Cheap intagra on line
Aerosol-incapacitating dose amounts to about 30 ng/person; lethal dose is approximately 1 erectile dysfunction psychogenic causes order cheap intagra line. Patients with mild fluid deficits can often be managed with oral fluid therapy consisting of clear liquids, or specially formulated glucose and electrolyte solutions. Significant nausea and vomiting in adults may be controlled with a suitable antiemetic agent. Chloramphenicol, tetracycline, kanamycin, gentamicin, clindamycin, vancomycin, and erythromycin are generally effective. Resistance has been reported to penicillin and cephalosporines secondary to beta-lactamase production. Inhalation of the toxins can cause sudden onset of fever, headache, chills, myalgia, non-productive cough, dyspnoea, and retrosternal chest pain. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea may occur as a result of inadvertent swallowing of the toxin. Staphylococcus aureus It is said to be the commonest cause of bacterial food poisoning. Staphylococcal food poisoning is usually a self limited illness; often no laboratory evaluation is required. Monitor electrolytes and fluid balance in patients with significant volume loss from vomiting and diarrhoea. Source 1 Previously cooked, proteinaceous food: meat, fish, milk, and milk products. Staphylococcal toxins are formed within a few hours when food is kept at room temperature. Most foods (particularly those high in protein) will support staphylococcal growth, especially custard or cream filled pastries, mayonnaise, ham, and dairy, poultry, potato and egg products. Pasteurising milk will kill the bacteria, but unfortunately will not inactivate the toxins. All persons with significant toxicity, dehydration, abnormal electrolyte levels, or a history of poor compliance should be admitted for intravenous fluid therapy. However, antiemetics are not usually required if alteration of the diet is successful. If cough or difficulty in breathing develops, evaluate for hypoxia, respiratory tract irritation, bronchitis, or pneumonitis. Food poisoning (Salmonella enterocolitis) can be caused by all salmonellae except S. Food products containing raw eggs are also capable of producing the illness-hollandaise sauce, eggnog, chocolate mousse, raw egg-based milk shakes, caesar salads, and home-made ice cream. Milk and milk products*: Consuming raw, unpasteurised milk poses a real risk of being infected with salmonellosis. Outbreaks of salmonella infections may be associated with multiple drug-resistant strains. Salmonella has also been detected in various sesame seed products, including sesame paste and halvah (a mixture of sesame seed paste and acidified heated glucose syrup). Household pets: Chicks, turtles, iguanas, and other reptiles are known to harbour salmonellae, and can transmit the Vomiting, crampy abdominal pain, diarrhoea. These symptoms may be absent in children, who may present only with abdominal pain and nausea, which could be confused with acute appendicitis. Toxic megacolon and intussusception have been reported with Salmonella typhimurium. The illness usually subsides in 2 to 4 days, but occasionally becomes prolonged and dysentery-like, with passage of mucus and pus in the stools. The carrier state is more common among females and elderly patients, and it may persist for months to years. Fluoroquinolones, ampicillin, ceftriaxone, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are also effective. Shigella Shigella microbes comprise non-motile, gram-negative rods that have the same characteristics (morphological and biochemical) as E. Faecal polymorphonuclear neutrophil leukocytes are present in many cases of shigellosis. While antibiotic resistance is a common problem, most cases still respond to nalidixic acid or norfloxacin. The following antibiotics are currently recommended by the World Health Organization for the treatment of Shigella dysenteriae serotype (Sd1) which is commonly seen in developing countries such as India: ampicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, nalidixic acid, pivmecillinam, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and enoxacin, though resistance is common with ampicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and nalidixic acid. Anti-motility agents (loperamide or diphenoxylate with atropine) are likely to make the illness worse and are not recommended. Fruits (stewed apples), vegetables (potato salad, mashed potatoes), tossed salad and milk products are the commonest vehicles. Children (6 months to 5 years) are at highest risk for developing shigellosis; especially children in daycare centers where the illness can spread rapidly. Also, individuals in custodial care centers, international travelers, homosexual males, and those living in houses with poor sanitation. Vibrio Vibrio cholerae is responsible for causing cholera, while several other species (V. Clinical Features Individual presentation varies with some patients demonstrating only minor symptoms, while others may suffer true dysentery with high fever, tenesmus, nausea, crampy abdominal pain, and profuse diarrhoea. Large, watery (relatively odourless) stools, followed by bloody diarrhoea in 24 hours. Two types of pathogenic Vibrio cholerae have been identified, both belonging to Group 1: a. The classical biotype which is responsible for the most severe form of the disease (now restricted mainly to Bangladesh). Both the classical and El Tor vibrios are further divided into 3 serological types-Inaba, Ogawa, and Hikojima. The former is the active sub-unit, and after being transported into the enterocytes, dissociates into two fragments, A1 and A2. Cholera usually manifests dramatically and abruptly as profuse painless watery diarrhoea and copious effortless vomiting. The condition varies in severity from mild watery diarrhoea to fatal cholera-like illness. Enterohaemorrhagic: contaminated food, especially inadequately cooked beef, raw milk, contaminated water, person-to-person contact. Enterotoxigenic: contaminated food and water; faecal transmission by contaminated hands. Enteropathogenic: contaminated infant foods; transmission by fomites and contaminated hands. Stool specimen is best collected by introducing a lubricated rubber catheter into the rectum and letting the liquid stool flow directly into a screw-capped container. If transport media are not available, strips of blotting paper may be soaked in the watery stool and sent to the laboratory packed in plastic envelopes. Diagnosis may be accomplished by demonstration of motile vibrio under dark field or phase contrast microscopy, and by culture in appropriate media. Serological examination: this is generally not helpful in diagnosis, but may help in assessing the prevalence of cholera in a region. Serotype O157 appears to be more prevalent in developed countries, while the non-O157 serotypes are more common in other countries. H7 may infect all age groups, and has been reported to occur in both developed and developing countries, although it is apparently more prevalent in developed countries. Children aged less than 5 years have the highest disease rates, followed by persons aged greater than 60 years. Enteropathogenic strains: 9 to 12 hours in adult volunteers; incubation in infants not known 2. Enteroinvasive strains: 10 to 18 hours Enterotoxigenic strains: 10 to 72 hours Enteroaggregative strains: 20 to 48 hours Enterohaemorrhagic strains: 3 to 4 days Enteroadherent strains: unknown.
