body. Peripheral neuropathy can be present at diagnosis, and can be related to the monoclonal protein or to concomitant amyloidosis. Patients who lack detectable M-protein by any of these tests, but have end-organ damage and clonal plasma cells in the bone marrow, are considered to have nonsecretory myeloma. Kappa is the predominant light chain isotype compared with lambda (ratio 2:1), except in IgD myeloma, where lambda isotype is more common. Gene expression profiling, when available, may also be considered for additional prognostic information. More recently, mutation panels that examine the plasma cells for common recurrent mutations have become available, but the clinical utiity remains to be demonstrated. Radiologic changes seen on a skeletal survey include punched-out lytic lesions, severe osteopenia or osteoporosis, and pathologic fractures. Another indication where these scans should be utilized is when solitary plasmacytoma is suspected, to reliably rule out bony or extramedullary disease. Both of these provide prognostic information but are not helpful in making therapeutic choices. Revised International Staging System for Multiple Myeloma: A Report from International Myeloma Working Group. Other laboratory parameters such as creatinine, calcium, lactate dehydrogenase, immunoglobulin subtype, plasmablastic morphology, circulating plasma cells, and Creactive protein have also been shown to be independent risk factors for survival in myeloma. A high plasma-cell proliferative rate also strongly predicts poor prognosis, but this test is not commonly available. A risk stratification model based on independent molecular cytogenetic markers to assess disease aggressiveness has been found useful for both prognosis and therapeutic decision-making. Median survival varies from 8 to 10 years for standard-risk patients versus 2 to 3 years for high-risk myeloma. Gene expression profiling has identified several signatures that allow for prognostication in patients with myeloma and at least two of these are available for use in the clinic. If the results are stable, the studies should be repeated every 4 to 6 months during the first year and, if stable, evaluation can be lengthened to every 6 to 12 months. Currently, treatment is indicated only when there is evidence of progression to symptomatic disease, or as a part of clinical trial, although there is increasing thought that treating high risk patients early (before they develop symptomatic disease) may lead to better outcomes. The initial evaluation is similar to that for myeloma, including a bone marrow aspirate and biopsy. These patients are primarily treated with radiation therapy to the affected area and surgery is reserved for specific situations such as bone lesions with extensive destruction that require stabilization or soft tissue masses with pressure symptoms. Older patients, plasmacytoma of bone, especially of the axial skeleton, persistent monoclonal protein after radiation therapy, presence of marrow involvement, increased angiogenesis in the plasmacytoma and presence of circulating plasma cells, all suggest a higher risk of progression. Multiple Myeloma the treatment approaches for myeloma has undergone significant shifts in the last decade, primarily driven by the increased availability of new drugs, development of effective multidrug combinations, and the concept of prolonged therapy. More recently newer drugs like carfilzomib, pomalidomide, ixazomib, panobinostat, and the monoclonal antibodies daratumumab and elotuzumab have become available for management of relapsed disease, allowing for better disease control than had been possible in the past. There is increasing use of aggressive multidrug treatment upfront to achieve deep responses or sequential disease control approach emphasizing quality of life and prolonged survival. In transplant-ineligible patients, initial therapy typically uses a doublet or dose-adjusted triplet combinations, given for a defined duration followed by the maintenance for variable duration. Eligible patients should always be considered for enrollment in clinical trials that evaluate novel treatment strategies. As a result of the improved therapies, we have been able to achieve deep responses, not previously seen with the older therapies. This exposed the limitations of the previous response assessment approaches that relied primarily on the serologic and/or urine monoclonal protein assessment along with marrow assessment using methods with low sensitivity. All patients should receive supportive care and must be considered for bisphosphonate treatment and clinical trials. High risk includes patients with del(17p), t(14;16) or t(14;20); intermediate risk includes patients with t(4;14); and standard risk includes patients with t(911;14), t(6;14) or trisomies. If serum and urine M-protein and serum free-light-chain assay are unmeasurable, 50% reduction in plasma cells in the bone marrow provided baseline percentage was 30%. In addition to the above listed criteria, if present at baseline, 50% reduction in the size of soft-tissue plasmacytomas. In addition to the above listed criteria, if present at baseline, a 50% reduction in the size of soft tissue plasmacytomas. Definite increase (>50% and 1 cm) in size of existing plasmacytomas or bone lesions.
