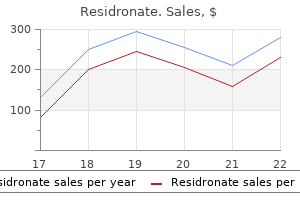
Order 35 mg residronate mastercard
The patient should receive three to four daily injections of a regular (human act rapid) and an intermediate acting insulin (isophane) symptoms 7 days before period order residronate no prescription, the latter is to be given before dinner. The aim is to maintain the blood sugar level as near to normal as possible without causing troublesome hypoglycemia. Use of subcutaneous insulin infusion by insulin pump is preferred as it is more physiological. Women are instructed on diet composition, insulin dose, recognition and treatment of hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia and ketosis, adjusting insulin dose in relation to exercise, food and sick days. Early hospitalization facilities: (1) Stabilization of diabetes (2) Minimizes the incidence of preeclampsia, polyhydramnios and preterm labor (3) To select out the appropriate time and method of delivery. Methods: Prior to the day of induction of labor, the usual bed time dose of insulin is administered. An intravenous drip of one liter of 5% dextrose is set up with 10 units of soluble insulin. Blood glucose levels are estimated hourly with a glucose meter and the soluble insulin dose is adjusted accordingly. Cesarean section: the indications are-(1) Fetal macrosomia (>4 kg) (2) Diabetes with complications or difficult to control (3) Fetal compromise as observed in antepartum fetal monitoring (4) Elderly primigravidae (5) Multigravidae with a bad obstetric history (6) Obstetric complications like preeclampsia, polyhydramnios, malpresentation. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion with insulin pump is preferred as it is more physiological. The insulin requirement suddenly falls following delivery and after the omission of the drip, pre-pregnant dose of insulin is to be administered or adjusted from the blood glucose level. Epidural or spinal anesthesia is better than general anesthesia as oral feeding could be started soon following the operation. Use of motorized syringe pump for insulin infusion is convenient (3) Hourly estimation of blood glucose levels is done with glucose meter and the insulin dose is adjusted accordingly. Fetal monitoring: Constant watch to note the fetal condition is mandatory, preferably with continuous electronic fetal monitoring. However, labor should not be allowed for more than an arbitrary 12 hours and should be augmented by low rupture of the membranes and oxytocin or delivered by cesarean section. Examination of the placenta and cord: Placenta is large, the cord is thick and there is increased incidence of a single umbilical artery. Microscopically, villi show edema and excessive syncytial knots, numerous cytotrophoblasts and thickened basement membrane. It may be precipitated with the use of -mimetic agents (Isoxsuprine) and corticosteroids. Management is done in an acute care unit where both neonatal care is also available. Parameters to assess are: Degree of acidosis, alterations in the level of arterial blood gas, blood glucose, ketones and electrolytes. A fresh blood glucose level after 24 hours will help to adjust the dose of insulin. The baby should preferably be kept in an intensive neonatal care unit and to remain vigilant for at least 48 hours, to detect and to treat effectively any complication likely to arise. All babies should have blood glucose to be checked within 2 hours of birth to avoid problems of hypoglycemia (blood glucose < 35 mg/dL). Early breastfeeding within half to 1 hour is advocated and to be repeated at three to four hourly intervals thereafter to minimize hypoglycemia and hyperbilirubinemia. Improvement in the care of diabetes in pregnancy has reduced perinatal mortality significantly (< 5%). Low dose combined oral pills containing third generation progestins, are effective and have got minimal effect on carbohydrate metabolism. Main worry is their effect on vascular disease (thromboembolism and myocardial infarction). Metabolic events for a woman with diabetes in pregnancy is maternal hyperglycemia Fetal hyperglycemia Fetal pancreatic islet cells hyperplasia and hypertrophy Increased fetal insulin secretion Excessive fetal growth Fetal macrosomia Increased birth injury. Fetal congenital malformations are high in diabetic woman (pregestational diabetes); commonest is cardiovascular (see p. Complications of diabetes in pregnancy are increased both for the mother, fetus and the neonates (see p. Oral hypoglycemic agents (glibenclamide, metformin) are also being used to maintain glycemic control. It depends on degree of glycemic control, presence of vascular disease (nephropathy, retinopathy) or hypertension. Textbook of Obstetrics Self monitoring of capillary blood glucose is encouraged for optimum glycemic control. Timing of delivery should be with fetal maturation provided diabetes is well controlled and fetal surveillance is normal. Mode of delivery depends on level of glycemic control, fetal size, associated complication if any (preeclampsia) and pelvic adequacy. However selected women may be considered for induction of labor and/or vaginal delivery. Pre-pregnancy counseling ideally be done for all such women for optimum glycemic control and pregnancy outcome. Other causes are: Nodular thyroid disease, sub-acute thyroiditis, hyperemesis gravidarum and trophoblastic disease. Thyroid stimulating antibodies cross the placenta and produce neonatal thyrotoxicosis with increased neonatal death. The risk is increased if the antithyroid drug is stopped in late pregnancy or following surgery. Ultrasonography of the fetal thyroid gland is done when the mother is taking antithyroid drugs. Radioactive iodine uptake and scans should not be done during pregnancy as it will cross the placenta and damage the fetal thyroid gland permanently. Then it is progressively reduced to a maintenance of between 5 mg and 15 mg daily. Patients having marked tachycardia or arrhythmias should also have propranolol (blocking agent). The drugs are not contraindicated during breastfeeding provided the dose is kept relatively low and close monitoring of the neonatal thyroid functions is carried out. Thyroidectomy, when required to relieve the pressure symptoms can be done safely in the second trimester with prior biochemical control. Chapter 20 Medical and Surgical Illness Complicating Pregnancy 335 Preconceptional counseling: Considering the hazards during pregnancy, preconceptional counseling is important. Adequate treatment should be instituted to bring down the thyroid function profile to normal. Radioactive iodine (131I) therapy should not be given to patients wanting pregnancy within one year. Oral pill is to be withheld because of accelerated metabolism and disturbed liver function. The clinical association of hypothyroidism in pregnancy may be due to (i) first time diagnosis in pregnancy (ii) hypothyroid women who either discontinue thyroid therapy or who need larger doses in pregnancy (iii) hyperthyroid women on excessive amounts of antithyroid drugs (iv) women with lithium or amiodarone therapy. Primary hypothyroidism met in pregnancy is mostly related to thyroid autoimmunity (Hashimoto thyroiditis). Untreated hypothyroidism in early pregnancy has a high fetal wastage in the form of abortion, stillbirth and prematurity and deficient intellectual development of the child. If the patient is having substitution therapy in pre-pregnant state, the dose of levothyroxine need to be increased in pregnancy.