Diseases
- Schimke syndrome
- Dobrow syndrome
- Pericardium absent mental retardation short stature
- Split hand split foot malformation autosomal reces
- Emery Nelson syndrome
- Poikiloderma of Rothmund Thomson
- Lichstenstein syndrome
- Holmes Borden syndrome
- Shwachman Bodian Diamond syndrome
- Dysgerminoma
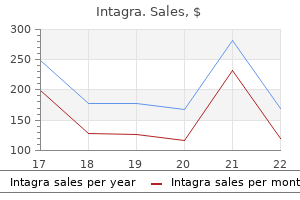
Order intagra 50 mg otc
Thyrotoxicosis can present in the elderly with atrial fibrillation erectile dysfunction pills for heart patients generic 75 mg intagra overnight delivery, and such patients may lack other common signs of thyrotoxicosis; this is known as apathetic hyper-thyroidism. Red reflex may be absent when there is a lens opacity, vitreous haemorrhage or retinal detachment. Look systematically at the following: the optic discs (comment on the colour, contour, cup and lamina cribrosa). It appears darker than the surrounding retina, and in young individuals has a central yellow point called the fovea centralis. The candidate should assess the transparency of the vessels (the arteries usually have a shiny central reflex stripe), the presence of pressure effects such as arteriovenous nicking, the presence of focal narrowing of arteries as well as tortuosity of the venules. Note Lesions in the fundus are measured using the disc diameter as the reference size. Elevation of 3 dioptre lens changes is approximately equal to 1 mm in actual elevation. You may have a clue about the underlying diabetes, either from a diabetic chart or from the presence of diabetic fruit juices at the bedside. Early treatment in the form of argon laser photocoagulation applied directly to leaking microaneurysms, as well as grid photo-coagulation applied to diffuse areas of leakage and thickening, is highly beneficial. There will be a gradual impairment of central vision, such as difficulty in reading small print or seeing road signs. Macular oedema includes any of the following signs: Retinal thickening at or within 500 pm of the centre of the macula. Non-urgent referral to an ophthalmologist for photocoagulation which will stabilize (seldom improve) visual acuity in 50% of patients. The ability to alter the course of visual loss in diabetic macular oedema favourably is a major advance but patients must be cautioned that the most likely result of treatment is stabilization, not im-provement, of visual acuity. The principal mechanisln of visual h)ss in non-proliferative retinopathy is macular oedema, which results from focal vascular leakage from microaneurysms in the macular capillaries, as well as diffuse vascular leakage. With time, areas of leakage progress to macular thickening associated with hard exudates or cystoid changes. Patients may present with no visual symptoms, paracentral scotomata or various degrees of central visual loss. Consequently, the diagnosis and management of macular oedema depend crucially on the determination of macular thickening by fundus examination. Ophthalmoscopy detects intraretinal haemorrhages and hard exudates but does not detect substantial retinal thickening. A critical evaluation of retinal thickening requires stereoscopic examination of the retina by slit-lamp bio-microscopy with lens for retinal visualization or stereoscopic fundus photography. Semiurgent referral to the ophthalmologist for close follow-up to enable early detection and treatment of proliferative retinopathy. In later stages they are elevated and may be associated with a white fibrous component. There is a close relationship: in patients diagnosed as having diabetes before the age of 30 years, the incidence of retinopathy is about 50% after 10 years and 90% after 30 years. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial compared intensive treatment for blood glucose control with conventional treatment in patients with and without retinopathy at baseline who were followed for a mean of 6. Intensive treat-ment has profound benefits in both subgroups and was associated with a reduction in the incidence of both the development of new retinopathy and the risk of pro-gression of existing retinopathy. An increase in capillary permeability, evidenced by the leakage of dye into the vitreous humour after fluorescein injection, is the earliest sign of retinal change in diabetes mellitus. It is not completely understood and current theories emphasize the production of angiogenic factors by areas of ischaemic and hypoxic retina. Photocoagulation is a technique whereby several thousand lesions are produced over a 2-week therapy period with lasers. The laser is used to ablate a portion of the retina and does not directly cauterize the neovascularization. It is believed that the regression of neovascularization due to laser is a result of the destruction of ischaemic and hypoxic retina with reduction in angiogenic factors. Photocoagulation decreases the incidence of haemorrhage or scarring in proliferative retinopathy. Photocoagulation is also useful in the treatment of microaneurysms, haemor-rhages and oedema. What surgical technique may be used for a non-resolving vitreous haemorrhage and retinal detachment Pars plana vitrectomy may be used hut is often complicated by retinal tears, retinal detachment, glaucoma, infection, cataracts and loss of the eye. Proceed as follows: Tell the examiner that you would like to: Check the blood pressure. Keith-Wagner-Barker classification (Am J Med Sci 1939; 197: 33243): Stage I - arteriolar narrowing. Dollery, was Dean of the Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital, London; his interests include clinical pharmacology, hypertension and medical education. John Swales, contemporary Professor of Medicine, Leicester; his chief interest is hypertension. Petrie, Professor and Head of Medicine and Therapeutics, Aberdeen; his interests included hypertension and cardiovascular prevention. Examination There is swelling of the optic disc (look for haemorrhages and soft exudates;. The colour of the disc becomes redder, approximating to that of the rest of the retina; its contour becomes blurred and the cup and cribrosa are filled in. Papilloedema is always associated with enlargement of the blind spot with a con-sequent diminution of visual fields and gradual loss of visual acuity, but a fair degree of acuity may remain until papilloedema is marked. The appearance is typically flared and on focusing will reveal fibres traversing the area. Elevation or swelling of the optic disc occurs in the following conditions: Papilloedema. Papillitis Papilloedema Usually unilateral Usually bilateral Visual acuity is considerably reduced Visual acuity only slightly reduced until in relation to the degree of swelling late stages of the disc Visual field defect is usually central, Peripheral constriction or enlargement particularly for red and green of the blind spot Marcus Gunn pupil may be present Marcus Gunn pupil is absent Eye movements may be painful Eye movements are never painful Note. A Marcus Gunn pupil is one that shows better constriction to an indirect response than to direct light. In many normal discs the nasal edge is less distinct and one of the most frequent false-positive signs is questionable blurring of the nasal disc margins. Proceed as follows: Tell the examiner that you would like to look for cerebellar signs (remember that multiple sclerosis is the commonest cause of optic atrophy). The differential diagnosis is as follows: Demyelinating disorders (multiple sclerosis). Primary Secondary White and flat with clear-cut edges Greyish-white, edges indistinct Visible lamina cribrosa Cup filled and lamina cribrosa not visible Arteries and veins normal Arteries thinner than normal Veins may be. Some use it as an equivalent or alternative for what has been described above as secondary optic atrophy, but others use the term to indicate an atrophy complicating retinitis or, rarely, Tay-Sachs disease or retinitis pigmentosa. Glaucomatous optic atrophy denotes loss of disc substance, referred to as increased cupping. Marcus Gunn (1850-1909), a Scottish ophthalmologist who worked at Moorfields Eye Hospital, London. Proceed as follows: Tell the examiner that you would like to check for the following conditions: Hypertension. These include dilatation of retinal capillaries, abnormal vascular permeability and retinal capillary closure. It varies from complete resolution with no residual visual deficits to a progressive deterioration resulting in permanent loss of vision. These include neovascularization of the retina, rubeosis iridis (usually visible by 1 month) and rubeotic glaucoma (usually by 3 months). Panretinal photocoagulation prevents the dreaded complication of neovascular glaucoma. Examination A large, solitary subhyaloid haemorrhage (there may be no fluid level if the patient is lying flat). The retinal veins (never the arteries) often have a sheath of pigmentation for part of their course. The pigment spots that lie near the retinal veins are seen to be anterior to them, so that they hide the course of the vessel. Proceed as follows: Look for polydactyly in the hands and feet (Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome). It occurs in both eyes, begins in early childhood, and often results in the loss of sight by middle or advanced age.