Buy epitol cheap
Approximately 17% to 25% of patients will develop duodenal adenomas medicine 8 iron stylings discount epitol online amex, with an estimated 4% lifetime risk of developing duodenal cancer. If polyps are identified, colonoscopy and polypectomy should be repeated every 1 to 2 years. Colectomy should be considered when the polyp burden is >20 on a single exam, when polyps have been previously ablated, when some polyps reach >1 cm, or when advanced histology is encountered. Upper endoscopy with visualization of the ampulla could be considered beginning at age 30 to 35. Individuals who harbor these germline mutations have a greater than 70% lifetime risk of developing diffuse gastric cancer by age 80 with a median age of onset of 38. These gastric cancers form beneath an intact mucosal surface, causing gastric wall thickening rather than the formation of a discrete mass. Because they are only visible late in the disease process, early detection is extremely challenging. Like diffuse gastric cancer, the absence of E-cadherin expression is also the key underlying defect in lobular breast carcinoma. Female carriers therefore have a 42% lifetime risk of developing lobular breast carcinoma by age 80. Risk reducing mastectomy is considered in patients with compelling family history. With the expansion of the above testing criteria, the mutation detection rate has decreased to 10% to 18%. Peutz-Jeghers polyps are characterized by a cerebriform appearance due to smooth muscle arborization within the polyps. These polyps often begin to develop in the first decade of life and are most common in the small bowel but can be observed in the colon, rectum, and stomach. The lesions are small (1 to 5 mm in size), flat, blue-gray to brown spots, and are commonly found around the mouth and nose, in the buccal mucosa, hands and feet, perianal areas, and genitals. The most common malignancies occur in the colon and rectum, but an increased risk is also seen in the breast, stomach, small bowel, pancreas, lung, cervix, ovaries, and testicles. This syndrome is characterized by gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyps and increased malignancy risk. Polyps often begin to develop in the teenage years and are most common in the colon and rectum. The lifetime risk of developing cancer ranges from 17% to 68%, with a 50% lifetime risk of developing colorectal cancer. Colonoscopy and upper endoscopy should begin around age 15 years with follow-up every 1 to 3 years. Colectomy and/or gastrectomy may be considered in cases where polyp burden is endoscopically unmanageable. Testing Considerations There is a shifting paradigm to move from single syndrome testing to performing next generation sequencing of multiple genes (panel testing). Gene panels include highly penetrant genes with established clinical utility; these panels also contain genes for which clinical validity or significance is less certain at this time. Panel testing may be a cost effective and efficient option, especially for individuals who have personal or family histories that are suspicious for more than one hereditary cancer syndrome, or for those who previously tested negative on single syndrome testing. In another large prospective study of a sequential series of breast cancer patients, 10. Most of these variants will eventually be reclassified, primarily as benign, but some will likely be pathogenic. Although multigene panels can significantly aid in cancer risk management and expedite clinical translation of new genes, they equally have the potential to provide clinical misinformation and harm at the individual level if the data are not interpreted cautiously. Given the potential issues for patients and their families, gene panel testing for inherited cancer risk is recommended to be offered in conjunction with consultation with an experienced cancer genetic specialist (counselor or geneticist) as part of the testing process. Inherited mutations in 17 breast cancer susceptibility genes among a large triple-negative breast cancer cohort unselected for family history of breast cancer. A comprehensive laboratory-based program for classification of variants of uncertain significance in hereditary cancer genes. Germline susceptibility to colorectal cancer due to base-excision repair gene defects. Somatic aberrations of mismatch repair genes as a cause of microsatellite-unstable cancers. Colon and endometrial cancers with mismatch repair deficiency can arise from somatic, rather than germline, mutations. Towards decreasing the relaparotomy rate in the PeutzJeghers syndrome: the role of peroperative small bowel endoscopy. Panel testing for familial breast cancer: calibrating the tension between research and clinical care. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome in children: report of two cases and review of the literature. Frequency of germline mutations in 25 cancer susceptibility genes in a sequential series of patients with breast cancer. Revised Bethesda Guidelines for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome) and microsatellite instability. Risk of metachronous colon cancer following surgery for rectal cancer in mismatch repair gene mutation carriers. For adjuvant treatment of melanoma interferon alpha 2b is administered subcutaneously at a dose of 6 mcg/kg per week for eight doses followed by 3 mcg/kg per week for up to 5 years. There is also a black box warning for the risk of worsening depression, suicidal ideation or other serious neuropsychiatric disorders. No treatment was given on days 6 to 14 and then dosing was repeated for up to 5 days on days 15 to 19 (maximum of 14 doses). Although up to 28 doses were allowed, the vast majority of patients had doses withheld due to toxicity. In eight clinical trials, 270 patients with metastatic melanoma were treated with single agent aldesleukin. Of the 270 patients, 43 (16%) had an objective response, with 17 (6%) having a complete response and 26 (10%) having a partial response. Of the 255 patients, 37 (15%) had an objective response with 17 (7%) having a complete response and 20 (8%) having a partial response. It should also be noted that patients achieving a complete response with this therapy have a near 90% ten year disease-free survival. Because of the potential for high-dose aldesleukin to cause capillary leak syndrome, hypotension, and reduced organ perfusion, it is recommended that aldesleukin be administered under the supervision of an experienced physician and in a hospital containing an intensive care unit. In addition, because of the potential for aldesleukin to cause cardiac arrhythmias, angina, myocardial infarction, and respiratory insufficiency, it is recommended that use of aldesleukin be limited to patients with normal cardiac and pulmonary function tests and without a history of cardiac or pulmonary disease. Aldesleukin may also cause gastrointestinal bleeding or infarction, renal insufficiency, edema, mental status changes, as well as an increased risk of sepsis due to impaired neutrophil function (reduced chemotaxis). Aldesleukin should be withheld in patients developing moderate to severe lethargy or somnolence as conti nued administration may result in coma. Vaccines Sipuleucel-T Sipuleucel-This an autologous dendritic cell-based vaccine platform. Based on this trial the approved dosing is every 2 weeks for a total of three doses. Patients receiving sipuleucel-T should be premedicated with acetaminophen and an antihistamine such as diphenhydramine. In the event of an acute infusion reaction, the infusion rate may be decreased or the infusion stopped, depending on the severity of reaction. The most common adverse reactions (incidence 15%) reported with sipuleucel-T are chills, fatigue, fever, back pain, nausea, joint ache, and headache. Most of these adverse events have been reported to occur within one day of the infusion and typically resolve within 1 to 2 days with supportive care. The combination of gp100 and ipilimumab did not show any added survival benefit compared to ipilimumab alone (10 vs. Ipilimumab is also approved as adjuvant therapy in patients who have cutaneous melanoma with pathologic involvement of regional lymph nodes of more than 1 mm and who have undergone complete resection, including total lymphadenectomy. The approved dose for adjuvant treatment is 10 mg/kg administered intravenously over 90 minutes every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by 10 mg/kg every 12 weeks for up to 3 years or until documented disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity. The most common adverse reactions at the 3 mg/kg dose (5%) are fatigue, diarrhea, pruritus, rash, and colitis. Additional common adverse reactions at the 10 mg/kg dose (5%) include nausea, vomiting, headache, weight loss, pyrexia, decreased appetite, and insomnia.
Epitol 100mg for sale
Abiraterone has also been shown to improve pain and quality of life in patients who have already received chemotherapy treatment of strep throat order epitol discount. Abiraterone requires co-administration of prednisone (10 mg daily) to limit treatment-related toxicity. Enzalutamide should not be used in patients with a seizure history or medications that may substantially lower the seizure threshold. Although the absolute magnitude of the difference between the two arms was less than 3 months, it is important to note that the study did employ a cross-over meaning that patients not randomized to docetaxel initially may have received docetaxel when they had progressive disease. It is important to note that there was an 8% incidence of febrile neutropenia, and 2% of patients died from neutropenia-related infections. Thus serious consideration should be given for the use of growth factor support in appropriate patients. Mitoxantrone may be appropriate for symptomatic patients who have either progressed on or who are not candidates for taxane-based chemotherapy regimens. This combination may be most appropriate in patients who have a small cell variant of CaP (~2% of patients). This benefit was seen in symptomatic patients regardless of previous chemotherapy. Radium-223 has less impact on the bone marrow, because alpha particles have a limited destruction radius, but anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia can still be encountered. Safety data has suggested radium-223 can be safely given with abiraterone and enzalutamide, but it remains unclear if either combination is more beneficial than sequential use. The potential side effects of these medicines also have to be taken into account when using them to treat hot flashes. Testosterone-lowering therapy causes a decrease in estradiol, needed to maintain bone density, which may lead to osteoporosis. Treatment with bisphosphonates should be considered in patients with low bone mineral density. Side effects generally are limited to fatigue and anemia that are usually reversible. Generally, the painful vertebral lesion and the two