Best residronate 35 mg
The plastic cannula has got advantages over the metallic one-as it causes less damage to the uterine wall and the product sucked out is visible treatment yeast diaper rash order 35 mg residronate mastercard. The rods are assembled in the blades of long-curved obstetric forceps prior to introduction and lastly the handle is attached to the rods. The devices are required where much forces are necessary for traction as in mid forceps operation. The cup is to be fitted to the scalp of the forecoming head by producing "chignon" with the help of vacuum. Total four forceps are ordinarily required-one for each angle and one for each flap. Its functions are hemostasis and to catch hold of the margins so that they are not missed during suture. To be of value, the mucus should be sucked prior to the attempt of respiration, otherwise the tracheobronchial tree may be occluded leading to inadequate pulmonary aeration and development of asphyxia neonatorum. The metal sucker requires a sterile simple rubber catheter to be fitted at one end and a sterile piece of gauze to the other end. The cord clamp is to be kept in place until it falls off together with the detached stump of umbilical cord. There is one small lobe (size of a cotyledon) situated at a distance from the main placental margin. Self-assessment: (i) What are the surfaces of a normal placenta and how they could be identified It is measured from outer edge of proximal skull to the inner edge of the distal skull. Hemorrhage, shock, pre-eclampsia, sepsis, acute pulmonary insufficiency and rarely coagulation failure. The late complications are: development of persistent trophoblastic neoplasia and choriocarcinoma (p. Principles of management are: (a) Supportive therapy (blood transfusion) (b) Suction evacuation of the uterus and (c) follow up (p. The normal gestational sac appears round in the early stages and gradually it becomes oval in shape. The gestational sac is filled with chorionic sac fluid which is more echogenic than the amniotic fluid as it contains more protein materials. A gestational sac diameter 16mm without an embryo is a strong sign of early pregnancy failure. The number of yolk sacs is helpful to determine amnionicity of a multifetal pregnancy. Absent cardiac activity in embryos is the most important factor in predicting poor pregnancy outcome. Fetal brain, foot (Lt), Placenta, attachments of the umbilical cord over the placenta and the herniated mass are seen (omphalocele). Ans: Presence of metallic implants, pace makers, any other metal or iron devices in the body may alter the study result. Self-assessment: (i) How a case of acute (ruptured) tubal ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed Disinfection is done by any one of the methods: Immersing instruments in (i) boiling water for 20 minutes, (ii) 2% glutaraldehyde (cidex) solution for 20 minutes, or (iii) 0. Cleaning: Instruments are disassembled and washed on all surfaces in running (preferably warm) water. Of these, keratinocytes are by far the most numerous, making up the bulk of the epidermis and giving it its characteristic microscopic appearance. The stratum basale (or stratum germinativum), also known as the basal cell layer, consists of a single layer of cuboidal keratinocytes that lie atop the basement membrane (see the following) and are connected to it by numerous hemidesmosomes. At this depth, keratinocytes have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and ovoid nuclei. As its name implies, division of keratinocytes occurs primarily in the stratum germinativum, although mitotic activity is occasionally seen in the lower part of the stratum spinosum, in particular the cell layer immediately above the stratum basale, the parabasal layer. In the process of self-renewal, these cells gradually ascend into the upper layers and are replaced. The stratum spinosum, also known as the spinous cell layer, is named after the spinous processes (or "prickles"), which connect the keratinocytes in this layer and the stratum basale to one another. These spinous processes provide contact points for desmosomes, which are the ultrastructural basis for the tight binding of keratinocytes to one another. These processes may be difficult to visualize in normal skin, but they become more evident by intercellular edema (also known as spongiosis). On most parts of the body, the skin possesses a single layer of dead (but functional) cells, the stratum corneum, consisting mostly of keratin. The cells in this layer are sometimes called corneocytes to distinguish them from the living cells in the layers below. Where the stratum corneum is particularly thick, another layer, the so-called stratum lucidum, may be present between it and the stratum granulosum. The stratum lucidum differs from the stratum corneum only by a pale eosinophilic appearance and higher lipid content. Although pyknotic nuclei may appear in the stratum corneum or stratum lucidum in pathologic processes, in normal skin, the keratinocytes of both these layers are anucleate. Keratinocytes stain positively for high molecular weight cytokeratins such as 34E12 but negatively for Cam5. Although the amount of melanin produced and stored varies between darker and lighter skinned individuals, the number of melanocytes does not. Immunostains for Melan-A/Mart-1 may lead to an overestimate of the density of melanocytes, especially if the antibody concentration is high. S100 protein stains normal intraepidermal melanocytes, but it is neither very sensitive nor specific. Histologically, the cells are characterized by small, dark, ovoid nuclei and scant, clear cytoplasm. Depending on anatomic site, they number from one per 10 to one per five basal keratinocytes, with higher concentrations on the face and genitalia. In routine practice, the basement membrane is visible under H&E, but it may be emphasized using the periodic acid-Schiff reaction. It is highly irregular, possessing an undulating system of dermal papillae, which complement the rete ridge system of the epidermis. I-6), a specialized mechanoreceptor involved in tactile sensation that is found in greatest concentration on the hands, feet, and lips and is characteristically located in the dermal papillae. The inferior edge of the papillary dermis is bounded by the subpapillary (or superficial vascular) arterial, venous, and lymphatic plexuses. It possesses a rich vascular supply, with a system of anastomosing small arteries, veins, and 4 lymphatics called the cutaneous (or deep vascular) plexuses at its inferior border. I-9), a specialized type of nerve ending that participates in the sensation of deep pressure and vibration. These are also found in the subcutis, as well as certain internal organs, and are found in greatest concentrations in the palms, soles, dorsal digits, and genitalia. Glomus bodies function in thermoregulation and are most frequently found in distal sites such as the ears and fingertips. The three main extracellular proteins that make up the dermis are collagen, providing strength; elastin, providing elasticity; and ground substance. In normal skin, elastin is a minor component, consisting of slender, amphophilic fibers that may be difficult to distinguish without the use of various special stains.
Purchase residronate canada
Depth should be adjusted so that the structure of interest (eg medicine kit for babies purchase residronate 35 mg otc, the heart) occupies the center of the screen. Gain can be increased or decreased to make structures brighter or darker, respectively. Probe Manipulation Operators should hold the ultrasound probe similar to how they hold a pen, allowing the base of the hand to rest on the patient to provide added stability. Operators should slide the probe across the surface of interest (eg, thorax) either medial lateral or cephalocaudal to obtain the appropriate window for the structure being examined (eg, lung). Rotating the probe clock or counterclockwise, fanning medial lateral, or angling the probe toward or away from the indicator all allow for optimizing or adjusting a scanning plane. Equipment It is imperative to have an easily accessible and portable machine that allows for rapid and repeated use. Appropriate manufacturer warranty and technical support should be included in the purchase because of heavy use and the high likelihood for maintenance. Basic Critical Care Echocardiography Basic critical care echocardiography is a qualitative "eyeball" assessment of global cardiac function done in a systematic fashion to answer a particular question. If possible, the operator should always be positioned immediately down- or upstream (adjacent) to the system console, allowing for ease of image acquisition and manipulation. If a patient can safely be turned to the left lateral decubitus position, this often yields a higher quality image. To correct an off-axis "basketball" shape, the operator often must slide the probe one intercostal space caudad. Although often used to indiscriminately evaluate "volume status," it has only been validated when certain criteria are met (eg, passive mechanical ventilation with 10 cc/kg of tidal volume while in sinus rhythm). The linear probe is best used in children to examine the pleural line and in the setting of evaluation before and after vascular access placement. The operator places a phased array probe in any thoracic rib interspace perpendicular to the pleural line to generate these artifacts or patterns. It is important to distinguish the edge of each rib, which are found superior to the pleural line and cause complete drop-off of