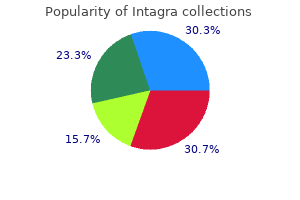
25 mg intagra with visa
Resolution of symptoms usually occurs rapidly with supportive care alone erectile dysfunction korean ginseng order intagra toronto, within hours to 1 to 2 days. Chronic Poisoning: It usually occurs as an occupational hazard in agriculturists, especially those who are engaged in pesticide spraying of crops. Organophosphate poisoning has been associated with a variety of subacute or delayed onset chronic neurological, neurobehavioural, or psychiatric syndromes. A person with a "high normal" level may become symptomatic with a "low normal" activity. Elevated levels may be seen with reticulocytosis due to anaemias, haemorrhage, or treatment of megaloblastic or pernicious anaemias. Depression of plasma cholinesterase level (to less than 50%) is a less reliable indicator of organophosphate toxicity, but is easier to assay and more commonly done. Depressions in excess of 90% may occur in severe poisonings, and is usually associated with mortality. For the purpose of estimation of cholinesterase level, blood should be collected only in heparinised tubes. Plasma cholinesterase usually recovers in a few days or weeks; red blood cell cholinesterase recovers in several days to 4 months depending on severity of depression. The sample is extracted twice with 5 ml of petroleum ether, and the extract is washed with distilled water. After the solvent has travelled a considerable distance, the plate is dried and exposed to iodine vapour. There may be evidence of leukocytosis (with relatively normal differential count), high haematocrit, anion gap acidosis, hyperglycaemia. Many organophosphate compounds are found in solution with a variety of hydrocarbon-based solvents. Bronchopneumonia may develop as a complication of organophosphate-induced pulmonary oedema. Depression in excess of 50 per cent of baseline is generally associated with severe symptoms (vide supra). Latex and vinyl gloves provide inadequate protection, unless a double pair is used. Actually, human studies have not conclusively substantiated the benefit of oxime therapy in acute organophosphate poisoning, but they are widely used. Most authors advocate the continued use of pralidoxime in the clinical setting of severe organophosphate poisoning. The antidotes for organophosphates have been discussed together in detail in Table 28. Monitor pulse oximetry or arterial blood gases to determine need for supplemental oxygen. However, since atropine affects only the postsynaptic muscarinic receptors, it has no effect on muscle weakness or paralysis Diagnostic dose: Organophosphate-poisoned patients are generally tolerant to the toxic effects of atropine (dry mouth, rapid pulse, dilated pupils, etc. Once the endpoint has been reached, the dose should be adjusted to maintain the effect for at least 24 hours Atropinisation must be maintained until all of the absorbed organophosphate has been metabolised. This may require administration of 2 to 2,000 milligrams of atropine over several hours to weeks Atropine therapy must be withdrawn slowly to prevent recurrence or rebounding of symptoms, often in the form of pulmonary oedema. This is especially true of poisonings from lipophilic organophosphates such as fenthion Precautions: Many parenteral atropine preparations contain benzyl alcohol or chlorobutanol as preservatives. High-dose therapy with these preparations may result in benzyl alcohol or chlorobutanol toxicity. Pralidoxime competes for the phosphate moiety of the organophosphorus compound and releases it from the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, thereby liberating the latter and reactivating it While it is advisable to begin pralidoxime therapy within 48 hours of poisoning, it can be administered even much later with beneficial effects Till recently, pralidoxime was said to be contraindicated in carbamate poisoning because experiments with carbaryl (Sevin) suggested a worsening of symptoms when it was administered. However, recent studies have pointed out that while pralidoxime is not a necessary adjunct to atropine in carbamate overdose, it may be beneficial in some cases Dose: For adults-1 to 2 gm in 100 to 150 ml of 0. Many workers feel that this high dose therapy minimises the incidence of complications such as the Intermediate Syndrome Maximum dose should not exceed 12 gm in a 24 hour period. Do not administer succinylcholine (suxamethonium) or other cholinergic medications. Prolonged neuromuscular blockade may result when succinylcholine is administered after organophosphate exposure. Prevention of Further Exposure: After the patient has recovered, he should not be re-exposed to organophosphates for at least a few weeks since he is likely to suffer serious harm from a dose that normally would be harmless, owing to alteration of body chemistry. Plateau has been obtained when sequential determinations differ by no more than 10%. Treatment of Pregnant Victim: Therapeutic choices during pregnancy depend upon specific circumstances such as stage of gestation, severity of poisoning, and clinical signs of mother and foetus. A severely poisoned patient with a late gestation viable foetus may be a candidate for emergency Caesarean section. However, the foetus may be best served by treating the mother to retain good respiratory function and foetal oxygenation. Forensic Issues Discussed at the end of the chapter, together with all the other pesticides. Carbamates Carbamates are as popular as organophosphates in their role as insecticides (and fungicides) and share a number of similarities. Mode of Action and Clinical Features Carbamates (like organophosphates) are inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase, but carbamylate the serine moiety at the active site instead of phosphorylation. This is a reversible type of binding and hence symptoms are less severe and of shorter duration. As a result both morbidity and mortality are limited when compared to organophosphate poisoning. They are rapidly hydrolysed by liver enzymes to methyl carbamic acid and a variety of low toxicity phenolic substances. These metabolites may sometimes be measured in urine as long as 2 to 3 days after significant pesticide absorption. Miosis, a muscarinic effect, is characteristic of severe and moderately severe poisonings, but may appear late. Pupil dilation may occur as a nicotinic effect and may be present in up to 10% of patients. Chest tightness, bronchospasm, increased pulmonary secretions, and rales may develop secondary to muscarinic effects. Acute lung injury (pulmonary oedema) is a potential clinical manifestation of severe carbamate poisoning and is attributed to the muscarinic action of the insecticide. Contributing factors to the development of pulmonary oedema include bradycardia and weakened cardiac contraction from an accumulation of acetylcholine on the cardiovascular system. Headache, dizziness, blurred vision, tremor, paresis, mental depression, coma, delayed neuropathies, various dystonias, weakness, muscle twitching, and convulsions have all been reported with carbamate poisoning. Absence of classic muscarinic effects has been reported in several children intoxicated with carbamate insecticides. The presence of either a cardiac arrhythmia or respiratory failure is associated with a higher incidence of fatal poisoning. Carbamylated cholinesterase activity follows a non-linear kinetic pattern over time, whereas phosphorylated enzyme activity is linear. At inhibition of greater than 40%, the non-linear pattern characteristic of carbamates is easily mapped. One technique for assessing absorption of the principal N-methyl carbamate compounds is measurement of specific phenolic metabolites in urine. The major cause of morbidity and mortality in carbamate insecticide poisonings is respiratory failure and associated pulmonary oedema. Organochlorines Organochlorine pesticides are one variety of chlorinated hydrocarbons. Cyclodienes and related compounds-for example, aldrin, dieldrin, endosulfan (thiodan), endrin, isobenzan, chlordane, chlordecone (kepone), heptachlor, mirex (dechlorane). Hydrocarbons and Pesticides Physical Appearance these compounds are available as dusting powders, wettable powders, emulsions, granules and solutions. Treatment An important differentiating point from organophosphates is that oximes are generally not recommended, while atropine can be given. Especially in carbaryl poisoning, oxime therapy can lead to the production of a carbamylated oxime which may be a more potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor than carbaryl itself. With other carbamate insecticides (particularly aldicarb), oximes may be a useful adjunct to atropine therapy. In 1986, a consensus of international experts concluded that pralidoxime can be used in conjunction with atropine for specific indications as follows: Life-threatening symptoms such as severe muscle weakness, fasciculations, paralysis, or decreased respiratory effort.