vertebrae superior to and inferior to the lesion are treated with 30 Gy. The spinal cord can tolerate radiation up to approximately 50 Gy, so retreatment of some lesions may be considered. Side effects include infusion-related myalgias, renal dysfunction, and osteonecrosis of the jaw. Even though it is mechanistically different from bisphosphonates, there is a similar incidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw. Muscle weakness or neurologic abnormalities are other indicators of spinal cord compression, along with weakness and/or sensory loss corresponding to the level of spinal cord compression, which often indicate irreversible damage. Genitourinary, gastrointestinal, and autonomic dysfunction are late signs; spinal cord compression usually progresses rapidly at this point. Diagnosis requires a thorough history and physical, with special attention to musculoskeletal and neurologic examinations. Neurologic/orthopedic surgeons and/or radiation oncologists should be consulted soon after diagnosis. Improved survival in patients with locally advanced prostate cancer treated with radiotherapy and goserelin. A controlled trial of leuprolide with and without flutamide in prostatic carcinoma. A contemporary prostate cancer grading system: A validated alternative to the Gleason score. Combined orchiectomy and external radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for nonmetastatic prostate cancer with or without pelvic lymph node involvement: a prospective randomized study. High dose rate brachytherapy in combination with external beam radiotherapy in the radical treatment of prostate cancer: initial results of a randomized phase three trial. A phase 2 study of carboplatin plus docetaxel in men with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer who are refractory to docetaxel. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of zoledronic acid in patients with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate carcinoma. Trial design and objectives for castration-resistant prostate cancer: updated recommendations from the prostate cancer clinical trials working group 3. Denosumab and bone-metastasis-free survival in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer: results of a phase 3, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Worldwide, more than 430,000 individuals are diagnosed with bladder cancer each year. The male:female ratio is 3:1, with a peak occurrence in the seventh decade of life, making bladder cancer the fourth and eighth most commonly diagnosed cancer in men and women, respectively. In fact for smokers, the risk of developing bladder cancer is twice what it is for nonsmokers. Smoking explains a similar proportion of bladder cancer in both sexes (50% in men and 52% in women). Occupational exposures to chemical carcinogens are associated with an increased risk of bladder cancer. Workers exposed to arylamines in the dye, paint, rubber, textile, and leather industries are at increased risk. Treatment-related risks: Prior treatment with pelvic radiation and cyclophosphamide increases the risk of urothelial cancers. Progressive inflammation of the renal parenchyma also occurs in patients with Balkan nephropathy, predisposing patients to low-grade cancers of the upper urinary tract. Arsenic-contaminated drinking water: Epidemiological studies provide solid evidence of the association of arsenic-contaminated drinking water and bladder cancer. These tumors are less common, accounting for 5% to 10% of all urothelial carcinomas. Urothelial carcinoma, previously called transitional cell carcinoma, accounts for 90% to 95% of all bladder tumors in the United States. Urothelial tumors often have divergent histologies, including urothelial carcinoma and squamous, sarcomatoid, adenocarcinoma, and/or nested micropapillary subtypes. Papillary tumors have a fibrovascular core and are typically raised on a stalk that can invaginate into the surface layer, lamina propria, or muscularis propria. They can be either low- or high-grade and have a risk of recurrence and progression over time. Patients with upper-tract urothelial tumors have a 20% to 40% incidence of synchronous or metachronous bladder cancer. Patients with bladder cancer have about a 1% to 4% incidence of synchronous or metachronous uppertract tumor. Patients with invasive disease may present with flank pain due to ureteral obstruction leading to hydronephrosis. Patients with advanced disease may present with constitutional symptoms such as weight loss, abdominal pain, or bone pain. Studies evaluating the role of screening for bladder cancer have examined the utility of conventional Hemastix testing. However, because hematuria per se is nonspecific, patients who test positive for hematuria need to undergo further tests to determine its etiology. Other noninvasive screening methods include urine cytology or urine-based markers. Markers such as nuclear matrix protein 22, bladder-tumor antigen, cytokeratins, and many others have widely variable sensitivity and specificity. It is especially important to fully investigate the upper tracts of patients with positive cytology and normal cystoscopy. A 99mTc bone scan is recommended for patients with elevated blood alkaline phosphatase or bone pain. Patients with muscle-invasive disease have a 50% likelihood of occult distant metastases at diagnosis. The usual sites of metastases are pelvic lymph nodes, liver, lung, bone, soft tissue, adrenal glands, and peritoneum/omentum.