ultrasound beams (ie, black immediately inferior to them) as opposed to the pleura, which creates a horizontal echogenic line (ie, A-line). A normal aerated lungs shows lung sliding, which is a predictable repetition of normal pleura undergoing horizontal movement throughout the respiratory cycle. Lung that becomes "wet" shows B-lines that originate from the pleural line; move horizontally with lung sliding; travel vertically, often obliterating the A-line pattern; and reach the end of the imaged field. As a lung fills with more fluid, an alveolar consolidation pattern (C pattern) will develop similar in appearance to the liver. Lung point is seen in the presence of a pneumothorax and is the loss of lung sliding within the same interspace being examined. Pleural ultrasound should be performed as part of every evaluation of a patient with dyspnea or respiratory failure. There is a significant increase in morbidity and mortality in these patients, particularly if treatment is withheld because of a delay in diagnosis. Bedside triplex ultrasound examination is considered the gold standard for diagnosis; however, sonographic technicians are not readily available to perform comprehensive examinations. Existing literature shows that intensivists with focused training can perform compression ultrasound to diagnose deep vein thrombosis with a high degree of accuracy. The examination can be categorized into five points in two separate regions, namely the femoral and popliteal. The probe is placed in transverse orientation perpendicular to the vein as high up toward inguinal ligament as possible. The examination can be continued distal to the superficial femoral vein and deep vein branch point with compressions every 1 to 2 cm on the medial portion of the thigh. A complete examination starts with preprocedural scanning of both the left and right neck to identify the safest site for insertion. After an operator has chosen an ideal site, confirming the presence of lung sliding on the anterior chest of the ipsilateral side to confirm is encouraged when there is concern for postprocedure pneumothorax. The procedure should be performed under standard sterile technique (sterile ultrasound probe cover) using dynamic needle guidance visualizing in real time the insertion of the needle tip into the lumen of the vein. Postprocedure, pneumothorax can be effectively ruled out by again checking for the presence of lung sliding (only if it had been present before the procedure). Various line placement techniques using saline injections to confirm venous location at the superior vena cava or right atrium have been studied and show a high degree of accuracy for appropriate line placement. Computed tomography will undoubtedly remain the gold standard for diagnosing abdominal pathology; however, abdominal ultrasound can be used in various trauma-related protocols to evaluate for a source of renal failure and the presence of ascitic fluid and to guide diagnostic paracentesis. Finally, intra-abdominal vascular pathology, including abdominal aortic aneurysms and dissections, should be evaluated for trauma and unexplained shock states. A 23-year-old woman presents with worsening of rightsided pleuritic chest pain, intermittent episodes of nighttime chills, and a cough productive of yellow sputum. Ultrasound-guided catheter insertion with instillation of dornase and alteplase C. A 52 year-old obese woman is admitted to the intensive care unit during the night for septic shock caused by a urinary tract infection. The patient is intubated for increased work of breathing, and the on-call resident performs an ultrasound-guided triple-lumen catheter insertion of the right internal jugular vein under your supervision for vasopressor use. The trainee requires three sticks for completion of the procedure because of excessive soft tissue at the neck; however, the procedure is seemingly completed without event. You suspect an iatrogenic pneumothorax from line insertion; however, the x-ray technician has not returned any pages. You perform a lung ultrasound with the phased array probe to assist with your suspected diagnosis. Which of the following statements is true about the sensitivity and specificity of lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumothorax A diagnosis of severe sepsis with shock is made, prompting initiation of a sepsis protocol. The patient receives 30 cc/kg of crystalloid and broadspectrum antibiotics; however, his shock state worsens, prompting intensive care unit evaluation. Cardiogenic shock from left ventricular failure from acute myocardial infarction B. A 65-year-old man recently diagnosed with metastatic colon cancer with significant disease burden in the liver and omentum is admitted because of 1 day of acute-onset weakness and general malaise. He is rushed to the trauma bay and found to be afebrile, tachycardic, hypotensive, and tachypneic. He receives 2 Liters of crystalloid with some improvement in his blood pressure and heart rate. He is sent for computed tomography of the chest and abdomen, which reveals a new subsegmental pulmonary embolism, omental and hepatic metastases, and newfound ascitic fluid in the abdomen. He is given Lovenox for the pulmonary emboli and admitted to the general medical floor. Six hours after admission at 3 am, the patient becomes acutely tachycardic and hypotensive again and complains of acute abdominal pain. While he is eating lunch, he becomes acutely diaphoretic and dyspneic, his blood pressure decreases from 110/80 to 70/40 mmHg, and his heart rate increases from 82 to 125 beats/min. As part of your evaluation of undifferentiated shock, you perform a goaldirected echocardiogram. Based on these images and the clinical scenario, what would be the appropriate treatment choice She cannot complete a full sentence, has bilateral wheezing in all the posterior lung fields, and has 3+ pitting edema in both legs with chronic venous stasis changes. She receives appropriate treatment with volume resuscitation, insulin, and antibiotics. On her fourth day of admission, the patient develops new bilateral lower extremity edema, right slightly greater than left. Thoracic ultrasound images A and B are representative of Zones 1 and 2 on the bilateral chest. She states she also has been experiencing cough, wheezing, orthopnea, and worsening swelling in her legs. Her physical examination reveals both bibasilar crackles and inspiratory and expiratory wheezing in all lung fields. Acute pulmonary edema Obstructive airways disease exacerbation Pneumothorax Pneumonia hyperlipidemia is sent in from a nursing home because of altered mental status. Laboratory studies and urinalysis are done and show a leukocytosis and white blood cells and nitrites, respectively.
Order residronate
A cohort study follows a group of participants with a known exposure and a group without the exposure to compare the incidence in both groups (choice C) medicine bobblehead fallout 4 order residronate with american express. A case-control study compares those who already have the disease with matched control participants to retrospectively identify the cause of the disease and hence cannot be used to estimate prevalence of the disease (choice D). Cohort studies compare the incidence of an event or disease in those with an exposure compared with those without an exposure (choice C). They, however, are of limited value in evaluating rare diseases because very few participants are likely to develop the disease. Case-control studies are well suited to study the cause of an uncommon or rare disease. Nonresponse bias In this scenario of a survey trying to establish current practice, only half of the providers responded. In such a scenario, the people who respond are likely to behave different than those who do not and may have different clinical practice from those who do not respond. Berkson bias is a form of a selection bias that occurs in hospital based case-control studies (choice B). Selection bias occurs when the method of selecting participants in the study results in a difference between the study population and the target population. Reporting bias occurs as enrolled participants tend to report or emphasize exposures that they believe to be more important (choice D). Selection bias Randomization prevents the allotting of a certain subset of patients to one arm of the trial versus the other. It ensures that investigators cannot select the arm of the study that the patient is allotted to , thereby minimizing selection bias (choice C). Recall bias occurs as participants interviewed tend to recall more recent and more severe events. The placebo effect is the subjective improvement felt because of knowledge that one is receiving treatment and is unaffected by randomization (choice D). Ascertainment bias occurs when the person determining the outcome is influenced by knowing which are the study the participant is in. Randomization helps minimize selection bias; it also aides in the equitable distribution of known as well as unknown confounders. The placebo effect occurs when patients report improvement as a result of knowing that they are receiving treatment. This can be minimized by blinding the patients to the arms of the study that they are in, with the use of placebos or sham treatments. In this hypothetical scenario, the above negative study falsely accepts the null hypothesis, which is that there is no benefit with the new intervention. A type I error is the false rejection of a true null hypothesis, or a false positive finding (choice A). A larger sample size would be required (choice B) to detect