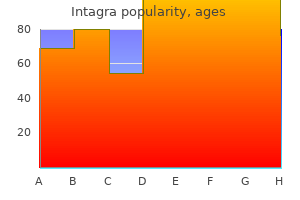
Discount intagra online mastercard
Those with artificial ventilation are not given cholinergics as this avoids stimulation of pulmonary secretions and uncertainties about overdosage erectile dysfunction self injection buy discount intagra on line. In the case of thymoma, thymectomy is necessary to prevent tumour spread, although most thymomas are benign. In the absence of a tumour, thymectomy has been found to be beneficial in 85% of patients, and 35% go into drug-free remission. The role of thymectomy in ocular myasthenia, in adults over 55 years of age (Acta Neurol Scand 1994; 12: 343-68) and in children is still under debate. Intravenous immunoglobulin seems as efficacious as plasma exchange (Ann Neuro/ 1997; 41:789 96). Eaton (1905-1958), Professor of Neurology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota. Myasthenia gravis was first described by the physiologist Thomas Willis in 1672 and by Erb in 1878. Jolly named the disease myasthenia gravis pseudoparalytica (Berl Kiln Wochenschr 1895; 32: 1-7). Also noticed in early infancy are difficulty in feeding and inability to reopen the eyes while having the face washed. Absence of deep tendon reflexes (due to degeneration of peripheral nerves) Distal muscle wasting (in 50% of cases), especially in the hands. Check for nystagmus (present in 25% of the cases), scanning speech, intention tremor. In which other condition is there a mixture of cerebellar, pyramidal and dorsal column signs Pcs cavus or hammer toes, without any other signs, are seen in family members of such patients. Other features (present in less than 50% of cases) are nystagmus, optic atrophy, deafness, distal muscle wasting and diabetes. Occasionally it may appear to be arrested, and abortive cases may be encountered in apparently healthy relatives of affected patients. Name a few syndromes with spinocerebellar degeneration (N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1351-3). Clinical features include progressive ataxia, ophthalmoparesis, spasticity, dystonia, amyotrophy and parkinsonism. Nikolaus Friedreich (1825-1882), Professor of Pathology and neurologist in Heidelberg, described this condition in a series of papers from 1861 to 1876. Anita Harding (1953-1995) Professor of Neurology at the National Hospital, Queen Square, London, died at the age of 42 years from colonic cancer. Characteristically there is retention of deep tendon reflexes in the presence of severe muscular atrophy. X-linked spinal muscular atrophy: the patient has associated testicular atrophy resulting in oligospermia and gynaecomastia. It is associated with the ampli-fication of a trinucleotide repeat in the coding sequence of the androgen receptor gene; the severity of the disease is directly related to the number of repeats present. The onset is early (before the age of 30); asymmetrical limb weakness and wasting, bulbar and facial involvement occur along with sensorineural deafness. Jagannathan K, Valmikinathan K 1984 the spectrum of motor neuron disease in Madras. It also tends to have an earlier onset and a more protracted course than the sporadic cases seen in Europe and America. The clinical manifestations are a result of degeneration of Betz cells, pyramidal tracts, cranial nerve nuclei and anterior horn cells. Both upper and lower motor neurons may be involved, but sensory involvement is not seen. It results from spontaneous firing of large motor units formed by branching fibres of surviving axons that are striving to innervate muscle fibres that have lost their nerve supply. This genetic locus appears to be the copper-zinc-binding superoxide dismutase gene, with various missense mutations identified in different families. Riluzole, a glutamate antagonist, is being used in limb or bulbar palsy (N Engl J Meal 1994: 330: 585-91). Patients often require treatment for painful muscle cramps, constant drooling, severe fatigability, sleep problems, incipient contractures, subluxation of the shoulder joint, dysphagia and neuralgia - all of which can be ameliorated. Patients often have extreme lability of emotion, particularly in the early stages of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In order to alleviate distress before or during respiratory failure, which is usually the terminal event, narcotic drugs should not be withheld. The suggestion that accumulation of toxic levels of glutamate at synapses may cause neuronal death through a calcium-dependent pathway. Riluzole has been shown to be useful in patients with disease of bulbar onset but not in those with disease of spinal onset. The risk of death or tracheostomy is lower with 100 mg riluzole than placebo in limb or bulbar onset disease (Lancet 1996; 347:1425-31), but it is debatable whether this translates into an improved quality of life. Antibodies to L-type voltage-gated calcium channels are present in the serum of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and antibody titres correlate with the rate of disease progression (N Engl J Med 1992; 327:1721 8). What is the role of magnetic cortical stimulation in amyotrophic la teral sclerosis Magnetic cortical stimulation uses time-varying magnetic fields to induce electrical currents within the brain painlessly. It is said to activate cortical motor neurons trans-synaptically through thalamocortical and corticocortical afferents, and allows detection of degeneration of cortical Betz cells. In patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis the sensitivity of this technique to detect upper motor neuron involvement in those with clinical signs is high, but the sensitivity of the technique in those without clinical signs is unknown. A transgenic mouse model possesses mutations in the gene encoding the cytosolic form of the enzyme copper-zinc superoxide dismutase (Nature 1993; 362: 59). Charcot gave a detailed clinical and pathological description of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in 1865. Professor Stephen Hawking, the Cambridge theoretical physicist, is the most famous sufferer of motor neuron disease. Obtain history of learning disabilities (about half the patients with neurofibroma I are affected; Nature 2000; 403: 846-7). The iris for Lisch nodules (often apparent only by slit-lamp examination) present in over 90% of patients. Tell the examiner that you would like to check the blood pressure (for renal artery stenosis or phaeochromocytoma). The triad for neurofibromatosis - neurofibromas, cafd-au-lait spots and Lisch nodules - allows identification of virtually all patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Plexiform neuro-fibroma is considered by some to be a defning lesion of neurofibromatosis type 1. A distinctive osseous lesion such as sphenoid dysplasia or thinning of long bone cortex with or without pseudoarthroses. A parent, sibling or child with neurofibromatosis according to the above criteria. Lisch nodules are melanocytic hamartomas that appear as well-defined, dome-shaped elevations projecting from the surface of the iris and are clear to yellow and brown. The incidence increases with age: at the age of 5 years only 22% have Lisch nodules whereas, at the age of 20 years, 100% have them. Older patients who do not have Lisch nodules are also, therefore, unlikely to have neurofibromatosis 1. Lisch nodules are an important tool in establishing the diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type I and in providing accurate genetic screening (N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 1264). The peripheral nerve tumours are of two types: Schwannomas: arise in cranial and spinal nerve roots and also in peripheral nerve trunks. Neurofibromas: composed of a proliferation of all elements of the peripheral nerve including nerve trunks, Schwann cells and fibroblasts. In sensory nerve twigs they appear as subcutaneous nodules, while in peripheral nerve trunks they may appear as a fusiform enlargement or a plexiform neurofibroma. The gene for neurofibromatosis type I encodes a protein called neurofibromin which downregulates the function of the p21 ras oncoprotein (Neuron 1993; 10: 335). Learning disabilities have been ascribed to abnormal brain development as a result of deficiency in neurofibromin signalling (Nature 2000; 403: 895-8).
Dattier (Date Palm). Intagra.
- Coughs and other breathing problems.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Date Palm work?
- What is Date Palm?
- Dosing considerations for Date Palm.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96434
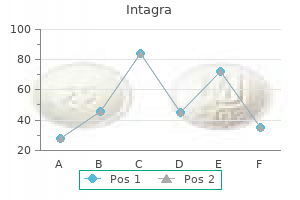
Order generic intagra on-line
One or two huffs will begin to intoxicate the user within seconds erectile dysfunction injection device buy genuine intagra, and the effects usually last for several hours. Chronic users can maintain a prolonged high with periodic inhalations every few hours. Chronic painter syndrome-A neurobehavioural syndrome due to solvent-induced encephalopathy, Section 5 b. The popularity of such drugs has been fuelled by their glamorous representation in films and rock music. Several horrific crimes have been committed by drug-crazed individuals acting out their bizarre fantasies. Spinal and Peripheral Neurotoxic Agents the most important drugs and poisons which act either on the spinal cord or on the peripheral nerve endings include strychnine, hemlock and neuromuscular blocking agents. Strychnine is the principal alkaloid in the strychnos plant (seeds), and is a powerful spinal stimulant. Toxic Principle Strychnine and brucine are the principal alkaloids, of which the former is much more powerful. It is a basic alkaloid and can be extracted from the seeds as an odourless, bitter-tasting, white crystalline material. Uses the main alkaloid strychnine has been in use as a rodenticide since the 16th century. Strychnine was first used medically in 1540, and continued to be used in many stimulants, tonics, and cathartics until as recently as the 1960s. Mode of Action Strychnine prevents the uptake of glycine at inhibitory synapses, especially in the ventral horns (anterior horn cells) of the spinal cord. It results in the competitive antagonism of the inhibitory neurotransmitter at the post-synaptic spinal cord motor neuron. There is a net excitatory effect, and minimal sensory stimulation can set off powerful muscle contractions. Muscle twitching, spasms, followed by overwhelming convulsions (each lasting from 30 seconds to 2 minutes) which are precipitated by minimal external stimuli. Less commonly, emprosthotonus (forward bending) and pleurosthotonus (lateral bending) are seen. An important diagnostic feature is that there is complete muscle relaxation in between spasms and convulsions. Another feature of significance is that the patient maintains a clear sensorium during and between convulsive episodes. Complications include hypoxia, hyperthermia, cardiac arrest, rhabdomyolysis, metabolic acidosis, and acute renal failure. The usual fatal event is respiratory failure consequent Differential Diagnosis Mentioned in Table 21. Induction of emesis is contraindicated, since vomiting may precipitate severe convulsive episodes. Cautious stomach wash with full protection of airway may be done in the absence of convulsions. Activated charcoal should be administered both prior to and following gastric lavage, and is said to be very beneficial. Diazepam can be tried first, and may have to be administered in large doses (up to , or more than 1 mg/ kg). Intractable convulsions may necessitate neuromuscular blockade with pancuronium (0. The larger stems are hollow and bear numerous purple spots that are very distinctive. Fruits are smooth skinned with crenate ribs, and are binoculated, measuring about 9 mm long, and 6 mm across. Neurotoxic Poisons Toxic Principles the toxins of poison hemlock are simple piperidine alkaloids: coniine and gamma-coniceine. They are structurally similar to nicotine and possess similar clinical features in toxicity. The most serious effect occurs at the neuromuscular junction where these alkaloids act as non-depolarising blockers causing respiratory failure due to flaccid paralysis. The second effect at the autonomic ganglia is nicotinic in nature resulting in salivation, mydriasis, and tachycardia, followed by bradycardia. This myth has been propagated in popular detective fiction by writers such as Agatha Christie. In reality, strychnine has been uncommonly employed in murder owing to various obvious reasons: bitter taste, dramatic nature of symptoms (that will always arouse suspicion of foul play), and easy detectability in body fluids and tissues. Accidental poisoning can result in children who chew on the seeds out of curiosity while playing or foraging in the countryside. Previously, therapeutic misadventures used to be fairly common when strychnine was an approved constituent of various over-the-counter tonics and cathartics. Even today, certain indigenous medicinal preparations (including Ayurvedic preparations) do contain significant concentrations of strychnine or brucine. Accidental poisoning can also result from inadvertent consumption of strychnine-containing rodenticides. The most famous personality executed in this fashion was Socrates, who was condemned to death for his "crime" of introducing new divinities. Today, most cases of hemlock poisoning result from accidental circumstances due to mistaken identity with edible vegetables such as wild carrot, parsley, or anise seeds. Forensic Issues Most cases of poisoning result from mistaken identity with edible plants (vide supra). Protein binding is to the extent of 94% for acetazolamide, 60% for brinzolamide, 33% for dorzolamide, and 55% for methazolamide. Acetazolamide, brinzolamide, and dorzolamide are primarily excreted unchanged in the urine. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are non-bacteriostatic sulfonamides that inhibit carbonic anhydrase, thereby reducing the rate of aqueous humour formation in the eye and resulting in decreased intraocular pressure. Acetazolamide is the prototype of this group, which also includes brinzolamide, dichlorphenamide, dorzolamide, ethoxzolamide, methazolamide, and sulthiame. These drugs act by inhibiting the membrane-bound as well as cytoplasmic forms of carbonic anhydrase, resulting in total abolition of sodium bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal renal tubule. This results in rapid rise of urinary bicarbonate excretion, raising urinary pH to 8 and causing metabolic acidosis. Adverse Effects and Toxic Features 1 Bone marrow depression (aplastic anaemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis), skin toxicity, urinary alkalinisation, confusion, lethargy, and metabolic acidosis are common adverse effects. Rare adverse effects may include taste disturbances, ataxia, gastritis, cholestatic hepatitis, and renal failure. Overdose causes drowsiness, lethargy, metabolic acidosis, tachycardia, tachypnoea, electrolyte imbalances, and paraesthesias. Paraesthesias of the extremities, of the tongue, and at the mucocutaneous junction of the lips are common occurrences following acetazolamide therapy, and will generally resolve upon discontinuation of the medication. Acetazolamide, dichlorphenamide, and methazolamide are primarily used for the treatment of glaucoma. Acetazolamide is used for the treatment of oedema resulting from congestive heart failure, as well as that which is drug-induced. Brinzolamide and dorzolamide are topical ophthalmic agents that are indicated for the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. In cases of carbonic anhydrase inhibitor overdose ingestions, treatment is usually symptomatic and supportive. Toxicokinetics Acetazolamide is almost completely absorbed on oral administration and demonstrates a plasma half-life of 6 to 9 hours. Dichlorphenamide acts within 1 hour, with a maximal effect usually observed in 2 to 4 hours. Monitor arterial blood gases in symptomatic patients for possible metabolic acidosis. Repeat doses of no more than one-half the original amount may be given no more often than every 10 minutes if required. Overdose causes hyponatraemia (with or without extacellular fluid volume depletion), hypotension, and circulatory collapse.
Cheap intagra 100 mg free shipping
James Parkinson (1755-1824) first reported six cases of this syndrome in 1817 (at the age of 62 yea rs) erectile dysfunction zinc deficiency buy online intagra. It is developed phylogenetically from a primary vestibular area and is involved in modulation of motor activity. It receives afferents from the vestibular nuclei, spinal cord and cerebral cortex via the pontine nuclei. If you were allowed to perform one investigation, which one would you choose in a patient with a suspected cerebellar lesion Holmes (1876-1965), consultant neurologist, National Hospital for Nervous Diseases, Queen Square, London, whose observations on wartime gunshot wounds allowed him to study cerebellar disease (Lancet 1922; ii: 59, 111; Brain 1939; 62: 1-30). Remember that if the patient has vertical nystagmus in addition to horizontal nystagmus it is more likely to be vestibular nystagmus or brainstem disease. I would like to examine her neurological system to evaluate the disability (functional status). In pendular nystagmus, the oscillations are equal in speed and amplitude in both directions of movement. It may be seen on central gaze when the vision is poor, as in severe refractive error or macular disease. Jerky or phasic nystagmus is a condition in which eye movement in one direction is faster than that in the other. This is usually seen in the horizontal plane and is brought out by lateral gaze to one or both sides. It is seen with lesions of the cerebellum, vestibular apparatus or their connections in the brainstem. It is due to a lesion in the medial longitudinal fasciculus (which links the sixth nerve nucleus on one side to the medial rectus portion of the third nerve on the other). Central (affecting vestibular nuclei), as in stroke, multiple sclerosis, tumours, alcoholism. Downbeat nystagmus is associated with brainstem lesions, meningoencephalitis and hypomagnesaemia. Wernicke (1848-1904) graduated from Poland; although aware that a toxic factor was important in the aetiology, he did not realize that this syndrome was due to a nutritional deficiency. They are most often seen in those with diffuse cerebral conditions that affect the frontal lobes and pyramidal tracts. The occurrence of more than one reflex is more suggestive of disease than normality. The presence of the grasp reflex indicates disease of the supplementary motor area of the frontal cortex. Dysphasia is a disorder of the content of speech and usually follows a lesion of the dominant cortex: When the speech dejectis expressive dysphasia or nominal dysphasia or motor dysphasia, the site of the lesion in the cortex is the posterior inferior part of the dominant frontal lobe, i. Dysarthria is an inability to articulate properly because of local lesions in the mouth or disorders of speech muscles or their connections. Agnosia is a failure to recognize objects despite the fact that the sensory pathways for sight, sound or touch are intact. This is tested by asking the patient to feel, name and describe the use of certain objects. Different types of agnosia include: Tactile agnosia and astereognosis: where the patient is unable to recognize objects placed in his hands despite the fact that the sensory system of the hands and fingers is intact and there is adequate motor function to allow him to examine the object. Visual agnosia: inability to recognize objects despite the fact that the main visual pathways to the occipital cortex are preserved. Anosognosia: the lack of awareness or realization that the limbs are paralysed, weak or have impaired sensation. Apraxia is the inability to perform purposeful volitional movements in the absence of motor weakness, sensory deficits or severe incoordination. Usually the defect is in the dominant parietal lobe, with disruption of connections to the motor cortex and to the opposite hemisphere. Different types ot apraxta include: Dressing apraxias: the patient is unable to put on his clothes correctly. Gait apraxia: difficulty in walking, although patients may show intact leg move-ments when examined in bed. Constructional apraxia: the patient has difficulty in arranging patterns of blocks or copying designs. Reading difficulties, including dyslexia, occur as a part of a continuum that also includes normal reading ability. It has been defined as a disorder that is manifested by difficulty in learning to read despite conventional instruction, adequate intelligence and sociocultural opportunity. Sir Charles Sherrington (1857-1952), Oxford University, and Lord Edgar Douglas Adrian (1889-1977), Cambridge University, were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1932 for their discoveries regarding the functions of neurons. Examination Patient has difficulty in finding the appropriate words, comprehension is intact and repetition may or may not be intact. Proceed as follows: Tell the examiner that you would like to carry out a neurological examination of the patient for a right-sided stroke. His notable achievements were in anthropology and his suggestion of cerebral localization of speech was first made at a French Anthropological Society meeting in 1861. He is reported to have described muscular dystrophy (before Duchenne), venous spread of cancer (before Rokitansky) and rickets as a nutritional disorder (before Virchow). Articulation is uneven, words are slurred and variations in pitch and loudness occur. Proceed as follows: Tell the examiner that you would like to carry out a neurological examination of the patient for cerebellar signs. It may result from lesions of muscles, myoneural junctions or motor neurons of lips, tongue, palate and pharynx. Common causes include mechanical defects such as ill-fitting dentures or cleft palate. Articulation can also be tested by asking the patient to repeat the following: British constitution. Painful onset (berry aneurysm or aneurysmal dilatation of the intracavernous part of the carotid artery causing third nerve palsy). Examination Unilateral ptosis (from paralysis of the levator palpebrae superioris). Proceed as follows: Exclude associated fourth cranial nerve lesion (supplies the superior oblique) by tilting the head of the patient to the same side - the affected eye will intort if the fourth cranial nerve is intact. Tell the examiner that you would like to check: -The urine for sugar (diabetes mellitus). Note, Vascular lesions (such as those associated with diabetes and arteritis) which infarct the third nerve [nay produce a complete oculomotor palsy with pupillary sparing. The presence of pain is not a good discriminating feature between diabetes and aneurysm, as pain is present in both. In the following instances: Unilateral third nerve palsy with contralateral superior rectus palsy and bilateral partial ptosis. Bilateral third nerve palsy (with or without internal ophthalmoplegia associated with spared levator function). Each eye is moved by three pairs of muscles, and the precise action of these muscles depends on the position of the eye; the actions are as follows: Medial and lateral recti (first pair of muscles): adduct and abduct the eye respectively. Examination the eye is deviated medially and there is failure of lateral movement. The outer image comes from the affected eye and disappears when the eye is covered. Proceed as follows: Tell the examiner that you would like to check the following: Blood pressure and urine sugar. The nuclei of the first four cranial nerves are situated above the pons and those of the last tour cranial nerves are situated below the pons. A combination of clinical findings pointing to the involvement of these structures indicates the presence of an intrapontine lesion. It is a lengthy one from the brainstem and base of the skull, through the petrous tip and cavernous sinus, to the superior orbital fissure and orbit. Do you know of any eponymous syndromes in which the pons is infarcted and consequently the sixth cranial nerve is involved Millard-Gubler syndrome, in which there is ipsilateral sixth and seventh nerve palsy with contralateral hemiplegia. It is a syndrome characterized by unilateral recurrent pain in the retro-orbital region with palsy of the extraocular muscles resulting from involvement of the third, fourth, fifth and sixth cranial nerves. Gradenigo (1859-1926), an Italian otolaryngologist, described this syndrome in 1904.