a smaller treatment benefit or effect. Increasing the power to 90% when designing the study would result in a larger sample size (choice D). Accuracy is the degree to which an obtained result represents the true population result and is an estimate of error due to bias. Larger sample sizes do not necessarily minimize reduce bias and hence would not improve accuracy (choice D). Increasing the power of the study to detect a difference would increase the sample size (choice A). Precision is the reproducibility of the result if the study were to be repeated under similar circumstances. Increasing the sample size would increase the precision (choice C) and decrease the standard error of measurement, which is an estimate of precision (choice B). Prevalence: 200; incidence: 5% Prevalence is the number of people with the disease divided by the total population. Here, the number with the disease at the start of the study is 1000, and the total population is 5000. Thus, the point prevalence at the start of the study is 1000/5000 = 20% or 200 per 1000 people (choice A). The incidence is the number of new cases of a disease as a percentage of the population at risk, which is the people who do not already have the disease. In this scenario, of the 5000 people, 1000 have the disease to begin with; hence, the at-risk population is 4000, of which 200 develop the condition. Because of improved therapy, people with the disease live longer with the disease. The prevalence of a disease is influenced by the incidence of the disease, as well as the average duration of the illness. A decrease in the incidence of disease would decrease the number of cases being added to the population and hence decrease the prevalence (choice A). An increased average duration of the disease would increase the number of people in the population who have the disease and hence increase the prevalence rather than reduce it (choice C). Large-scale immigration of healthy people to the region would increase the total population (the denominator) and hence decrease the prevalence (choice B). The death of a large number of those with the disease would decrease the total number in the population with the disease (the numerator) and hence decrease the prevalence (choice D). And as discussed previously, the sensitivity and specificity of a test are unaffected by the prevalence of a disease in the population being tested. Daily blood draws To combat the rising costs of health care without compromising the quality of care, the Choosing Wisely Campaign was developed. An official American Thoracic Society/American Association of Critical-Care Nurses/American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine policy statement: the Choosing Wisely Top 5 list in Critical Care Medicine. Ethics is a moral code of what we believe to be universally accepted principles of rightness and wrongness that influences our medical decisions. Ever-advancing technology and therapies constantly challenge and call into question previously established ethical norms. The most accessible approach is committing to the following principles: respect for autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice. What to advise may not be so easy and often the progress of the clinical course and morbidity and predictive scores are used to give the physician, patient, and family the global perspective into his illness. Thus, if a patient has more than one condition listed for a specific variable, points are assigned for all applicable combinations. It may represent lifesaving benefit for one patient with a mostly sedentary lifestyle, but the same surgery could represent unacceptable harm (absence of mobility) to another patient whose quality of life hinges on being mobile. At 9-12 points, mortality was 25%; at 13-16 points, mortality was 50%; at 17-20 points, mortality was 75%; and more than 20 points mortality was 100%. A patient has the right to accept or refuse the care that is offered provided that the patient has a well-rounded perspective regarding the present clinical condition and any proposed treatment or procedure and has decision-making capacity. Beneficence and nonmaleficence are considered together because the first refers to the principle of treating patients in a way that will benefit them, and the latter demands we act in such a way that will not harm our patients. Therefore, healthcare providers must be aware of the current trends and developments for that particular disease. For example, it is true that patients with cancer have lower survival rates than patients without cancer, but their in-hospital mortality rate is not higher compared with other patients with chronic disease. Palliative care is a multidisciplinary specialty that treats patients with the primary goals of relieving suffering. Working group on "sepsis-related problems" of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Patients receiving palliative care need not forgo curative or life-prolonging treatments. Ethics, Death, and Organ Donation support for the patient and family and provides bereavement services to family after the patient has passed. Hospice care is palliative treatment for a dying patient with the goal of accepting the imminence of death and achieving a comfortable death with dignity. At home, the burden of the care of the patient (bathing, medicating, feeding) falls primarily on family members with hospice providing weekly or biweekly visiting nurses and 24-hour on call hospice assistance via phone. Under this belief, they insist that extraordinary measures be taken to keep nonviable patients alive. Simply discussing quality of life with family members in these situations may not make much headway because these beliefs are frequently woven into fabric of their belief system and identity. The most important concept of surrogate decision making is that of substituted judgment. This is striving to make decisions based on what the patient, if she or he were able, would have decided.
Order genuine residronate on line
In mild affection treatment 20 nail dystrophy purchase residronate once a day, the pregnancy may be continued up to 38 weeks and then termination is to be done. In severe affection: It is reasonable to terminate the pregnancy around 34 weeks after maternal steroid administration (p. In every case of premature termination before 34 weeks, it is desirable to confirm the fetal lung maturation by measuring the L: S ratio in the amniotic fluid. In a specialized center where there is severe affection before 34 weeks, intrauterine fetal transfusion (intraperitoneal or intravascular) is done (p. Methods of delivery: (1) Amniotomy (low rupture of the membranes) is quite effective, if termination is done near term. Clamping the umbilical cord: In either methods, the cord is to be clamped as quickly as possible to minimize even minute amount of antibody to cross to the fetus from the mother. Collection of cord blood for investigation: Cord blood sample is to be taken from the placental end of the cut cord. It is indicated in selected cases where there is severe affection of the fetus in utero prior to 34 weeks. The advantages are: (i) Correction of fetal anemia and improvement of oxygenation and (ii) improved fetal hepatic function. Fetal anemia is corrected when the transfused erythrocytes are taken up by the sub-diaphragmatic lymphatics. Type and amount of blood-blood group "O" Rh-negative packed cells (hematocrit, 80%) cross matched with the mother, are to be transfused. The quantity of blood is to be calculated as number of weeks of gestation over 20 multiplied by 10 in mL. Severity of fetal affection is best assessed by fetal hemoglobin and hematocrit levels as determined by cordocentesis. Generally a fetus whose hemoglobin deficit is 2 g/dL or more from the mean of a normal fetus of corresponding gestational age (hematocrit < 30%) should be transfused. Procedure: Transfusion is generally made through umbilical cord vessel (vein) near its insertion into the placenta under real time ultrasound. Hematocrit level is checked at intervals during the procedure to determine the volume. Fetal injury, volume overload, preterm labor and fetomaternal hemorrhage are the common complications. Fetal surveillance with ultrasound and continuous electronic fetal monitoring is performed at the posttransfusion phase. Betamethasone (24 mg in three divided doses) should be administered to the mother 24 hours before transfusion from 26 weeks onwards to enhance pulmonary maturity, in case delivery becomes necessary during transfusion. To neutralize the established anti-D antibodies by developing antibody to the RhD antigen and monoclonal anti-D blocking antibodies are being investigated currently. With the advent of wider use of prophylactic anti-D immunoglobulin, less and less problem babies are born and through exchange transfusion, the incidence of kernicterus has also been reduced. Thereafter, the baby is quite capable to get rid of the maternal antibodies by producing sufficiently his own Rh-positive blood. A plastic catheter of 1 mm diameter is passed about 7 cm beyond the umbilicus so as to place it in the inferior vena cava. Entire set should be air tight and to be periodically flushed with heparinized saline (1,000 units in 100 mL) to prevent clotting. For every 100 mL of blood transfused, one milliequivalent of sodium bicarbonate is given to combat metabolic acidosis and 1 mL of 10% calcium gluconate to prevent tetany due to transfusion of citrated blood. To estimate the hemoglobin and bilirubin concentration prior to and after the exchange transfusion. Occasionally, the level of conjugated bilirubin may remain higher and phototherapy should be continued and (4) hypoglycemia (due to increased insulin secretion) is to be checked by blood glucose estimation posttransfusion 4 hourly. Immediate complications: (1) Cardiac failure due to raised venous pressure and overloading of the heart; (2) air embolism; (3) clotting and massive embolism; (4) hyperkalemia; (5) tetany; (6) acidosis; (7) sepsis; (8) hypocalcemia; (9) hypoglycemia and (10) coagulopathies due to thrombocytopenia. Delayed complications: (1) Necrotizing enterocolitis; (2) extrahepatic portal hypertension due to thrombosis of portal vein and (3) other complications are mostly attributed to prematurity, hyperbilirubinemia and hypoxia. These products are water soluble and therefore readily excreted in the bile and urine. Phenobarbitone increases the glucuronyl transferase enzyme activity in the fetal and neonatal liver to conjugate the bilirubin which hastens its clearance. With alloimmunization of the mother, the prognosis of the baby depends on: (1) Genotype of the father; (2) genotype of the fetus; (3) maternal antibody level; (4) history of previous affection of the baby due to hemolytic disease and (5) availability of sophisticated diagnostic and therapeutic facilities for the affected babies (specialist fetal medicine care unit). The age limit is arbitrary and is based on the fact that the outcome of the pregnancy is adversely affected beyond the specified age limit. There are two groups of patients: (1) one with high fecundity-a women married late but conceives soon after and (2) one with low fecundity-woman married early but conceives long after marriage. The latter one is prognostically more unfavorable so far as the obstetric outcome is concerned after conception occurs following treatment of infertility (ovulation induction or assisted reproductive technology). During labor: There is increased incidence of: (1) preterm labor; (2) prolonged labor due to (a) uterine inertia caused by anxiety or malposition (occipito-posterior); (b) impaired joint mobility and (c) inelasticity of the soft tissues of the birth canal; (3) maternal and fetal distress appears early; (4) increased cesarean delivery and (5) retained placenta due to uterine atony and increased association of fibroid. Puerperium: (1) Increased morbidity due to operative interference and (2) failing lactation. The perinatal mortality is increased due to prematurity, increased congenital malformation (trisomy 21) and operative interference. Considering the risks involved in pregnancy and labor, the patients are considered "high risk" They require meticulous antenatal. The following principles are to be followed: (1) result of induction is unsatisfactory and as such cesarean section is a preferred alternative; (2) prenatal diagnosis and sonography (targeted) are done to exclude fetal genetic or structural anomaly and (3) development of other complications should be viewed with concern. The incidence has been gradually declining over the couple of decades due to acceptance of small family norm but it still constitutes to about one-tenth of the hospital population and accounts for one-third of the maternal deaths in the developing countries. Puerperium: (1) Increased morbidity due to sepsis, intranatal hazards; (2) subinvolution and (3) failing lactation. To find out the etiological factor: At the first antenatal visit, detailed in depth relevant history should be taken in an attempt to find out the cause of mishaps. In the developing countries, too often the disaster is linked with inadequate or neglected antenatal, intranatal or neonatal care. Previous history of congenital deformity of the baby, especially a neural tube defect should be excluded as there is likely chance of recurrence (see p. These antibodies are either IgG or IgM or both and bind to negatively charged phospholipids. There is inhibition in release of prostacyclin (vasodilator) from vascular endothelium with rise in the level of thromboxane (vasoconstrictor) from platelets. Other pathological changes like placental vascular atherosis, intervillous and spiral artery thrombosis and decidual vasculopathy with fibrinoid necrosis lead to inadequate maternal blood supply to fetus. Thrombophilias: Some regulatory proteins act as inhibitors in the coagulation cascade. Inherited or acquired deficiencies of these inhibitory proteins are collectively known as thrombophilias. To treat the offending factor: When the responsible factor is detected, appropriate therapy can be directed so as to prevent repetition of the mishaps. A good example is to perform encerclage operation in recurrent midtrimester abortion. Diabetes in pregnancy, if discovered during such investigation, should be adequately supervised all throughout pregnancy and a suitable time is selected for its termination (see p. Proved cases of fetal wastage due to red cell alloimmunization of the mother should be managed in specialized fetal medicine unit to deal with Rh problems. If environmental factors are involved, extension of adequate antenatal and intranatal care is enough to prevent repetition of the mishaps.
Qian Ceng Ta (Chinese Club Moss). Residronate.
- Dosing considerations for Chinese Club Moss.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Chinese Club Moss work?
- What is Chinese Club Moss?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96213
Order residronate 35mg mastercard
Dietary prescription: A realistic balanced diet medicine 94 generic residronate 35 mg visa, rich in iron and protein, should be prescribed which should be within the reach of the patient and should be easily digestible. Iron utensils should preferably be used for cooking and the water used in rice and vegetable cooking should not be discarded. Adequate treatment should be instituted to eradicate hookworm infestation, dysentery, malaria, bleeding piles, and urinary tract infection. Hemoglobin level should be estimated at the rst antenatal visit, at the 30th week and nally at 36th week. Treatment must be preceded by an accurate diagnosis of the cause of anemia and type of anemia. Hospitalization: (1) Ideally all patients having hemoglobin level 9 gm/100 mL or less should be admitted for investigation and treatment. But due to high prevalence of anemia and inadequate hospital beds, an arbitrary hemoglobin level of 7. General treatment: Diet: A realistic balanced diet rich in proteins, iron and vitamins and which is easily assimilable is prescribed. To improve the appetite and facilitate digestion, preparation containing acid pepsin may be given thrice daily after meals. Specific therapy the principle is to raise the hemoglobin level as near to normal as possible. Thereafter, an attempt is made to restore the iron reserve at least in part, if possible, before the patient goes in labor. Choice of therapy depends on: (1) Severity of anemia (2) Duration of pregnancy (time available before delivery). The preparations available are ferrous gluconate, ferrous fumarate or ferrous succinate. In spite of claims about the superiority of one preparation over the other, ferrous sulfate is widely used. Fersolate tablet contains 325 mg ferrous sulfate which contains 60 mg of elemental iron, trace of copper and manganese. The treatment should be continued till the blood picture becomes normal; thereafter a maintenance dose of one tablet daily is to be continued for at least 100 days following delivery to replenish the iron stores. Drawbacks: (1) Intolerance- e intolerance is evidenced by epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea or constipation. To avoid intolerance, it is preferable to start the therapy with a smaller dose-one tablet daily and then to increase the dose to a maximum three tablets a day. If such a procedure fails to stop the symptoms, an alternate preparation may be prescribed. Antacids, oxalates and phosphates will reduce absorption while ascorbic acid, lactate and various amino acids increase its absorption. If no signi cant improvement is evident clinically and hematologically within 3 weeks, diagnostic re-evaluation is needed. After a lapse of few days, the hemoglobin concentration is expected to rise at the rate of about 0. Causes of failure of improvement: (1) Improper typing of anemia (2) Defective absorption due to associated gastrointestinal disorders (3) e patient fails to take iron (4) Concurrent blood loss as in hookworm infestation or bleeding piles (5) Inhibition of erythropoiesis by infection (6) Coexistent folate de ciency. Contraindications of oral therapy: the following are the contraindications of oral therapy: (1) Intolerance to oral iron. Considering the unpredictable absorption and utilization following oral therapy, parenteral therapy is the preferred choice. The main advantage of parenteral therapy is the certainty of its administration to correct the hemoglobin deficit and to fix up the iron store. The compounds used are: iron (ferrous) sucrose compound, sodium ferric gluconate or iron dextran. Iron (ferrous) Sucrose: (20 mg elemental iron/mL) 100 mg/dose, usually one dose daily for 10 days. Example (iron dextran): the total elemental iron required in an anemic patient weighing 100 lb with hemoglobin 50% is calculated as follows: 0. Prerequisites: (1) Correct diagnosis of true iron deficiency anemia (2) Adequate supervision (3) Facilities for management of anaphylactic reaction. Chapter 20 Procedures: - - Medical and Surgical Illness Complicating Pregnancy 311 e patient is admitted in the morning for infusion e required iron is mixed with 500 mL of 0. Total dose