Buy intagra in united states online
Consider discarding contaminated clothing erectile dysfunction treatment toronto purchase intagra with visa, as washing does not easily remove naphthalene. This may prevent renal deposition of red blood cell break down products in the renal tubules and resultant renal failure. Add 132 mEq (3 ampoules) sodium bicarbonate and 20 to 40 mEq potassium chloride (as needed) to one litre of dextrose 5% in water and infuse at approximately 1. Additional sodium bicarbonate (1 to 2 mEq/kg) and potassium chloride (20 to 40 mEq/L) may be needed to achieve an alkaline urine. Treat haemolysis with blood transfusion, packed red cell transfusions, or exchange transfusion. Monitor methaemoglobin level and treat if symptomatic, or if methaemoglobin levels are greater than 30%. It is important to remember that large doses of methylene blue may itself cause methaemoglobinaemia or haemolysis. Haemodialysis may help enhance elimination, though it is not routinely recommended. In the case of mothball ingestion (suicidal or accidental), sometimes there is confusion as to whether the active ingredient is naphthalene, camphor or paradichlorobenzene. Placing a small piece of the mothball in a test tube heated to 600 C in water bath may simplify the melting point test. Chapter 27 Hydrocarbons Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons these compounds (also called polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons) contain three or more fused benzene rings in varying arrangements that consist of carbon and hydrogen. Charring, barbecuing, smoking of foods; foodstuffs such as coffee, roasted peanuts; refined vegetable oils, crude coconut oil, heavily smoked ham. Chronic exposure in the form of inhalation or dermal contact can predispose to lung and skin cancer. For instance, methyl bromide is a toxic inhalant, and an intense vesicant, with dermal exposures resulting in burns. It is nearly odourless, though chloropicrin is typically added to commercial forms of methyl bromide to give it an intense odour. Hydrocarbons and Pesticides Toxicokinetics the usual route of exposure is either inhalation or ingestion. After absorption they are distributed mainly in the blood, brain, and adipose tissue. Section 8 Gauge fluid, solvent, refractive index liquid in microscopy Manufacture of fluorocarbon propellants (Freon), solvent, cleansing and degreasing agent, grain fumigant, dry cleaning, fire extinguisher Anaesthetic agent Degreaser, solvent, fumigant, manufacture of nylon, rayon, etc. Soil fumigant Cleansing and degreasing agent, solvent, grain fumigant Solvent for cleaning electronic equipment, degreaser, refrigerant, fire extinguisher, dry cleaning Fire extinguisher, fumigant insecticide, refrigerant Refrigerant (now obsolete) Solvent, paint remover, degreaser, manufacture of aerosol propellants and urethane foam Degreaser, dry cleaning, stain remover, manufacture of cellulose plastics Feed stock, cleanser, degreaser Solvent, dry cleaning, pesticide, metal cleaner Solvent, degreaser, pesticide Solvent, degreaser, refrigerant, typewriter cleaning fluid, paint remover, adhesive, anaesthetic *Banned from most commercial uses in Western countries Mode of Action Most of these agents are powerful hepatorenal toxins, producing centrilobular liver necrosis and renal tubular degeneration. It may be released from the cytochrome P 450 or may be converted to chloroform via a one-electron reduction and abstraction of a proton. The trichloromethyl radical may alternatively react with oxygen to form a trichloromethyl peroxy free radical, which may react to form phosgene. This may play a significant role in mediation of carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. The latter may be a toxic second messenger that activates mechanisms which destroy cellular membranes resulting in cell death. Methyl bromide, and possibly some other hydrocarbons, behave as alkylating agents and sulfhydryl enzyme inhibitors in mammalian tissues. The similarity of neuropathological manifestations of methyl bromide toxicity to those seen in thiamine deficiency may be related to effects of methyl bromide interference with metabolism of pyruvate, where thiamine acts as a co-factor. Headache, fatigue, confusion, altered mental status, delirium, amnesia, incoherent speech, ataxia, intention tremor, and positive Rhomberg sign may occur. Behavioural disturbances resembling psychosis may be noted as an early manifestation of methyl bromide toxicity. Liver damage results in hepatitis, jaundice, and hepatic encephalopathy (Table 27. Renal involvement is manifested by oliguria or anuria, haematuria and renal failure. Hypotension, ventricular arrhythmias, depressed cardiac muscles, fatty degeneration, and a slowed or irregular pulse may occur. Signs and symptoms may include blurred or double vision, nystagmus, hypotension, cough, tachypnoea, cyanosis, lethargy, profound weakness, dizziness, slurring of speech, hyperreflexia, albuminuria, haematuria, oliguria, anuria, and impaired liver function. Methyl bromide is an intense vesicant with the capacity to penetrate protective clothing. Skin blisters are produced, but are rarely deep enough to destroy entire skin layer. Spillage of liquid fumigant on the skin is likely to result in injury ranging from erythema to vesiculation. Skin contact with many halogenated hydrocarbons, especially carbon tetrachloride can lead to dermatitis through defatting action. Gastrointestinal effects (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea) and renal or hepatic damage can occur even from dermal exposure. Occurrence of a protracted extrapyramidal syndrome following low-level methyl bromide exposure has been documented in several cases. Other long-term effects include myoclonus, difficult speech, cognitive impairment, muscular atrophy, peripheral neuropathy and seizure disorders. Chronic exposure to carbon tetrachloride has been possibly associated with myasthenic reaction, a defect in neuromuscular transmission. There are reports suggesting that some halogenated hydrocarbons are carcinogenic and may cause renal cancer (especially carbon tetrachloride, tetrachloroethylene, and trichloromethane). Effects of chronic exposure to carbon tetrachloride include liver cancer in persons with acute poisoning, which might occur with prior chronic exposure, even in the absence of cirrhosis, and a possible association with brain tumours, lymphatic leukaemias and lymphosarcomas. Decontamination-dermal exposure should be treated by stripping the patient and washing copiously with soap and water. Administer oxygen if there is evidence of altered mental status or respiratory failure. Watch out for cardiac arrhythmias, aspiration pneumonitis, and hepatorenal failure. Carbon tetrachloride-induced liver cirrhosis results in bile acids not being detoxified in the enterohepatic circulation. In rat studies administration of cholestyramine, which has a strong affinity for bile acids in the intestine, prevents their enteral resorption and decreases the induction of cirrhosis. It is probably most effective if given within 16 hours following ingestion of carbon tetrachloride. Alternatively, the Prescott protocol can be followed: gastric lavage followed by intravenous infusion of N-acetylcysteine at 150 mg/kg over 15 minutes, then 50 mg/kg over 4 hours, followed by 100 mg/kg over 16 hours. However, this treatment cannot be recommended until further studies are done to confirm efficacy. Treat renal failure with dialysis and hepatic failure with fresh frozen plasma, vitamin K, low-protein diet, neomycin and lactulose. A review of subsequent literature suggests that hyperbaric oxygen treatment is appropriate treatment for carbon tetrachloride intoxication. Haemodialysis is generally not effective, though an anecdotal report suggests it may be useful in methyl bromide poisoning. Haemodialysis or haemoperfusion may be necessary to support patients in renal or hepatic failure, respectively. Treatment of dermal burns (methyl bromide): Usual Fatal Dose About 4 to 5 ml for most halogenated hydrocabons; 20 to 25 ml for a few others. With reference to methyl bromide, airborne concentrations as low as 100 ppm have been reported to be harmful, while concentrations of 8,000 to 60,000 ppm may be fatal. Isonitrile Test: 10 ml of distillate or a small amount of the suspected liquid in 10 ml of water is placed in a test tube. To this, 1 ml of purified aniline and 2 ml of 20% sodium hydroxide are added and gently heated. A positive result is indicated by the development of a foul skunk-like odour due to formation of phenyl isonitrile. Gas chromatography can be used to quantitate halogenated hydrocarbons in biological samples.