to be administered is calculated as that previously mentioned in intravenous therapy. Procedure of injections: After an initial test dose of 1 mL, the injections are given daily or on alternate days in doses of 2 mL intramuscularly. An additional precaution is to inject small quantity of air or saline down the needle before withdrawing it. These procedures prevent even a slight drop of the solution to come beneath the skin surface so as to stain it. The indications are: (1) To correct anemia due to blood loss and to combat postpartum hemorrhage. To allow time for circulatory readjustment, transfusion should not be repeated within 24 hours. Advantages of blood transfusion: (1) Increases oxygen carrying capacity of the blood (2) Hemoglobin from the hemolyzed red cells may be utilized for the formation of new red cells (3) Stimulates erythropoiesis. Precautions: Utmost precautions are to be taken to minimize reaction and over loading of the heart. Its indications are: (1) Cardiac failure due to severe anemia (2) Cases of severe anemia requiring surgery (3) Severe anemia whatever may be the type (with packed cell volume less than 13%) near term as a safer alternative to simple transfusion. The main drawbacks are: (1) Large quantity of fresh blood is required and that too has to be collected from several donors. Quantity of blood transfused: this is in fact a partial exchange transfusion when 1300 mL of packed cells are transfused under pressure through an antecubital vein with simultaneous withdrawal of 1500 mL of blood from the opposite femoral vein. Thus the patient ends up with a deficit in blood volume although with marked improvement of oxygen carrying capacity of the red cells. Prophylactic low forceps or vacuum delivery may be done to shorten the duration of second stage. Significant amount of blood loss should be replenished by fresh packed cell transfusion after taking the usual precautions mentioned earlier. Even in an otherwise normal case, iron therapy should be continued for at least 3 months following delivery. Thus, it may be regarded as a deficiency disease caused by lack of either vitamin B12 or folate or both. Vit B12 is first bound to intrinsic factor which is secreted by the gastric parietal cells. Folate deficiency rarely occurs in the fetus and it is not associated with any significant perinatal morbidity. Chapter 20 Medical and Surgical Illness Complicating Pregnancy 313 Addisonian pernicious anemia is caused by lack of absorption of vitamin B12 due to lack of intrinsic factor. It is an extremely rare autoimmune disease in pregnancy because of: (1) Rare occurrence during child-bearing period (usually manifests above 40 years). For Cobalamin absorption, the requirements are: (i) Stomach acid pepsin (ii) Intrinsic factors secreted by gastric parietal cells (iii) Pancreatic proteases (iv) Intact ileum with mucosal receptors. Because of abundant vitamin B12 stores in the body (liver), clinical Vit B12 deficiency takes several years to occur. Increased demand due to: (a) Increased maternal tissue including red cell volume (b) Growing fetus (c) Multiple pregnancy.
Syndromes
- You have thoughts of harming yourself or of committing suicide
- Malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies
- Ethyl alcohol
- STD tracking
- Certain types of pneumonia
- CBC, including differential count
- Blepharitis (swelling along the edge of the eyelid)
- Cervical spine CT or MRI to be sure there is no disease or injury to the neck, which can mimic ALS
- Itching
- Tumors in the spine
Purchase residronate in united states online
Respiratory- e patient may su er from dyspnea or even remain in the sitting position for easier breathing medications narcolepsy cheap residronate 35 mg with mastercard. Amniotic uid: Estimation of alpha fetoprotein which is markedly elevated in the presence of a fetus with an open neural tube defect. Twins: the diagnosis is often confused and difficult because of its association with hydramnios. Pregnancy with huge ovarian cyst: (i) the gravid uterus can be felt separate from the cyst, (ii) internal examination shows the cervix to be pushed down into the pelvis. In hydramnios, the lower segment has to ride above the pelvic brim, so that the cervix is drawn up, (iii) X-ray of the abdomen or sonography is helpful. Maternal ascites: (i) Presence of shifting dullness, (ii) resonance on the midline due to floating gut whereas in hydramnios, it becomes dull, (iii) internal examination and palpation of the normal size uterus, if possible, can give the clue, (iv) straight X-ray of the abdomen or sonography helps to exclude pregnancy. During labor: (1) Early rupture of the membranes (2) Cord prolapse (3) Uterine inertia (4) Increased operative delivery due to malpresentation (5) Retained placenta, postpartum hemorrhage and shock. Puerperium: (1) Subinvolution (2) Increased puerperal morbidity due to infection resulting from increased operative interference and blood loss. Other contributing factors are cord prolapse, hydrops fetalis, effects of increased operative delivery and accidental hemorrhage. Treatment of polyhydramnios is usually tailored according to the underlying cause. Principles: (1) To relieve the symptoms (2) To find out the cause (3) To avoid and to deal with the complication. Supportive therapy includes bed rest, if necessary, with a back rest and treatment of the associated conditions like preeclampsia or diabetes on the usual line. Further management depends on: (1) Response to treatment (2) Period of gestation (3) Presence of fetal malformation (4) Associated complicating factors. Response to treatment is good: the pregnancy is to be continued awaiting spontaneous delivery at term. Slow decompression is done at the rate of about 500 mL per hour and the amount of fluid to be removed should be sufficient enough to relieve the mechanical distress. Because of slow decompression, chance of accidental hemorrhage is less but liquor amnii may again accumulate, for which the procedure may have to be repeated. This will minimize sudden decompression with separation of the placenta, change in the lie of the fetus and cord prolapse. With congenital fetal abnormality: Referral to a maternal fetal medicine unit should ideally be done. When decision for termination is made, it is to be done irrespective of duration of pregnancy. If, accidentally, low rupture of the membranes occurs, escape of gush of liquor should be immediately controlled by placing the palm over the introitus to avoid accidental hemorrhage. The lie should be checked and if found longitudinal, oxytocin infusion may be started. Internal examination should be done soon after the rupture of the membranes to exclude cord prolapse. If the uterine contraction becomes sluggish, oxytocin infusion may be started, if not contraindicated. One must remain vigilant following the birth of the baby for retained placenta, postpartum hemorrhage and shock. Maternal conditions: (i) Hypertensive disorders (ii) Uteroplacental insufficiency (iii) Dehydration (iv) Idiopathic. Ultrasound visualization is done following amnioinfusion of 300 mL of warm saline solution (7) Visualization of normal filling and emptying of fetal bladder essentially rules out urinary tract abnormality. The deformities include alteration in shape of the skull, wry neck, club foot, or even amputation of the limb (3) Fetal pulmonary hypoplasia (may be the cause or effect) (4) Cord compression (5) High fetal mortality. Maternal: (1) Prolonged labor due to inertia (2) Increased operative interference due to malpresentation. When decision for delivery is made, it should be done irrespective of the period of gestation. Isolated oligohydramnios in the third trimester with a normal fetus may be managed conservatively. Amnioinfusion (prophylactic or therapeutic) for meconium liquor is found to improve neonatal outcome. Oligohydramnios may be due to pregnancy complications with hypertensive disorders, placental insu ciency or idiopathic. Transient polyhydramnios has got favorable outcome compared to persistent or worsened group. Persistent polyhydramnios needs investigations for fetal anomalies and genetic syndromes. Complications of polyhydramnios are grouped into (a) Maternal and (b) Fetal (see p. Important management issue in both the groups is to detect any fetal congenital malformation. Referral to a fetal medicine unit should ideally be done when it is present and delivery is planned specially when associated with major structural anomaly or genetic syndromes. Clinical significance: If the succenturiate lobe is retained, following birth of the placenta, it may lead to: (1) Postpartum hemorrhage which may be primary or secondary (2) Subinvolution (3) Uterine sepsis (4) Polyp formation. Recurrent marginal hemorrhage as diagnosed on serial ultrasound is thought to be the cause. The membranes (amnion and chorion) are folded, rolled back upon itself to form a ring which is reflected centrally. Placenta marginata-A thin fibrous ring is present at the margin of the chorionic plate where the fetal vessels appear to terminate. Clinical significance: There is increased chance of: (1) Abortion (2) Hydrorrhea gravidarum (excessive watery vaginal discharge) (3) Antepartum hemorrhage (4) Growth retardation of the baby (5) Preterm delivery (6) Retained placenta or membranes. The placenta not only develops from the chorion frondosum but also from the chorion laeve so that the whole of the ovum is practically covered by the placenta. Clinical significance: (1) Encroachment of some part over the lower segment leads to placenta previa. The branching