Buy intagra with a mastercard
Abstinence symptoms are seen in the first and second postnatal days erectile dysfunction without drugs cheap intagra 75 mg, and may last for several weeks. Symptoms of neonatal cocaine abstinence syndrome include irritability, hypertonia/poor muscle tone, tremor, hyperactive Moro reflex, loose stools, sleep disturbances, poor feeding/ excessive sucking, nasal stuffiness, tachypnoea, visual function disturbance. It must be noted that external contamination of hair can occur from crack smoke, but that can be washed off, whereas systemic exposure is not affected by washing the hair. Two-dimensional echocardiography may be useful in detecting the presence of new regional wall-motion abnormalities in patients experiencing cocaine-induced chest pain. Troponin levels may be more useful in evaluating potential myocardial injury than creatinine kinase. Acid-base abnormalities: Arterial blood gases in cocaine abusers show a pH varying from 7. Metabolic acidosis is not uncommon, and usually results from convulsions, agitation, or trauma. It is therefore advisable to perform a contrast study of the bowel with follow-up X-rays 5 hours after the oral ingestion of a water-soluble contrast compound such as meglumine amidotrizoate (50 ml). Daily views are performed thereafter until negative views coincide with the passage of two drug packet-free stools. Diagnosis Blood or plasma cocaine levels are not clinically useful, although they may be advisable to be done in medico-legal cases. Qualitative urine tests using kits may be helpful in clinical diagnosis (by utilising chromatography, radioimmunoassay, enzyme immunoassay, fluorescence polarisation immunoassay, and enzyme-multiplied immunoassay technique). Benzoylecgonine, the major metabolite of cocaine, can usually be detected in urine for 48 to 72 hours after cocaine use. Acute Poisoning Activated charcoal adsorbs cocaine in vitro under both acidic and alkaline conditions, and can be administered in cases of ingestion. Hypertension: It is usually short-lived and often followed by significant hypotension. Myocardial infarction: Acute myocardial infarction due to cocaine toxicity must be treated on the same lines as myocardial infarction in non-cocaine users, except for the use of beta blockers. Thrombolytics should be avoided in patients with cocaine-induced myocardial infarction and uncontrolled hypertension, because of the increased risk of intracranial haemorrhage. Aortic dissection: the hypertension that precipitated aortic dissection must be controlled immediately with nitroprusside and calcium channel blockers. Rhabdomyolysis: Early aggressive fluid replacement is the mainstay of therapy and may help prevent renal insufficiency. Acidosis: Correction of acidaemia through supportive care measures such as hyperventilation, sedation, active cooling, and sodium bicarbonate infusion can have beneficial effects on conduction defects. Increasing the level of butyrylcholinesterase in the blood (which metabolises cocaine to inactive compounds) could help in rapidly inactivating cocaine in acute intoxications. Chronic Poisoning A number of psychological and pharmacological approaches to the treatment of cocaine dependence have been tried with varying degrees of success. A combined approach judiciously tailored to - the needs of individual patients offers the best hope of preventing relapses. Psychotherapy: this involves cognitive-behavioural, psychodynamic, and general supportive techniques. Group counselling: the most widely used form of psychosocial treatment for cocaine dependence is group counselling, in which the group is open-ended with rolling admissions; the group leaders are drug counsellors, many of whom are recovering from addiction, and the emphasis is on providing a supportive atmosphere, discussing problems in recovery, and encouraging participation in multistep programmes. Section 11 Substance Abuse Initial studies with fluoxetine promised good results, but craving actually worsened in some patients. Several studies indicated better efficacy with carbamazepine for controlling craving. Acupuncture: Use of auricular acupuncture to treat cocaine abuse has become popular of late, though controlled studies of its efficacy have not shown convincing results. This must be differentiated from "body stuffing" in which an individual who is on the verge of being arrested for possession of illegal drugs, swallows his illicit contraband to conceal the evidence. Sudden death due to massive overdose can occur in either a bodypacker or a bodystuffer, if one or more of the ingested packages burst within the gastrointestinal tract. Symptomatic patients should be considered a medical emergency, and be evaluated for surgical removal of the packets. Asymptomatic patients should be monitored in an intensive care unit until the cocaine packs have been eliminated. There are no specific findings at autopsy, except for nasal septal ulceration and perforation if the deceased had been a long-term abuser of cocaine. Specimens obtained postmortem should be preserved with sodium fluoride, refrigerated, and analysed quickly. In the current drug subculture, cocaine has become the "champagne drug" because of its cost and relative scarcity. Therefore in India, cocaine abuse is restricted mainly to the affluent classes of society. The prevalence and extent of the problem among newer generation Indian film actors in recent times has become apparent with the arrest of several filmstars for possession of cocaine. Several high profile artists, socialites, and even politicians have been caught with cocaine possession. Cocaine has always been popular with musicians (especially jazz and rock), other artistes, and film personalities. Today cocaine has made inroads into the general population, especially adolescents. After the cocaine epidemic of the 1970s ("snorting seventies") in the West, there had been 562 Section 11 a relative lull in the 1980s and early 1990s. Cocaine abuse by pregnant mothers can lead to devastating effects on the foetus and the new-born (Table 34. There is convincing evidence that cocaine is teratogenic and can play an important role in the causation of several serious congenital anomalies (Table 34. Cocaine abuse is well known for its propensity to cause sudden death not only due to its deleterious effects on health (cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial infarction, malignant hyperthermia, renal failure), but also due to its capacity to provoke the user to commit acts of aggression and violence. Cocaine toxicity has been reported in children receiving topical adrenaline and cocaine for local anaesthesia. The plant grows to a height of 5 to 15 feet, and is characterised by an odd number of leaflets on each leaf (varying from 5 to 9), all having serrated or saw-tooth edges, and small, green flowers. It is usually smoked in a pipe ("chillum") or in the form of cigarettes ("reefer" or "joint" or "number"). Hashish oil or "liquid hashish" is an alcohol or petrol extract which occurs as a dark green viscous liquid with the consistency of tar. Marijuana "Blunts": this is nothing but cheap cigars sliced open, packed with cannabis, and resealed. The durable fibres of the woody trunk of cannabis, referred to collectively as Indian hemp, has been used for centuries to produce rope and twine, as well as fine or rough cloth. The cannabis plant is possibly the most efficient source of paper pulp, producing up to 5 times as much cellulose per acre per year, as trees. It is available from Roxane under the trade name Marinol, as round, amber, soft gelatin capsules filled with sesame oil in which either 2. Another synthetic cannabinoid, nabilone, is available from Lilly under the trade name Cesamet in the form of 1 mg capsules. Some studies suggest a possible role for cannabis in the treatment of multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and dystonic states, though convincing scientific evidence is lacking. A cannabinoid antagonist was also discovered that antagonises cannabinoidinduced inhibition of adenylcyclase and smooth muscle contraction. It appears that cannabinoids exert many of their actions by influencing several neurotransmitter systems and their modulators. Cannabinoid receptor location and density in animal models has correlated well with clinical effects in humans. The highest density of receptors occurs in the basal ganglia and molecular layer of cerebellum, which correlates with its interference in motor co-ordination. After binding to receptors, cannabinoids also produce effects through second-messenger systems including inhibition of adenylcyclase and calcium channels, and also probably by enhancing potassium channels activity.
Purchase intagra 50 mg mastercard
Mebendazole has also been used as a fungicide for controlling spoilage in citrus fruits and Dutch Elm disease erectile dysfunction operation purchase intagra canada. Adverse effects include headache, nausea, metallic taste, anorexia, and occasionally vomiting and diarrhoea. Concomitant intake of metronidazole with alcohol induces a disulfiram-like reaction. Psychotic responses have also been reported with concurrent ethanol and metronidazole therapy. Alcoholic beverages or products containing ethanol or propylene glycol should not be used during tinidazole therapy also (and for 3 days after the cessation of therapy), because nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, headaches and flushing may occur. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and vertigo, while ocasionally there may be diarrhoea, headache, rash, fever, haematuria, and intrahepatic cholestasis. Colour vision disturbances and tinnitus have been reported during therapeutic use of thiabendazole. Sicca complex occurs rarely during thiabendazole therapy; symptoms include reduced tear production and dry mouth. Animal experiments suggest that these drugs are teratogenic and hence should not be administered to pregnant women. Single oral doses of metronidazole of 15 grams have been tolerated with only minimal clinical effects. However, standard treatment measures may be indicated in ingestions of greater than 1 to 2 grams. Activated charcoal/stomach wash may be helpful in the early stages of an overdose. Common worms encountered include nematodes (round worms), trematodes (flukes), and cestodes (tapeworms). Diethylcarbamazine It is a piperazine derivative and remains the drug of choice for filariasis and tropical pulmonary eosinophilia, more than 50 years after it was introduced into therapeutics. Diethylcarbamazine is also used in the treatment of loiasis,* onchocerciasis, and ascariasis. Peak plasma concentrations are reached in 1 to 2 hours, followed by a rapid decline, then a secondary rise 3 to 6 hours after dosing. The drug does not distribute in the fat and consequently has a volume of distribution, close to that of body water. It is primarily excreted in the urine as unchanged drug, but a relatively small amount is excreted as the N-oxide metabolite. Most of the severe clinical effects following diethylcarbamazine ingestion are due to allergic reactions to the protein substance elaborated by the dying microfilariae and not to diethylcarbamazine alone. The most disturbing adverse effect is the Mazotti reaction which is a result of the host response to destruction of parasites, and is characterised by rash, itching, tender lymphadenopathy, fever, arthralgia, and headache. Rare toxic effects include encephalitis and retinal haemorrhages (invariably during the course of treatment of loiasis). Corneal opacities, anterior uveitis, visual field restriction, optic atrophy, punctate keratitis, and chorioretinal changes have been observed when diethylcarbamazine has been administered as eye drops (or even orally) in onchocerciasis. Dose-related responses to diethylcarbamazine, when used for therapy of filariasis, include weakness, dizziness, lethargy, anorexia, and nausea. These effects generally occur within 1 to 2 hours following a dose and may persist for several hours. In a study of almost 300,000 therapeutic administrations of the drug, approximately 29% of the patients experienced adverse reactions. Praziquantel It is a pyrazinoisoquinoline derivative and is effective against tapeworms, liver flukes, and schistosomiasis. Praziquantel displays two major effects: it causes spastic paralysis of worms, and (at higher doses) induces tegumental damage which activates host defence mechanisms resulting in the destruction of the worms. Side effects include abdominal pain, headache, drowsiness, vertigo, urticaria, rash, fever, and arthralgia. They usually respond to symptomatic measures such as administration of analgesics. Praziquantel is contraindicated in ocular cysticercosis since the host response can cause irreversible damage to the eye. Concomitant intake of alcohol can aggravate vertigo that is often associated with this drug. Miscellaneous Drugs and Poisons Pyrantel Pamoate It is a depolarising neuromuscular blocking agent and causes spastic paralysis of pinworm, roundworm, and hookworm. Adverse effects are mild and comprise headache, drowsiness, insomnia, anorexia, nausea, abdominal cramps, diarrhoea, rash, and occasional dizziness. Transient elevations of serum transaminase levels have been reported in a small percentage of patients. It must not be given along with piperazine because both are mutually antagonistic. Section 9 Levamisole this drug is not in use in Western countries because of the risk of agranulocytosis, but still finds a place in India. Haematologic toxicity has included neutropenia, anaemia, thrombocytopenia, and fatal cases of agranulocytosis have occurred with therapy. Initially there may be stimulation of the ganglionic and skeletal muscle transmission, followed by blockade. An encephalopathy-like syndrome has developed in some patients during chronic therapy; onset of symptoms is variable. Taste perversion, salivation, lip licking, and head shaking have occurred with therapeutic doses. Do not administer antacids since levamisole may be better absorbed in an alkaline medium. Niclosamide Niclosamide is a halogenated salicylanilide derivative which is mainly used in the treatment of tapeworm infestation. Unfortunately, while the drug may kill adult worms, ova are usually unaffected, which may result in cysticercosis due to liberation of viable ova into the lumen of the gut following digestion of dead worm segments. However, niclosamide is a very safe drug and is virtually free from serious side effects. Piperazine Piperazine is a cyclic secondary amine which is very effective against roundworm, pinworm, and threadworm infestations. It is also used as a corrosion inhibitor, insecticide, and accelerator for curing polychloroprene. Piperazine is given orally and acts by inducing flaccid muscle paralysis in the worms facilitating their expulsion by peristalsis. In therapeutic doses piperazine is safe, but overdose results in convulsions, hallucinations, and respiratory failure. Toxicity has been reported to develop at doses as low as 30 mg/kg/day in patients with renal failure, and 50 to 75 mg/kg/day in patients with normal renal function. Common effects include nausea, vomiting, confusion, muscular weakness, and ataxia. There may have been considerable time elapsed between the time of ingestion and death as a result of which the offending drug may have been metabolised and excreted completely. Analysis of therapeutic drugs in body fluids and tissues is usually difficult because of lack of facilities. Sufficient postmortem data do not exist for most of the therapeutic drug-related fatalities. Most pharmaceutical drugs do not leave behind characteristic or specific features in a dead body, and this is especially true of anti-infective drugs. Sometimes residues of the drug involved may be obtainable from the stomach or intestine in the form of powder particles, concretions, or distinctively coloured fluid material. These can be submitted for toxicological analysis which in any case is the only authentic method of confirming a drug-related death (if it can be successfully accomplished! Apart from toxicological analysis, one other investigation which can sometimes help is histopathological analysis of viscera, and this must always be undertaken especially with reference to target organs. Poisoning from anti-infective drugs is relatively uncommon, though adverse (side) effects especially at high therapeutic doses frequently occur, which is all the more likely if the duration of therapy is prolonged. However as the incidence of poisoning relentlessly rises in India, the agents employed for deliberate self-ingestion have undergone a subtle but definite change over a period of time. While chemicals and plant products were overwhelmingly common in the past, today pharmaceutical preparations are making significant inroads.