vessels traverse between the membranes for a varying distance before they reach and supply the placenta. If the leash of blood vessels happens to traverse through the membranes overlying the internal os, in front of the presenting part, the condition is called vasa previa. Rupture of the membranes involving the overlying vessels leads to vaginal bleeding. Short cord: the short cord may be true (less than 20 cm or 8") or commonly relative due to entanglement of the cord round any fetal part. In exceptional circumstances, the cord may be absent and the placenta may be attached to the liver as in exomphalos. Long cord: the clinical significance due to the presence of a long cord is that there is an increased chance of: (1) Cord prolapse. The condition may produce sufficient compression on the cord vessels so as to produce fetal distress or rarely death. It may be due to failure of development of one artery or due to its atrophy in later months. It is more common in twins and in babies born of women with diabetes, epilepsy, oligohydramnios, hydramnios, preeclampsia and antepartum hemorrhage. Hypertension is a sign of an underlying pathology, which may be pre-existing or appears for the first time during pregnancy. The identification of this clinical entity and effective management play a significant role in the outcome of pregnancy, both for the mother and the baby. In developing countries, with inadequately cared pregnancy, this entity on many occasions remains undetected till major complications supervene. The criteria for diagnosis of superimposed preeclampsia: New onset of proteinuria >0. The preeclamptic features may appear even before the 20th week as in cases of hydatidiform mole and acute polyhydramnios. Rise of blood pressure should be evident at least on two occasions, at least 6 hours apart. The level is arbitrary and is based on the observation that complications are likely to be more beyond this level.
Order residronate uk
It is the second most common nongynecological condition that needs surgery during pregnancy medicine allergy effective residronate 35mg. Deterioration of clinical condition despite medical therapy or recurrent billiary colic needs cholecystectomy regardless of trimester. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy can be done in the second trimester of pregnancy safely. Fetal risks and preterm labor are less as the uterine manipulation and the use of narcotics are less. Obstetric consultation is essential for preoperative and postoperative management. Risk of aspiration during anesthesia could be reduced using antacid, and H2 blocker beforehand. Patient should be in the left lateral decubitus with minimum reverse trendelenburg 5. Antithrombotic prophylaxis are: use of pneumatic compression devices (intraoperative as well as postoperative) and early postoperative ambulation. Fetal monitoring is to be continued and pneumoperitoneum is to be released if fetal distress arises. One should be very careful to distinguish the pathological variety from the physiological one. A meticulous history coupled with systematic and thorough examinations (general, abdominal and vaginal) are mandatory to arrive at a diagnosis on the real state of affairs. Many a times a delay in the diagnosis of a nongestational cause terminates fatally. Consultation with a surgeon or a physician should be done whenever felt necessary. The physician should be conscious of the entity of disturbed tubal pregnancy in early months and rupture of the uterus, in the later months while dealing with acute abdomen in pregnancy. Mention the different complications that are faced when a pregnant woman su ers from severe anemia in pregnancy Outline in brief the place of iron therapy in the management of anemia in pregnancy Microscopic examination reveals preponderance of cornified squamous cells with few pus cells. Treatment consists of prescribing metronidazole (Flagyl) 200 mg thrice daily for 7 days. Its growth is favored by the high acidic pH of vaginal secretions and frequent presence of sugar in the urine during pregnancy. Treatment is by use of miconazole vaginal cream, one applicator full, high up in the vagina at bedtime for 7 nights. This results in the downgrowth of the columnar epithelium to a variable extent beyond the external os replacing the squamous epithelium producing "pregnancy ectopy" It appears for. The polyp should be removed as in the non-pregnant state and should be sent for histological examination. Difficult repair for stress incontinence or vesicovaginal fistula indicates an elective cesarean section. It is the moderate degree of malformations that has got an adverse effect on pregnancy and labor. The Chapter 21 Gynecological Disorders in Pregnancy 357 diagnosis is made during (a) abdominal inspection - fundal notching, (b) cesarean section, (c) manual removal or evacuation operation, (d) hysterosalpingography or hysteroscopy, and (e) laparoscopy for infertility investigation. The common types of malformations are: (a) Arcuate; (b) Subseptate; (c) Bicornuate with equal horn or unequal horn (rudimentary). Septate vagina hardly produces any difficulty during delivery, but a transverse septum or partial atresia may necessitate delivery by cesarean section. The diagnosis is confused with disturbed ectopic pregnancy in early months or abruptio placentae in later months. Pitfalls in diagnosis during pregnancy: Because of increased vascularity, softening of cervix and gestational hyperplasia of the cervical mucosa, the following problems may arise in diagnosis: (1) Indurated feel of malignancy may not be evident; (2) Benign lesions such as ectopy or polyp may bleed to touch; (3) Extension to the parametrium may not be well defined and as such, cases are often understaged. Abnormal cytology detected on routine screening procedure during antenatal checkup is placed under the following evaluation protocol. First trimester: Radical hysterectomy (with the fetus in uterus), pelvic lymphadenectomy and aortic node sampling are done. Chapter 21 Gynecological Disorders in Pregnancy 359 Third trimester: Radical hysterectomy, pelvic lymphadenectomy after classical cesarean delivery. Second or third trimester: Classical cesarean delivery neoadjuvant chemotherapy and irradiation (external beam and brachytherapy). Prognosis: Stage for the survival outcome of women with cervical cancer in pregnancy is no different when compared to the non-pregnant women. The tumor feels soft (2) changes in position, (3) changes in shape - becomes flattened, (4) degenerative changes, especially red degeneration, (5) torsion of pedunculated subserous fibroid, and (6) infection and polypoidal changes are more in puerperium. Naked eye appearance of the tumor shows dark red areas with cut section revealing raw-beef appearance often containing cystic spaces. Clinical features: (1) Acute onset of focal pain over the tumor; (2) Malaise or even rise of temperature; (3) Dry or furred tongue; (4) Rapid pulse; (5) Constipation; (6) Tenderness and rigidity over the tumor; (7) Blood count 360 Textbook of Obstetrics shows leukocytosis. When laparotomy is done with mistaken diagnosis, abdomen is to be closed without any intervention. Marked softening and alteration in the shape (flattening) make it difficult to differentiate from the pregnant uterus. In an uncomplicated tumor, it is confused with ovarian tumor, retroverted gravid uterus, non-gravid half of a double uterus. In early months, fibroid is diagnosed but pregnancy is missed whereas in later months, pregnancy is diagnosed but the fibroid is missed. Impaction in early months followed by retention of urine - e same management protocol as prescribed in retroverted gravid uterus is to be followed. If manual correction fails, laparotomy and myomectomy is rarely indicated leaving behind the undisturbed pregnancy. Acute pain following red degeneration - Medical management is usually done (mentioned earlier). Place of elective cesarean section: (1) Cervical or broad ligament fibroid; (2) Associated complicating factors such as elderly primigravida or malpresentation. Fibroid situated below the presenting part-spontaneous vaginal delivery may occur. Myomectomy for a case with intramural myoma during pregnancy or during cesarean delivery cause profuse hemorrhage. Although serous cystadenoma is common even during pregnancy the incidence of germ cell tumor (dermoid) is increased two fold during pregnancy compared to the non-pregnant state. This is because of its high prevalence during childbearing period and its detection due to increased complications during pregnancy. On labor: ere is chance of obstructed labor if the tumor is impacted in the pelvis. Abdominal examination reveals the cystic swelling felt separated from the gravid uterus. The patient is examined vaginally in head down Trendelenburg position to elicit the groove between the two swellings. Differential diagnosis includes pelvic kidney, uterine fibroids, colorectal or bladder tumors. Beyond 36 weeks - e operation is better to be withheld till delivery and the tumor is removed as early in puerperium as possible. Most ovarian tumors in pregnancy are either germ cell tumors or epithelial cancer of early stage and lowgrade variety. Treatment in majority of cases is continuation of pregnancy and preservation of fertility. When the tumor is found malignant on laparotomy, surgical intervention should be similar to that of non-pregnant patient. As the uterus grows, the fundus rises spontaneously from the pelvis beyond 12 weeks. The developing uterus gradually fills up the pelvic cavity and becomes incarcerated.
Buy generic residronate 35mg online
Infants with regular breathing and heart rate > 100 bpm need no further intervention; if cyanotic symptoms 2dpo discount residronate 35 mg amex, provide O 2 supplementation. Reversal of narcotic drug is needed when mother has been given pethidine or morphine within 3 hours of delivery. Volume expansion is needed when blood pressure is low and tissue perfusion is poor. Delayed: (a) Retarded mental and physical growth; (b) Epilepsy-up to 30% in severe asphyxia; (c) Minimal brain dysfunction. Supplemental oxygen supply is required to maintain PaO2 > 50 mm Hg or pulse oximeter saturation > 85%. Use of exogenous surfactant has significantly reduced the risk of neonatal death by <10%. Antenatal corticosteroids enhances but fetal hyperinsulinemia delays surfactant synthesis. There is poor lung compliance, reduction in ventilation- perfusion ratio and progressive atelectasis. A homogenous eosinophilic membrane (hyaline membrane) plastering the alveolar ducts and terminal bronchioles is found. Blood biochemical changes: the infant develops both metabolic and respiratory acidosis. Excess negative pressures generated to open the collapsed airways cause retraction and deformation of chest wall. Chest X-ray shows uniform reticulogranular pattern known as ground glass mottling due to extensive atelectatic process. Acidosis should be corrected by intravenous administration of sodium bicarbonate 4. Reduction of surface tension and stabilization of alveolar air-water interface is its basic function. Surfactants of human, bovine (survanta), porcine (poractant) or synthetic preparations have been used. Prophylactic therapy is given (within 15 minutes of birth) in very premature infants. Changes in positioning of the infant during therapy are done to facilitate distribution. Surfactant replacement therapy has reduced neonatal mortality and pulmonary morbidity. If there is risk of vomiting and aspiration, intravenous administration of 10% glucose in amount of 60 mL/kg body weight per day may be given to a term baby on 1st day through a catheter inserted into peripheral or umbilical vein. Antibiotic therapy against common neonatal infections should be started initially. In mild affection with good vigor, the baby may survive, if acidosis and biochemical abnormalities are corrected effectively. The long-term sequelae of the infants in terms of respiratory and neurological development is dependent on the birth weight and gestational age. Chronic placental insufficiency leads to intrauterine hypoxia with passage of meconium. The meconium stained liquor may be aspirated by the fetus-in-utero or during first breath. The infant manifests with tachypnea, nasal flaring, intercostal retractions and cyanosis. Diagnosis is mainly based on: (a) Aspiration of meconium from the trachea at birth; (b) Signs of respiratory distress; (c) Radiologically hyperinflated lung fields, flattened diaphragm with coarse and patchy infiltration and (d) Cyanosis. Management: Proper intrapartum monitoring and care; Amnio infusion in oligohydramnios-may reduce cord compression, grasping and intrapartum aspiration; Maintenance of (a) Thermoneutral environment; (b) Minimum handling; (c) To correct metabolic abnormalities; (d) Circulatory support (N. Saline or whole blood) and (e) Airway and oral suctioning may be needed; Liberal oxygen supply; Antibiotic coverage, as meconium invites infection; In a severe case arterial blood gas analysis should be done; Inhaled nitric oxide or surfactant therapy may be beneficial; General management includes correction of hypoxia, acidosis, hypoglycemia and hypocalcemia. Bilirubin bound to serum albumin is transported to the liver cells carried to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum by cytoplasmic ligandin (Y protein). In premature babies, careful observation is required and evidences of rising bilirubin near critical level need exchange transfusion. Excessive red cell hemolysis Absolute Features of Nonphysiologic Jaundice (i) Hemolytic disease of the newborn: Jaundice appearing within 24 hours of birth. Clinical jaundice persisting > 1 week in a term infant Increased red cell fragility-Congeor > 2 weeks in a preterm infant. Defective conjugation of bilirubin (i) Congenital de ciency of glucuronyl transferase Crigler-Najjar syndrome (autosomal recessive), Gilbert syndrome (autosomal dominant), Preterm babies with impaired liver function. If the bilirubin level is more, temporary withdrawal of breastfeeding cures jaundice. Breastfeeding jaundice is due to decreased intake of milk that leads to increased enterohepatic circulation. Metabolic and endocrine disorders: Galactosemia, hypothyroidism (unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia). Galactosemia-There is hereditary deficiency of an enzyme-galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase which converts galactose derived from the milk into glucose-1-phosphate. As a result there is increased accumulation of galactose that leads to periportal fibrosis and cirrhosis of liver. The biliary canaliculi are blocked by inspissated bile and obstructive jaundice results. Increased enterohepatic circulation of unconjugated bilirubin: Duodenal atresia, pyloric stenosis, less frequent feeding. Substances and disorders that affect binding of bilirubin to albumin: Aspirin, sulfonamides, fatty acids and asphyxia, acidosis, sepsis, or hypothermia increases free unconjugated bilirubin level. Miscellaneous: Congenital obstruction (atresia or stricture of biliary canaliculi), asphyxia, polycythemia and thalassemia. Clinical: Evaluation of jaundice is done by blanching the skin with digital pressure. Dermal icterus zone and serum bilirubin (indirect) level in a term infant (Kramer-1969). Abnormal neurologic signs are: lethargy, poor feeding, vomiting, hypotonia and seizures. Laboratory studies: Serum bilirubin level > 12 mg/dL, requires further investigations. Complete hemogram including reticulocyte count: Hemolytic anemia: Hb%, Reticulocyte count, presence of nucleated red cells. Serum albumin to detect total bilirubin binding sites and to assess the need of albumin infusion. Other laboratory tests: Urine for reducing substance (galactosemia), culture for infection. Radiology and Ultrasonography to detect intestinal obstruction, intraventricular hemorrhage and tumor. Basal ganglia, cranial nerve nuclei, hippocampus, brainstem nuclei and anterior horn cells of the spinal cord are commonly affected. Risk of bilirubin encephalopathy is unlikely, if the total bilirubin level is < 20 mg/dL. Hypoxia, acidosis, hypoglycemia, hypothermia, sepsis or prematurity enhances the pathogenesis so that affection may occur even at a low level of bilirubin.